Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Reagents and plasmids
2. Real-time PCR
Table 1
4. Clinical samples
5. Construction of the plasmids containing different regions of C5AR1 promoter
6. Luciferase reporter gene assays
7. Western blot analysis
8. Immunohistochemistry analysis
9. Immunofluorescence analysis
10. ELISA
11. Animal transplantation
12. Cell viability assay
13. Plate clone formation assay
14. Transwell assay
15. Wound healing assay
16. Statistical analysis
Results
1. HBc facilitates the expression of C5AR1 in HBV-related hepatoma cells
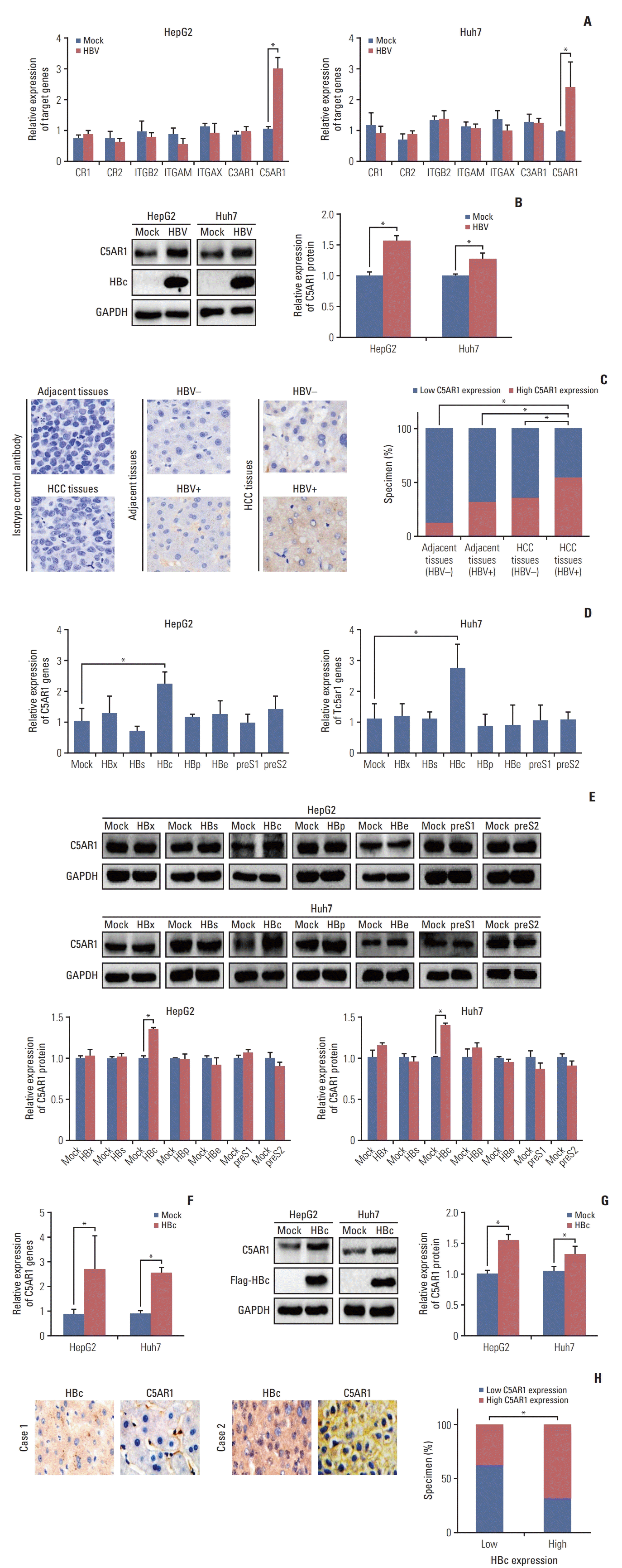 | Fig. 1The role of HBc on C5AR1 expression in HBV-related hepatoma cells. (A) The role of HBV on the expression of complement receptors in hepatoma cells at mRNA levels detected by real-time PCR. (B) The expression of C5AR1 protein mediated by HBV was measured by western blot. (C) The expression of C5AR1 protein in HBV-negative adjacent tissues (n=40), HBV-positive adjacent tissues (n=50), HBV-negative tumor tissues (n=50), and HBV-related tumor tissues (n=65) assessed by IHC analysis (×400). (D) The role of different viral genes on C5AR1 mRNA expression in hepatoma cells that measured by real-time PCR. (E) The role of different viral genes on C5AR1 protein expression in hepatoma cells. (F) The expression of C5 AR1 mRNA in HBc stably-transfected HCC cells, which