1. Cole AJ. Status epilepticus and periictal imaging. Epilepsia. 2004; 45:72–7.

2. Lansberg MG, O’Brien MW, Norbash AM, Moseley ME, Morrell M, Albers GW. MRI abnormalities associated with partial status epilepticus. Neurology. 1999; 52:1021–7.

3. Briellmann RS, Wellard RM, Jackson GD. Seizure-associated abnormalities in epilepsy: evidence from MR imaging. Epilepsia. 2005; 46:760–6.

4. Szabo K, Poepel A, Pohlmann-Eden B, Hirsch J, Back T, Sedlaczek O, et al. Diffusion-weighted and perfusion MRI demonstrates parenchymal changes in complex partial status epilepticus. Brain. 2005; 128:1369–76.

5. Wieshmann UC, Symms MR, Shorvon SD. Diffusion changes in status epilepticus. Lancet. 1997; 350:493–4.

6. Ebisu T, Rooney WD, Graham SH, Mancuso A, Weiner MW, Maudsley AA. MR spectroscopic imaging and diffusion-weighted MRI for early detection of kainate-induced status epilepticus in the rat. Magn Reson Med. 1996; 36:821–8.
7. Petroff OA, Prichard JW, Ogino T, Avison M, Alger JR, Shulman RG. Combined 1H and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic studies of bicuculline-induced seizures in vivo. Ann Neurol. 1986; 20:185–93.
8. Petroff OA, Prichard JW, Behar KL, Alger JR, Shulman RG. In vivo phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in status epilepticus. Ann Neurol. 1984; 16:169–77.

9. Young RS, Osbakken MD, Briggs RW, Yagel SK, Rice DW, Goldberg S. 31P NMR study of cerebral metabolism during prolonged seizures in the neonatal dog. Ann Neurol. 1985; 18:14–20.

10. Najm IM, Wang Y, Shedid D, Lüders HO, Ng TC, Comair YG. MRS metabolic markers of seizures and seizure-induced neuronal damage. Epilepsia. 1998; 39:244–50.

11. Najm IM, Wang Y, Hong SC, Luders HO, Ng TC, Comair YG. Temporal changes in proton MRS metabolites after kainic acid-induced seizures in rat brain. Epilepsia. 1997; 38:87–94.

12. Hufnagel A, Weber J, Marks S, Ludwig T, De Greiff A, Leonhardt G, et al. Brain diffusion after single seizures. Epilepsia. 2003; 44:54–63.
13. Doherty CP, Cole AJ, Grant PE, Fischman A, Dooling E, Hoch DB, et al. Multimodal longitudinal imaging of focal status epilepticus. Can J Neurol Sci. 2004; 31:276–81.

14. Raghavendra S, Ashalatha R, Krishnamoorthy T, Kesavadas C, Thomas SV, Radhakrishnan K. Reversible periictal MRI abnormalities: Clinical correlates and long-term outcome in 12 patients. Epilepsy Res. 2007; 73:129–36.

15. Costello DJ, Simon MV, Eskandar EN, Frosch MP, Henninger HL, Chiappa KH, et al. Efficacy of surgical treatment of de novo, adult-onset, cryptogenic, refractory focal status epilepticus. Arch Neurol. 2006; 63:895–901.

16. Bouilleret V, Nehlig A, Marescaux C, Namer IJ. Magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of progressive hippocampal changes in a mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2000; 41:642–50.

17. Righini A, Pierpaoli C, Alger JR, Dichiro G. Brain Parenchyma Apparent Diffusion-Coefficient Alterations Associated with Experimental Complex Partial Status Epilepticus. Magn Resone Imaging. 1994; 12:865–71.
18. Grant PE, He J, Halpern EF, Wu O, Schaefer PW, Schwamm LH, et al. Frequency and clinical context of decreased apparent diffusion coefficient reversal in the human brain. Radiology. 2001; 221:43–50.

19. Heinrich A, Runge U, Kirsch M, Khaw AV. A case of hippocampal laminar necrosis following complex partial status epilepticus. Acta Neurol Scand. 2007; 115:425–8.

20. VanLandingham KE, Heinz ER, Cavazos JE, Lewis DV. Magnetic resonance imaging evidence of hippocampal injury after prolonged focal febrile convulsions. Ann Neurol. 1998; 43:413–26.

21. Diehl B, Najm I, Ruggieri P, Tkach J, Mohamed A, Morris H, et al. Postictal diffusion-weighted imaging for the localization of focal epileptic areas in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2001; 42:21–8.
22. Diehl B, Najm I, Ruggieri P, Foldvary N, Mohamed A, Tkach J, et al. Periictal diffusion-weighted imaging in a case of lesional epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1999; 40:1667–71.

