Abstract
Background
Emergence agitation (EA) in children after sevoflurane anesthesia is common. The purpose of this study was to compare the incidences of EA between ketamine and thiopental sodium induction in children underwent sevoflurane anesthesia. We also evaluated if a small dose of fentanyl could reduce the incidence of EA.
Methods
The patients who were scheduled for strabismus or entropion surgery were divided into 4 groups. The patients in Groups 1 and 2 were induced anesthesia with ketamine 1.5 mg/kg; those in Groups 3 and 4 were induced with thiopental sodium 5 mg/kg. The patients in Groups 1 and 3 received an injection of fentanyl 1.5 µg/kg, whereas the patients in Groups 2 and 4 received IV saline of the same volume. Anesthesia was maintained with sevoflurane. The recovery characteristics and EA in recovery room were assessed.
Results
The incidence of EA was significantly higher in Groups 2 and 4 and there was no difference between Groups 2 and 4. Group 2 had almost an eleven-fold higher risk of developing EA than did Group 1, and the incidence of EA in Group 4 was sixty-nine-fold higher than that of Group 1. The risk factor for EA was only the kind of medication. Preoperative anxiety had no significant correlation with EA.
Go to : 
Sevoflurane is a popular anesthetic for children because it is less pungent and it has a rapid onset and offset because of its lower solubility in blood, and this drug shows a relative lack of airway irritation and greater hemodynamic stability. Yet sevoflurane anesthesia is frequently associated with emergence agitation (EA) in children.
The purpose of this study was to compare the incidences of EA between ketamine and thiopental sodium anesthetic induction in children underwent sevoflurane anesthesia. Also, we investigated if a small dose of fentanyl could reduce the incidence of EA. The relation between preoperative anxiety and postoperative agitation was studied.
Go to : 
After obtaining the approval of the Ethics Committee at the author's institution and informed parental consent, 95 children who were 3-10 yrs old, pertaining to ASA physical status 1 and undergoing surgery for strabismus or entropion were studied. None of the patients had a history of previous anesthesia, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary or neurologic disease and/or current upper respiratory infection.
The patients were not premedicated, and the standard monitoring included an electrocardiogram, a sphygmomanometer and a pulse oximeter. The patients were randomly assigned to one of four groups. The patients received an IV injection of an equal volume of either 1.5 µg/kg of fentanyl or saline. The patients of Groups 1 and 2 were induced anesthesia with ketamine 1.5 mg/kg; those of Groups 3 and 4 were induced with thiopental sodium 5 mg/kg. The patients in Groups 1 and 3 received an injection of fentanyl 1.5 µg/kg after anesthetic induction, whereas the patients in Groups 2 and 4 received the same volume of IV saline. If the patients were anxious with receiving anesthesia or separation from the parents in the preanesthetic room, then a 1/2 dose of ketamine or thiopental sodium was injected. After loss of the eyelid reflex, the face mask was fitted with sevoflurane 3 vol% in O2 4 L/min, then rocuronium 0.4 mg/kg was injected and endotracheal intubation was performed after 3 minutes. Ketorolac 0.5 mg/kg and ondansetron 0.1 mg/kg were administered to each child immediately after the induction of anesthesia. Anesthesia was maintained with O2 1.5 L/min, N2O 1.5 L/min and sevoflurane 2-3 vol%. The anesthetic gas concentrations were adjusted to maintain adequate anesthesia and stable hemodynamics. Lung ventilation was controlled to maintain the end-tidal carbon dioxide tension at 30-35 mmHg. At the completion of surgery, the anesthetics were discontinued and neuromuscular blockade was antagonized with pyridostigmine 0.2 mg/kg and glycopyrrolate 0.008 mg/kg, and the children were allowed to breathe spontaneously. The endotracheal tube was removed after the return of sufficient spontaneous ventilation and the gag reflex. The time from discontinuation of the anesthetic gas to extubation and the duration of anesthesia were recorded.
The patients were subsequently transferred to the recovery room. In the recovery room, the state of emergence was evaluated by an anesthesiologist who was blind to the anesthetic technique used for each patient. The state of Emergence was characterized on a 3-point scale: 1 = asleep, calm or mildly agitated; 2 = moderately agitated or restless, but consolable; 3 = hysterical, crying inconsolable or thrashing. For purposes of the study, the patients were considered agitated if they had a score of 3.
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows, V.16.O (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The demographic data was analyzed using chi-square tests and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Turkey's test. Fisher's exact test was applied to compare the preoperative anxiety and the incidence of agitation between the four groups. EA was analyzed using a multivariate logistic regression model in which the dependent variable was the presence or absence of EA and the independent variables included the kind of medication, gender, age, weight, the presence of preoperative anxiety, the extubation time and the duration of anesthesia. The Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test was performed to determine whether any association was present between the presence of preoperative anxiety and the incidence of agitation. Statistical significance was assumed for P values < 0.05.
Go to : 
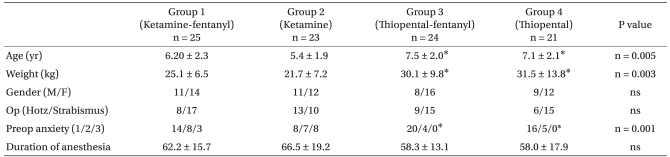
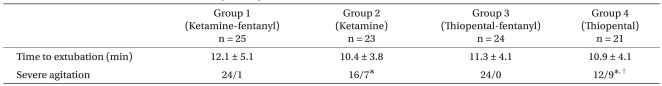
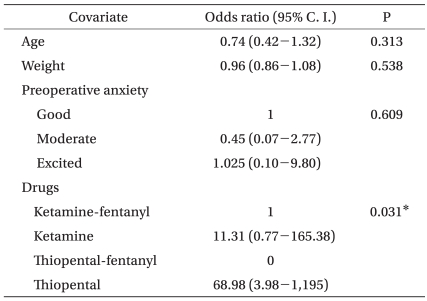
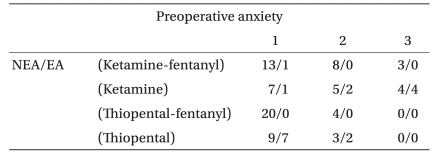
The groups were similar in gender, the kind of operation and the duration of anesthesia, but the preoperative anxiety was different in Groups 3 and 4 than that in Groups 1 and 2. And the age and weight were higher in Groups 3 and 4 than that in Groups 1 and 2 (Table 1) (P < 0.05). The incidence of emergence agitation was significantly higher in Groups 2 and 4, but there was no difference between Groups 2 and 4. There was no statistically significant difference among the four groups for the time to extubation (Table 2) (P > 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed the risk factor for EA was only the kind of medication. Group 2 had almost an eleven-fold higher risk of developing EA than Group 1, and Group 4's risk of developing EA was sixty-nine-fold higher than that of Group 1 (Table 3). The incidence of preoperative anxiety was higher in Group 1 and 2, but this had no correlation with EA (Table 4).
