Abstract
Even with the rapid development of pediatric postoperative pain management, pediatric patients have remained undertreated for postoperative pain because of difficulty in pain assessment and concerns regarding side effects of opioid analgesics. Although there are no perfect pain assessment techniques and no absolutely safe analgesics, proper monitoring and an individualized analgesic plan after due consideration of age, operative procedures, and underlying illness, using multimodal analgesics may improve the quality of pain control in children.
Go to : 
Pediatric postoperative pain management has developed rapidly accompanying the development of new drugs. However, children have remained undertreated for postoperative pain because of the difficulty of pain assessment, apprehension regarding cardiorespiratory depression, restriction of national insurance, etc. Anesthesia and operative fields are unfamiliar and unpleasant environments for children. In addition, separation from caregivers, hunger, fear of strange places, and perioperative pain can cause stress and result in indistinct behavioral and physiological changes. Although pain is often regarded as an inevitable consequence of operative procedures, its control is important to improve both clinical outcome and patient comfort [1]. As preoperative anxiety is associated with greater pain during postoperative recovery in children [2], preoperative planning for postoperative pain control is desirable [3]. Postoperative pain control should begin with preoperative assessment of anxiety, as well as assessment of pain and the efficacy and safety of analgesic techniques and drugs in pediatric patients.
Go to : 
Although numerous pain assessment tools are available, many scoring tools are complicated and not well validated, and are difficult to use in clinical practice. When choosing a pain assessment tool, it is necessary to take into consideration the child's age, stage of development, and clinical condition [4]. In addition, cultural appropriateness, language, familiarity, and training requirements of tools are also important. However, no individual tool can be universally recommended in children of all ages.
Several physiological changes are used to assess pain in children; i.e., increases in heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure, sweating, and decreases in oxygen saturation and vagal tone. Heart rate is the simplest and the most appropriate indicator. However, physiological parameters are influenced by associated clinical conditions, such as sepsis, distress, hypoxemia, hypovolemia, and fever. Therefore, physiological changes alone cannot be used to properly evaluate pain in children. Behavioral changes are also used for pain assessment but these are influenced by other states of distress, such as hunger, fear, and anxiety [5,6].
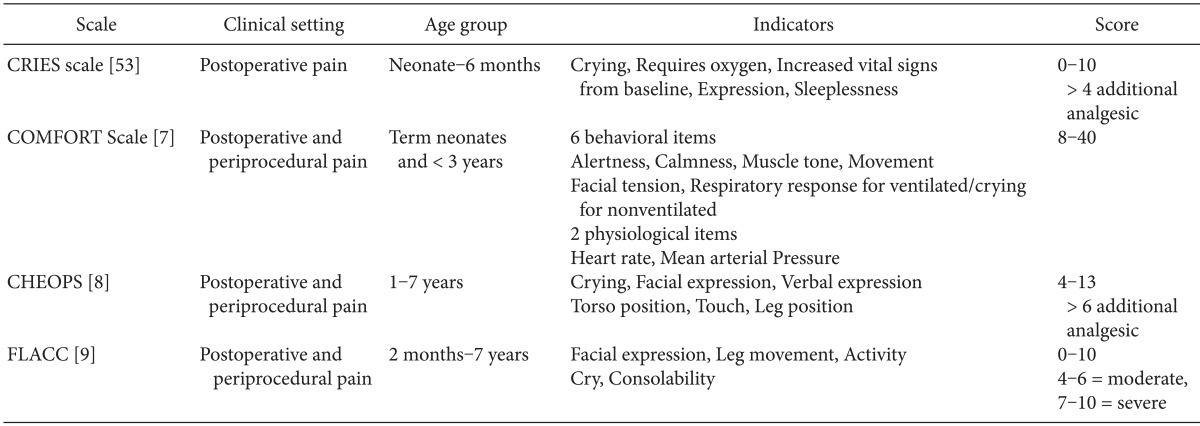
Many composite tools include both physiological and behavioral measures for determining pain scores, such as the COMFORT scale [7], Children Hospital of Eastern Ontario Pain scale [8], and Face, Leg, Activity, Cry, Consolability (FLACC) tool [9] (Table 1). No single composite scale is clearly superior to the others [10].
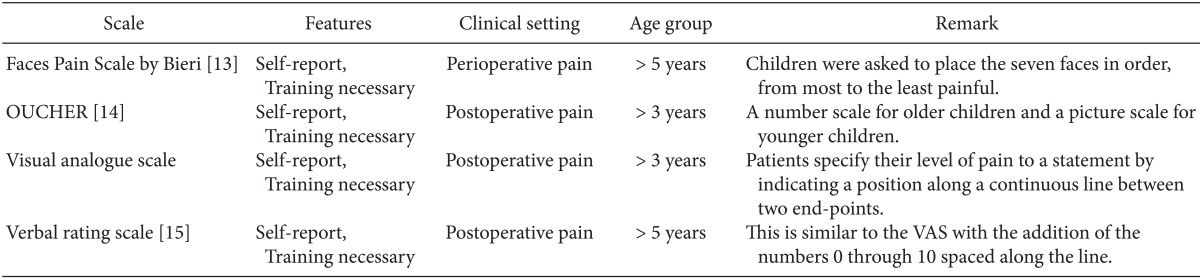
Self-reporting is the most reliable indicator of pain. Unfortunately, this is usually possible only in the children over 4 years who are cognitively and emotionally mature. At this age, children can localize and quantify the intensity of pain and can use a Faces Pain scale. Children older than 6-8 years can use visual analog scales [11]. There are many pain rating scales for self-reporting in verbal children, including the Wong-Baker FACES scale [12], Faces scale of Bieri [13], OUCHER Scale of Beyer and Wells [14], Visual Analog Scale, and Verbal rating scale [15] (Table 2). For optimal pain measurement, it may be helpful to have the participation of the parents.
Go to : 
