Abstract
Purpose
Chronic stress and related hormones are key in cancer progression. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and its agonists was reported that inducing anti-tumor effect. However, the function of PPARγ in pro-tumorigenic effects induced by chronic stress in breast cancer remains unknown. Herein, we have characterized a novel role of PPARγ and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) signals in breast cancer promoted by chronic stress.
Materials and Methods
We performed experiments in vivo and in vitro and used bioinformatics data to evaluate the therapeutic potential of PPARγ in breast cancer promoted by stress.
Results
Chronic stress significantly inhibited the PPARγ expression and promoted breast cancer in vivo. VEGF/FGF2-mediated angiogenesis increased in the chronic stress group compared to the control group. PPARγ agonist pioglitazone (PioG) injection offset the pro-tumorigenic effect of chronic stress. Moreover, specific β2-adrenergic receptor (β2R) antagonist ICI11-8551 inhibited the effect of chronic stress. In vitro, norepinephrine (NE) treatment had a similar tendency to chronic stress. The effect of NE was mediated by the β2R/adenylate cyclase signaling pathway and suppressed by PioG. PPARγ suppressed VEGF/FGF2 through reactive oxygen species inhibition. Bioinformatics data confirmed that therewas a lowPPARγ expression in breast invasive carcinoma. Lower PPARγ was associated with a significantly worse survival.
Conclusion
β2R activation induced by chronic stress and related hormones promotes growth and VEGF/FGF2-mediated angiogenesis of breast cancer by down-regulating PPARγ. Our findings hint that β receptor and PPARγ as two target molecules and the novel role for their agonists or antagonists as clinical medicine in breast cancer therapy
Social-psychological stress has been implicated in the development of cancer, hematopoietic, and cardiovascular diseases [1,2]. Previous studies have reported that sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activation or catecholamine secretion induced by chronic stress act on adrenoceptors to modulate cell behavior, which plays a significant role in multiple solid tumors, including ovarian, breast, and pancreatic cancers [3-5]. Our earlier work has confirmed that chronic stress can strengthen breast cancer progression in mice [6]. The mammary gland and pancreas were innervated by SNS fibers and both of cancer cells had receptors for SNS neurotransmitters [7], strongly suggesting that these cancers may be sensitive to neural signaling.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) belong to a nuclear receptor superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors, which play crucial roles in several types of metabolic processes. Three types of PPARs (α, β, and γ) have been identified thus far. The most studied subtype PPARγ, which was identified as a critical regulatory factor in adipogenesis, is also involved in islet cell sensitization, cell cycle arrest, and proliferation [8]. PPARγ agonist has been used for type II diabetes and related metabolic disease therapy, including obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Recently, more studies have suggested that PPARγ and its agonists play an anti-tumor role in cancer biology by suppressing angiogenesis [9,10], inducing apoptosis [11] and matrix metalloproteinase degradation [12].
To date, the role of PPARγ in pro-tumorigenic effects induced by chronic stress in breast cancer remains unclear. Stress-related hormone norepinephrine (NE) has been shown to repress the PPARγ gene expression in brown adipocytes [13]. In addition, chronic social stress decreases the PPARγ levels in adipose adiponectin production [14]. Thus, we hypothesized that chronic stress promotes breast cancer by suppressing PPARγ expression. It is well known that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2)-dependent angiogenesis acts as a crucial factor in tumor metastasis, and PPARγ activation inhibited angiogenes. Thus, it was important to explore whether VEGF and FGF2 was involved in PPARγ inhibition of tumor progression induced by chronic stress. We found that chronic stress and NE decreases the PPARγ levels and facilitates VEGF/FGF2-related vascularization in breast cancer. The β2 receptor was also determined to be involved in the effect of stress.
NE, phentolamine (phent), propranolol (PPL), metoprolol, ICI118551, forskolin, pioglitazone (PioG), and GW9662 were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Shanghai, China). Murine breast cancer cells 4T1 were incubated in 10% fetal bovine serum (BI) RPMI1640 medium. NE was treated at a concentration of 0, 1, 10, and 100 μM. After conducting the dose response and time course experiments, 10 μM NE [5] was added to 4T1 cells for 3 hours. Phent, PPL, metoprolol, and ICI118551 were used at a concentration of 1 μM. Concentrations of forskolin and PioG were 10 and 50 μM [15], respectively. H2O2 (250 μmol/L) and the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC, 5 mmol/L) was treated for 24 hours.