Go to : 
This study shows that the incidences of emergence agitation (EA) are similar between ketamine and thiopental sodium anesthetic induction in children undergoing strabismus and entropion surgery. In addition, 1.5 µg/kg of fentanyl after anesthetic induction markedly decreased the incidence of EA. Because there was a significant difference in the age, weight and preoperative anxiety between the groups, we analyzed the data with multivariate logistic regression analysis to determine what variables affected the incidence of EA, and the only variable that correlated with EA was the kind of medication.
Some investigator has asserted that the fentanyl doesn't decrease the EA [1], but our current results are consistent with those of the other studies that had demonstrated a decrease of EA with the use of fentanyl. One microgram of fentanyl per kilogram of body weight during anesthetic induction can reduce the EA in patients with moderate developmental disabilities [2], but other data has revealed that more than 2-5 µg/kg of fentanyl was effective [3-6]. A minimum 3 µg/kg of fentanyl will be needed to achieve adequate analgesia because a steady state plasma concentration of about 1.5 ng/ml of fentanyl provides adequate analgesia [7]. In our hospital, we use 1.5 µg/kg of fentanyl for anesthetic induction because of the concerns about bradycardia, delayed awakening and respiratory depression after surgery with the use of more than 2 µg/kg of fentanyl. Yet other reports have shown that there were no significant adverse effects after the use 2 µg/kg of fentanyl.
The effect of an anesthetic inducting agent causing EA has showed a lack of consistency in several studies. The incidence of EA after sevoflurane anesthesia during inguinal herniorraphy was similar in the thiopental sodium, propofol or ketamine induction groups. Some investigators have reported that ketamine, but not propofol, provides additional effects on decreasing the incidence of EA in pediatric patients [8], and ketamine induction provides less EA when compared to thiopental induction for desflurane anesthesia for a tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy without delayed recovery [9]. However, another report showed that the EA after sevoflurane anesthesia was significantly reduced by propofol induction, as compared with thiopental sodium [10]. Our study demonstrated no difference in the incidence of EA between ketamine and thiopental anesthetic induction for sevoflurane anesthesia. Meanwhile, the administration of alfentanil 10 µg/kg after induction reduced the EA [11], and 1 mg/kg of ketorolac, 0.5-1 µg/kg of dexmedetomidine and caudal block after anesthetic induction markedly diminished the EA [3,12-14]. Also, premedication with midazolam and oral ketamine has been shown to decrease the EA [4,15,16].
An effective method to reduce the EA is the addition of drugs at the end of sevoflurane anesthesia and 1 µg/kg of fentanyl, 1 mg/kg of propofol, 0.1 mg/kg of nalbuphine and 0.25 mg/kg of ketamine can decrease the EA without delaying recovery or discharge from the postanesthesia care unit (PACU) [17-22]. In children undergoing strabismus surgery, 1 mg/kg of propopfol at the end of surgery decreased the incidence of EA and improved the parents' satisfaction [18].
EA often results in physical harm to the child that may require additional treatment and increase the length of the postanesthesia care unit stay. There are many factors that can cause EA such as anesthetic agents, rapid emergence from anesthesia, otolaryngologic and ophthalmologic procedures, a previous op history, age, preoperative anxiety, pain, bladder expansion and a non-familiar environment [23,24]. EA occurs most frequently in the initial 10 min of recovery, the duration is generally limited and it resolves spontaneously within 30 min. However, prolonged episodes of agitation lasting for up to 2 days have been described, and additional medications such as opioids, benzodiazepine and hypnotics to address the retractable excitation may delay discharge from the recovery room and add additional costs [23,25].
Postoperative pain is an important factor leading to EA, and it is difficult to differentiate the agitated behavior resulting from pain or EA. But the incidence of EA was still high in the studies that used 0.5 mg/kg of ketorolac or regional anesthetic techniques for low abdominal surgery, and even pain-free radiologic procedures [14,17,21,26]. Postoperative nausea and vomiting further increase the severity and the incidence of EA, so we injected 0.1 mg/kg of ondansetron. Preoperative anxiety may be associated with adverse postoperative events, such as emergence agitation, or even behavioral changes during the postoperative period. Yet other studies haven't demonstrated that a relationship between preoperative anxiety and EA [24,27], and we could find no correlation between preoperative anxiety and EA.
Sevoflurane, with its low blood-gas solubility and blood-tissue solubility, has gained increasing acceptance for pediatric anesthesia. However, there are concerns about the EA after sevoflurane anesthesia, and the Incidence of EA has varied between 10-80% depending on the definition of EA used and the study design [28]. Several previous studies found no significant difference between sevoflurane and desflurane for the incidence of EA [1,29], but some prospective studies have shown that sevoflurane resulted in EA more frequently [26] or vice versa [28,30]. There are also conflicting results in the literature for the incidence of EA between sevoflurane and isoflurane anesthesia.
In conclusion, anesthetic induction with thiopental and ketamine showed no difference in the incidence of EA, and the administration of 1.5 µg/kg of fentanyl after the anesthetic induction reduced the incidence of EA without delaying the recovery time in children undergoing strabismus or entropion surgery under sevoflurane anesthesia. Preoperative anxiety had no significant relationship with EA.
Go to : 
References
1. Demirbilek S, Togal T, Cicek M, Aslan U, Sizanli E, Ersoy MO. Effects of fentanyl on the incidence of emergence agitation in children receiving desflurane or sevoflurane anaesthesia. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2004; 21:538–542. PMID: 15318465.

