Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Patients
2. Immunohistochemical staining
3. Immunohistochemical staining scoring
4. Genotyping
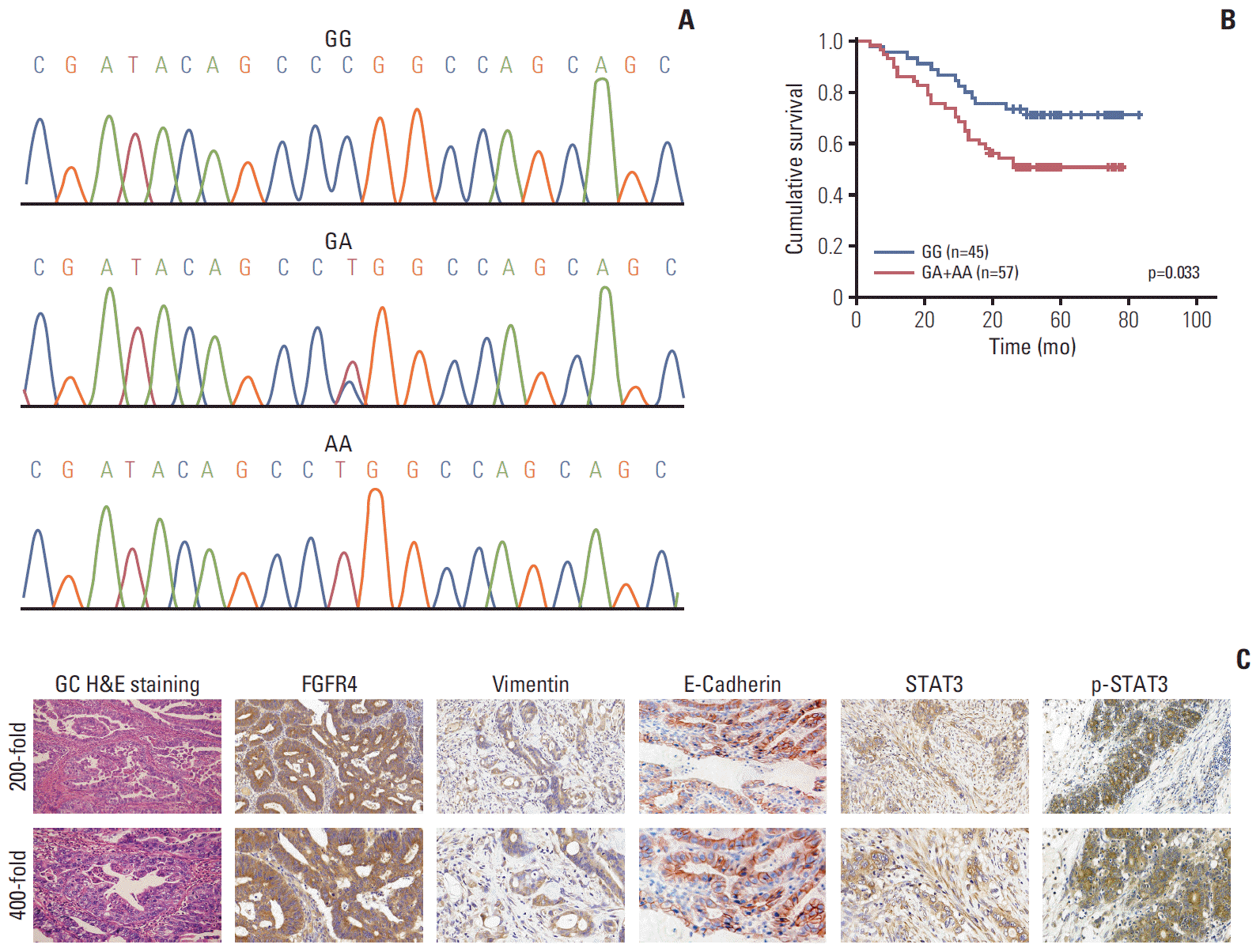 | Fig. 1.(A) Gene sequencing including three specific fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) Gly388Arg polymorphic genotype (including Gly/Gly, Gly/Arg, and Arg/Arg). (B) Significant difference was observed between patients with FGFR4-Gly388 allele and FGFR4-Arg388 variant among 102 gastric cancer (GC) patients after stratified Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. (C) Strong positive expressions of immunohistochemical markers in GC tissue were demonstrated. All H&E staining and immunohistochemical pictures were amplified 200-fold (upper) and 400-fold (lower). |
5. Cell lines and cell culture
6. Antibodies and reagents
7. Lentiviral overexpression vector construction and transfection
8. Reverse transcription PCR and quantitative real-time PCR
9. Protein extraction and western blot
10. Apoptosis assay
11. Cell proliferation assays
1) CCK-8 proliferation assay
2) Gradient concentration CCK-8 assays
3) EdU proliferation assay
12. Matrigel invasion and invasion assay
13. Statistical analysis
14. Ethical statement
Results
1. Correlation of FGFR4 Gly388Arg single nucleotide polymorphism with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of GC patients
Table 1.
