Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Data source
2. Study population
3. Statistical analysis
4. Ethical statement
Results
Table 1.
Values are presented as number (%). DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; CLL/SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic; FL, follicular lymphoma; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma; BNHL, B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; NHL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma. %=percentage of all NHL
1. Incidence, prevalence, and all-cause mortality rates in patients with BNHL
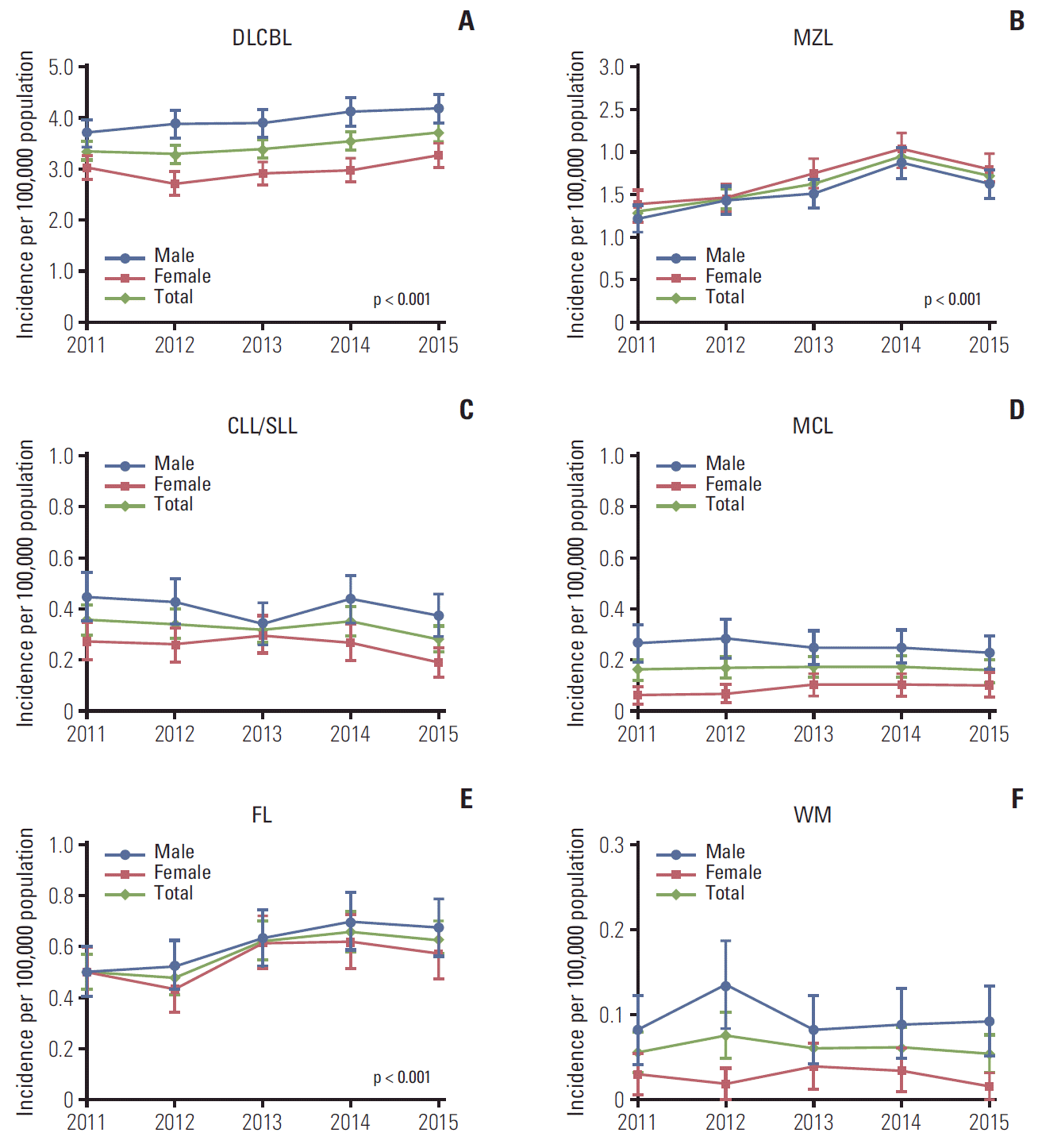 | Fig. 1.Age-standardized incidence rates (95% confidence intervals) of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes in South Korea, 2011-2015. Age-standardized rates were calculated by direct standardization method, using the 2011 Korean population as the reference. p-values for trend: DLBCL p < 0.001 (A), MZL p < 0.001 (B), CLL/SLL p=0.489 (C), MCL p=0.077 (D), FL p < 0.001 (E), WM p=0.661 (F). DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; CLL/SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. |
Table 2.
