1. Zhang A, Zhu QY, Luk YS, Ho KY, Fung KP, Chen ZY. Inhibitory effects of jasmine green tea epicatechin isomers on free radical-induced lysis of red blood cells. Life Sci. 1997; 61:383–394. PMID:
9244364.

2. Mabe K, Yamada M, Oguni I, Takahashi T. In vitro and in vivo activities of tea catechins against Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999; 43:1788–1791. PMID:
10390246.
3. Han MK. Epigallocatechin gallate, a constituent of green tea, suppresses cytokine-induced pancreatic beta-cell damage. Exp Mol Med. 2003; 35:136–139. PMID:
12754418.
4. Hara S, Endo T, Kuriiwa F, Kano S. NADPH-dependent reaction of paraquat in mouse brain microsomes. Toxicol Lett. 1990; 54:271–277. PMID:
2124383.
5. Yang CS, Maliakal P, Meng X. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by tea. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002; 42:25–54. PMID:
11807163.

6. Lim DY, Lee ES, Park HG, Kim BC, Hong SP, Lee EB. Comparison of green tea extract and epigallocatechin gallate on blood pressure and contractile responses of vascular smooth muscle of rats. Arch Pharm Res. 2003; 26:214–223. PMID:
12723935.

7. Miura Y, Chiba T, Tomita H, Koizumi H, Miura S, Umegaki K. Tea catechins prevent the development of atherosclerosis in apoprotein E-deficient mice. J Nutr. 2001; 131:27–32. PMID:
11208934.

8. Hertog MG, Feskens EJ, Hollman PC, Katan MB, Kromhout D. Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of coronary heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Lancet. 1993; 342:1007–1011. PMID:
8105262.

9. Jin JY, Park SH, Bae JH, Cho HC, Lim JG, Park WS. Uncoupling by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate of ATP-sensitive potassium channels from phosphatidylinositol polyphosphates and ATP. Pharmacol Res. 2007; 56:237–247. PMID:
17656102.

10. Park JW, Jang YH, Kim JM, Lee H, Park WK, Lim MB. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin gallate reduces neuronal cell damage and up-regulation of MMP-9 activity in hippocampal CA1 and CA2 areas following transient global cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 2009; 87:567–575. PMID:
18752302.

11. Jang YH, Lee YC, Park NH, Shin HY, Mun KC, Choi MS. Polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin gallate protection from ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38:2190–2194. PMID:
16980039.

12. Townsend PA, Scarabelli TM, Pasini E, Gitti G, Menegazzi M, Suzuki H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits STAT-1 activation and protects cardiac myocytes from ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis. FASEB J. 2004; 18:1621–1623. PMID:
15319365.
13. Aneja R, Hake PW, Burroughs TJ, Denenberg AG, Wong HR, Zingarelli B. Epigallocatechin, a green tea polyphenol, attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Med. 2004; 10:55–62. PMID:
15502883.

14. Lee YC, Jang YH, Kim JM, Kim AR, Kim CJ, Kim YN. Effect of a kappa-opioid receptor agonist U50488H given at early reperfusion phase in isolated rat hearts. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008; 54:S29–S34.

15. Li D, Yang C, Chen Y, Tian J, Liu L, Dai Q. Identification of a PKCepsilon-dependent regulation of myocardial contraction by epicatechin-3-gallate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008; 294:H345–H353. PMID:
17951366.
16. Hirai M, Hotta Y, Ishikawa N, Wakida Y, Fukuzawa Y, Isobe F. Protective effects of EGCg or GCg, a green tea catechin epimer, against postischemic myocardial dysfunction in guinea-pig hearts. Life Sci. 2007; 80:1020–1032. PMID:
17174345.

17. Lochner A, Genade S, Moolman JA. Ischemic preconditioning: infarct size is a more reliable endpoint than functional recovery. Basic Res Cardiol. 2003; 98:337–346. PMID:
12955407.