23. Oh JB, Lee SK, Kim KK, Song IC, Chang KH. Role of immediate postictal diffusion-weighted MRI in localizing epileptogenic foci of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and non-lesional neocortical epilepsy. Seizure. 2004; 13:509–16.

24. Fazekas F, Kapeller P, Schmidt R, Stollberger R, Varosanec S, Offenbacher H, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy findings after focal status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1995; 36:946–9.

25. Nagasaka T, Shindo K, Hiraide M, Sugimoto T, Shiozawa Z. Ipsilateral thalamic MRI abnormality in an epilepsy patient. Neurology. 2002; 58:641–4.

26. Meierkord H, Wieshmann U, Niehaus L, Lehmann R. Structural consequences of status epilepticus demonstrated with serial magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Neurol Scand. 1997; 96:127–32.

27. Yaffe K, Ferriero D, Barkovich AJ, Rowley H. Reversible MRI abnormalities following seizures. Neurology. 1995; 45:104–8.

28. Kim JA, Chung JI, Yoon PH, Kim DI, Chung TS, Kim EJ, et al. Transient MR signal changes in patients with generalized tonicoclonic seizure or status epilepticus: periictal diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1149–60.
29. Toledo M, Munuera J, Sueiras M, Rovira R, Alvarez-Sabin J, Rovira A. MRI findings in aphasic status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2008; 49:1465–9.

30. Boyd JG, Taylor S, Rossiter JP, Islam O, Spiller A, Brunet DG. New-onset refractory status epilepticus with restricted DWI and neuronophagia in the pulvinar. Neurology. 2010; 74:1003–5.

31. Gong G, Shi F, Concha L, Beaulieu C, Gross DW. Insights into the sequence of structural consequences of convulsive status epilepticus: A longitudinal MRI study. Epilepsia. 2008; 49:1941–5.

32. Canas N, Soares P, Calado S, Pestana R, Ribeiro C, Vale J. Pathophysiology and long-term outcome of reversible tumor-like lesions induced by presenting status epilepticus. J Neuroimaging. 2010; 20:169–74.

33. Prichard JW, Neil JJ. Diffusion-weighted MRI: periictal studies. Adv Neurol. 2000; 83:279–84.
34. Förster A, Griebe M, Gass A, Kern R, Hennerici MG, Szabo K. Diffusion-weighted imaging for the differential diagnosis of disorders affecting the hippocampus. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 33:104–15.

35. Penfield W. The evidence for a cerebral vascular mechanism in epilepsy. Ann Intern Med. 1933; 7:303–10.

36. Warach S, Levin JM, Schomer DL, Holman BL, Edelman RR. Hyperperfusion of ictal seizure focus demonstrated by MR perfusion imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994; 15:965–8.
37. Rowe CC, Berkovic SF, Sia ST, Austin M, McKay WJ, Kalnins RM, et al. Localization of epileptic foci with postictal single photon emission computed tomography. Ann Neurol. 1989; 26:660–8.

38. O’Brien TJ, So EL, Cascino GD, Hauser MF, Marsh WR, Meyer FB, et al. Subtraction SPECT coregistered to MRI in focal malformations of cortical development: localization of the epileptogenic zone in epilepsy surgery candidates. Epilepsia. 2004; 45:367–76.

39. O’Brien TJ, So EL, Mullan BP, Hauser MF, Brinkmann BH, Bohnen NI, et al. Subtraction ictal SPECT co-registered to MRI improves clinical usefulness of SPECT in localizing the surgical seizure focus. Neurology. 1998; 50:445–54.

40. O’Brien TJ, So EL, Mullan BP, Hauser MF, Brinkmann BH, Jack CR Jr, et al. Subtraction SPECT co-registered to MRI improves postictal SPECT localization of seizure foci. Neurology. 1999; 52:137–46.

41. Leonhardt G, de Greiff A, Weber J, Ludwig T, Wiedemayer H, Forsting M, et al. Brain perfusion following single seizures. Epilepsia. 2005; 46:1943–9.

42. Pendse N, Wissmeyer M, Altrichter S, Vargas M, Delavelle J, Viallon M, et al. Interictal arterial spin-labeling MRI perfusion in intractable epilepsy. J Neuroradiol. 2010; 37:60–3.

43. Petersen ET, Lim T, Golay X. Model-free arterial spin labeling quantification approach for perfusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2006; 55:219–32.

44. Williams DS, Detre JA, Leigh JS, Koretsky AP. Magnetic resonance imaging of perfusion using spin inversion of arterial water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89:212–6.

45. Detre JA, Leigh JS, Williams DS, Koretsky AP. Perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1992; 23:37–45.

