Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Study design and patients
2. Outcomes and assessments
3. Statistical analyses
Results
1. Patients and treatment
Fig. 1
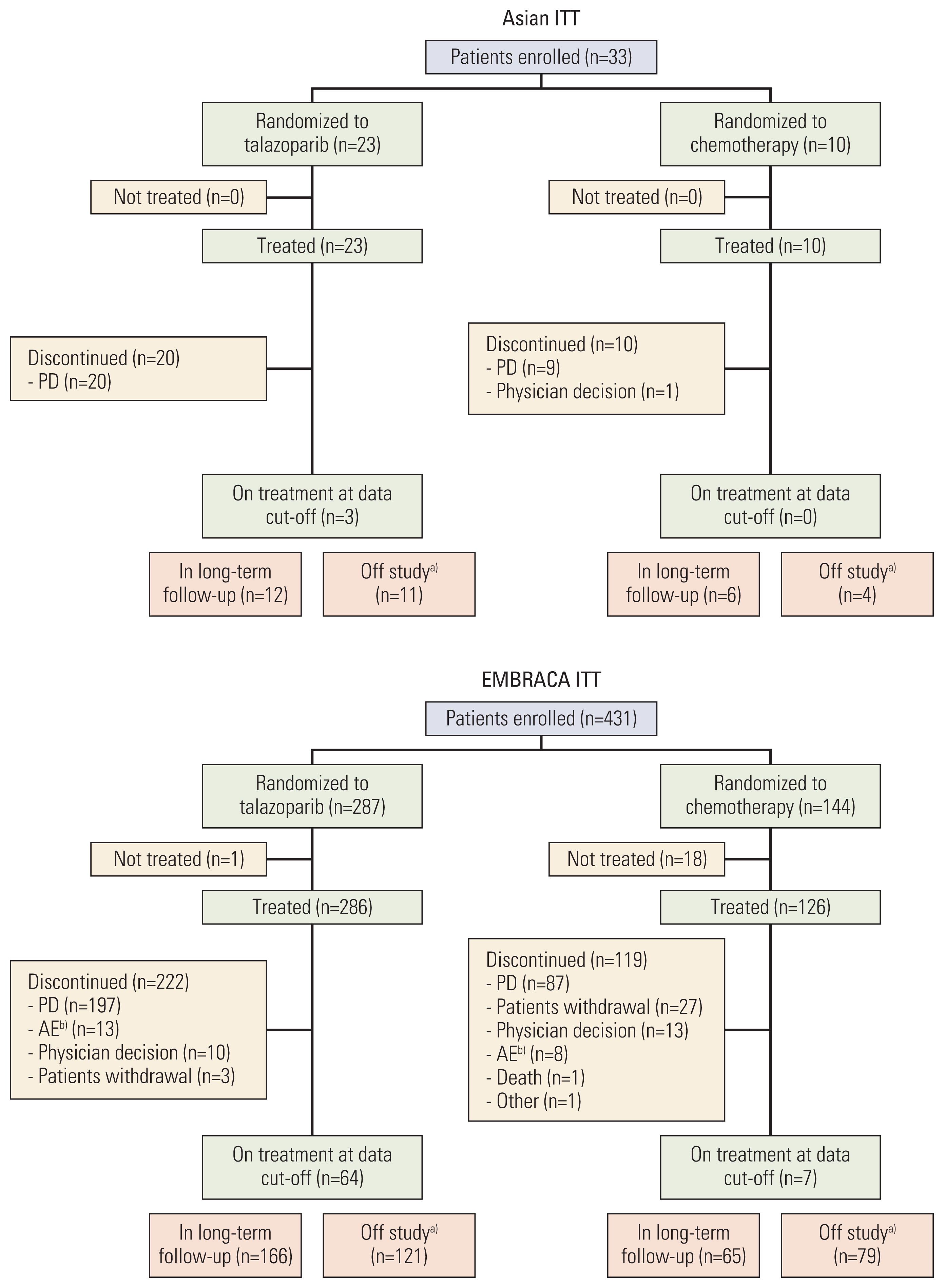
Table 1
| Asian, ITT | EMBRACA, ITTa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| Talazoparib (n=23) | Chemotherapy (n=10) | Talazoparib (n=287) | Chemotherapy (n=144) | |
| Age, median (yr) | 41 | 45 | 45 | 50 |
|
|
||||
| < 50 | 17 (73.9) | 6 (60.0) | 182 (63.4) | 67 (46.5) |
|
|
||||
| Female sex | 23 (100) | 10 (100) | 283 (98.6) | 141 (97.9) |
|
|
||||
| Weight, median (kg) | 58.6 | 52.0 | 65.6 | 66.0 |
|
|
||||
| Race | ||||
|
|
||||
| Asian | 23 (100) | 10 (100) | 31 (10.8) | 16 (11.1) |
|
|
||||
| White | 0 | 0 | 192 (66.9) | 108 (75.0) |
|
|
||||
| Otherb)/Not reported | 0 | 0 | 64 (22.3) | 20 (13.9) |
|
|
||||
| Visceral disease | 17 (73.9) | 6 (60.0) | 200 (69.7) | 103 (71.5) |
|
|
||||
| HR status | ||||
|
|
||||
| TNBC | 10 (43.5) | 4 (40.0) | 130 (45.3) | 60 (41.7) |
|
|
||||
| HR-positive | 13 (56.5) | 6 (60.0) | 157 (54.7) | 84 (58.3) |
|
|
||||
| BRCA status | ||||
|
|
||||
| BRCA1 mutation | 11 (47.8) | 3 (30.0) | 133 (46.3) | 63 (43.8) |
|
|
||||
| BRCA2 mutation | 12 (52.2) | 7 (70.0) | 154 (53.7) | 81 (56.3) |
|
|
||||
| Disease-free interval (initial diagnosis to ABC) < 12 mo | 10 (43.5) | 1 (10.0) | 108 (37.6) | 42 (29.2) |
Values are presented as number (%) unless otherwise indicated. ABC, advanced breast cancer; BRCA1/2, breast cancer susceptibility genes 1 or 2; HR, hormone receptor; ITT, intent-to-treat; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer.