transfected with Flag-HBc plasmid and selected by G418. (G) The expression of C5AR1 protein in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. (H) The correlation of C5AR1 protein and HBc protein in HBV-related tumor tissues assessed by IHC analysis, the tumor tissues with low HBc expression (n=24), the tumor tissues with high HBc expression (n=41) (×400). C5AR1, C5α receptor 1; HBc, the cells transfected with HBc plasmids; HBV, the cells transfected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) plasmids; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IHC, immunohistochemistry; Mock, the cells transfected with control plasmids; PCR, polymerase chain reaction. *p < 0.05. |
2. HBc promotes the activity of C5AR1 promoter via the NF-κB pathway in hepatoma cells
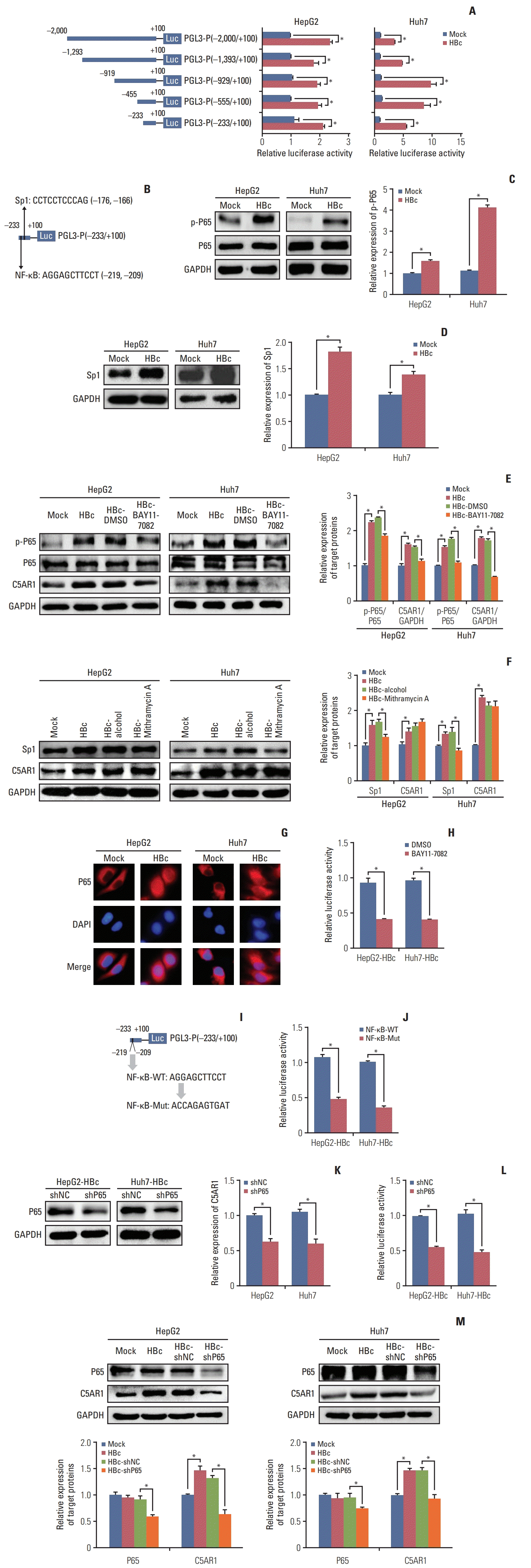 | Fig. 2The effect of the NF-κB pathway in activating the promoter of the C5AR1 mediated by HBc in hepatoma cells. (A) The identification of the regulatory region of C5AR1 promoter mediated by HBc via luciferase reporter gene assay. (B) The information of potential NF-κB and Sp1 binding site in C5AR1 promoter in PGL3-P (−233/+100) plasmid. (C) The activation of p65 in HBc-positive hepatoma cells and control cells. (D) The expression of Sp1 in HBc-positive hepatoma cells and control cells. (E) The effect of inhibition of p65 via BAY11-7082 on C5AR1 