1. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues Revised. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2017.
2. Vaidya R, Witzig TE. Prognostic factors for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the R(X)CHOP era. Ann Oncol. 2014; 25:2124–33.

3. International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:987–94.
4. Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:235–42.

5. Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood. 2010; 116:2040–5.

6. Horvat M, Zadnik V, Juznic Setina T, Boltezar L, Pahole Golicnik J, Novakovic S, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: 10 years’ real-world clinical experience with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisolone. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15:3602–9.
7. Zhou Z, Sehn LH, Rademaker AW, Gordon LI, Lacasce AS, Crosby-Thompson A, et al. An enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the rituximab era. Blood. 2014; 123:837–42.

8. Montalban C, Diaz-Lopez A, Dlouhy I, Rovira J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Alonso S, et al. Validation of the NCCN-IPI for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): the addition of beta2-microglobulin yields a more accurate GELTAMO-IPI. Br J Haematol. 2017; 176:918–28.
9. Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007; 109:1857–61.

10. Chen Y, Han T, Iqbal J, Irons R, Chan WC, Zhu X, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Chinese patients: immunophenotypic and cytogenetic analyses of 124 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010; 133:305–13.
11. Hwang HS, Yoon DH, Suh C, Huh J. Body mass index as a prognostic factor in Asian patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy for diffuse large B cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. Ann Hematol. 2015; 94:1655–65.

12. Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004; 103:275–82.

13. Lister TA, Crowther D, Sutcliffe SB, Glatstein E, Canellos GP, Young RC, et al. Report of a committee convened to discuss the evaluation and staging of patients with Hodgkin’s disease: Cotswolds meeting. J Clin Oncol. 1989; 7:1630–6.

14. Kwak LW, Halpern J, Olshen RA, Horning SJ. Prognostic significance of actual dose intensity in diffuse large-cell lymphoma: results of a tree-structured survival analysis. J Clin Oncol. 1990; 8:963–77.

15. Lyman GH, Dale DC, Friedberg J, Crawford J, Fisher RI. Incidence and predictors of low chemotherapy dose-intensity in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a nationwide study. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:4302–11.