Female BALB/c mice (6-8 weeks old, Vital River Lab Animal Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) were inoculated subcutaneously with 1×106 of 4T1 cells. The animals were then randomly divided into experimental groups. For chronic stress group, the mice were exposed to social isolation stress, as described by Thaker et al. [3]. Briefly, each mouse was individually housed in a cage with a wall of at least 24 inch between cages. For control or PioG groups, five mice were housed per cage. PioG (25 mg/kg, intraperitoneally, four times a week) [16], ICI118551 (25 mg/kg, intraperitoneally, every 2 days), or GW9662 (1 mg/kg/day, intraperitoneally) was injected on day 7 after the 4T1 cell inoculation. The mice were sacrificed 28 days after inoculation and tumors were weighed and frozen for other experiments.
Briefly, 2 mL of India ink was injected directly into the trachea. After dissection, some lung samples were washed with Fekete's solution and lung nodules were observed and counted. The other lung samples were fixed and used for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining to observe the metastasis more clearly.
Matrigel plug assay was used for angiogenesis measurement in vivo. 4T1 cells (1×105) mixed with 250 μL of Matrigel (Corning 354234, Shanghai, China) were injected subcutaneously into the backs of mice. The mice were then randomly divided into four groups: control, PioG, chronic stress with or without PioG. After 10 days, the resulting Matrigel plugs were extracted, photographed and then measured hemoglobin content (QuantiChrom hemoglobin assay, BioAssay Systems, Hayward, CA).
Total RNA (1 μg) from each sample was collected using the TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher, Shanghai, China) and used for first-strand cDNA synthesis using M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI). The quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) amplifications were performed using the SYBR Green Mix (TransGen, Beijing, China). Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as an internal control. Primers were listed as follows: PPARγ: 5′-GGGATCAGCTCCGTGGATCT-3′ (F); 5′-TGCACTTTGGTACTCTTGAAGTT-3′ (R). VEGF: 5′-GTGAGGTGTGTATAGATGTGGGG-3′ (F); 5′-ACGTCTTGCTGAGGTAACCTG-3′ (R); FGF2: 5′-GCGACCCACACGTCAAACTA-3′ (F); 5′- TCCCTTGATAGACACAACTCCTC-3′ (R).
Preparation of total cell or tumor tissue extracts and immunoblotting with appropriate antibodies was performed. Primary antibodies were used to detect PPARγ (ab41928, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), VEGF (sc-7296, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) or FGF2 (MA1-24682, Invitrogen, Shanghai, China). Labeled proteins were visualized using the enhanced chemiluminesence chemiluminescence kit (Millipore, Bedford, MA).
4T1 cells after different treatments resuspended and incubated with primary anti-PPARγ for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and then incubated with phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated secondary antibody for 30 minutes. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) intensity was measured by a DCFH-DA probe kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China). 4T1 cells with different treatments were trypsinized, incubated with DCFH-DA for 20 minutes at 37°C, washed with PBS and then detected the intensity of DCF signal to examine the ROS levels. The cells were measured using flowcytometry and analyzed with FlowJo software (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA).
For immunohistochemistry, tumor tissue paraffin sections from tumor-bearing mice were stained with anti-CD31 (1:100, sc-71873, Santa Cruz Biotechnology) or anti-PPARγ primary antibodies (1:100). The immunoactivity was detected with diaminobenzidine (ZSGB-BIO, Beijing, China). The micro-vascular density (MVD) was measured by 10 independent fields.
SiCtrl, siβ2R(1) (target sequence 5′-CAGAGTGGATATCACGTGGAA-3′) and siβ2R(2) (target sequence 5′-CCGATAGCAGGTGAACTCGAA-3′); si-PPARγ (target sequence 5′-CACTGATATTCAGGACATTTTTA-3′) (Qiagen, Shanghai, China) were transfected into 4T1 cells with lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Shanghai, China).
For immunofluorescence analysis, 4T1 cells were washed twice with PBS, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, and then incubated with anti-PPARγ monoclonal antibody (ab41928, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) overnight at 4°C. Immunoreactive proteins were detected by incubating with TRITC-conjugated IgG. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (50 μg/mL) for 5 minutes. Images were assessed using a fluorescence inversion microscope system (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
Cells were incubated in a 96-well plate at a density of 4×103 cells per well treated with NE alone or in combination with PioG for 48 hours. Cell viability was detected using the Cell Counting Kit-8 assay (CCK-8, Dojindo, Kyushu, Japan). Each assessment was performed in triplicate in three independent experiments.
