Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Cell culture, antibodies, and reagents
2. Cell viability assay
3. Immunoblotting
4. Analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential
5. Clinical study design
6. Statistical analysis
Results
1. In vitro synergistic effect of roflumilast and commonly used chemotherapy agents on cell viability
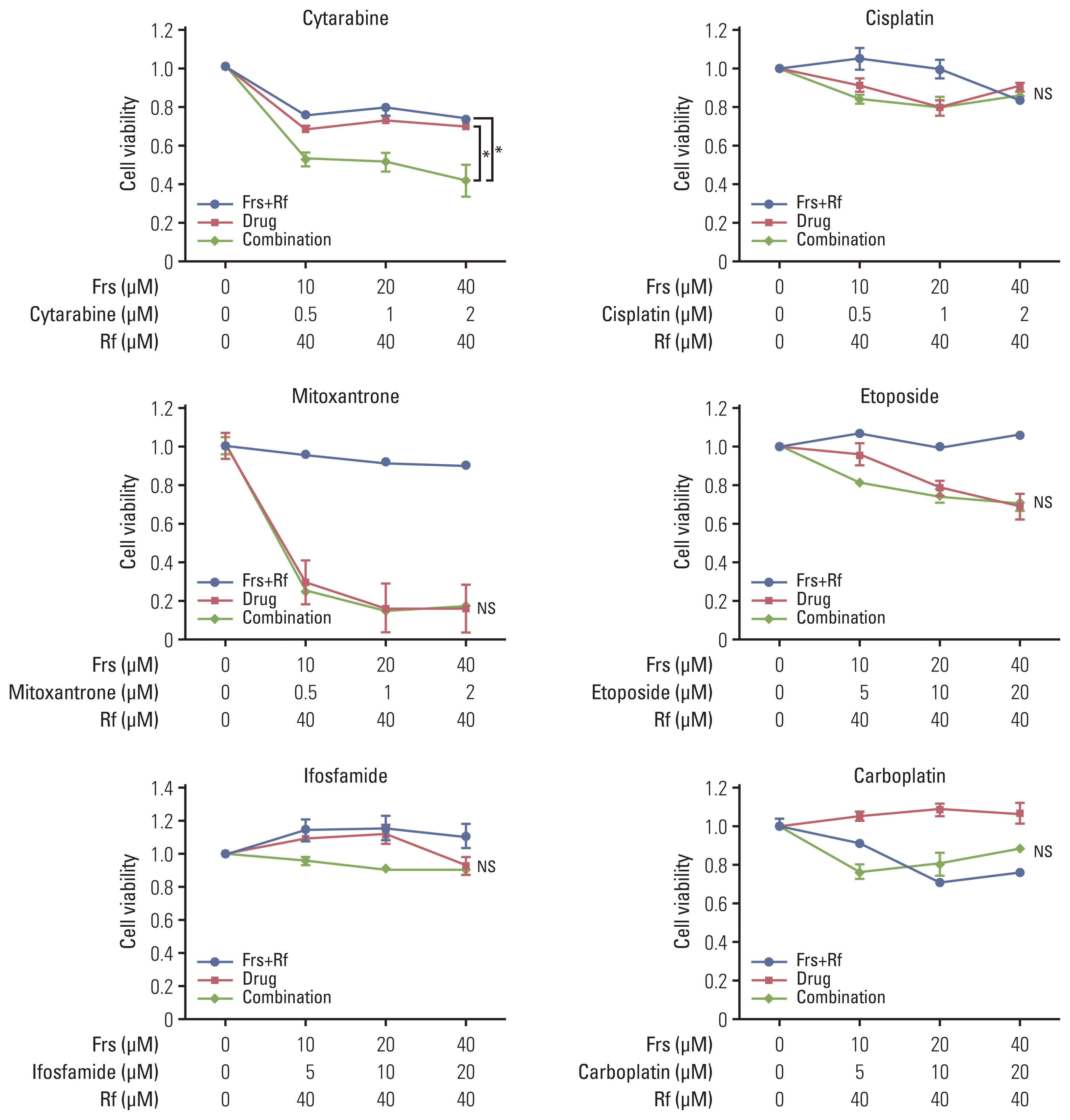 | Fig. 1Synergistic effect of roflumilast with chemotherapy drugs. A PDE4B-high cell line, OCI-Ly1, was treated with was treated with roflumilast (0 or 40 μM) in combination with forskolin (0, 10, 20, or 40 μM) and one of the six chemotherapy agents (cytarabine, cisplatin, mitoxantrone, etoposide, carboplatin, ifosfamide) that are commonly used for salvage chemotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. The treatment was conducted for 48 hours, as indicated and the MTS assay were performed to measure cell viability. The results are presented as mean±standard deviation and are representative of three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, One-way ANOVA). Frs, forskolin; Rf, roflumilast. |