protein expression in hepatoma cells. (F) The effect of inhibition of Sp1 via Mithramycin A on C5AR1 protein expression in hepatoma cells. (G) The location of p65 in HBc-positive hepatoma cells and control cells. (H) The effect of inhibition of NF-κB via BAY11-7082 on the activity of C5AR1 promoter in PGL3-P (−233/+100) plasmid in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. (I) The information on the mutations in the NF-κB binding site in PGL3-P (−233/+100) plasmid. (J) The influence of the mutation in the NF-κB binding site on activation of C5AR1 promoter in PGL3-P (−233/+100) plasmid. (K) The inhibition of p65 using shRNA plasmids on the expression of p65 protein in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. (L) The effect of inhibition of p65 via shRNA on the activity of C5AR1 promoter in PGL3-P (−233/+100) plasmid in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. (M) The effect of inhibition of p65 by shRNA on C5AR1 protein expression in hepatoma cells. C5AR1, C5α receptor 1; HBc, cells transfected with HBc plasmid; HBc-shC5AR1, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA plasmid targeting C5AR1; HBc-shNC, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA control plasmid; Mock, the cells transfected with control plasmid; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB. *p < 0.05. |
3. C5AR1 mediated by HBc enhances the activation of signal pathways as well as the expression and secretion of IL-6 in hepatoma cells
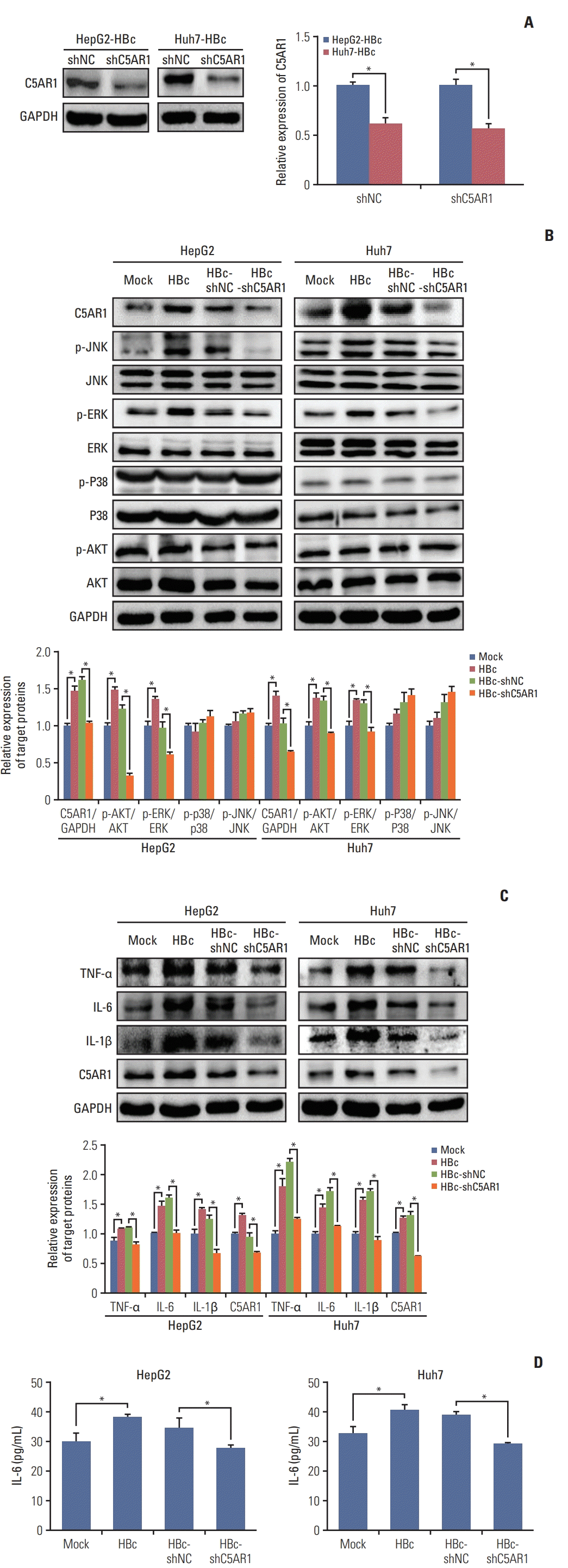 | Fig. 3The role of C5AR1 in intracellular signal pathways and inflammatory cytokines in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. (A) The inhibition of C5AR1 mediated by shRNA in the expression of C5AR1 protein in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. (B) The effect of inhibition of C5AR1 expression mediated by shRNA on the activation of JNK, ERK, p38, and P13K (AKT) pathway in hepatoma cells stably-transfected with HBc. (C) The effect of inhibition of C5AR1 expression mediated by shRNA on the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. (D) The effect of inhibition of C5AR1 expression mediated by shRNA on the secretion of IL-6 in HBc-positive hepatoma cells. C5AR1, C5α receptor 1; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HBc, cells transfected with HBc plasmid; HBc-shC5AR1, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA plasmid targeting C5AR1; HBc-shNC, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA control plasmid; IL, interleukin; Mock, cells transfected with control plasmid; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α. *p < 0.05. |
4. C5AR1 contributes to the growth and migration of hepatoma cells mediated by HBc