2. FGFR4 expression differed in various GC cell lines
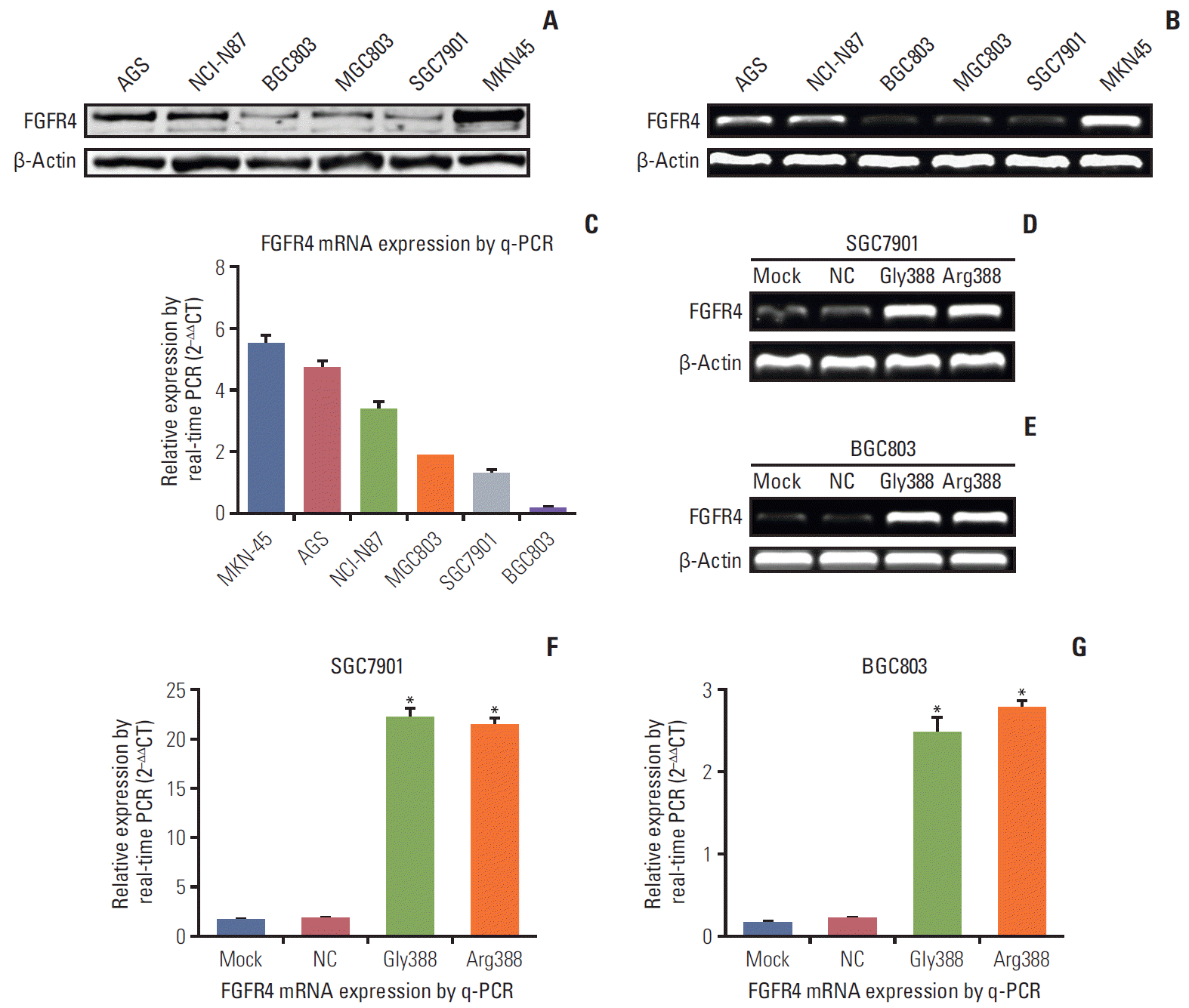 | Fig. 2.The expressions of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) mRNA and protein were illustrated in various gastric cancer (GC) cell lines and transfected cells. (A) Expressions of FGFR4 protein in different GC cell lines by western blot. (B) Expressions of FGFR4 mRNA in different GC cells by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). (C) Expressions of FGFR4 mRNA in different GC cells by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (q-PCR). Expressions of FGFR4 mRNA in SGC7901 (D) and BGC803 (E) cells (mock, negative control [NC], Gly388-transfected, and Arg388-transfected) by RT-PCR. Expressions of FGFR4 mRNA in SGC7901 (F) and BGC803 (G) cells (mock, NC, Gly388-transfected, and Arg388-transfected) by q-PCR. β-Actin was served as loading control. At least three independent detecting were performed. *p < 0.05. |