2. Synergistic effect of roflumilast and cytarabine on inhibition of B-cell lymphoma viability
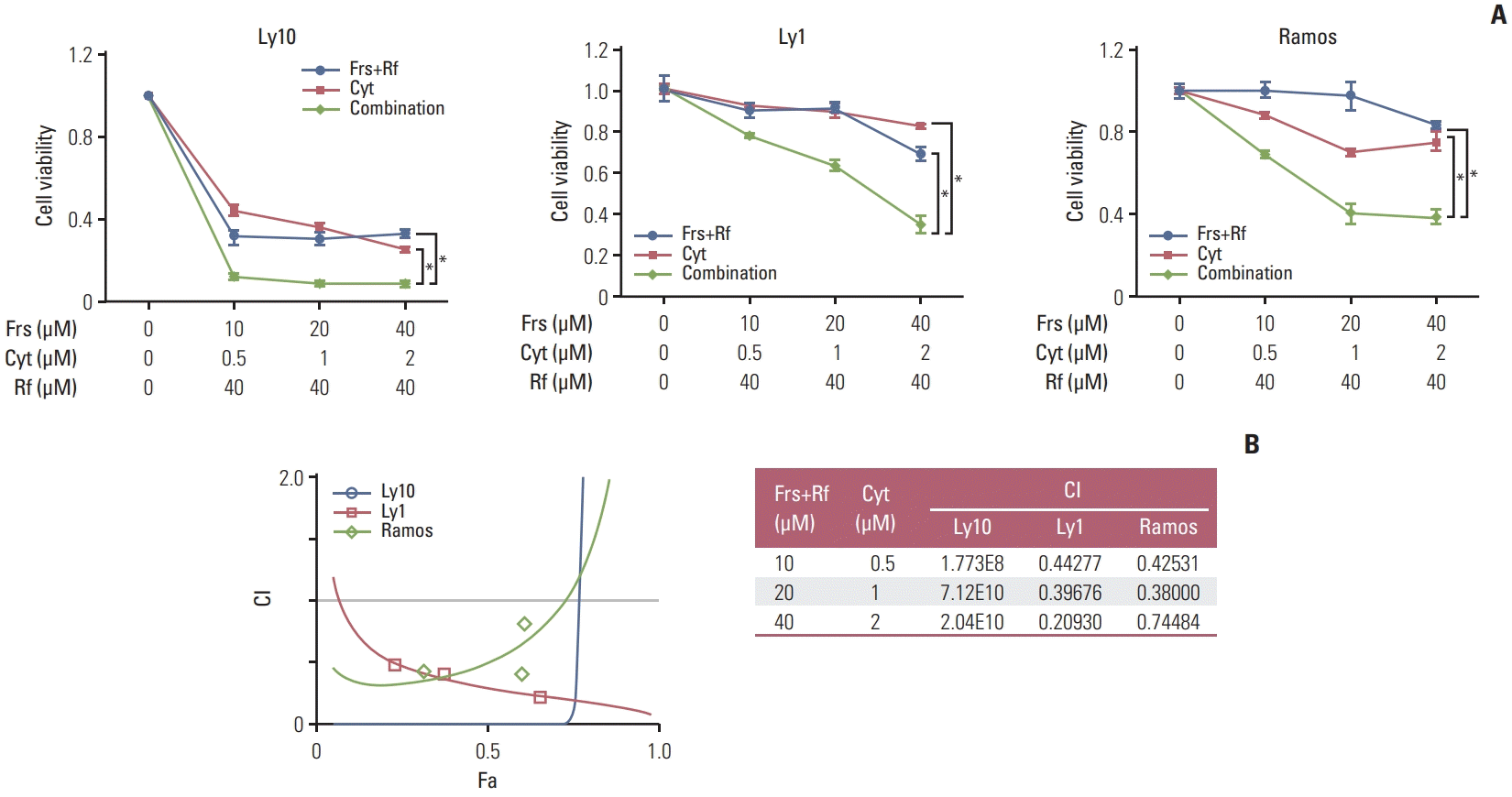 | Fig. 2Combination of roflumilast and cytarabine have synergistic effects on cell death. (A) Three PDE4B-high cell lines (Ly10, Ly1, and Ramos) were treated with forskolin (0, 10, 20, or 40 μM), cytarabine (0, 0.5, 1, or 2 μM) and roflumilast (0 or 40 μM) for 48 hours, as indicated and the MTS assay were performed to measure cell viability. The results are presented as mean±standard deviation and are representative of three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, One-way ANOVA). (B) To evaluate the levels of drug synergy, combination index (CI) values were estimated using the CompuSyn software. The percent inhibition (fraction affected, Fa) from drug combinations was compared with that from individual drugs. Synergy levels are as follows: < 0.1 very strong synergy; 0.1–0.3, strong