Morphine has long been the opioid of choice for postoperative pain control in children. Its pharmacokinetics are well known even in pre-term infants [16,17]. The volume of distribution of morphine is similar regardless of age, while its half-life and clearance are related to age. The half-life was estimated to range from 9 h in pre-term neonates, decreasing with age to ~2 h for infants and children aged 11 days to 15 years [16,18].
Although many clinicians are cautious regarding the risk of respiratory depression associated with morphine administration, acute pain counteracts the respiratory depression induced by opioids [18]. Background infusion of low-dose morphine (4 µg/kg/h) in a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) regimen for children did not increase the incidence of side effects and was associated with less hypoxemia and a better sleep pattern than no background infusion [19]. It is important to note that there is no advantage of high or multiple doses of morphine with regard to analgesic effect [20,21].
Even considering its advantages of cost and familiarity, morphine may not be superior to other systemic analgesics, especially with regard to analgesic efficacy and the incidence of side effects, such as vomiting, sedation, and pruritus [21,22]. In a previous meta-analysis, morphine was reported to show significant improvement in analgesic effect only compared with inactive control intervention; significantly higher incidences of vomiting and sedation were observed in half of all comparisons, and lower morphine dosage did not decrease the incidence of side effects [21].
Meperidine has been in widespread use due to its rapid onset and short duration of action. It has been preferred in patients with cholecystitis or pancreatitis for antispasmodic action. However, its active metabolite, normeperidine, is associated with naloxone refractive neurotoxicity [23] in infants. Many case reports and studies have highlighted the toxicity, inadequate pain relief, and drug interactions of meperidine [24,25,26]. Since 2001, the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Pain Society recommended not to use meperidine as an analgesic for infants and children [27], and many pediatric hospital have limited the use of this agent via a restriction policy or removal of the drug from the institution's formulary [25].
Fentanyl is a highly lipophilic agent with less central respiratory depression and hemodynamic stability than morphine [28,29]. Fentanyl has an additional benefit of the availability of noninvasive administration routes (intranasal, transdermal, rectal, etc.), in addition to conventional intravenous or epidural routes. Intranasal fentanyl at a dose of 2 µg/kg provides effective analgesia for pediatric patients with orthopedic trauma [30]. Although fentanyl skin patches are occasionally used in pediatric palliative care [31], it is not used in postoperative pain control. The US National Institutes of Health recommendations indicate that fentanyl skin patches should not be used in children less than 2 years of age due to the risk of serious or life-threatening respiratory problems [32]. Oral transmucosal fentanyl is safe and effective for painful procedures, but the high frequency of vomiting may restrict its clinical usefulness [33]. Intravenous administration of fentanyl has been used for postoperative analgesia [34,35] and sedation/anesthesia even in newborn infants [36,37]. Although even fewer side effects have been reported compared to morphine, fentanyl and other synthetic opioids may induce skeletal muscle rigidity and can involve respiratory structures, including the chest wall and laryngeal structures. Chest wall rigidity can occur with even low analgesic doses, especially in neonates and infants, and can lead to significant impairment of ventilation [38,39].
