Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Patients and tumor samples
2. WES analysis
3. TACE procedure
4. Evaluation of TACE response
5. Statistical analyses
6. Ethical statement
Results
1. Study population and HCC characteristics at baseline
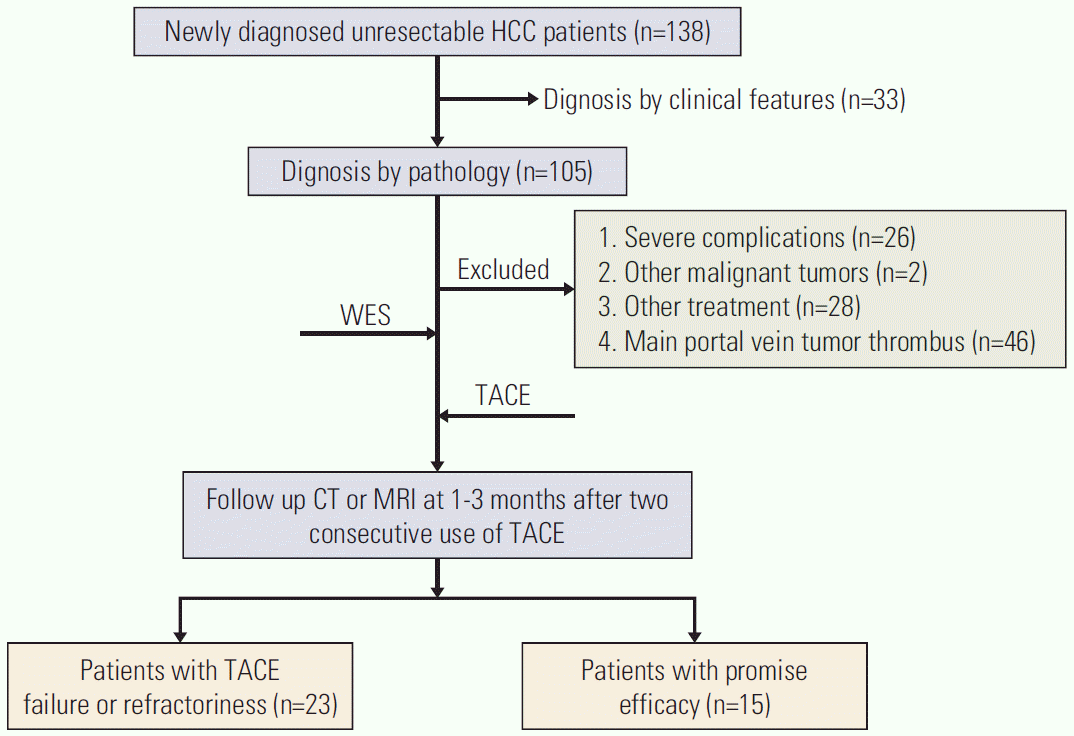 | Fig. 1.Flow chart of enrolled patients. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; WES, whole-exome sequencing; TACE, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging. |
Table 1.
2. Overview of genetic alterations in 38 patients with HBV-related advanced HCC
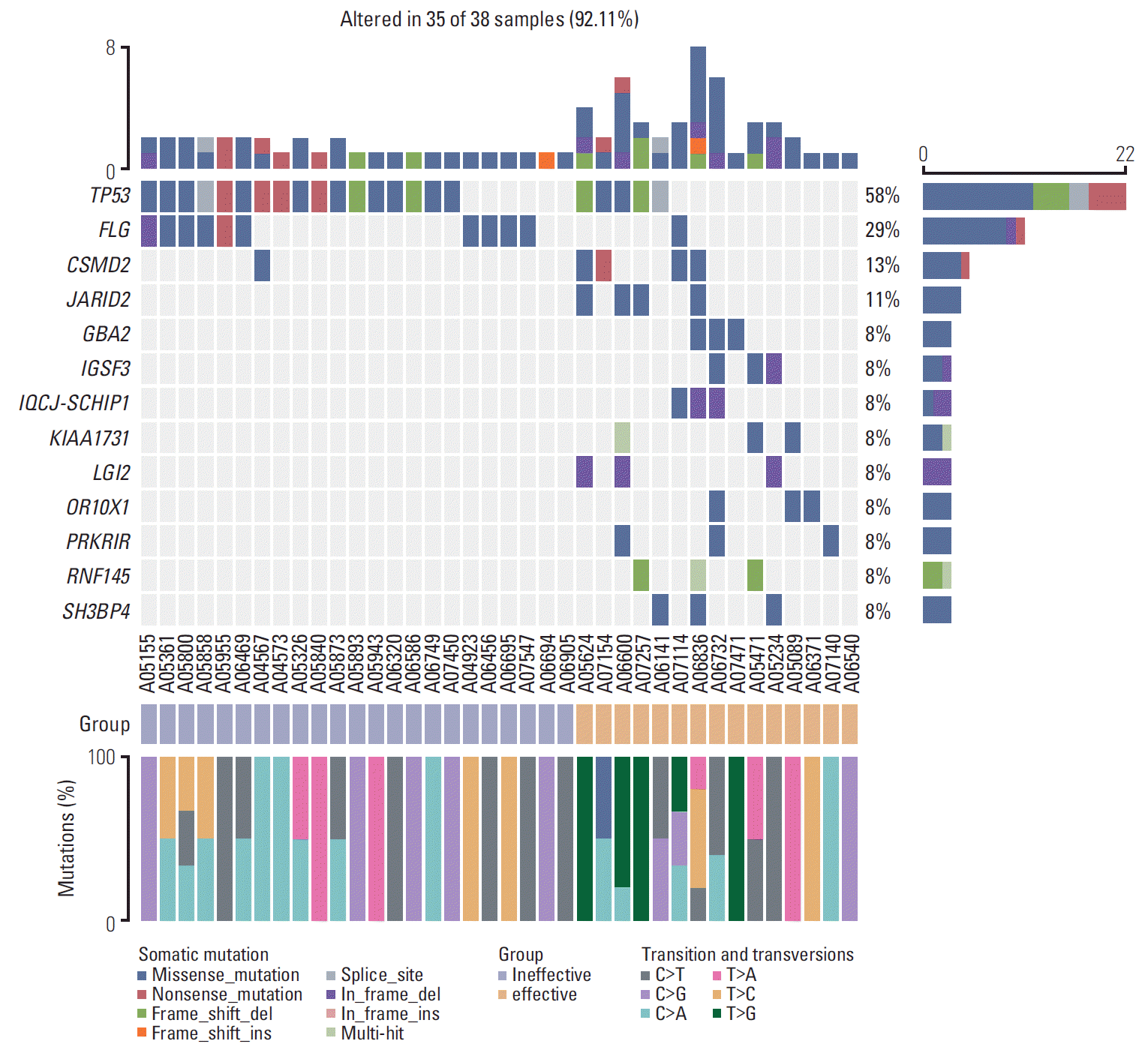 | Fig. 2.Heatmap of somatic genetic alterations in significant variation genes between groups A and B. Group A is defined as a group where transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) failure/refractoriness. And group B is defined as a group which can benefit from TACE therapy. Top and right panel shows the frequency of somatic