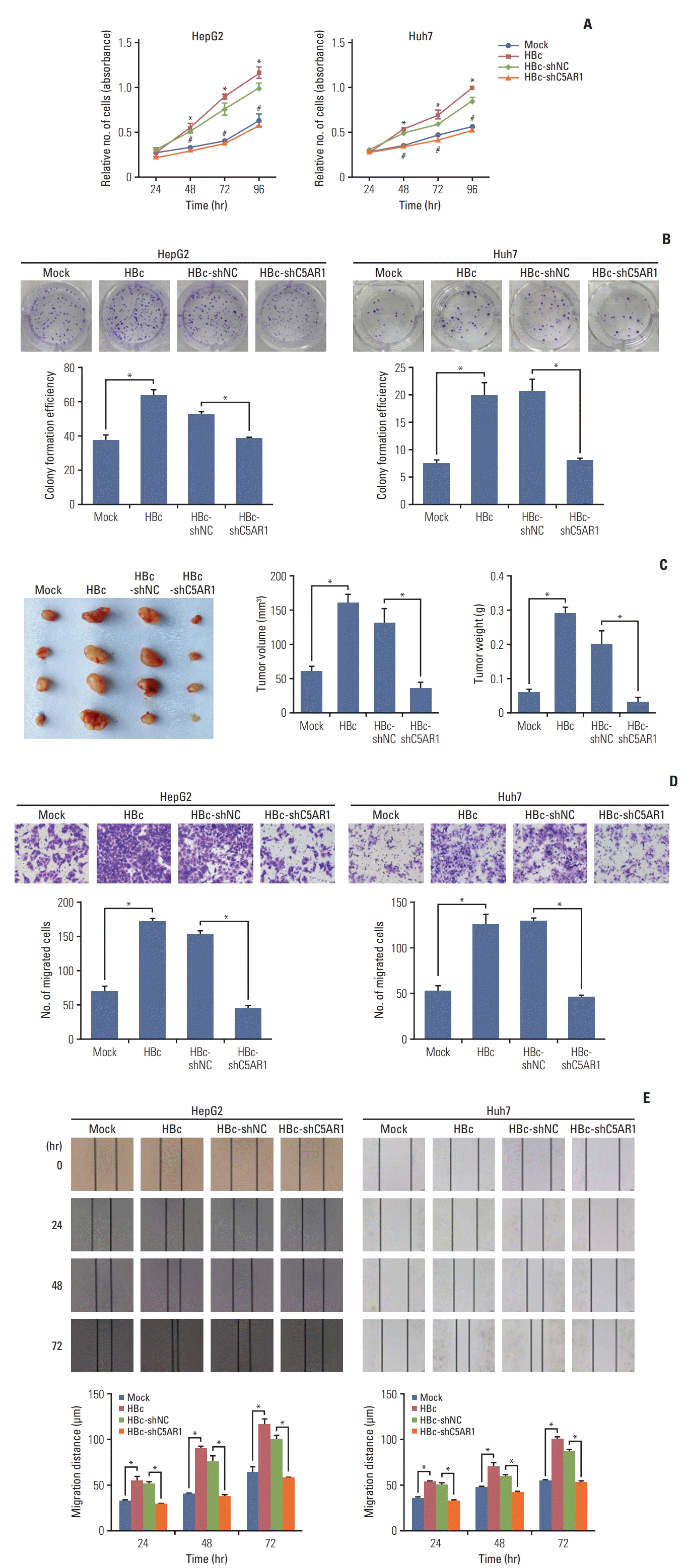 | Fig. 4The role of C5AR1 in the growth and migration of HCC cells mediated by HBc. (A) The effect of inhibition of C5AR1 expression by shRNA on the growth of HBc-positive hepatoma cells detected by CCK-8 assay. (B) The effect of inhibition of C5AR1 expression via shRNA on the growth of HBc-positive hepatoma cells assessed by plate clone formation assay. (C) The role of C5AR1 in the growth of hepatoma cells mediated by HBc in nude mice. (D) The inhibition of C5AR1 expression via shRNA on the migration of HBc-positive hepatoma cells detected by transwell assay. (E) The effect of inhibition of C5AR1 expression using shRNA on the migration of HBc-positive hepatoma cells was examined by wound healing assay. C5AR1, C5α receptor 1; CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8; HBc, cells transfected with HBc plasmid; HBc-shC5AR1, the HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA plasmid targeting C5AR1; HBc-shNC, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA control plasmid; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; Mock, cells transfected with control plasmid. In Fig. 4A, *p < 0.05, the Mock group compared with HBc group; #p < 0.05, the HBc-shNC group compared with HBc-shC5AR1 group. |
5. C5α facilitates the activation of signal pathways as well as the expression and secretion of IL-6 in HBc-positive hepatoma cells via C5AR1