Remifentanil is an ultra-short-acting opioid with esterase clearance. Remifentanil showed increased clearance in young infants but the half-life was similar in children of all age groups from birth to 18 years [40]. Rapid metabolism without a cumulative effect may make it an ideal agent for postoperative analgesia. However, compared with fentanyl, it may have no additional benefits in analgesic efficacy or incidence of side effects [41,42]. Rather, special attention must be given to respiratory depression during the establishment of PCA with remifentanil [41]. Fast-acting remifentanil alters the carbon dioxide ventilation-response curve before the patient's PaCO2 rises sufficiently to sustain ventilatory drive [43]. While using remifentanil infusion for postoperative pain control, an extremely small dose of remifentanil can cause serious respiratory depression [42]. Remifentanil contains glycine and is should not be administered by epidural or intrathecal injection.
The clearance rate of sufentanil in normal children between 2 and 8 years of age is twice that in adults and adolescents, and a greater maintenance dose is therefore required in pediatric compared to adult patients [44]. Sufentanil provides longer lasting elevated pain threshold (180 vs. 90 min) with less respiratory depression than fentanyl [37]. The magnitude and duration of depression of the ventilatory (30 vs. 240 min) and occlusion pressure (30 vs. 120 min) responses were significantly less with sufentanil compared to fentanyl.
Alfentanil has the most rapid analgesic onset and time to peak effect as well as the shortest elimination half-life when compared with fentanyl and sufentanil [45]. A low-dose bolus of alfentanil may be an efficient means of controlling pain during and after minor abdominal and genitourinary surgery in children [46]. The analgesic efficacy and respiratory depressant effects of equianalgesic concentrations are comparable between alfentanil and fentanyl [47].
Ketorolac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug with a low incidence of side effects. The volume of distribution in children is increased by twofold compared to adults and plasma clearance is also high due to lower binding to plasma proteins. The elimination half-life (∝Vd/CL) is similar in children and in adults, so children require a higher dosage at similar intervals [48]. Ketorolac is not associated with common opioid side effects, such as respiratory depression, nausea and vomiting, urinary retention, or sedation [35,48]. However, attention must be paid to postoperative bleeding after tonsillectomy [49]. A single bolus dose of intravenous ketorolac has been used for opioid dose sharing with superior analgesic effects [48,50]. Continuous infusion of ketorolac has also been shown to reduce both the frequency of bladder spasm and the analgesic requirements in children undergoing urological procedures [35].
Paracetamol is the most commonly prescribed drug for the control of pain in children and provides good analgesic and morphine-sparing effects, even in neonates and infants, after major surgery [51]. It has a very low incidence of toxic side effect and has a ceiling effect with no advanced analgesia despite increases in dosage [26]. However, overdosing or multiple dosage and administration along with hepatotoxic drugs can lead to fatal hepatic toxicity [52], so a proper dosage regimen is necessary.
Go to : 
There are no perfect pain assessment techniques and no absolutely safe analgesics for use in children. Most opioids share common side effects, such as respiratory depression, sedation, nausea, and vomiting, although they show differences in degree of these effects. Monitoring and an individualized analgesic plan after due consideration of age, operative procedures, and underlying illness, is necessary when using multimodal analgesics.
Go to : 
References
1. Kehlet H, Holte K. Effect of postoperative analgesia on surgical outcome. Br J Anaesth. 2001; 87:62–72. PMID: 11460814.