mutation, middle panel shows patients ID, mutational spectra of single-nucleotide variants in different group, and types of mutation are indicated in the legend at the bottom (n=38). We found that the occurrence probability of TP53 and FLG mutations in the invalid group was significantly higher than that in group A. T>G mutation did not occur in group A during the transformation and alteration. |
Table 2.
3. Significant mutated genes and clinical features between different response groups
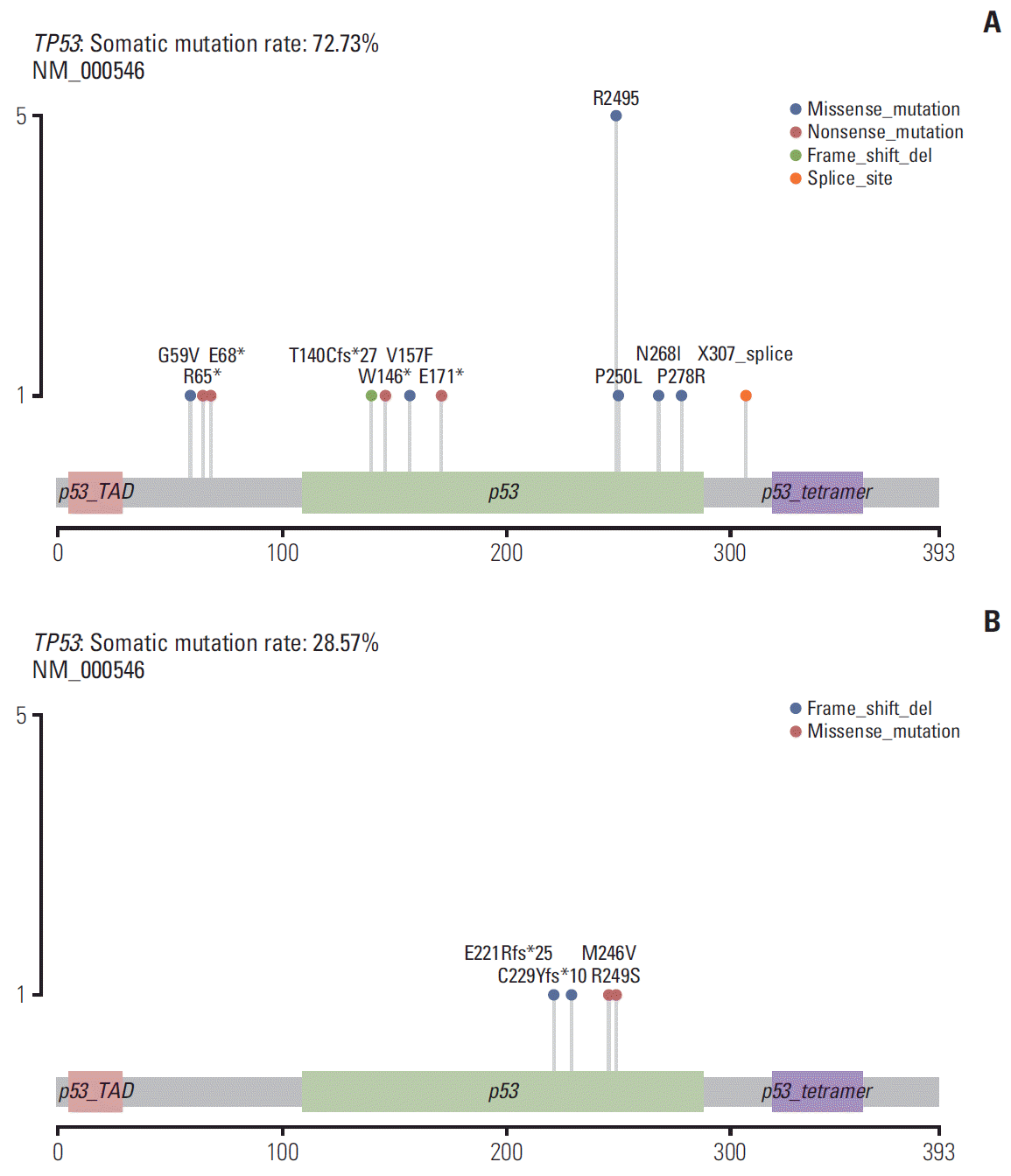 | Fig. 3.Distribution of somatic mutations in the TP53 gene. The structural domains of TP53 mutations were different between the two groups, and the occurrence probability of TP53 R249S mutation in group A was higher than that in group B. Alteration frequency was represented as a percentage of significant variation genes in two groups: the left box represents group A and the right represents group B. Alteration types and frequencies were represented by different colors and color gradients, respectively. |
Table 3.
TACE, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; TP53, tumor protein p53; MYC, proto-oncogene; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; JAK1, Janus kinase 1; NOTCH, neurogenic locus notch homolog; SOX2, SRY-box transcription factor 2; CTNNB1, catenin beta 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RB1, RB transcriptional corepressor 1; TERT, telomerase reverse transcriptase; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; -, none.
Table 4.
HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCC, hepatocellular carcinomas; WBC, white blood cell; NEUT, neutrophil count; HB, hemoglobin; PLT, platelet; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALB, albumin; TBIL, total bilirubin; PT, prothrombin time; AFP, α-fetoprotein; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; PS, performance status.