3. FGFR4-Gly388 allele and FGFR4-Arg388 allele were verified to be over-expressed
4. FGFR4-Arg388 allele enhanced proliferation, invasion, and migration
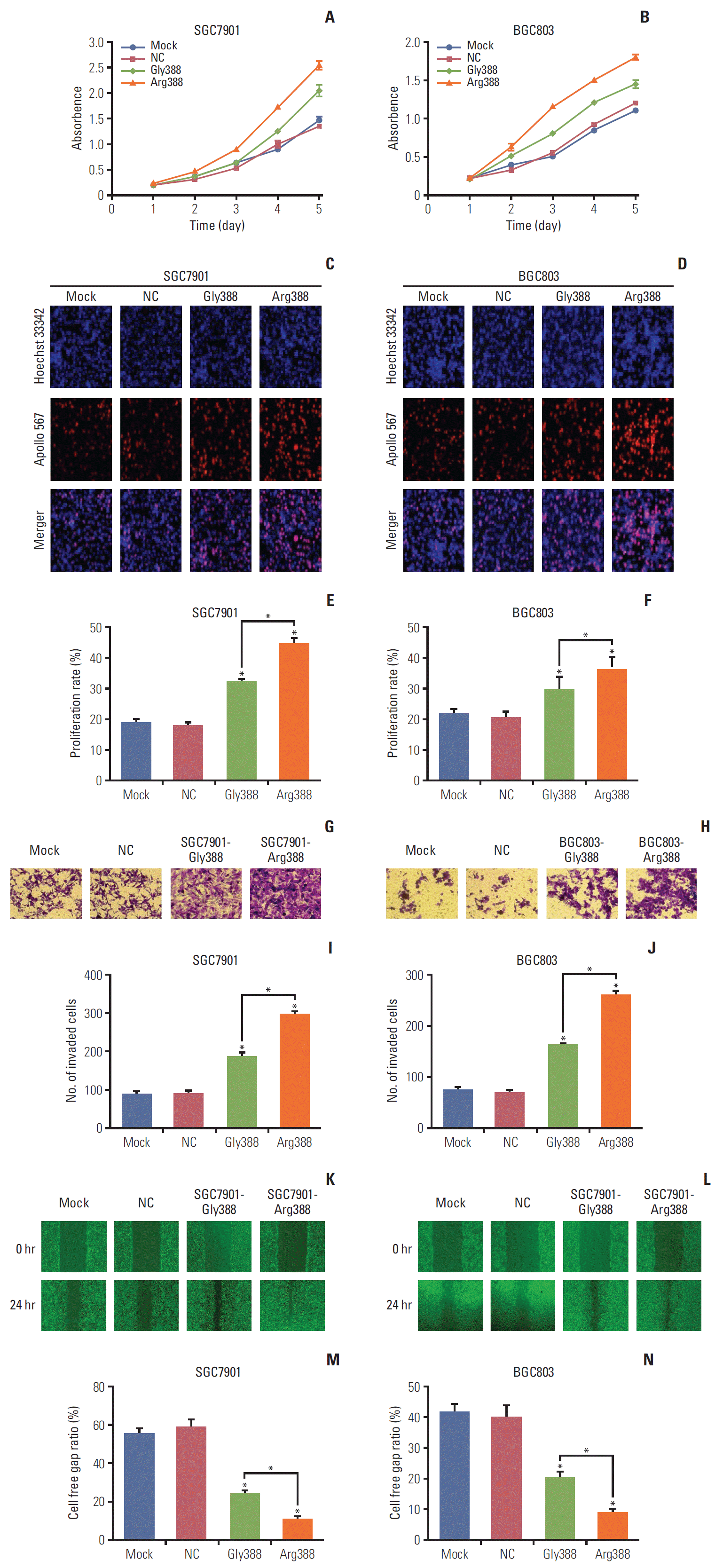 | Fig. 3.Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) genotype on proliferation, invasion, and migration. (A, B) Compared with mock and negative control (NC) cells, the proliferation of Gly388- and Arg388-transfected cells was significantly enhanced. In addition, Arg388-transfected cells have a faster proliferation than Gly388-transfected cells. In addition, Arg388-transfected cells have a faster proliferation than Gly388-transfected cells. Similar results were also observed in the EdU fluorescence staining test (C-F), Transwell chambers invasion assay (G-J), and cell scratch assay (K-N). *p < 0.05. Similar results were also observed in the EdU fluorescence staining test (C-F), Transwell chambers invasion assay (G-J), and cell scratch assay (K-N). *p < 0.05. |