2. Kain ZN, Mayes LC, Caldwell-Andrews AA, Karas DE, McClain BC. Preoperative anxiety, postoperative pain, and behavioral recovery in young children undergoing surgery. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:651–658. PMID: 16882820.

3. Gehdoo RP. Post operative pain management in paediatric patients. Indian J Anaesth. 2004; 48:406–414.
4. Rose JB, Logan DE. Pediatric pain assessment. In : Litman RS, editor. Pediatric Anesthesia. The Requisites in Anesthesiology. Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby;2004. p. 191–195.
5. Lamontagne LL, Hepworth JT, Salisbury MH. Anxiety and postoperative pain in children who undergo major orthopedic surgery. Appl Nurs Res. 2001; 14:119–124. PMID: 11481590.

6. Büttner W, Finke W. Analysis of behavioural and physiological parameters for the assessment of postoperative analgesic demand in newborns, infants and young children: a comprehensive report on seven consecutive studies. Paediatr Anaesth. 2000; 10:303–318. PMID: 10792748.
7. Ambuel B, Hamlett KW, Marx CM, Blumer JL. Assessing distress in pediatric intensive care environments: the COMFORT scale. J Pediatr Psychol. 1992; 17:95–109. PMID: 1545324.

8. McGrath PJ, Johnson G, Goodman JT, Schillinger J, Dunn J, Chapman J. CHEOPS: a behavior scale for rating postoperative pain in children. In : Fields H, Dubner R, Cervero F, editors. Advances in pain research and therapy. New York: Raven Press;1985. p. 395–402.
9. Merkel SI, Voepel-Lewis T, Shayevitz JR, Malviya S. The FLACC: a behavioral scale for scoring postoperative pain in young children. Pediatr Nurs. 1997; 23:293–297. PMID: 9220806.
10. Franck LS, Greenberg CS, Stevens B. Pain assessment in infants and children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2000; 47:487–512. PMID: 10835987.

11. Vetter TR, Heiner EJ. Discordance between patient self-reported visual analog scale pain scores and observed pain-related behavior in older children after surgery. J Clin Anesth. 1996; 8:371–375. PMID: 8832447.

12. Wong DL, Baker CM. Pain in children: comparison of assessment scales. Pediatr Nurs. 1988; 14:9–17. PMID: 3344163.
13. Bieri D, Reeve RA, Champion GD, Addicoat L, Ziegler JB. The Faces Pain Scale for the self-assessment of the severity of pain experienced by children: development, initial validation, and preliminary investigation for ratio scale properties. Pain. 1990; 41:139–150. PMID: 2367140.

14. Beyer JE, Wells N. The assessment of pain in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1989; 36:837–854. PMID: 2666931.

15. Briggs M, Closs JS. A descriptive study of the use of visual analogue scales and verbal rating scales for the assessment of postoperative pain in orthopedic patients. J Pain Symptom Manage. 1999; 18:438–446. PMID: 10641470.

16. Kart T, Christrup LL, Rasmussen M. Recommended use of morphine in neonates, infants and children based on a literature review: Part 1-Pharmacokinetics. Paediatr Anaesth. 1997; 7:5–11. PMID: 9041568.

17. Bouwmeester NJ, Anderson BJ, Tibboel D, Holford NH. Developmental pharmacokinetics of morphine and its metabolites in neonates, infants and young children. Br J Anaesth. 2004; 92:208–217. PMID: 14722170.