4. TP53 mutation and vascular invasion as predictive factors for TACE failure/refractoriness
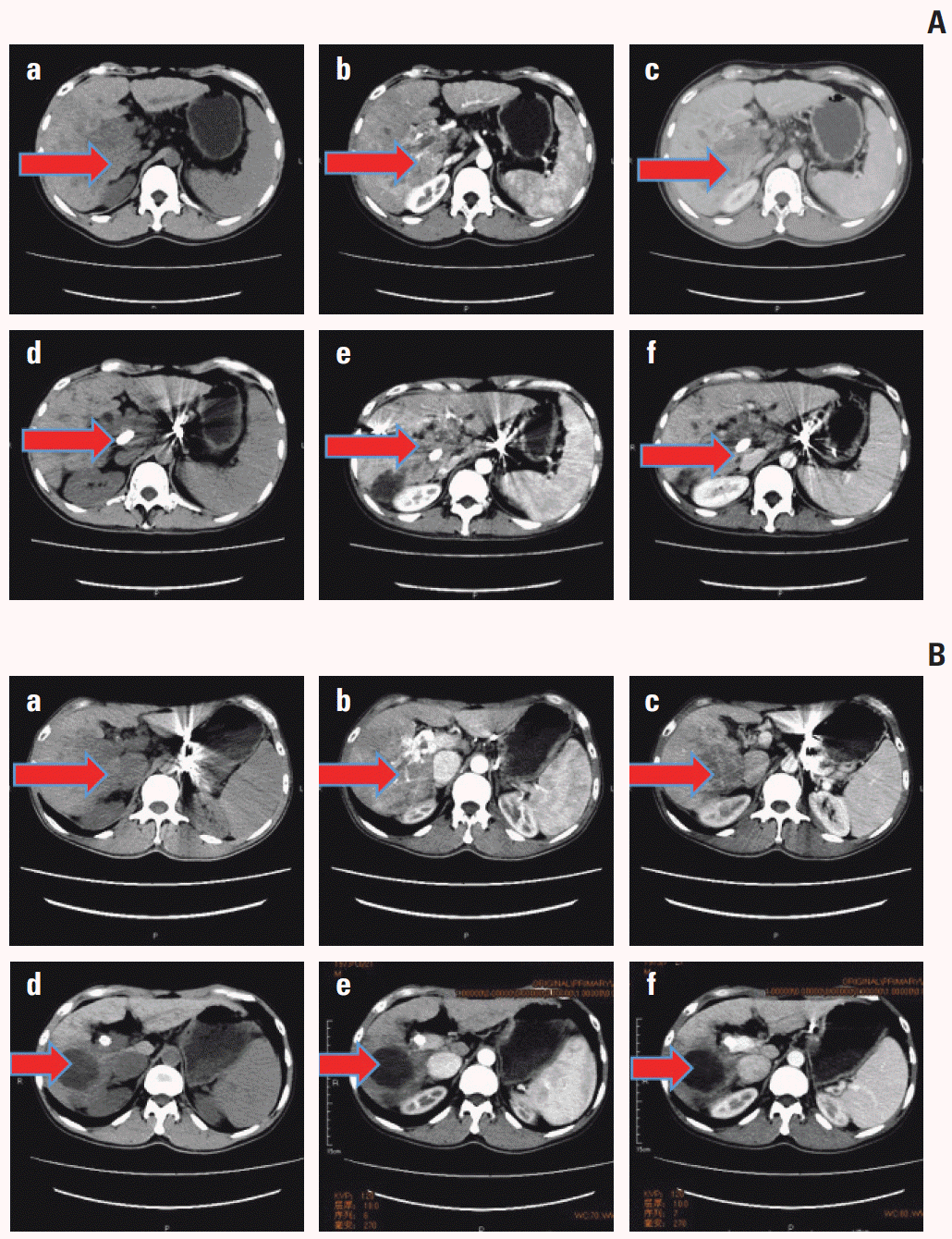 | Fig. 4.
TP53 mutated and wild-type cases were compared before and after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) by using computed tomography (CT) scan. For TP53 mutated case in A, plain sweep, augmentation, and portal phase were shown respectively in a, b, and c before TACE, while they were shown in d, e, and g after TACE. We found that TACE failure/refractoriness was assessed in the TP53 mutated case. Meanwhile, the TP53 wild-type case was shown in B and effective for TACE. The two cases were evaluated according to the criteria mentioned above. |
Table 5.