Agar (0.5%, diluted with serum-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium) was added to 6-well plates as a bottom layer and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes. The 4T1 cells treated with NE alone or in combination with PioG (1,000 cells/well) were mixed with 0.375%-agar to form a middle layer. Serum-free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium was then added as a top layer. The 6-well plates were incubated for 2 weeks, at which point the cell colonies were counted.
Data were represented as mean±standard error of mean and analyzed with SigmaStat 10.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). The differences between two groups were analyzed using the Student’s t test. The differences among three or more groups were evaluated by one-way ANOVA, followed by Turkey test. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
First, the role of PPARγ in tumor progression induced by chronic stress in vivo was determined. After 4T1 cells were injected into the mammary fat pads of female BALB/c mice to establish a mouse xenograft model, social isolation was also imposed for 4 weeks to implement a chronic stress model until the mice were sacrificed on day 28. One week after cell inoculation, PPARγ-specific agonist PioG (25 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally four times a week (Fig. 1A). In our previous work [6], we have reported that chronic stress can strengthen breast cancer progression. In the current study, this result was also explicitly confirmed. Moreover, PioG treatment markedly inhibited tumor growth compared to the control group. When PioG was injected after the chronic stress stimulation, tumor growth was inhibited compared to the chronic stress alone group (Fig. 1B). Compared with the tumor volume on day 28 in control group (1,960.838±380.528 mm3), the chronic stress group (2,643.856± 197.824 mm3) bore biggertumors while PioG group (1,360.097± 213.938 mm3) bore smaller tumors. The tumor volume on day 28 in the combination group was smaller than chronic stress alone group (2,119.997±405.572 mm3 vs. 2,643.856±197.824 mm3, p < 0.05) (Fig. 1C). The PioG group also showed the lowest tumor weight, while the chronic stress group showed the heaviest tumor weight on day 28 (Fig. 1D). In addition, lung metastasis was observed using the India ink staining and H&E staining. This result was similar to the tumor growth volume and weight. The chronic stress group had the most lung metastatic nodules, while the PioG group had the fewest nodules. The number of lung nodules in the combination group was moderate (Fig. 1E). H&E staining revealed a similar tendency to the ink staining (Fig. 1F). These data imply that PPARγ inhibits the tumor growth and distant metastasis induced by chronic stress.
To confirm the role of PPARγ in tumors in vivo, PPARγ levels in the tumor tissues were detected. Both PPARγ mRNA and protein expression levels detected by RT-PCR, qPCR and western blot were lowest in the tumor from chronic stress group and highest in the PioG alone group. The PioG injection reversed PPARγ inhibition induced by chronic stress (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2A-C).
Angiogenesis is one of the most crucial factors that promotes cancer metastasis. Thus, it was important to explore whether angiogenesis was involved in PPARγ inhibition of tumor progression induced by chronic stress. An in vivo angiogenesis Matrigel plug assay was performed, where 4T1 cells were mixed with the Matrigel solution and then injected subcutaneously into the backs of BALB/c mice. After 10 days, Matrigel plugs in the chronic stress group were red and contained many blood vessels (Fig. 2D). In contrast, Matrigel plugs from the PioG alone group remained clear and were poorly vascularized (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2D). Assay images further revealed a functional vascular network invading into the tumors in the chronic stress group, whereas vessels in the PioG-treated tumors were only found at the tumor periphery (Fig. 2D). Similarly, the number of blood vessels in the chronic stress with PioG treatment group showed a decreased blood vessel number in contrast to the chronic stress group (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2D).
An endothelial marker, CD31, was also tested by immunohistochemistry staining of tumor sections. CD31-positive results validated the presence of blood vessels in the tumors. The bar graph showed that tumor tissue derived from the chronic stress group demonstrated a significant increase in the MVD compared to the control group, while in the PioG alone group the MVD was the lowest among all groups. Angiogenesis was thus restrained after the PioG injection combined with chronic stress treatment (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2E).