18. Kokinsky E, Thornberg E. Postoperative pain control in children: a guide to drug choice. Paediatr Drugs. 2003; 5:751–762. PMID: 14580224.
19. Doyle E, Harper I, Morton NS. Patient-controlled analgesia with low dose background infusions after lower abdominal surgery in children. Br J Anaesth. 1993; 71:818–822. PMID: 8280546.

20. Kart T, Christrup LL, Rasmussen M. Recommended use of morphine in neonates, infants and children based on a literature review: Part 2--Clinical use. Paediatr Anaesth. 1997; 7:93–101. PMID: 9188108.

21. Duedahl TH, Hansen EH. A qualitative systematic review of morphine treatment in children with postoperative pain. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007; 17:756–774. PMID: 17596221.

22. Carbajal R, Lenclen R, Jugie M, Paupe A, Barton BA, Anand KJ. Morphine does not provide adequate analgesia for acute procedural pain among preterm neonates. Pediatrics. 2005; 115:1494–1500. PMID: 15930209.

23. Saneto RP, Fitch JA, Cohen BH. Acute neurotoxicity of meperidine in an infant. Pediatr Neurol. 1996; 14:339–341. PMID: 8962593.

24. Buck ML. Is meperidine the drug that just won't die. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 16:167–169. PMID: 22479158.

25. Benner KW, Durham SH. Meperidine restriction in a pediatric hospital. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 16:185–190. PMID: 22479160.

26. Lönnqvist PA, Morton NS. Postoperative analgesia in infants and children. Br J Anaesth. 2005; 95:59–68. PMID: 15668207.
27. American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health. Task Force on Pain in Infants, Children, and Adolescent. The assessment and management of acute pain in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2001; 108:793–797. PMID: 11533354.
28. Goodarzi M. Comparison of epidural morphine, hydromorphone and fentanyl for postoperative pain control in children undergoing orthopaedic surgery. Paediatr Anaesth. 1999; 9:419–422. PMID: 10447905.

29. Santeiro ML, Christie J, Stromquist C, Torres BA, Markowsky SJ. Pharmacokinetics of continuous infusion fentanyl in newborns. J Perinatol. 1997; 17:135–139. PMID: 9134513.
30. Saunders M, Adelgais K, Nelson D. Use of intranasal fentanyl for the relief of pediatric orthopedic trauma pain. Acad Emerg Med. 2010; 17:1155–1161. PMID: 21175512.

31. Hunt A, Goldman A, Devine T, Phillips M. Transdermal fentanyl for pain relief in a paediatric palliative care population. Palliat Med. 2001; 15:405–412. PMID: 11591092.

32. Hardwick WE Jr, King WD, Palmisano PA. Respiratory depression in a child unintentionally exposed to transdermal fentanyl patch. South Med J. 1997; 90:962–964. PMID: 9305315.

33. Schechter NL, Weisman SJ, Rosenblum M, Bernstein B, Conard PL. The use of oral transmucosal fentanyl citrate for painful procedures in children. Pediatrics. 1995; 95:335–339. PMID: 7862469.
34. Mendel HG, Guarnieri KM, Sundt LM, Torjman MC. The effects of ketorolac and fentanyl on postoperative vomiting and analgesic requirements in children undergoing strabismus surgery. Anesth Analg. 1995; 80:1129–1133. PMID: 7762839.
35. Jo YY, Hong JY, Choi EK, Kil HK. Ketorolac or fentanyl continuous infusion for post-operative analgesia in children undergoing ureteroneocystostomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011; 55:54–59. PMID: 21083540.

36. Cathelin M, Vignes R, Malki A, Viars P. Comparison between the side-effects of fentanyl and morphine in conscious man (author's transl). Anesth Analg (Paris). 1980; 37:265–273. PMID: 7457946.
37. Bailey PL, Streisand JB, East KA, East TD, Isern S, Hansen TW, et al. Differences in magnitude and duration of opioid-induced respiratory depression and analgesia with fentanyl and sufentanil. Anesth Analg. 1990; 70:8–15. PMID: 2136976.