46. Wolf RL, Detre JA. Clinical neuroimaging using arterial spinlabeled perfusion MRI. Neurotherapeutics. 2007; 4:346–59.
47. Detre JA, Alsop DC, Vives LR, Maccotta L, Teener JW, Raps EC. Noninvasive MRI evaluation of cerebral blood flow in cerebrovascular disease. Neurology. 1998; 50:633–41.

48. Pizzini FB, Farace P, Manganotti P, Zoccatelli G, Bongiovanni LG, Golay X, et al. Cerebral perfusion alterations in epileptic patients during peri-ictal and post-ictal phase: PASL vs DSC-MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 2013; 31:1001–5.

49. Wakisaka K, Morioka T, Shimogawa T, Murao K, Kanazawa Y, Hagiwara N, et al. Epileptic Ictal Hyperperfusion on Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion and Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images in Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016; 25:228–37.

50. Chakravarty A. MR evaluation of crossed and uncrossed cerebral-cerebellar diaschisis. Acta Neurol Scand. 2003; 108:60–5.

51. Mewasingh LD, Christiaens F, Aeby A, Christophe C, Dan B. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis secondary to refractory frontal seizures in childhood. Seizure. 2002; 11:489–93.

52. Bohnen NI, O’Brien TJ, Mullan BP, So EL. Cerebellar changes in partial seizures: clinical correlations of quantitative SPECT and MRI analysis. Epilepsia. 1998; 39:640–50.

53. Stübgen JP. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis related to recurrent focal seizures. Epilepsia. 1995; 36:316–8.

54. Katramados AM, Burdette D, Patel SC, Schultz LR, Gaddam S, Mitsias PD. Periictal diffusion abnormalities of the thalamus in partial status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2009; 50:265–75.

55. Oster J, Doherty C, Grant PE, Simon M, Cole AJ. Diffusion-weighted imaging abnormalities in the splenium after seizures. Epilepsia. 2003; 44:852–4.

56. Mirsattari SM, Lee DH, Jones MW, Blume WT. Transient lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum in an epileptic patient. Neurology. 2003; 60:1838–41.

57. Polster T, Hoppe M, Ebner A. Transient lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum: three further cases in epileptic patients and a pathophysiological hypothesis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001; 70:459–63.

58. Kim SS, Chang KH, Kim ST, Suh DC, Cheon JE, Jeong SW, et al. Focal lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum in epileptic patients: antiepileptic drug toxicity? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:125–9.
59. Cohen-Gadol AA, Britton JW, Jack CR Jr, Friedman JA, Marsh WR. Transient postictal magnetic resonance imaging abnormality of the corpus callosum in a patient with epilepsy. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:714–7.
60. Prilipko O, Delavelle J, Lazeyras F, Seeck M. Reversible cytotoxic edema in the splenium of the corpus callosum related to antiepileptic treatment: report of two cases and literature review. Epilepsia. 2005; 46:1633–6.

61. Carrara G, Ferlazzo E, Tampieri D, Andermann F, Melanson D. Transient edematous lesions of the splenium in epileptic patients. Can J Neurol Sci. 2005; 32:352–5.

62. Gürtler S, Ebner A, Tuxhorn I, Ollech I, Pohlmann-Eden B, Woermann FG. Transient lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum and antiepileptic drug withdrawal. Neurology. 2005; 65:1032–6.

63. Gröppel G, Gallmetzer P, Prayer D, Serles W, Baumgartner C. Focal lesions in the splenium of the corpus callosum in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2009; 50:1354–60.

64. Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:494–500.

65. Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1038–48.
66. Bakshi R, Bates VE, Mechtler LL, Kinkel PR, Kinkel WR. Occipital lobe seizures as the major clinical manifestation of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: Magnetic resonance imaging findings. Epilepsia. 1998; 39:295–9.

67. Riela AR, Sires BP, Penry JK. Transient magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities during partial status epilepticus. J Child Neurol. 1991; 6:143–5.

68. Mathews MS, Smith WS, Wintermark M, Dillon WP, Binder DK. Local cortical hypoperfusion imaged with CT perfusion during postictal Todd’s paresis. Neuroradiology. 2008; 50:397–401.

69. Eastwood JD, Lev MH, Wintermark M, Fitzek C, Barboriak DP, Delong DM, et al. Correlation of early dynamic CT perfusion imaging with whole-brain MR diffusion and perfusion imaging in acute hemispheric stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1869–75.
70. Yang TW, Nam W, Son S, Kim SK, Kang H, Park KJ, et al. Seizure-induced cerebral edema mimicking multiple cerebral infarction. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2015; 33:54–6.