The in vivo angiogenic properties suggested that chronic stress produced pro-angiogenic factors. VEGF and FGF2 are two of the most well-known proangiogenic factors commonly up-regulated in human tumors [17] and were induced by chronic stress [3]. Therefore, their expression was examined in this study. qPCR and western blot analysis showed that both of VEGF and FGF2 expression was up-regulated in the chronic stress group and down-regulated in the PioG alone group compared to the control group. The PioG treatment attenuated VEGF/FGF2 upregulation induced by chronic stress (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2F and G). Hence, the angiogenic properties reflected that chronic stress enhanced the production of two proangiogenic factors and new blood vessel formation, which correlated with the rapid growth and metastasis of tumors in vivo. Therefore, PioG inhibited the VEGF/FGF2 production and angiogenesis potentiated by chronic stress, thus inhibiting tumor promotion.
NE released under stress condition. Thus, it was important to explore whether NE could affect the PPARγ expression in vitro. PPARγ mRNA expression was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in 4T1 cells after NE treatment for 10 minutes, 1, 3, or 12 hours with different concentrations (0, 1, 10, and 100 μM). PPARγ mRNA expression detected by RT-PCR and qPCR was decreased in 4T1 cells treated with 10 or 100 μM of NE for 1 hour, 3 hours, or longer durations (Fig. 3A-C). According to these results, 10 μM and 3 hours were chosen as the optimum conditions for NE treatment in the subsequent experiments (Fig. 3B and C). PPARγ expression in 4T1 cells was detected using cytofluorescence staining. Compared with the vehicle group, PE-conjugated PPARγ fluorescence intensity in 4T1 cells decreased significantly after treatment with NE (Fig. 3D). To investigate whether PPARγ inhibition affected cell viability and proliferation, CCK-8 (Fig. 3E) and clonogenic assays (Fig. 3F) were performed. The data showed that NE alone enhanced the viability and proliferation ability, where the latter was measured by counting clone numbers growing in soft agar. PioG inhibited cell viability and proliferation. Consistent with the in vivo results, NE in combination with PioG offset their individual effects (p < 0.05) (Fig. 3E and F).
We also investigated whether the effect of PPARγ on angiogenesis in 4T1 cells induced by NE was similar to that in vivo. 4T1 cells were treated with NE (10 μM) for 3 hours or PioG (50 μM) for 24 hours. PPARγ mRNA and protein expression was significantly decreased after NE stimulation (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4A and B). PioG, the PPARγ agonist, triggered PPARγ mRNA and protein upregulation (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4A and B). VEGF/FGF2 expression showing an opposite trend to that of PPARγ (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4A and B). NE and PioG combination treatment offset the effect achieved by single stimulation (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4A and B).
Stress hormones function by binding to the adrenergic receptors, including subtypes α1 or α2 and β1, β2, or β3. The roles of all the subtypes involved in PPARγ inhibition induced by NE were detected in 4T1 cells. As shown in Fig. 4C, β receptor inhibitor PPL and not α receptor inhibitor phent reversed the NE-induced PPARγ inhibition (0.267±0.016 vs. 0.893±0.04, p < 0.05) and blocked NE-induced VEGF and FGF2 (2.6±0.35 vs. 1.4±0.1; 3.3±0.75 vs. 1.2±0.15, p < 0.05) (Fig. 4C). A specific β2 receptor antagonist ICI118551 but not a β1 receptor antagonist (metoprolol) inhibited NE-induced changes (p < 0.05) (Fig. 4D). In addition, we also confirmed the PPARγ expression in protein level by flow cytometry. The result showed that β2 receptor inhibition by ICI118551 induced PPARγ enhancement (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5A). To further illustrate the role of β2 receptor in PPARγ inhibition induced by NE, siβ2Rs experiments were performed. Both of two siβ2Rs silenced β2R protein expression effectively (data not shown). Compared with siCtrl group, PPARγ protein expression was no longer suppressed by NE treatment in siβ2R(1) group (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5B). The PPARγ fluorescence intensity also showed the same results (Fig. 5C). It is well known that β receptor activate the cAMP signaling pathway through stimulation of adenylyl cyclase (AC) [18]. The cells were treated with an AC activator forskolin, causing a decrease in PPARγ and an increase in VEGF and FGF2, in accordance with the results of NE-alone treatment (Fig. 5D). Because cAMP activates both cyclic-AMP response binding (CREB) and EPAC-mediated downstream events, it is unclear whether PPARγ is associated with the forskolin-induced VEGF expression. For clarification, PPARγ was silenced and then we examined whether the forskolin-mediated VEGF modulated or not. The data showed that after PPARγ silenced, VEGF expression was not increased (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5E).