5. FGFR4-Arg388 variant can increase the resistance of OXA
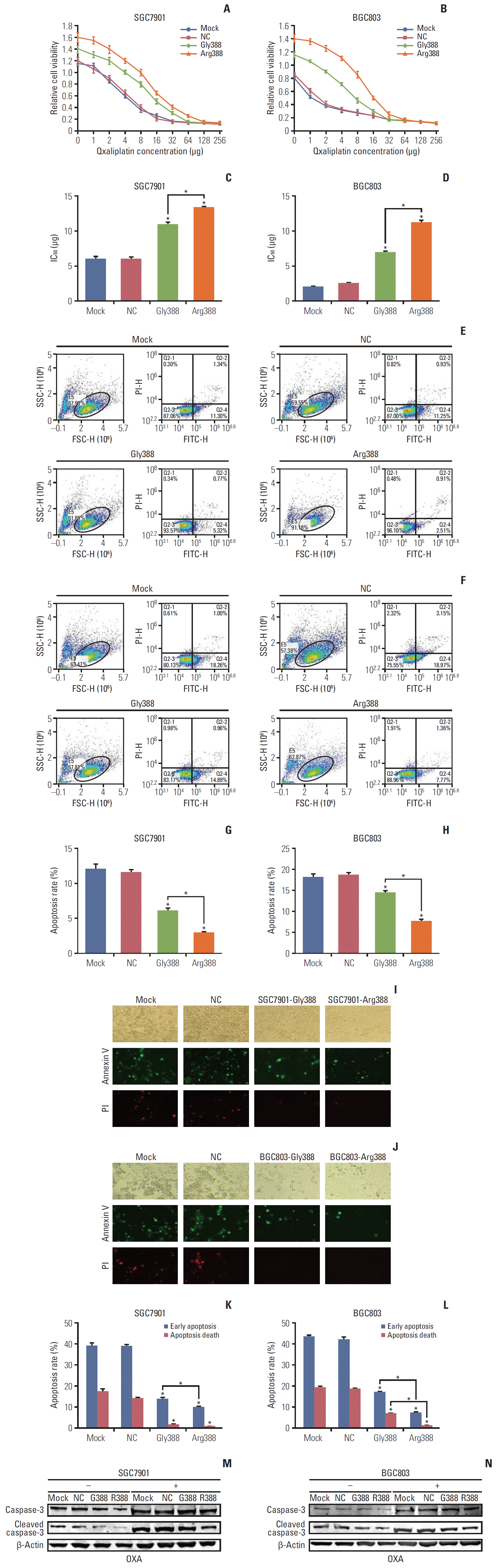 | Fig. 4.The relationship between fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) genotype and oxaliplatin (OXA) resistance. (A-D) Effects of different OXA concentrations on the activity of SGC7901 and BGC803 cells. NC, normal control. (E-H) Flow cytometry: apoptosis rate of gastric cancer (GC) cells with different FGFR4 genotypes after OXA addition for 24 hours. (I-L) Fluorescent staining for apoptosis of GC cells with different FGFG4 genotypes (green represents early apoptosis and red represents apoptosis death). PI, propidium iodide. (M, N) Western bolt was used to detect the changes of apoptosis molecules in GC cells with different FGFG4 genotypes before and after OXA addition. *p < 0.05. |