synergy; 0.3–0.7, synergy; 0.7–0.85, moderate synergy; 0.85–0.90, slight synergy; 0.90–1.10, nearly additive; 1.10–1.20, slight antagonism; 1.20–1.45, moderate antagonism; and 1.45–3.30, antagonism. Cyt, cytarabine; Frs, forskolin; Rf, roflumilas. |
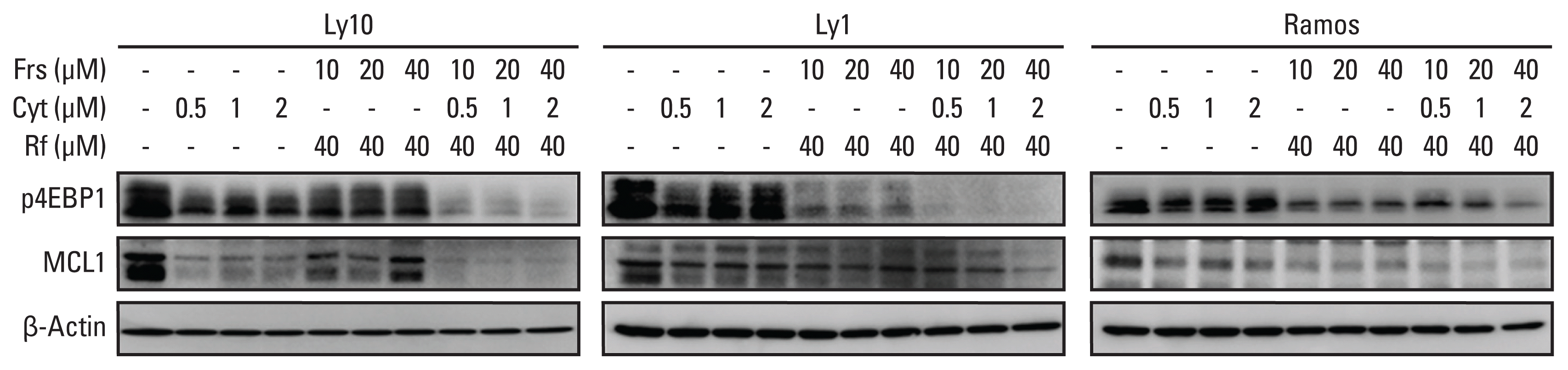
3. Synergistic effects between roflumilast and cytarabine influence mammalian target of rapamycin signaling and MCL1 levels
4. The combinatorial effects of roflumilast and cytarabine on mitochondrial membrane potential in B-cell lymphoma
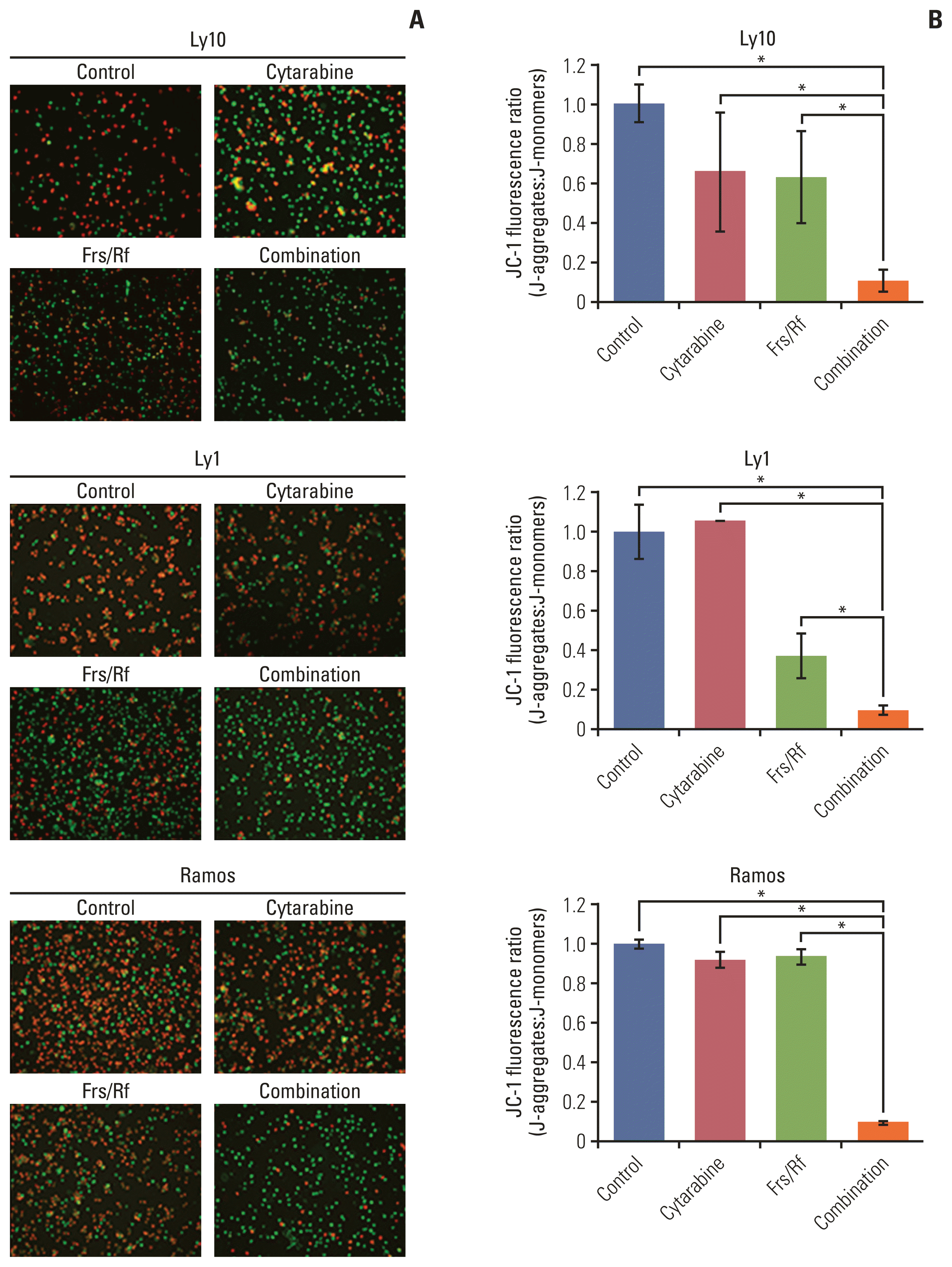 | Fig. 4Synergistic effect of roflumilast and cytarabine on mitochondrial membrane potential. (A) To identify the potential role of disruption of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) in apoptosis, an MMP assay was performed. First, all three cell lines (Ly1, Ly10, and Ramos) were treated with forskolin/roflumilast (40 μM), cytarabine (0.5 μM), or their combination for 48 hours and stained with the membrane-permeant dye JC-1. Subsequently, mitochondrial states were observed using fluorescence microscopy. Red-stained cells indicate live cells and green-stained cells indicate dead cells. (B) To quantify the number of cells with MMP disruption, all stained cells were counted and the ratio of red-stained cells to all stained cells was determined. The ratio was normalized to the control (DMSO) group. The results are presented as mean±standard deviation and are representative of three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, One-way ANOVA). Frs, forskolin; Rf, roflumilast. |
5. Characteristics of patients in the pilot study
Table 1
Values are presented as median (range) or number (%). ABC, activated B-cell; B2MG, beta-2 microglobulin; DLBCL, diffuse large B cell lymphoma; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; GCB, germinal center B-cell; IPI, International Prognostic Index; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; ORR, overall response rate; R-CHOP, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine, and prednisolone.