38. Dewhirst E, Naguib A, Tobias JD. Chest wall rigidity in two infants after low-dose fentanyl administration. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012; 28:465–468. PMID: 22561320.

39. Coruh B, Tonelli MR, Park DR. Fentanyl-induced chest wall rigidity. Chest. 2013; 143:1145–1146. PMID: 23546488.

40. Ross AK, Davis PJ, Dear Gd GL, Ginsberg B, McGowan FX, Stiller RD, et al. Pharmacokinetics of remifentanil in anesthetized pediatric patients undergoing elective surgery or diagnostic procedures. Anesth Analg. 2001; 93:1393–1401. PMID: 11726413.

41. Choi SH, Koo BN, Nam SH, Lee SJ, Kim KJ, Kil HK, et al. Comparison of remifentanil and fentanyl for postoperative pain control after abdominal hysterectomy. Yonsei Med J. 2008; 49:204–210. PMID: 18452255.

42. Jabalameli M, Rouholamin S, Gourtanian F. A comparison of the effects of fentanyl and remifentanil on nausea, vomiting, and pain after cesarean section. Iran J Med Sci. 2011; 36:183–187. PMID: 23357939.
43. Bouillon T, Bruhn J, Radu-Radulescu L, Andresen C, Cohane C, Shafer SL. A model of the ventilatory depressant potency of remifentanil in the non-steady state. Anesthesiology. 2003; 99:779–787. PMID: 14508307.

44. Guay J, Gaudreault P, Tang A, Goulet B, Varin F. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in normal children. Can J Anaesth. 1992; 39:14–20. PMID: 1531117.
45. Scholz J, Steinfath M, Schulz M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of alfentanil, fentanyl and sufentanil. An update. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1996; 31:275–292. PMID: 8896944.
46. Leoni F, Benni F, Iacobucci T, de Francisci G. Pain control with low-dose alfentanil in children undergoing minor abdominal and genitourinary surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2004; 21:738–742. PMID: 15595588.

47. Mildh LH, Scheinin H, Kirvelä OA. The concentration-effect relationship of the respiratory depressant effects of alfentanil and fentanyl. Anesth Analg. 2001; 93:939–946. PMID: 11574361.

48. Forrest JB, Heitlinger EL, Revell S. Ketorolac for postoperative pain management in children. Drug Saf. 1997; 16:309–329. PMID: 9187531.

49. Rusy LM, Houck CS, Sullivan LJ, Ohlms LA, Jones DT, McGill TJ, et al. A double-blind evaluation of ketorolac tromethamine versus acetaminophen in pediatric tonsillectomy: analgesia and bleeding. Anesth Analg. 1995; 80:226–229. PMID: 7818104.
50. Vetter TR, Heiner EJ. Intravenous ketorolac as an adjuvant to pediatric patient-controlled analgesia with morphine. J Clin Anesth. 1994; 6:110–113. PMID: 8204227.

51. Ceelie I, de Wildt SN, van Dijk M, van den Berg MM, van den Bosch GE, Duivenvoorden HJ, et al. Effect of intravenous paracetamol on postoperative morphine requirements in neonates and infants undergoing major noncardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2013; 309:149–154. PMID: 23299606.
52. Rivera-Penera T, Gugig R, Davis J, McDiarmid S, Vargas J, Rosenthal P, et al. Outcome of acetaminophen overdose in pediatric patients and factors contributing to hepatotoxicity. J Pediatr. 1997; 130:300–304. PMID: 9042136.

53. Krechel SW, Bildner J. CRIES: a new neonatal postoperative pain measurement score. Initial testing of validity and reliability. Paediatr Anaesth. 1995; 5:53–61. PMID: 8521311.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download