It has been reported that PPARγ inhibited proliferation of lung cancer cells was based on metabolic changes, especially targeting ROS [19]. ROS played a prominent role in VEGF-dependent angiogenesis [20]. Therefore, we further explore the underlying role of ROS by flowcytometry in cross-talk between PPARγ and VEGF. Compared with that in dimethyl sulfoxide group, PPARγ agonist PioG inhibited ROS level, while it could not induce the same effect in siPPARγ group (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5F). Does ROS affect the expression of VEGF induced by PPARγ activation at least partly? To probe into this, H2O2 (250 μmol/L) and NAC (5 mmol/L) was used to increase and eliminate ROS,respectively. As shown in Fig. 5G and H, PioG treatment inhibited VEGF expression (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5G), which was rescued by H2O2 addition. Similarly, NAC suppressed VEGF increase induced by PPARγ silencing (p < 0.05) (Fig. 5H).
Therefore, all above data supported the contribution of β2 receptor in regulating PPARγ and VEGF/FGF2 induced by stress hormones.
The in vitro results suggested that β2 receptor is mainly involved in NE function. The role of the β2 receptor was also investigated in vivo. Mice bearing xenograft tumors were exposed to chronic stress and then divided into four groups: control (n=3), chronic stress group (n=4), chronic stress+ICI1-18551 (25 mg/kg every other day, intraperitoneally, n=4), and chronic stress+PPARγ antagonist GW9662 (1 mg/kg/day, intraperitoneally, n=5). As expected, chronic stress accelerated the tumor promotion again (p < 0.05) (Fig. 6A-C). After blocking the β2 receptor with ICI118551, tumor growth was inhibited significantly compared to the chronic stress only group. While after PPARγ inhibition by GW9662, the tumor growth was strengthened markedly (p < 0.05) (Fig. 6A and B). Tumor weight on day 28 showed a similar trend. The mice treated with GW9662 were burdened with the heaviest tumors. However, ICI-118551 injection reduced the tumor weight (p < 0.05) (Fig. 6C). Furthermore, PPARγ expression and angiogenesis in tumors were measured using RT-PCR, qPCR, western blotting, and immunohistochemistry staining. As shown in Fig. 6D-F, both PPARγ mRNA and protein expression levels were greater in the ICI118551 group and lower in the GW9662 group compared with chronic stress alone group. VEGF/FGF2 expression showed a reverse tendency. Immunohistochemistry results also showed a similar PPARγ change (Fig. 6G). Finally, the numbers of blood vessels in the tumor tissue labeled with CD31 were counted. Blood vessel numbers were the greatest in mouse tumors treated with GW9662 and the least with ICI118551 among all the three groups (Fig. 6H left and right panel). Combined results in vitro and in vivo demonstrated that chronic stress heightens VEGF/FGF2-mediated angiogenesis and then promotes breast cancer progression by β2R activation and PPARγ inactivation.
According to the experimental results, PPARγ can serve as a key player in stress-induced tumor progression. A possible explanation for this result may be partly due to poor PPARγ expression in cancer tissue. Data analysis of 1,104 breast cancer samples and 113 normal mammary tissue samples that were catalogued in the StarBase v3.0 [21], revealed an obvious decrease in PPARγ mRNA levels (Fig. 7A). Another result from GEPIA database [22] also displayed the same result as data from StarBase (p < 0.05) (Fig. 7B). Moreover, in this population, high PPARγ (greater than median) was associated with a significantly better overall survival, compared to patients with lower than median PPARγ expression (p=0.039) (Fig. 7C). High PPARγ was also associated with a significantly better relapse-free survival (p < 0.001) (Fig. 7D), when analyzing data from the Kaplan-Meier plotter (http://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=breast). This result was consistent with findings from the above experimental data, further highlighting PPARγ’s potential clinical relevance and application.
It can be concluded that β2 receptor activation by chronic stress and NE silences PPARγ and promotes ROS-VEGF/FGF2-mediated angiogenesis to accelerate tumor growth and metastasis (Fig. 7E). Therefore, a combination of PPARγ agonist and β-blocker may be used as a promising approach in clinical cancer therapy.