a) From The New England Journal of Medicine, Litton JK et al., Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation, 379:753–63 [8]. Copyright © (2020) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society,
2. Efficacy
Fig. 2
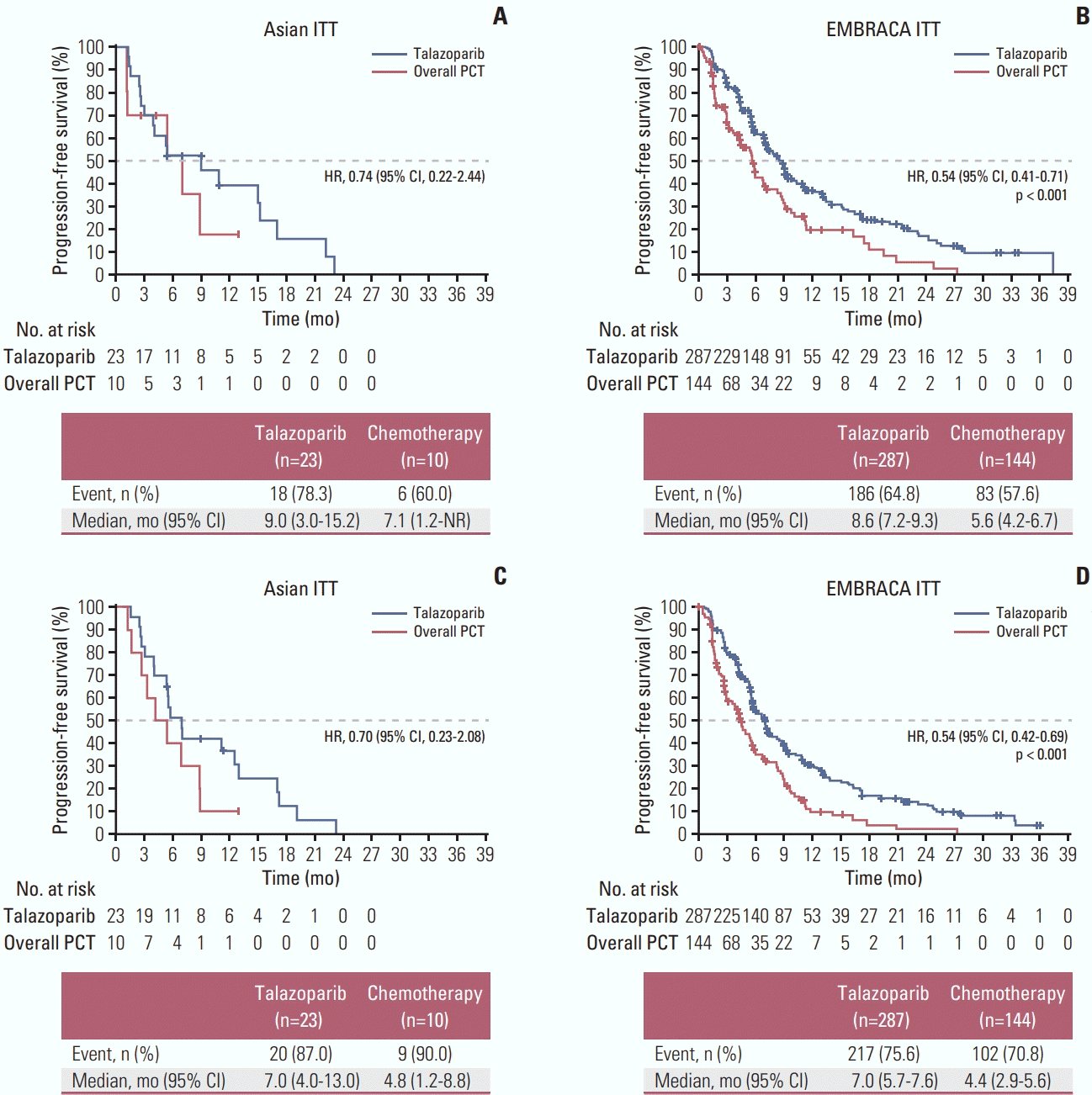
Table 2
| Asian, measurable disease | EMBRACA, measurable diseasea) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| Talazoparib (n=16) | Chemotherapy (n=8) | Talazoparib (n=219) Chemotherapy (n=114) | ||
| Best overall response, n (%)b) | ||||
|
|
||||
| CR | 0 | 0 | 12 (5.5) | 0 |
|
|
||||
| PR | 10 (62.5) | 2 (25.0) | 125 (57.1) | 31 (27.2) |
|
|
||||
| SD | 4 (25.0) | 4 (50.0) | 46 (21.0) | 36 (31.6) |
|
|
||||
| PD | 2 (12.5) | 2 (25.0) | 32 (14.6) | 28 (24.6) |
|
|
||||
| NE | 0 | 0 | 4 (1.8) | 19 (16.7) |
|
|
||||
| ORR, n (%) [95% CI] | 10 (62.5) [35.4–84.8] | 2 (25.0) [3.2–65.1] | 137 (62.6) [55.8–69.0] | 31 (27.2) [19.3–36.3] |
|
|
||||
| Odds ratio (95% CI) | 1.88 (0.07–117.85) | 4.99 (2.93–8.83) | ||
|
|
||||
| p-valuec) | - | < 0.001 | ||
|
|
||||
| Median duration of objective response (95% CI, mo) | 9.5 (1.0–14.4) | 5.2 (2.8–7.6) | 5.4 (4.2–6.3) | 3.1 (2.8–5.6) |
CI, confidence interval; CR, complete response; NE, not evaluable; ORR, objective response rate; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease.
a) From The New England Journal of Medicine, Litton JK et al., Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation, 379:753–63 [8]. Copyright © (2020) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society,
Table 3
| Asian, ITT | EMBRACA, ITTa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| Talazoparib (n=23) | Chemotherapy (n=10) | Talazoparib (n=287) | Chemotherapy (n=144) | |
| Median OS (95% CI, mo) | 20.7 (9.4–40.1) | 21.2 (2.7–35.0) | 19.3 (16.6–22.5) | 19.5 (17.4–22.4) |
|
|
||||
| HR (95% CI) | 1.41 (0.49–4.05) | 0.85 (0.67–1.07) | ||
a) From Litton et al. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1526–35 [26].
3. Exposure and safety
Table 4
| Asian, safety | EMBRACA, safetya) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| Talazoparib (n=23) | Chemotherapy (n=10) | Talazoparib (n=286) | Chemotherapy (n=126) | |
| Duration of treatment (mo) | ||||
|
|
||||
| Median overall (range) | 5.7 (1.9–23.5) | 4.9 (1.2–13.1) | 6.1 (0.03–36.9) | 3.9 (0.2–18.1) |
|
|
||||
| Capecitabine, median (n) | - | 6.2 (4) | - | 4.1 (55) |
|
|
||||
| Eribulin, median (n) | - | 3.7 (3) | - | 2.9 (50) |
|
|
||||
| Gemcitabine, median (n) | - | 0 | - | 5.5 (12) |
|
|
||||