2. Hung WT, Chen CC, Liou CM, Tsai WY. The effects of low-dose fentanyl on emergence agitation and quality of life in patients with moderate developmental disabilities. J Clin Anesth. 2005; 17:494–498. PMID: 16297747.

3. Cohen IT, Hannallah RS, Hummer KA. The incidence of emergence agitation associated with desflurane anesthesia in children is reduced by fentanyl. Anesth Analg. 2001; 93:88–91. PMID: 11429345.

4. Kararmaz A, Kaya S, Turhanoglu S, Ozyilmaz MA. Oral ketamine premedication can prevent emergence agitation in children after desflurane anaesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004; 14:477–482. PMID: 15153210.

5. Guler G, Akin A, Tosun Z, Ors S, Esmaoglu A, Boyaci A. Single-dose dexmedetomidine reduces agitation and provides smooth extubation after pediatric adenotonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005; 15:762–766. PMID: 16101707.

6. Cook BA, Bass JW, Nomizu S, Alexander ME. Sedation of children for technical procedures: current standard of practice. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1992; 31:137–142. PMID: 1547584.
7. Mishra LD, Tiwari A. Pain and emergence agitation in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006; 50:124. PMID: 16451163.

8. Cohen IT, Drewsen S, Hannallah RS. Propofol or midazolam do not reduce the incidence of emergence agitation associated with desflurane anaesthesia in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy. Paediatr Anaesth. 2002; 12:604–609. PMID: 12358656.

9. Kim HS, Lee SK, Kang HS, Kim YM, Choi H, Moon HS. Comparison of thiopental and ketamine induction on emergence agitation after desflurane anesthesia in children undergoing a tonsillectomy. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2007; 53:356–360.
10. Hwang SM, Kim KS, Lim SY. Comparison of emergence agitation from sevoflurane anesthesia in propofol or thiopental sodium induction. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2004; 46:647–651.