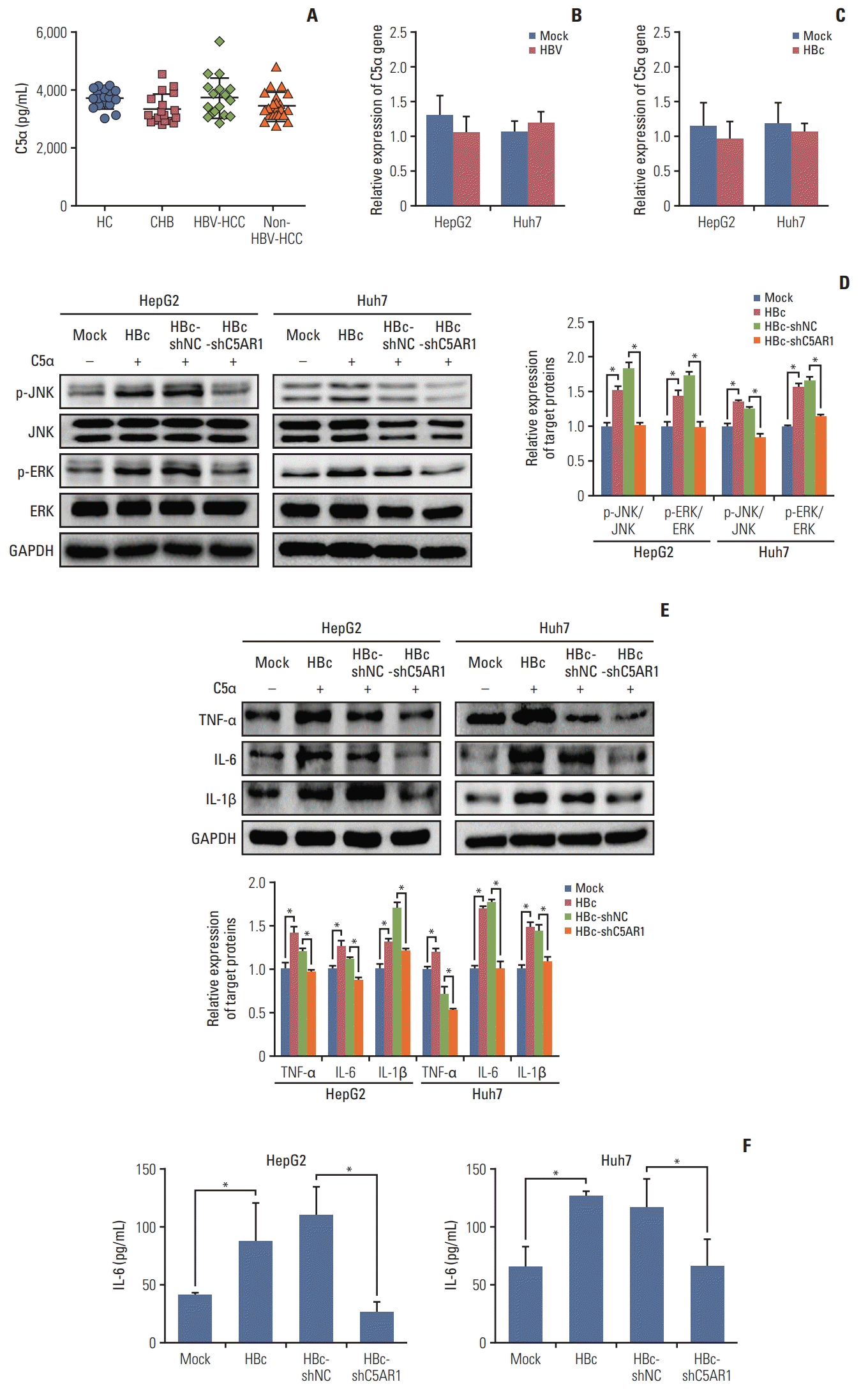 | Fig. 5C5α gene expression medicated by HBV or HBc, and the role of C5AR1 intracellular signal pathways and inflammatory cytokines in HBc-positive hepatoma cells stimulated by C5α. (A) The serum levels of C5α in HC, CHB patients, HCC patients with HBV infection (HBV-HCC), and HBV-negative HCC patients (non-HBV-HCC) were detected by ELISA. (B) The role of HBV on the expression of C5α at mRNA levels detected by real-time PCR. (C) The role of HBc on the expression of C5α at mRNA levels. (D) The role of C5AR1 in the C5α-mediated activation of intracellular signaling pathways in HBc-positive hepatoma cells (20 ng/mL). (E) The effect of C5AR1 on C5α-induced expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in HBc-positive hepatoma cells that measured by western blot. (F) The effect of C5AR1 on C5α-induced secretion of IL-6 in HBc-positive hepatoma cells detected by ELISA. C5AR1, C5α receptor 1; CHB, chronic hepatitis B; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HBc, cells transfected with HBc plasmid; HBc-shC5AR1, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA plasmid targeting C5AR1; HBc-shNC, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA control plasmid; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HC, health controls; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IL, interleukin; Mock, the cells transfected with control plasmid; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. *p < 0.05. |