| Year | No. of cases |
Incidence (95% CI) per 100,000 |
Prevalence (95% CI) per 100,000 |
Mortality (95% CI) per 100,000 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | Age-standardizeda) | Crude | Age-standardizeda) | Crude | Age-standardizeda) | ||
| 2011 | 2,298 | 5.74 (5.51-5.98) | 5.74 (5.51-5.98) | 10.62 (10.28-10.92) | 10.62 (10.28-10.92) | 1.33 (1.22-1.44) | 1.33 (1.22-1.44) |
| 2012 | 2,436 | 6.00 (5.77-6.25) | 5.90 (5.67-6.13) | 14.82 (14.45-15.20) | 14.56 (14.19-14.93) | 1.62 (1.50-1.75) | 1.55 (1.43-1.67) |
| 2013 | 2,722 | 6.62 (6.37-6.87) | 6.39 (6.15-6.63) | 18.93 (18.52-19.36) | 18.31 (17.90-18.72) | 1.80 (1.67-1.93) | 1.65 (1.52-1.77) |
| 2014 | 3,087 | 7.39 (7.14-7.66) | 7.06 (6.81-7.31) | 23.41 (22.95-23.87) | 22.35 (21.91-22.79) | 2.07 (1.94-2.21) | 1.82 (1.69-1.95) |
| 2015 | 3,128 | 7.39 (7.13-7.65) | 6.96 (6.72-7.20) | 28.32 (27.82-28.83) | 26.69 (26.21-27.17) | 2.24 (2.10-2.39) | 1.89 (1.76-2.02) |
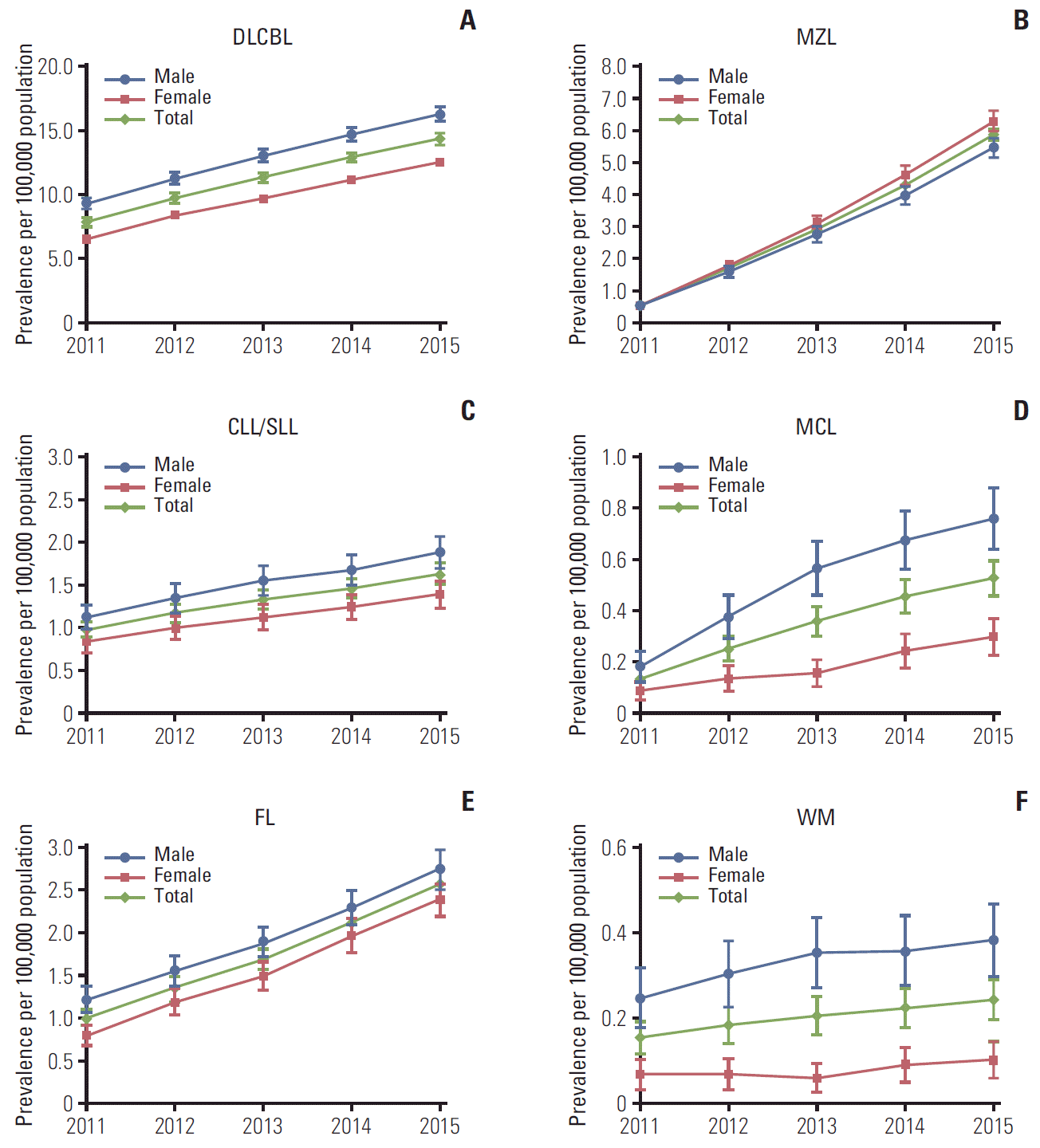 | Fig. 2.Age-standardized prevalence (95% confidence intervals) of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes in South Korea, 2011-2015. Age-standardized rates were calculated by direct standardization method, using the 2011 Korean population as the reference. p-values for trend: DLBCL p & 0.001 (A), MZL p & 