Abstract
Brain edema is defined as an increase in brain volume resulting from abnormal accumulation of fluid within the brain parenchyma. Brain edema is a potentially life-threatening complication of neurocritical illness as it raises the intracranial pressure and may progress to brain herniation and death. The management of brain edema and increased intracranial pressure is a significant challenge in neurocritical care. The purpose of this review is to describe the pathophysiology of diverse types of brain edema.
Go to : 
뇌부종(brain edema)이란‘뇌실질(brain parenchyma) 내의 수분 함량이 비정상적으로 증가하여 뇌조직의 용적이 증가한 상태’라고 정의할 수 있다[1]. 뇌부종은 뇌경색, 두개내출혈, 외상성 뇌손상, 뇌종양, 감염 등 다양한 질환에서 발생할 수 있으며, 뇌병변의 종류, 중증도 및 질병의 진행시기에 따라 다양한 형태의 뇌부종이 나타난다[1-3]. 다양한 급성 뇌질환에서 뇌부종이 발생하면 두개내압 상승을 유발하여 이차적 뇌손상을 일으킬 수 있다. 특히, 신경계 중환자실에서 뇌부종과 이로 인한 두개내압 상승은 사망률을 증가시키고 신경학적 예후를 악화시키는 주요 원인이다[4,5]. 따라서 중증 신경계 질환에서 동반될 수 있는 뇌부종의 병태 생리를 이해하고 이를 적절히 치료하는 것이 환자의 생존율을 높이고 신경학적 예후를 향상시키기 위해 매우 중요하다.
본 종설에서는 뇌부종이 두개내압 상승을 유발하는 기전과 뇌부종의 종류에따른 병태생리를 중심으로 살펴보도록 하겠다.
Go to : 
뇌부종은 뇌경색, 두개내출혈, 외상성 뇌손상, 뇌종양, 뇌염 등과 같이 두개내에서 발생하는 다양한 질환들에 의해서 유발될 수 있다. 또한 간성혼수, 저산소뇌손상, 각종 중독증 등 신경계 증상을 보이는 전신질환에서도 흔하게 동반될 수 있다[3,6,7]. 뇌부종이 경미하거나 뇌의 일부에 국한되어 발생하는 경우 임상적 증상을 나타내지 않는 경우가 대부분이지만, 뇌부종이 심한 경우 전반적 혹은 국소 뇌기능장애가 나타나며 두개내압 상승을 유발하여 다양한 임상 증상을 보일 수 있다. 특히, 중증 신경계 질환에서 발생한 뇌부종과 이로 인한 두개내압 상승은 사망에 이르는 중요한 원인 중의 하나라는데 그 중요성이 있다[8,9].
뇌부종이 두개내압 상승을 유발하는 기전으로는 몬로-켈리가설(Monro-Kellie hypothesis)이 널리 받아들여지고 있다[9-11]. 성인에서 두개강(cranial cavity) 전체 부피는 약 1700 mL인데, 뇌실질이 1200-1400 mL, 뇌척수액이 70-160 mL, 혈액이 150 mL 정도를 차지하고 있다. 두개강은 두개골(cranium)로 싸여 있는 한정된 공간으로 그 용적은 항상 일정하게 유지되고 있는데, 두개강 내에서 공간 점유 병소(space-occupying lesion)가 발생하거나 두개강 구성 성분 중 일부가 증가하면 한정된 공간내의 부피가 증가하게 되고 이로 인해 두개내의 압력이 상승하게 된다. 뇌부종이 발생하면 뇌실질 내의 수분 함량이 증가하여 뇌조직의 부피가 증가하고 이로 인해 두개내압이 상승하게 된다.
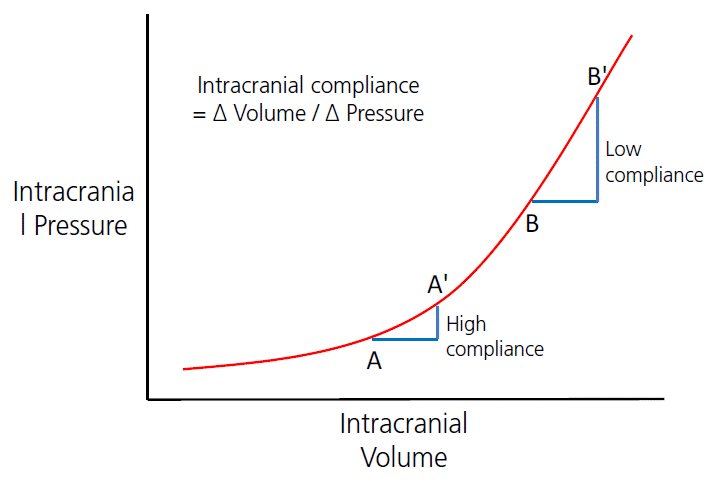