| Vinorelbine, median (n) | - | 4.3 (3) | - | 4.2 (9) |
|
|
||||
| Relative dose intensity (%)b) | ||||
|
|
||||
| Talazoparib, median (n) | 99.7 (23) | - | 87.2 (286) | - |
|
|
||||
| Capecitabine, median (n) | - | 99.6 (4) | - | 87.9 (55) |
|
|
||||
| Eribulin, median (n) | - | 93.8 (3) | - | 96.4 (50) |
|
|
||||
| Gemcitabine, median (n) | - | 0 | - | 87.2 (12) |
|
|
||||
| Vinorelbine, median (n) | - | 65.0 (3) | - | 64.3 (9) |
|
|
||||
| Patients with at least 1 dose reduction due to AEs, n (%) | 5 (21.7) | - | 149 (52.1) | - |
|
|
||||
| No. of dose reductions due to AEs, n (%) | ||||
|
|
||||
| 1 | 3 (13.0) | - | 70 (24.5) | - |
|
|
||||
| 2 | 1 (4.3) | - | 58 (20.3) | - |
|
|
||||
| 3 | 1 (4.3) | - | 20 (7.0) | - |
|
|
||||
| > 3 | 0 | - | 1 (0.3) | - |
a) From The New England Journal of Medicine, Litton JK et al., Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation, 379:753–63 [8]. Copyright © (2020) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society,
Table 5
| Asian, safety | EMBRACA, safetya) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| Talazoparib (n=23) | Chemotherapy (n=10) | Talazoparib (n=286) | Chemotherapy (n=126) | |
| Any TEAE | 22 (95.7) | 9 (90.0) | 282 (98.6) | 123 (97.6) |
|
|
||||
| Grade 3 or 4 | 10 (43.5) | 6 (60.0) | 193 (67.5) | 80 (63.5) |
|
|
||||
| Seriousb) | 3 (13.0) | 3 (30.0) | 91 (31.8) | 37 (29.4) |
|
|
||||
| Serious, grade 3 or 4 | 2 (8.7) | 2 (20.0) | 73 (25.5) | 32 (25.4) |
|
|
||||
| Resulting in dose modifications c) | 10 (43.5) | 6 (60.0) | 190 (66.4) | 75 (59.5) |
|
|
||||
| Resulting in permanent drug discontinuationd) | 0 | 0 | 17 (5.9) | 11 (8.7) |
a) From The New England Journal of Medicine, Litton JK et al., Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation, 379:753–63 [8]. Copyright © (2020) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society,
Table 6
| Asian, safety | EMBRACA, safetya) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Talazoparib (n=23) | Chemotherapy (n=10) | Talazoparib (n=286) | Chemotherapy (n=126) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| All | Grade 3/4 | All | Grade 3/4 | All | Grade 3/4 | All | Grade 3/4 | |
| Hematologic toxicity | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Anemia | 4 (17.4) | 4 (17.4) | 1 (10.0) | 1 (10.0) | 151 (52.8) | 112 (39.2)b) | 23 (18.3) | 6 (4.8) |
|
|
||||||||
| Neutropenia | 9 (39.1) | 6 (26.1) | 5 (50.0) | 5 (50.0) | 99 (34.6) | 60 (21.0)c) | 54 (42.9) | 44 (34.9) |
|
|
||||||||
| Thrombocytopenia | 6 (26.1) | 2 (8.7) | 1 (10.0) | 0 | 77 (26.9) | 42 (14.7)c) | 9 (7.1) | 2 (1.6) |