6. Survival and response to ESHAP chemotherapy combined with roflumilast
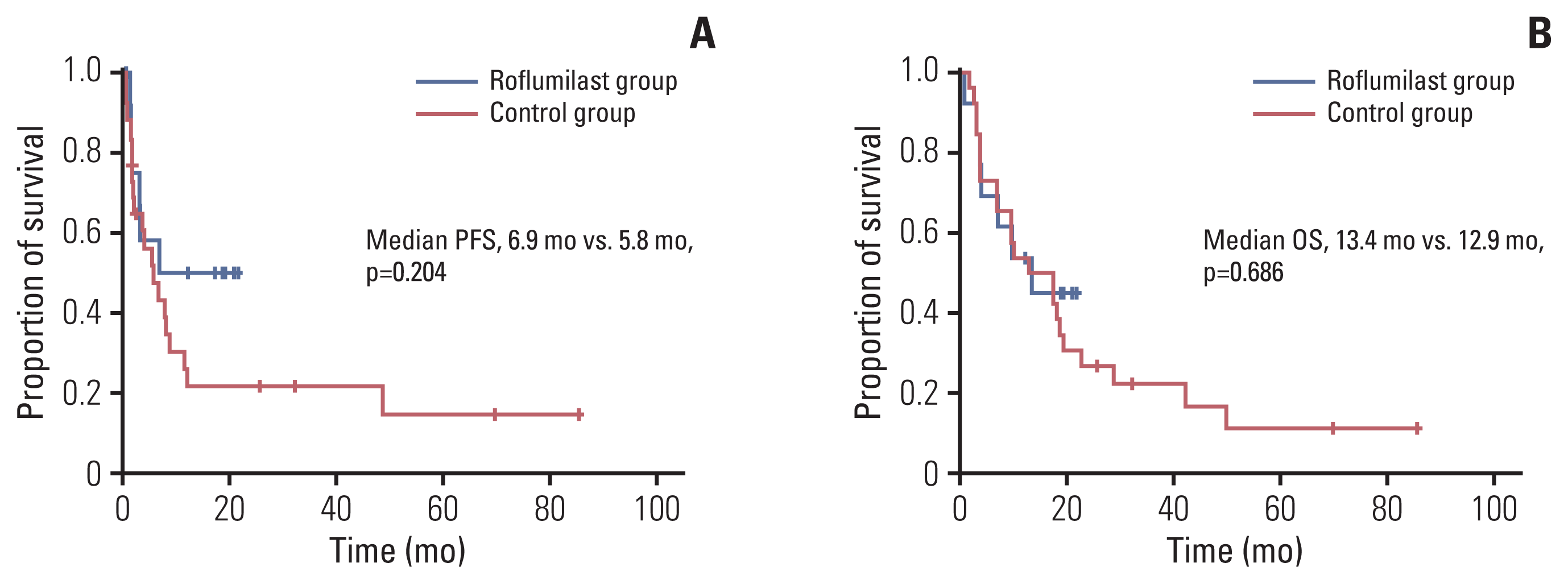 | Fig. 5Kaplan-Meier curves showing the progression-free survival (PFS) (A) and overall (OS) (B) of the patients. |