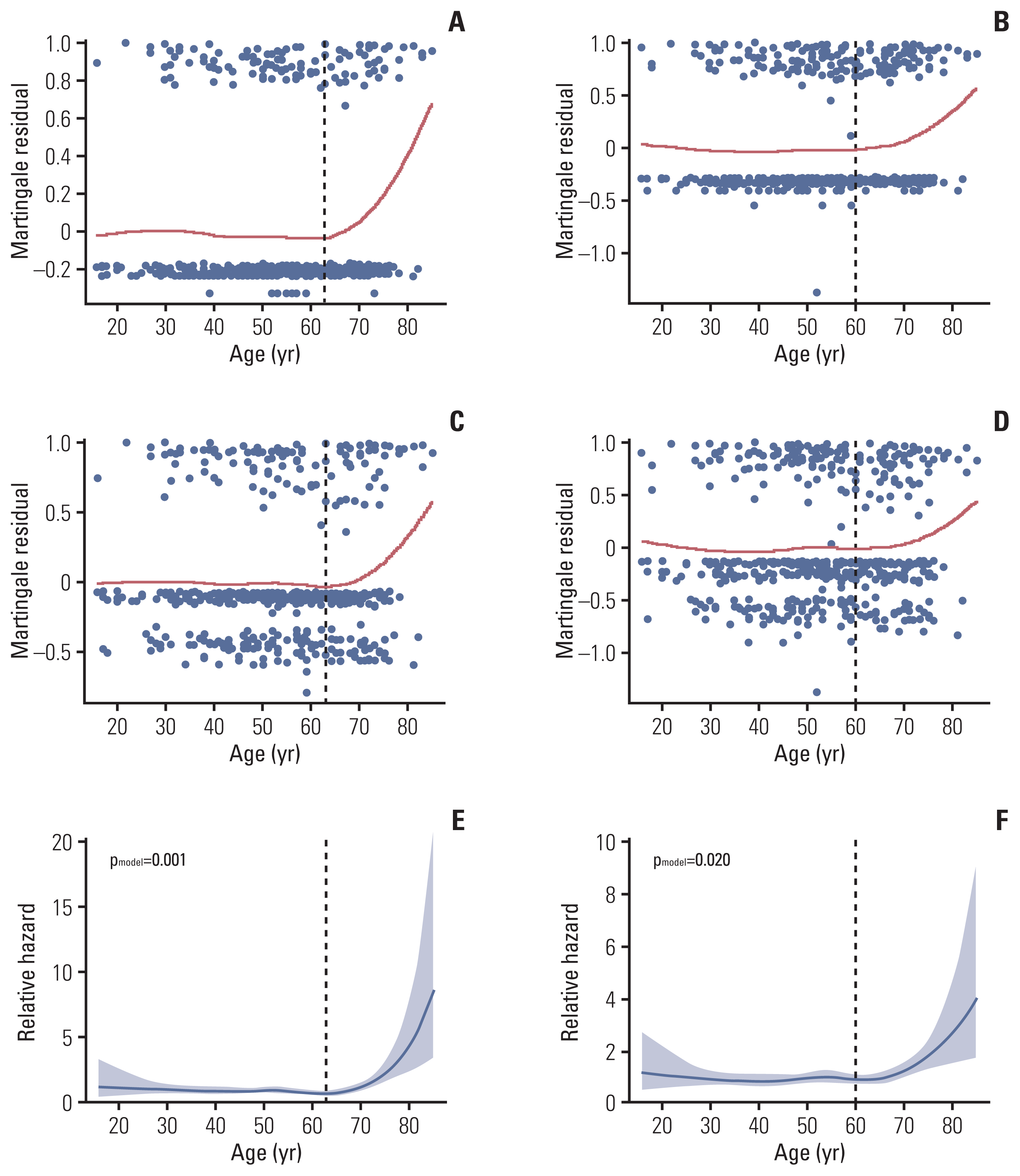
16. Therneau TM, Grambsch PM, Fleming TR. Martingale-based residuals for survival models. Biometrika. 1990; 77:147–60.

17. Harrell FE Jr. Regression modeling strategies: with applications to linear models, logistic and ordinal regression, and survival analysis. 2nd ed. New York: Springer;2015.
18. Castillo JJ, Winer ES, Olszewski AJ. Sites of extranodal involvement are prognostic in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: an analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database. Am J Hematol. 2014; 89:310–4.