6. FGFR4-Arg388 variant affects the EMT process and STAT3 signaling pathway, and inhibition of the STAT3 pathway reduces Arg388 variant induced EMT
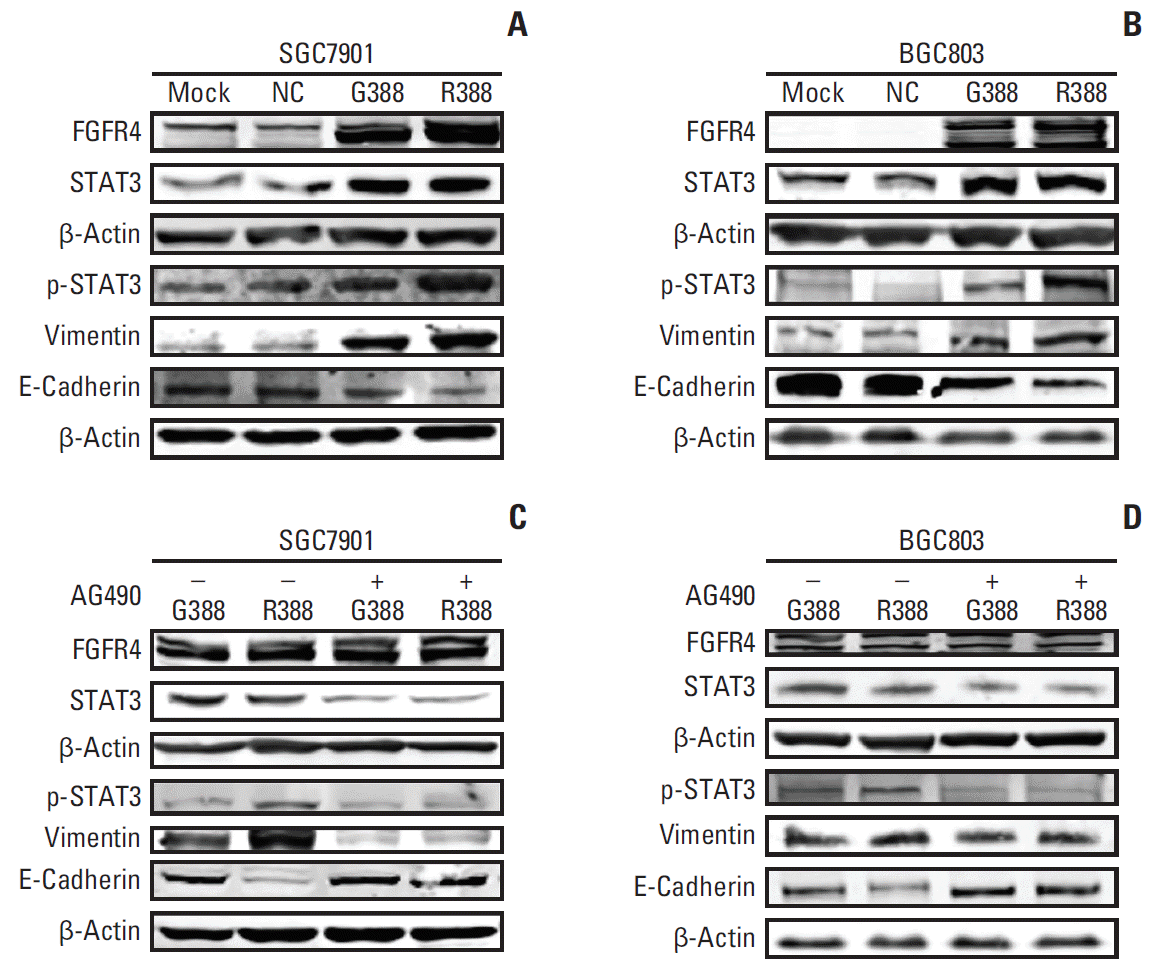 | Fig. 5.The mechanism of fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4)-Arg388 influencing the oncogenic properties of gastric cancer cells. (A, B) Western blot detection of the expression of related molecules including FGFR4, signal pathway (STAT3), and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (E-cadherin and vimentin) in SGC7901 and BGC803 cells with different FGFG4 genotypes (mock, normal control [NC], Gly388, and Arg388). (C, D) The changes of related molecules between overexpression Gly388- and Arg388-transfected cells were detected, when cells were incubated with the Jak2 inhibitor AG490 to block STAT3 activation. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download