In this study, it was found that the tumorigenic effect of chronic stress is chiefly mediated by inhibition of PPARγ, leading to VEGF upregulation and resulting in neovascularization in vitro and in vivo. These findings correlate chronic stress and breast cancer with PPARγ, which classical role is maintaining lipid and glucose homeostasis. Our results demonstrated that PPARγ, which was implicated in the inhibition of carcinogenic processes, is suppressed after chronic stress stimulation. The critical anti-tumor effect of PPARγ was also confirmed using bioinformatics analysis. Taken together, these data indicate that PPARγ is a promising target for cancer therapy.
Catecholamines such as NE and epinephrine are released from the SNS and adrenal medulla by chronic stress conditions. Of note, adrenal medulla secrets NE as hormone that circulates systemically, while sympathetic nerve releases NE as neurotransmitter from nerve ending. In our previous study in Chinese, we found that with using surgical adrenalectomy, the tumor growth and metastasis was also inhibited [23]. In view of the nerve end innervation in the mammary tissue, chronic stress–induced NE release derived from both adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nerve system.
Previous studies on breast cancer have been focusing on genetic and environmental factors [24]. In recent years, more evidence has revealed that social-psychological factors play a critical role in carcinogenesis progression [25]. The relationship between social-psychological factors and breast cancer have attracted extensive attention and is regarded as a key factor in evaluating and formulating comprehensive therapy regimens for breast cancer patients. Our previous report [6] and this study consistently propose that chronic stress promotes breast cancer via stress-related hormone by activating adrenergic receptors. In non-small cell lung cancer tumor cells, stress hormones act on β2 receptors and promote epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor resistance [5]. In addition, β blockers drugs intake is associated with a significantly decreased risk of breast cancer recurrence and death in postmenopausal women [26]. These findings consistently suggest that adrenergic system plays a crucial role in tumor development and provide a wider therapeutic window for a social-psychological aspect in addition to conventional chemotherapy. It was also confirmed that the effect of chronic stress is mainly mediated by activating β2 receptor. However, a detailed mechanism between β2 receptor and PPARγ has not yet been fully investigated.
Adrenergic β receptors and G-protein coupled receptors activate the AC-cAMP–protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathway [27]. This study demonstrated that β2 receptors act after activation of the AC signaling pathway. In fatty metabolism, PKA induces the CREB phosphorylation, which then directly results in PPAR activation [28]. CREB is able to target PPARγ and is known to be its coactivator [29]. In our study, we found that after β2 receptor silenced, PPARγ expression was no longer suppressed by NE. Therefore, it is possible that the adrenergic system can inhibit PPARγ via the PKA/CREB pathway, although this needs to be confirmed by further study.
PPARγ triggers several types of biological effects, including regulation of fatty metabolism, enhanced sensitivity to insulin, and tumor inhibition. It has been reported that the level of PPARγ may be associated with tumor incidence [30]. This result was also validated by the current study analysis, where PPARγ expression is demonstrated to be obviously lower in breast cancer than in normal tissue. PPARγ agonist can suppress cell proliferation, enhance apoptosis [31], and inhibit cell migration by repressing angiogenesis and matrix metalloproteinase activity [32]. In this study, chronic stress was shown to inhibit the anti-tumor function of PPARγ and the resulting VEGF and FGF2 expression and neovascularization. This is consistent with previous research showing that PPARγ or PPARαaffect the expression of VEGF in colon tumors [33]. Aljada et al. [9] found that PPARγ ligands, rosiglitazone and pioglitazone, inhibit FGF2- and VEGF-mediated angiogenesis.
Some authors have reported that PPARγ agonist could enhance VEGF expression [34,35]. The reason for this kind of discrepancy in the literature on PPARγ agonists-induced expression of VEGF could be due to variation in the experimental design, cell line types and passage, tissue specificity, experimental conditions and reagent difference. In this study, after PPARγ was knock down by siPPARγ, forskolin did not activate VEGF production. We also found that ROS was involved in PPARγ-induced VEGF suppression. In our study, PPARγ inhibited ROS level and then VEGF expression. Even though this result is not accordance with another study [19] in which PPARγ increasing ROS, the inconsistency may be due to the different cancer and the double-edged role of ROS in cancer progression [36]. Hence, no matter what effect, our data and the previous research about PPARγ/VEGF axis [37] confirmed that PPARγ directly or indirectly influenced VEGF expression.