6. C5α facilitate the growth and migration of HBc-positive hepatoma cells relied on the interaction with C5AR1
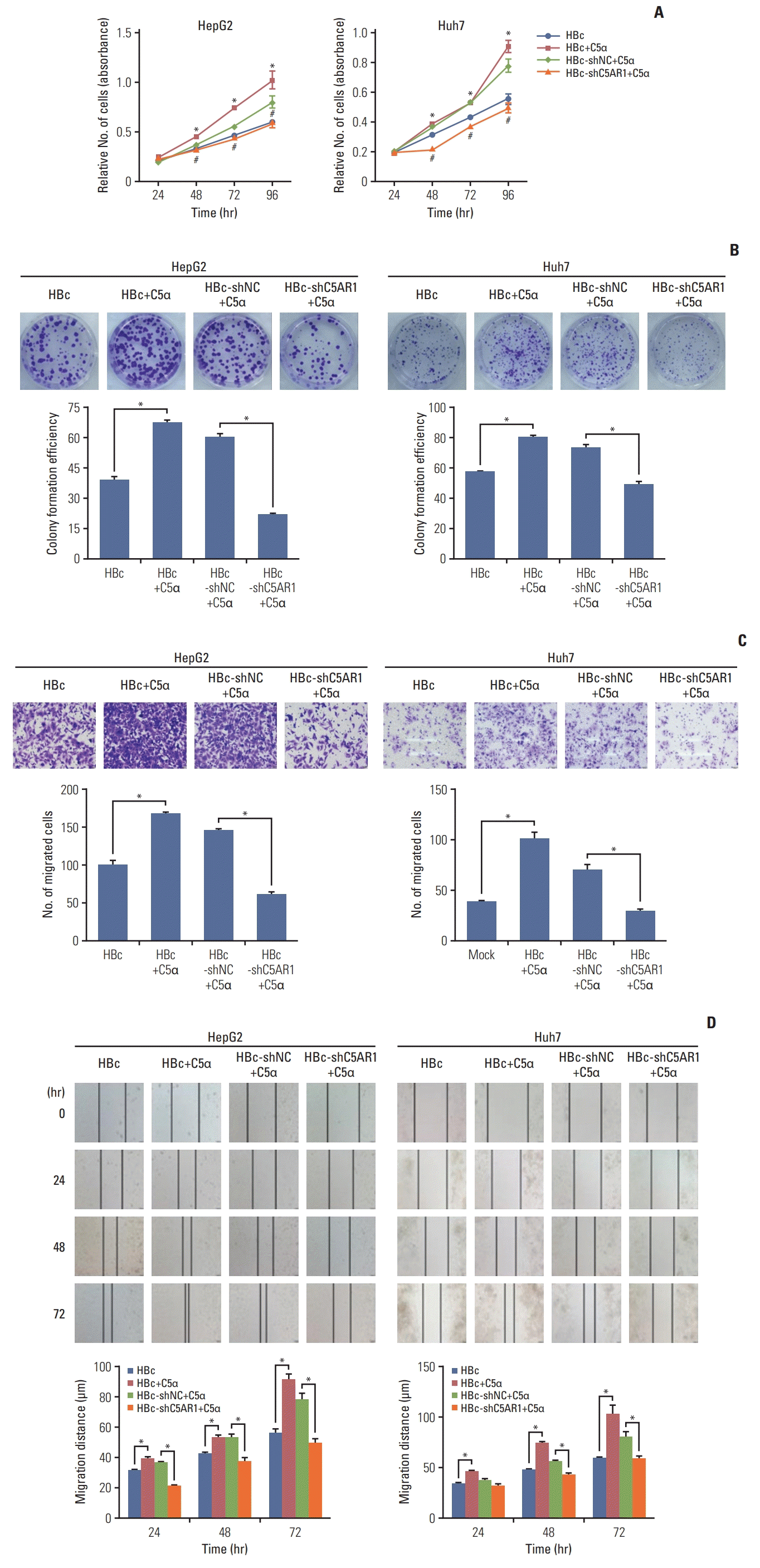 | Fig. 6The role of C5AR1 in the growth and migration of HBc-positive hepatoma cells stimulated by C5α. (A) CCK-8 assay was used to detect the effect of inhibition of C5AR1 using shRNA on the growth of HBc-positive hepatoma cells stimulated by C5α. (B) Plate clone formation assay was utilized to explore the effect of inhibition of C5AR1 via shRNA on the growth of HBc-positive hepatoma cells stimulated by C5α. (C) Transwell assay was used to assess the inhibition of C5AR1 via shRNA on the migration of HBc-positive hepatoma cells stimulated by C5α. (D) Wound healing assay was utilized to examine the effect of inhibition of C5AR1 by shRNA on the migration of HBc-positive hepatoma cells stimulated by C5α. C5AR1, C5α receptor 1; CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8; HBc, cells transfected with HBc plasmid; HBc-shC5AR1, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA plasmid targeting C5AR1; HBc-shNC, HBc-positive hepatoma cells transfected with shRNA control plasmid; shRNA, short hairpin RNA. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download