18. Nakachi K, Matsuyama S, Miyake S, Suganuma M, Imai K. Preventive effects of drinking green tea on cancer and cardiovascular disease: epidemiological evidence for multiple targeting prevention. Biofactors. 2000; 13:49–54. PMID:
11237198.

19. Sano J, Inami S, Seimiya K, Ohba T, Sakai S, Takano T. Effects of green tea intake on the development of coronary artery disease. Circ J. 2004; 68:665–670. PMID:
15226633.

20. Kuriyama S. The relation between green tea consumption and cardiovascular disease as evidenced by epidemiological studies. J Nutr. 2008; 138:1548S–1553S. PMID:
18641205.

21. Kuriyama S, Shimazu T, Ohmori K, Kikuchi N, Nakaya N, Nishino Y. Green tea consumption and mortality due to cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all causes in Japan: the Ohsaki study. JAMA. 2006; 296:1255–1265. PMID:
16968850.
22. Potenza MA, Marasciulo FL, Targuinio M, Tiravanti E, Colantuono G, Federici A. EGCG, a green tea polyphenol, improves endothelial function and insulin sensitivity, reduces blood pressure, and protects against myocardial I/R injury in SHR. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 292:E1378–E1387. PMID:
17227956.

23. Xi JK, Jin YZ, Cui X, Xu Z. Cardioprotection against reperfusion injury: updated mechanisms and strategies. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2007; 59:553–561. PMID:
17940694.
24. Hausenloy DJ, Tsang A, Yellon DM. The reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway: a common target for both ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005; 15:69–75. PMID:
15885573.

25. Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Survival kinases in ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 2006; 70:240–253. PMID:
16545352.

26. Dreger H, Lorenz M, Kehrer A, Baumann G, Stangl K, Stangl V. Characteristics of catechin- and theaflavin-mediated cardioprotection. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008; 233:427–433. PMID:
18367631.
27. Hausenloy DJ, Maddock HL, Baxter GF, Yellon DM. Inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening: a new paradigm for myocardial preconditioning? Cardiovasc Res. 2002; 55:534–543. PMID:
12160950.

28. Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore: its fundamental role in mediating cell death during ischaemia and reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003; 35:339–341. PMID:
12689812.

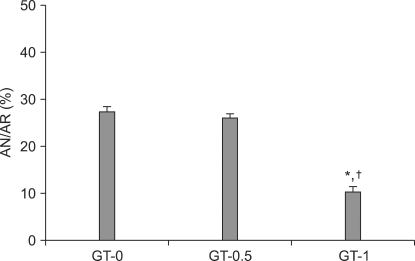
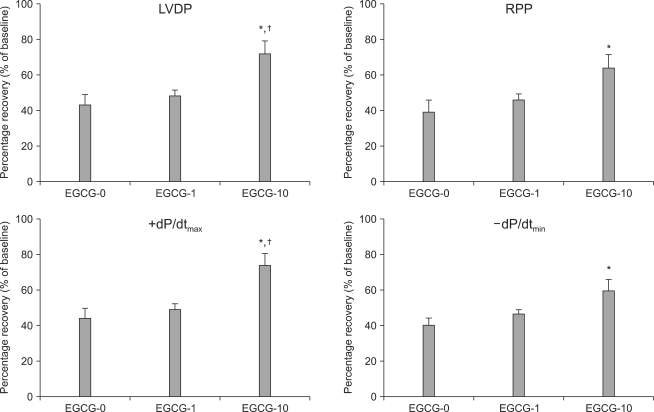
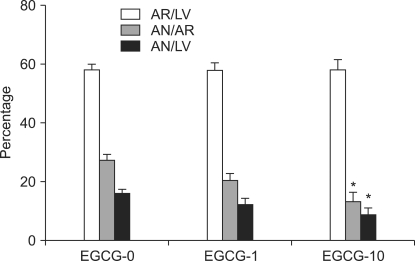
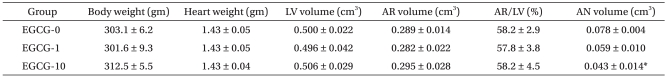




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download