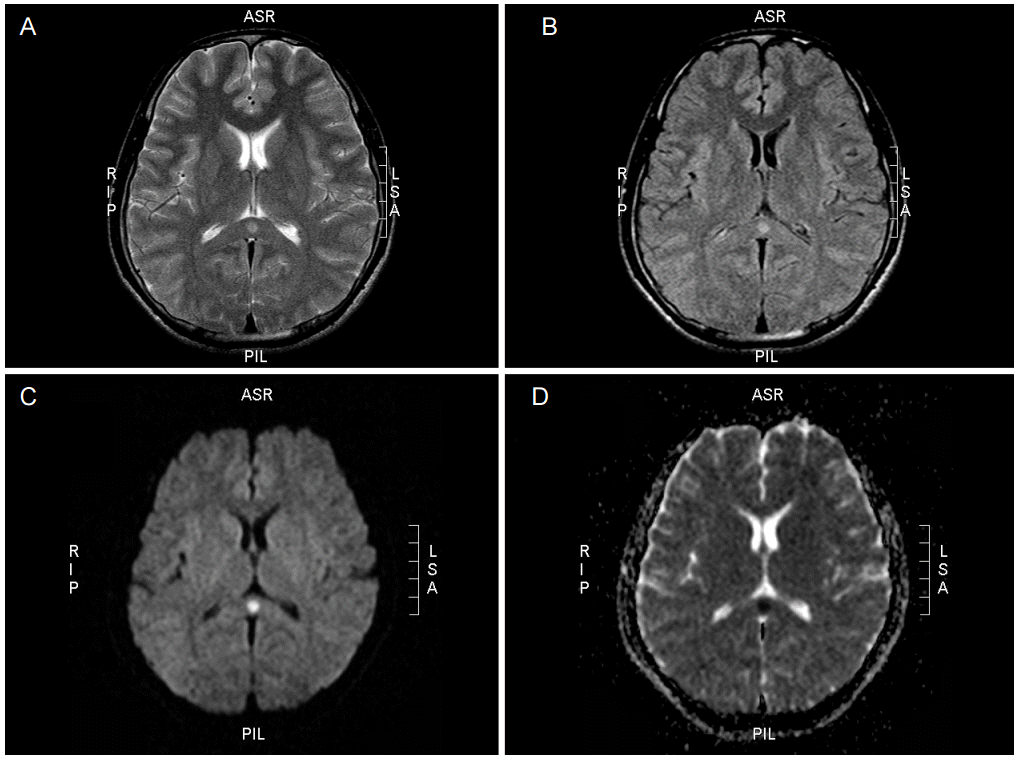
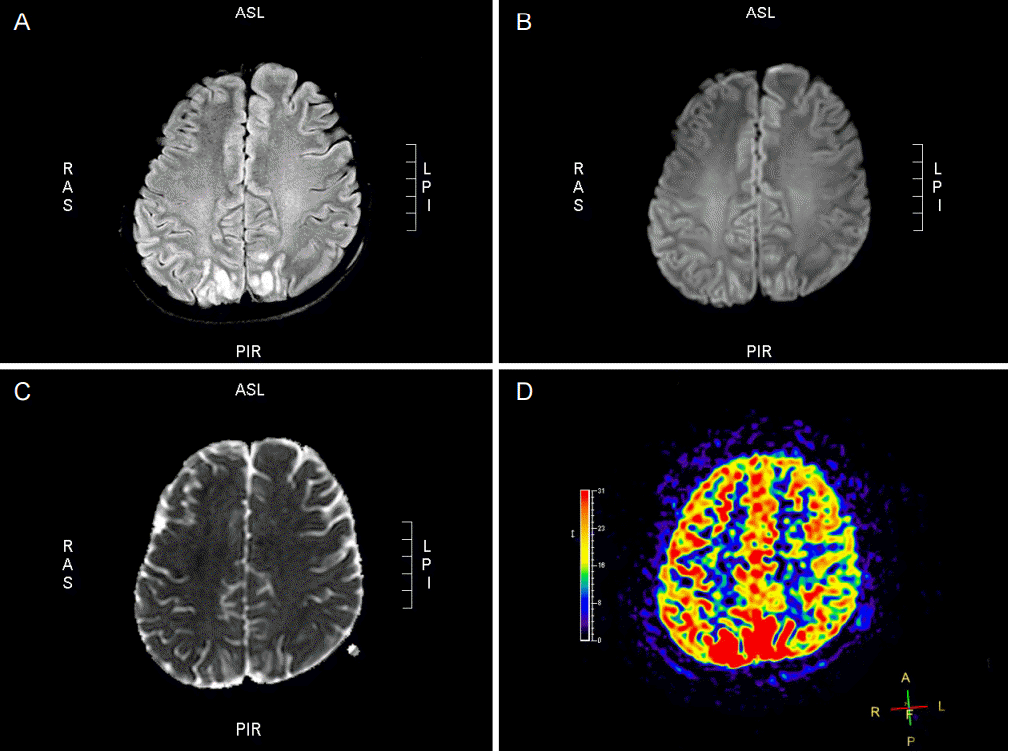




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download