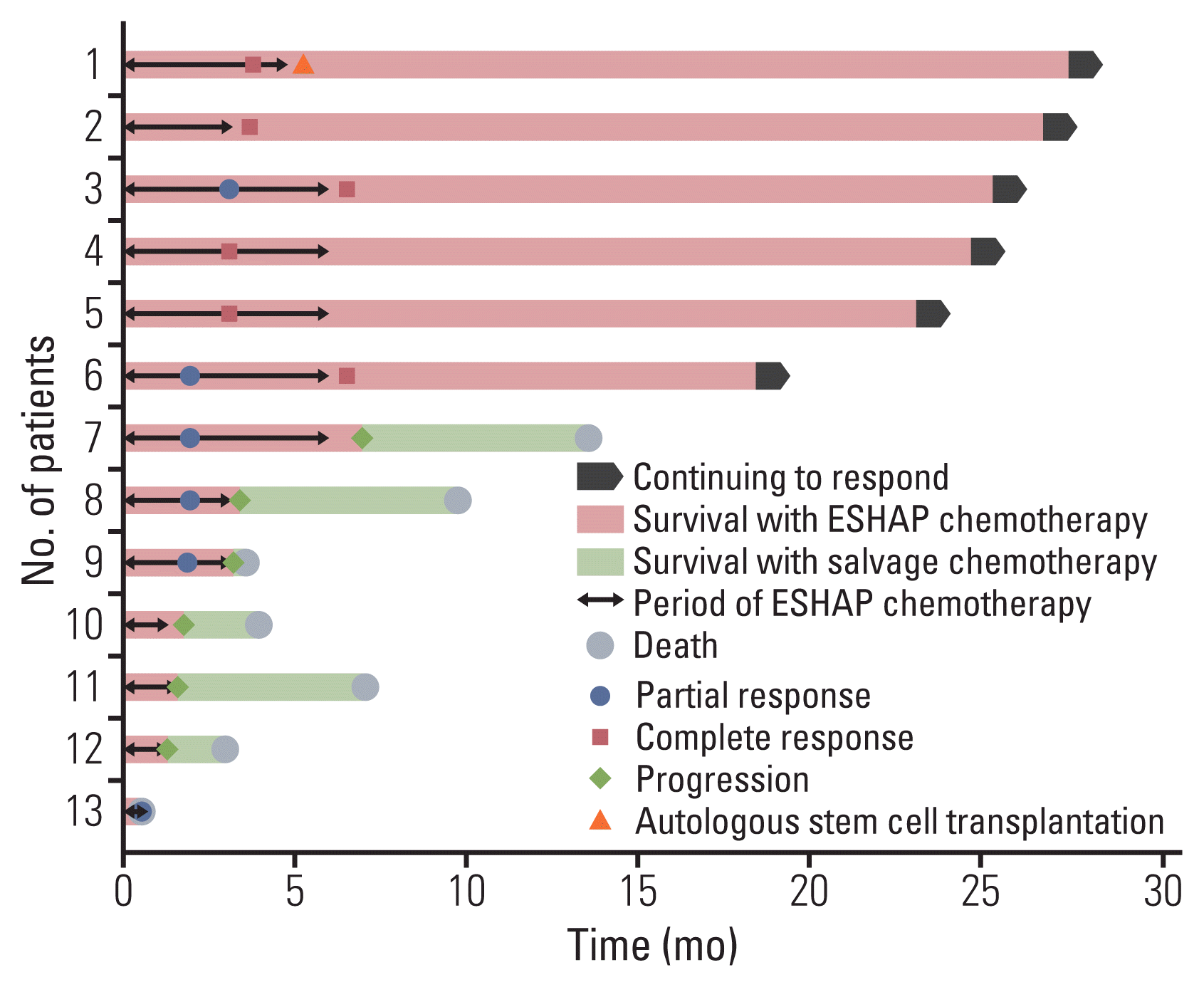 | Fig. 6Swimmer plot of 13 patients who received ESHAP (etoposide, cisplatin, methylprednisolone, and cytarabine) chemotherapy combined with roflumilast. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download