| Variable |
Univariate analysis |
Multivariate analysis |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-value | OR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age (> 50 yr vs. ≤ 50 yr) | 0.563 | 0.151-2.096 | 0.391 | - | - | - |
| AFP (> 400 μg/L vs. ≤ 400 μg/L) | 1.246 | 0.312-4.977 | 0.755 | - | - | - |
| Maximum tumor size (> 5 cm vs. ≤ 5 cm) | 2.333 | 0.617-8.820 | 0.212 | - | - | - |
| Tumor number (multiple vs. simple) | 0.938 | 0.237-3.705 | 0.927 | - | - | - |
| Vascular invasion (presence vs. absence) | 19.000 | 3.604-100.154 | 0.001** | 18.204 | 1.392-238.090 | 0.027* |
| Liver cirrhosis (presence vs. absence) | 1.111 | 0.162-7.632 | 0.915 | - | - | - |
| Ascites (presence vs. absence) | 2.294 | 0.396-13.277 | 0.354 | - | - | - |
| Child-Pugh classification (A vs. B) | 15.273 | 1.714-136.126 | 0.015* | 23.352 | 0.767-710.623 | 0.071 |
| ECOG PS (0 vs. 1) | 0.145 | 0.031-0.677 | 0.014* | 0.192 | 0.008-4.742 | 0.192 |
| TP53 mutation (presence vs. absence) | 5.667 | 1.369-23.462 | 0.017* | 13.287 | 1.114-158.451 | 0.041* |
5. Frequently altered cancer pathways related to TP53 mutation status
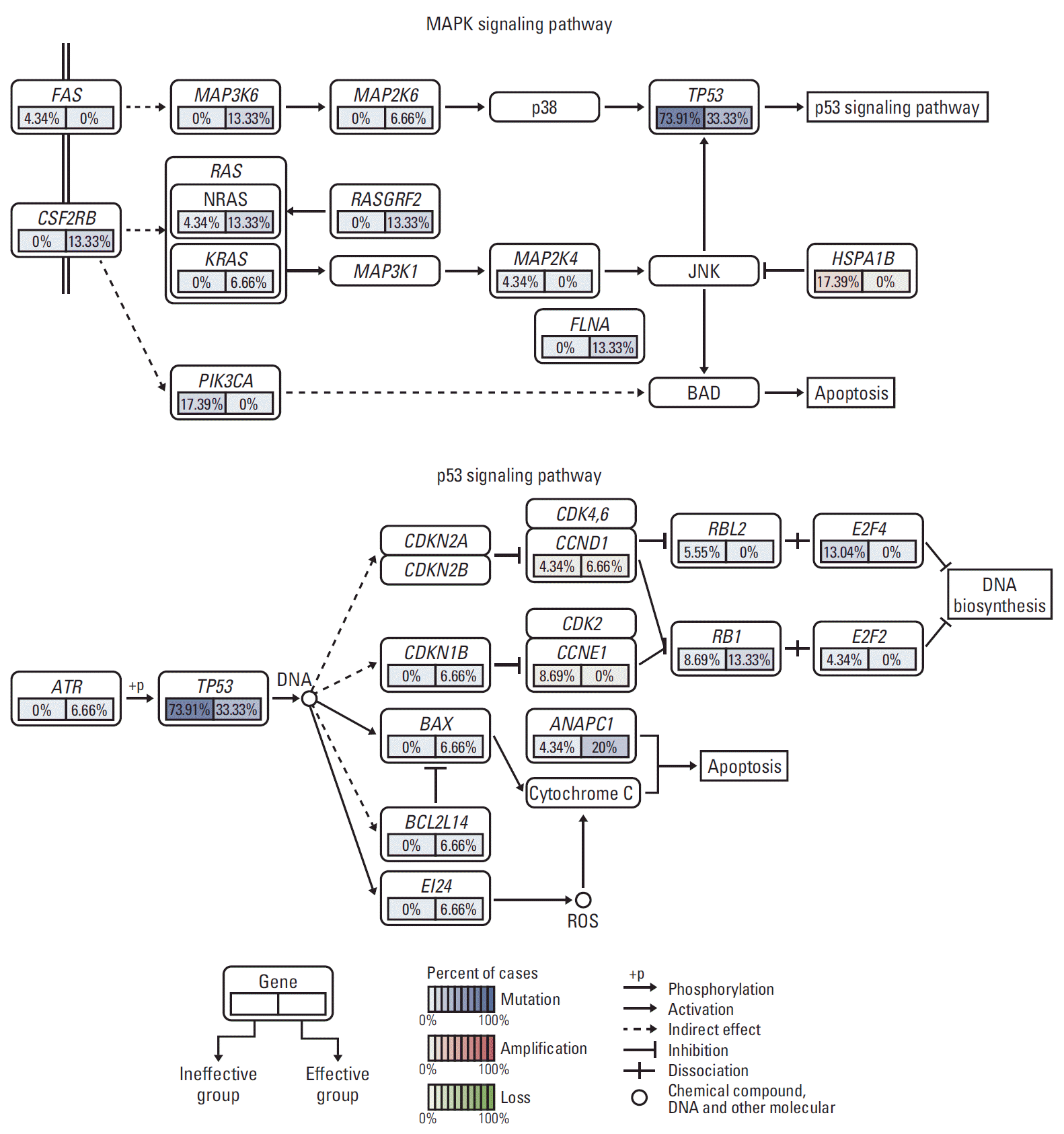 | Fig. 5.Frequently altered cancer pathways for TP53 using gene set enrichment analysis pathway enrichment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Core pathway analysis identified frequent genomic alterations in multiple cancer pathways including mitogen-activated protein kinase and apoptosis. MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download