0.001 (B), CLL/SLL p & 0.001 (C), MCL p & 0.001 (D), FL p & 0.001 (E), WM p & 0.001 (F). DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; CLL/SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. |
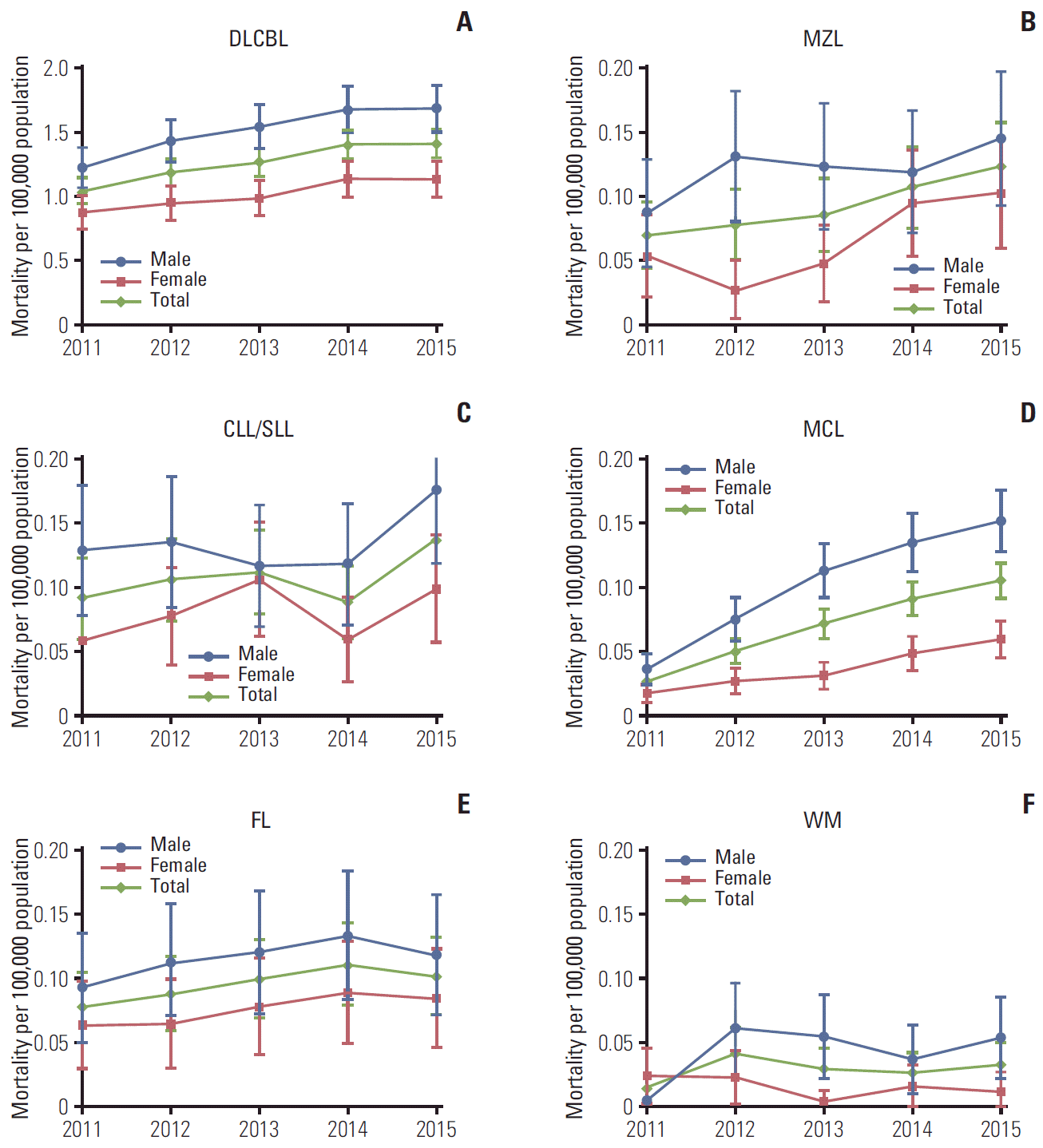 | Fig. 3.Age-standardized all-cause mortality rates (95% confidence intervals) in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes in the Korean population, 2011-2015. Age-standardized rates were calculated by direct standardization method, using the 2011 Korean population as the reference. p-values for trend: DLBCL p < 0.010 (A), MZL p < 0.001 (B), CLL/SLL p < 0.001 (C), MCL p < 0.001 (D), FL p=0.937 (E), WM p=0.923 (F). DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; CLL/SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. |
2. Overall survival
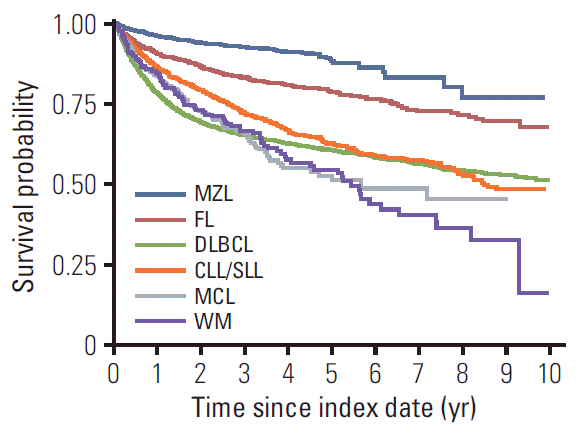 | Fig. 4.Overall survival after B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma diagnosis index date: follow-up of all patients enrolled from 2006-2015 and death from any cause. MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; CLL/SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. |
Table 3.
BNHL, B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; CI, confidence interval; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; CLL/SLL, chronic lymphocytic and small lymphocytic lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma.