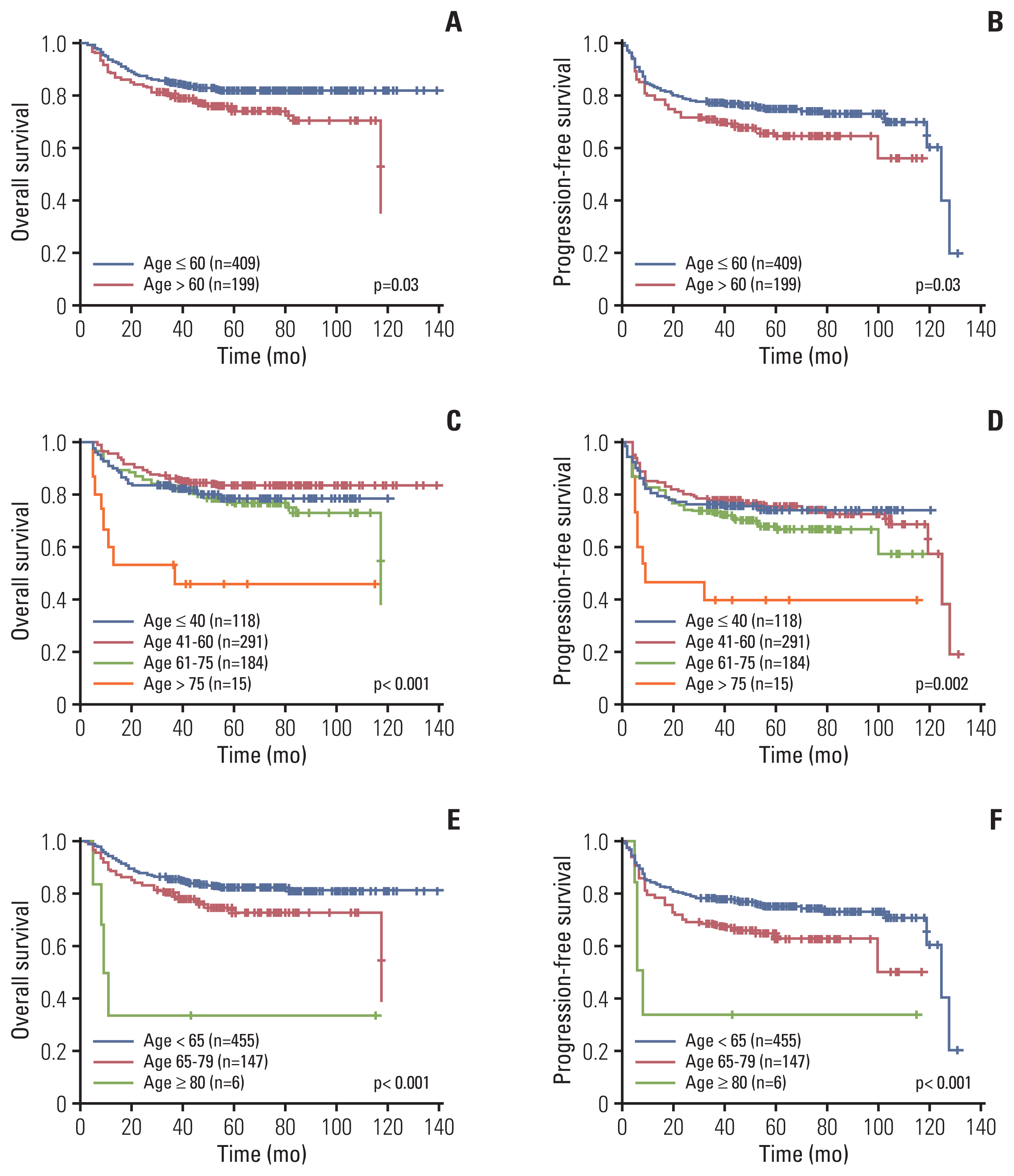
19. Hedstrom G, Hagberg O, Jerkeman M, Enblad G; Swedish Lymphoma Study G. The impact of age on survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a population-based study. Acta Oncol. 2015; 54:916–23.
20. Hong J, Kim SJ, Chang MH, Kim JA, Kwak JY, Kim JS, et al. Improved prognostic stratification using NCCN- and GELTAMO-international prognostic index in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:92171–82.

21. Chen HL, Zhou MQ, Tian W, Meng KX, He HF. Effect of age on breast cancer patient prognoses: a population-based study using the SEER 18 database. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0165409.

22. Lu CH, Lee SH, Liu KH, Hung YS, Wang CH, Lin YC, et al. Older age impacts on survival outcome in patients receiving curative surgery for solid cancer. Asian J Surg. 2018; 41:333–40.

23. Tas F, Ciftci R, Kilic L, Karabulut S. Age is a prognostic factor affecting survival in lung cancer patients. Oncol Lett. 2013; 6:1507–13.

24. Balducci L. Pharmacology of antineoplastic medications in older cancer patients. Oncology (Williston Park). 2009; 23:78–85.
25. Thieblemont C, Coiffier B. Lymphoma in older patients. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1916–23.

26. Mareschal S, Lanic H, Ruminy P, Bastard C, Tilly H, Jardin F. The proportion of activated B-cell like subtype among de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma increases with age. Haematologica. 2011; 96:1888–90.

27. Klapper W, Kreuz M, Kohler CW, Burkhardt B, Szczepanowski M, Salaverria I, et al. Patient age at diagnosis is associated with the molecular characteristics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2012; 119:1882–7.

28. Juul MB, Jensen PH, Engberg H, Wehberg S, Dessau-Arp A, Haziri D, et al. Treatment strategies and outcomes in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma among 1011 patients aged 75 years or older: A Danish population-based cohort study. Eur J Cancer. 2018; 99:86–96.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download