뇌부종에 의한 두개내압 상승에서 중요한 것이 두개내순응도(intracranial compliance)의 개념이다[9,12]. 뇌부종 초기에는 뇌 실질의 부피상승에 대한 보상기전으로 뇌척수액과 혈액량이 감소하여 두개내압 상승을 억제한다. 하지만 뇌부종이 진행하면서 보상 범위를 넘어서게 되면 두개내압이 상승하게 되고, 특정 지점을 넘어가게 되면 두개내압의 급격한 상승이 나타난다(Fig. 1). 두개내순응도가 높은 경우 뇌부종이 발생하더라도 두개내압 상승이 크지 않은데 비해 (A → A') 뇌부종의 보상범위를 넘은 경우 두개내순응도가 감소하면서 똑같은 정도의 부피 변화에도 급격한 두개뇌압상승이 발생한다 (B → B'). 뇌부종이 심한 경우 두개내압 상승 외에도 덩이효과(mass effect)를 통해 주변 조직을 압박하여 뇌전위(brain displacement), 뇌탈출(brain herniation)까지 발생할 수 있다.
뇌부종은 발생기전에 따라 수분이 세포 내에 축적되는 세포독성 부종(cytotoxic edema), 세포 사이 공간에 축적되는 혈관성 부종(vasogenic edema)으로 나눌 수 있다(Table 1) [1,13,14]. 그리고 수두증(hydrocephalus)에서 뇌실의 압력이 상승되어 뇌실주변 백색질(white matter)에 수분이 축적되는 사이질 부종(interstitial edema)을 따로 분류하여 크게 세 종류로 나누기도 한다. 뇌부종이 발생하는 원인 질환에 따라 특정 형태의 뇌부종이 잘 동반되는 것으로 알려져 있지만, 대부분의 뇌병변에서 시기에 따라 다양한 형태의 뇌부종이 복합적으로 발생하게 된다[14]. 예를 들어 허혈성 뇌경색에서는 세포독성 부종이 잘 동반된다고 알려져 있지만, 실제로는 시기에 따라 세포독성 부종과 혈관성 부종이 모두 발생하게 된다[15]. 허혈성 뇌경색 초기에는 뇌세포들이 허혈 손상을 받아 세포독성 부종이 주로 발생하지만 이후 뇌허혈이 지속되면 모세혈관의 내피세포 손상이 발생하면서 혈관성 부종이 진행하게 된다. 반대로 혈관성 뇌부종이 심하게 동반된 경우 덩이효과를 통해 주변 뇌혈관을 압박하여 다시 세포독성 부종을 발생시킬 수도 있다.
Features of the two types of brain edema
혈관성 부종은 가장 흔한 형태의 뇌부종으로 혈액뇌장벽(blood-brain barrier)의 손상이나 모세혈관의 투과성(permeability) 변화로 혈장내의 수분, 이온, 단백질 등이 세포 사이 공간으로 이동하여 발생한다[2,14,16]. 혈액뇌장벽은 모세혈관의 내피세포, 모세혈관바닥막(capillary basement membrane), 별아교세포 다리돌기(astrocyte footprocess), 혈관주변세포(pericyte)로 구성되어 있으며, 평소에는 혈액과 뇌척수액 사이의 자유로운 물질 교환을 막아 뇌부종이 발생하는 것을 억제하고 있다. 혈액뇌장벽이 손상되면 혈청 단백질에 대한 투과성이 증가되어 혈청 단백질이 세포 사이 공간으로 이동하게 되고, 단백질을 따라 수분이 세포 사이 공간으로 이동하여 부종이 발생하게 된다. 혈관성 부종의 발생에 있어서 혈액뇌장벽 중 치밀이음(tight junction)의 손상이 중요한 것으로 알려져 있다[17,18].
수분이 세포 밖에 축적되는 혈관성 부종은 주로 백색질에 많이 발생한다. 혈관성 부종이 백색질에 호발하는 기전에 대해서는 정확히 밝혀져 있지 않으나 구조적 차이에 의한 것으로 생각된다[2]. 회색질(gray matter)은 뇌세포의 밀도가 높은데 비해 백색질은 뇌세포 사이를 연결하는 신경섬유들로 이루어진 성긴 공간이다. 따라서 회색질보다 세포 사이 공간이 넓은 백색질에 혈관성 부종이 자주 발생하며, 부종액(edema fluid)은 삼투압과 정수압(hydrostatic pressure)의 차이에 의해서 세포외 공간과 혈관주변의 공간을 따라서 백색질에 널리 퍼지게 된다.