3. Occurrence of SPM
Table 4.
BNHL, B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; CI, confidence interval; SPM, second primary malignancy; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; CLL/SLL, chronic lymphocytic and small lymphocytic lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. a)Acute myeloid leukemia (C92), monocytic leukemia (C93), myelodysplastic syndrome (D46), or myeloproliferative neoplasms (D47).
Table 5.
CI, confidence interval; SPM, second primary malignancy; BNHL, B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; CLL/SLL, chronic lymphocytic and small lymphocytic lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; WM, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia or lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma.
Discussion
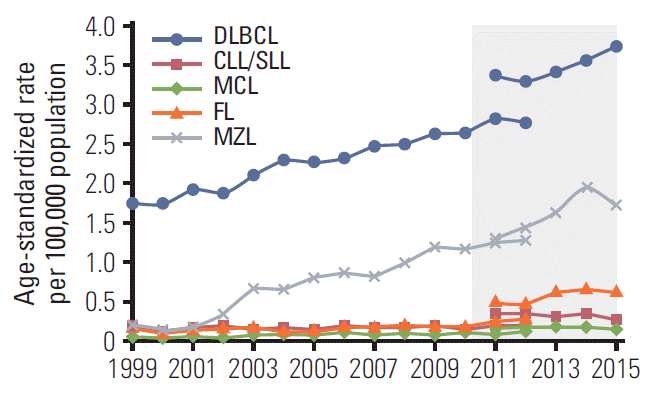 | Fig. 5.Age-standardized incidence of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes as reported fan Central Cancer Registry from 1999-2012 [2] and the National Health Information database from 2011-2015 (shaded). DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; CLL/SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download