|
|
||||||||
| Leukopenia | 1 (4.3) | 1 (4.3) | 0 | 0 | 49 (17.1) | 19 (6.6) | 17 (13.5) | 11 (8.7) |
|
|
||||||||
| Lymphopenia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 (7.3) | 9 (3.1) | 4 (3.2) | 1 (0.8) |
|
|
||||||||
| Nonhematologic TEAEs | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Fatigue | 10 (43.5) | 2 (20.0) | 144 (50.3) | 54 (42.9) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Nausea | 11 (47.8) | 4 (40.0) | 139 (48.6) | 59 (46.8) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Headache | 5 (21.7) | 1 (10.0) | 93 (32.5) | 28 (22.2) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Alopeciad) | 4 (17.4) | 3 (30.0) | 72 (25.2) | 35 (27.8) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Diarrhea | 4 (17.4) | 0 | 63 (22.0) | 33 (26.2) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Constipation | 5 (21.7) | 3 (30.0) | 63 (22.0) | 27 (21.4) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Decreased appetite | 7 (30.4) | 1 (10.0) | 61 (21.3) | 28 (22.2) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 7 (30.4) | 3 (30.0) | 37 (12.9) | 13 (10.3) | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Dyspepsia | 6 (26.1) | 1 (10.0) | 28 (9.8) | 9 (7.1) | ||||
a) From The New England Journal of Medicine, Litton JK et al., Talazoparib in patients with advanced breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation, 379:753–63 [8]. Copyright © (2020) Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society,
b,c) Number of patients receiving talazoparib who permanently discontinued due to a grade 3/4 hematologic treatment-emergent adverse event: b)n=2; c)n=1 in overall safety,
d) The majority of nonhematologic toxicities were grade 1 or 2; for the talazoparib arm, alopecia was reported only as grade 1 (17.4%), no grade 2 in the Asian safety population and mostly grade 1 (22.7%) in the EMBRACA safety population.
Patients with multiple events for a given preferred term were counted only once for each preferred term. The anemia category includes preferred terms: anemia, decreased hemoglobin, decreased hematocrit. The neutropenia category includes preferred terms: neutropenia, decreased neutrophil count. The thrombocytopenia category includes preferred terms: thrombocytopenia, platelet count decreased. The leukopenia category includes preferred terms: leukopenia, white blood cell count decreased. The lymphopenia category includes preferred terms lymphopenia, lymphocyte count decreased.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download