혈관성 부종은 뇌종양, 뇌농양에서 흔히 나타나며 외상성 뇌손상, 뇌수막염 및 뇌졸중에서도 나타날 수 있다. 뇌종양에서 동반되는 혈관성 부종의 발생에는 뇌종양에서 분비되는 혈관내피성장인자(vascular endothelial growth factor), matrix metalloproteinase, 각종 사이토카인(cytokine) 및 단백분해효소(protease) 등이 중요한 역할을 한다[19]. 이는 모세혈관 투과성 변화를 일으켜 단백질과 같은 고분자 물질이 모세혈관 내피세포를 통과하게 한다. 또한 뇌종양의 크기가 증가하면서 덩이효과에 의해 종양 주변의 세정맥을 압박하고 이로 인해 모세혈관의 압력이 증가하여 정수압 차이가 발생하는데 이는 종양 주변부의 혈관성 부종 발생에 기여하게 된다.
세포독성 부종은 뇌세포의 손상으로 인해 세포 바깥의 수분이 세포 내로 이동하여 발생한다[2,14,15,20]. 세포독성 부종은 뇌허혈 상황에서 가장 흔히 발생하는데, 세포 내의 에너지 부족으로 삼인산 아데노신(adenosine triphosphate, ATP)이 고갈되면 세포 내의 전해질평형을 유지하던 세포막의 나트륨펌프(ATP-dependent Na+ pump)의 활성이 감소하게 된다. 이로 인해 세포 안에 나트륨이 축적되고 삼투압이 증가하면서 세포 밖의 수분이 세포 안으로 이동하게 된다. 세포독성 부종이 발생하면 상대적으로 세포 밖의 나트륨 농도가 감소하면서 이에 대한 보상으로 혈관 내의 나트륨이 세포 사이 공간으로 이동하게 되고 이에 따라 수분도 혈관 밖으로 이동하여 뇌의 용적이 증가하게 된다. 일반적으로 순수한 세포독성 부종의 초기에는 혈장 단백질에 대한 혈관의 투과성은 정상이다[21]. 세포독성 부종의 발생에는 나트륨펌프 외에도 aquaporin, sulfonylurea receptor, Na+-K+-Cl- Co-transporter 등이 관여하는 것으로 알려져 있다[18,22].
세포독성 부종은 회색질, 백색질에서 모두 발생할 수 있으며 뇌세포가 많은 회색질에 조금 더 호발하는 것으로 알려져 있다. 세포독성의 원인으로는 뇌경색, 저산소허혈손상, Reye증후군, 간성뇌병증(hepatic encephalopathy), 각종 중독증 등이 있다. 그 외에도 혈장의 삼투 농도가 급격히 감소하는 항이뇨 호르몬부적절분비증후군(SIADH), 투석불균형증후군(dialysis disequilibrium syndrome) 등에서도 발생할 수 있다[3]. 급성 간기능상실(acute hepatic failure)에 의한 뇌부종의 발생에는 암모니아 등과 같은 독성 물질이 중요한 역할을 한다[6]. 간에서 대사되지 못한 독성 물질은 주로 별아교세포(astrocyte) 내에 축적되고 이는 산화스트레스(oxidative stress) 유발, 글루타민(glutamine) 축적 등을 통해 세포독성 부종을 유발하게 된다.
사이질 부종은 뇌실내의 압력이 증가하면서 정수압의 차이에 의해서 뇌척수액의 수분이 뇌실 주변으로 이동하면서 발생한다. 수분이 세포 사이 공간에 축적된다는 점에서 혈관성 부종으로 분류할 수도 있으나 주로 뇌실 주변부에 부종이 발생한다는 점에서 차이가 있다[1]. 혈관성 부종이나 세포독성 부종보다 임상적인 중요성은 떨어지며, 폐쇄수두증(obstructive hydrocephalus)에서 나타날 수 있다.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2. Nag S, Manias JL, Stewart DJ. Pathology and new players in the pathogenesis of brain edema. Acta Neuropathol. 2009; 118:197–217.