11. Kim JY, Chang YJ, Lee JY, Park HY, Kwak HJ. Post-induction alfentanil reduces sevoflurane-associated emergence agitation in children undergoing an adenotonsillectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009; 53:678–681. PMID: 19419364.

12. Davis PJ, Greenberg JA, Gendelman M, Fertal K. Recovery characteristics of sevoflurane and halothane in preschool-aged children undergoing bilateral myringotomy and pressure equalization tube insertion. Anesth Analg. 1999; 88:34–38. PMID: 9895062.

13. Isik B, Arslan M, Tunga AD, Kurtipek O. Dexmedetomidine decreases emergence agitation in pediatric patients after sevoflurane anesthesia without surgery. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006; 16:748–753. PMID: 16879517.

14. Shin HL, An TH, Chung CD, Yu BS, So KY. The comparative effects of caudal block and IV ketorolac on emergence delirium after sevoflurane anesthesia in children. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2004; 47:233–237.

15. Flynn F, Lane M, Morgan P. Regarding sevoflurane and emergence agitation...again! Paediatr Anaesth. 2008; 18:82–83. PMID: 18095974.

16. Ko YP, Huang CJ, Hung YC, Su NY, Tsai PS, Chen CC, et al. Premedication with low-dose oral midazolam reduces the incidence and severity of emergence agitation in pediatric patients following sevoflurane anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 2001; 39:169–177. PMID: 11840583.
17. Cravero JP, Beach M, Thyr B, Whalen K. The effect of small dose fentanyl on the emergence characteristics of pediatric patients after sevoflurane anesthesia without surgery. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:364–367. PMID: 12873918.

18. Aouad MT, Yazbeck-Karam VG, Nasr VG, El-Khatib MF, Kanazi GE, Bleik JH. A single dose of propofol at the end of surgery for the prevention of emergence agitation in children undergoing strabismus surgery during sevoflurane anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2007; 107:733–738. PMID: 18073548.

19. Kim HJ, Kim HS, Kim SD, Kim CS, Kim JT, Lee KJ, et al. Effects of propofol and nalbuphine on emergence agitation after sevoflurane anesthesia in children for strabismus surgery. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008; 55:575–578.

20. Abu-Shahwan I, Chowdary K. Ketamine is effective in decreasing the incidence of emergence agitation in children undergoing dental repair under sevoflurane general anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2007; 17:846–850. PMID: 17683402.

21. Abu-Shahwan I. Effect of propofol on emergence behavior in children after sevoflurane general anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2008; 18:55–59. PMID: 18095967.

22. Dalens BJ, Pinard AM, Letourneau DR, Albert NT, Truchon RJ. Prevention of emergence agitation after sevoflurane anesthesia for pediatric cerebral magnetic resonance imaging by small doses of ketamine or nalbuphine administered just before discontinuing anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2006; 102:1056–1061. PMID: 16551898.

23. Aouad MT, Nasr VG. Emergence agitation in children: an update. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2005; 18:614–619. PMID: 16534301.

24. Keaney A, Diviney D, Harte S, Lyons B. Postoperative behavioral changes following anesthesia with sevoflurane. Paediatr Anaesth. 2004; 14:866–870. PMID: 15385017.

25. Kuratani N, Oi Y. Greater incidence of emergence agitation in child-ren after sevoflurane anesthesia as compared with halothane: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology. 2008; 109:225–232. PMID: 18648231.
26. Bortone L, Ingelmo P, Grossi S, Grattagliano C, Bricchi C, Barantani D, et al. Emergence agitation in preschool children: double-blind, randomized, controlled trial comparing sevoflurane and isoflurane anesthesia. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006; 16:1138–1143. PMID: 17040302.

27. Przybylo HJ, Martini DR, Mazurek AJ, Bracey E, Johnsen L, Cote CJ. Assessing behaviour in children emerging from anaesthesia: can we apply psychiatric diagnostic techniques? Paediatr Anaesth. 2003; 13:609–616. PMID: 12950862.

28. Welborn LG, Hannallah RS, Norden JM, Ruttimann UE, Callan CM. Comparison of emergence and recovery characteristics of sevoflurane, desflurane, and halothane in pediatric ambulatory patients. Anesth Analg. 1996; 83:917–920. PMID: 8895263.

29. Bae JY, Son E, Kim JT, Kim HS, Kim CS, Kim SD. Comparison of emergence agitaiton between sevoflurane, desflurane, and propofol with bispectral index monitoring in pediatric anesthesia. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008; 55:161–165.
30. Valley RD, Freid EB, Bailey AG, Kopp VJ, Georges LS, Fletcher J, et al. Tracheal extubation of deeply anesthetized pediatric patients: a comparison of desflurane and sevoflurane. Anesth Analg. 2003; 96:1320–1324. PMID: 12707126.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download