3. Adeva MM, Souto G, Donapetry C, Portals M, Rodriguez A, Lamas D. Brain edema in diseases of different etiology. Neurochem Int. 2012; 61:166–74.

4. Battey TW, Karki M, Singhal AB, Wu O, Sadaghiani S, Campbell BC, et al. Brain edema predicts outcome after nonlacunar ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2014; 45:3643–8.

5. Kinoshita K. Traumatic brain injury: pathophysiology for neurocritical care. J Intensive Care. 2016; 4:29.

6. Blei AT. Pathophysiology of brain edema in fulminant hepatic failure, revisited. Metab Brain Dis. 2001; 16:85–94.
7. Glaser N, Barnett P, McCaslin I, Nelson D, Trainor J, Louie J, et al. Risk factors for cerebral edema in children with diabetic ketoacidosis. The Pediatric Emergency Medicine Collaborative Research Committee of the American Academy of Pediatrics. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:264–9.
8. Brogan ME, Manno EM. Treatment of malignant brain edema and increased intracranial pressure after stroke. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2015; 17:327.

9. Bershad EM, Humphreis WE 3rd, Suarez JI. Intracranial hypertension. Semin Neurol. 2008; 28:690–702.

10. Kellie G. Appearances observed in the dissection of two individuals; death from cold and congestion of the brain. Trans Med Chir Soc Edinb. 1824; 1:84–169.
11. Kim DJ, Czosnyka Z, Kasprowicz M, Smieleweski P, Baledent O, Guerguerian AM, et al. Continuous monitoring of the Monro-Kellie doctrine: is it possible? J Neurotrauma. 2012; 29:1354–63.

13. Klatzo I. Presidental address. Neuropathological aspects of brain edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967; 26:1–14.
15. Simard JM, Kent TA, Chen M, Tarasov KV, Gerzanich V. Brain oedema in focal ischaemia: molecular pathophysiology and theoretical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6:258–68.

16. Xi G, Hua Y, Bhasin RR, Ennis SR, Keep RF, Hoff JT. Mechanisms of edema formation after intracerebral hemorrhage: effects of extravasated red blood cells on blood flow and blood-brain barrier integrity. Stroke. 2001; 32:2932–8.
17. Rosenberg GA, Yang Y. Vasogenic edema due to tight junction disruption by matrix metalloproteinases in cerebral ischemia. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22:E4.

18. Stokum JA, Gerzanich V, Simard JM. Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral edema. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016; 36:513–38.

20. Liang D, Bhatta S, Gerzanich V, Simard JM. Cytotoxic edema: mechanisms of pathological cell swelling. Neurosurg Focus. 2007; 22:E2.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download