Another intriguing aspect of this work included the result showing that chronic stress suppresses the expression of PPARγ through activation of β2 receptor. β blocker is possible to be used as an ancillary drug in cancer therapy. PPARγ ligands thiazolidinediones, including pioglitazone as well as rosiglitazone, have been used clinically as anti-diabetic drugs. The current data indicates that usage of PPARγ in combination with βR inhibitors, such as PPL hydrochloride in triple-negative breast cancer therapy, may be more economic than a new drug that needs long-term research and development with numerous clinical trials.
In conclusion, β2 receptor activation induced by chronic stress potentiates breast cancer progression by suppressing PPARγ, VEGF/FGF2-mediated angiogenesis. β2 receptors and PPARγ may be new valuable targets for cancer treatment.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31800661), Nankai University National Students’ Innovation training program, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Nankai University (63191161).
References
1. Heidt T, Sager HB, Courties G, Dutta P, Iwamoto Y, Zaltsman A, et al. Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med. 2014; 20:754–8.

2. Cole SW. Nervous system regulation of the cancer genome. Brain Behav Immun. 2013; 30 Suppl:S10–8.

3. Thaker PH, Han LY, Kamat AA, Arevalo JM, Takahashi R, Lu C, et al. Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med. 2006; 12:939–44.

4. Watkins JL, Thaker PH, Nick AM, Ramondetta LM, Kumar S, Urbauer DL, et al. Clinical impact of selective and nonselective beta-blockers on survival in patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer. 2015; 121:3444–51.

5. Nilsson MB, Sun H, Diao L, Tong P, Liu D, Li L, et al. Stress hormones promote EGFR inhibitor resistance in NSCLC: Implications for combinations with beta-blockers. Sci Transl Med. 2017; 9:eaao4307.

6. Qin JF, Jin FJ, Li N, Guan HT, Lan L, Ni H, et al. Adrenergic receptor beta2 activation by stress promotes breast cancer progression through macrophages M2 polarization in tumor microenvironment. BMB Rep. 2015; 48:295–300.
7. Kim-Fuchs C, Le CP, Pimentel MA, Shackleford D, Ferrari D, Angst E, et al. Chronic stress accelerates pancreatic cancer growth and invasion: a critical role for beta-adrenergic signaling in the pancreatic microenvironment. Brain Behav Immun. 2014; 40:40–7.

8. Kwon KA, Yun J, Oh SY, Seo BG, Lee S, Lee JH, et al. Clinical significance of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and TRAP220 in patients with operable colorectal cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2016; 48:198–207.
9. Aljada A, O'Connor L, Fu YY, Mousa SA. PPAR gamma ligands, rosiglitazone and pioglitazone, inhibit bFGF- and VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2008; 11:361–7.
10. Shigeto T, Yokoyama Y, Xin B, Mizunuma H. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and gamma ligands inhibit the growth of human ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 2007; 18:833–40.
11. Messmer D, Lorrain K, Stebbins K, Bravo Y, Stock N, Cabrera G, et al. A selective novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-alpha antagonist induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of CLL cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med. 2015; 21:410–9.
12. Hong OY, Youn HJ, Jang HY, Jung SH, Noh EM, Chae HS, et al. Troglitazone inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and invasion of breast cancer cell through a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-dependent mechanism. J Breast Cancer. 2018; 21:28–36.
13. Lindgren EM, Nielsen R, Petrovic N, Jacobsson A, Mandrup S, Cannon B, et al. Noradrenaline represses PPAR (peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor) gamma2 gene expression in brown adipocytes: intracellular signalling and effects on PPARgamma2 and PPARgamma1 protein levels. Biochem J. 2004; 382:597–606.
14. Guo M, Li C, Lei Y, Xu S, Zhao D, Lu XY. Role of the adipose PPARgamma-adiponectin axis in susceptibility to stress and depression/anxiety-related behaviors. Mol Psychiatry. 2017; 22:1056–68.
15. Huber S, Valente S, Chaimbault P, Schohn H. Evaluation of ∆2-pioglitazone, an analogue of pioglitazone, on colon cancer cell survival: evidence of drug treatment association with autophagy and activation of the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. Int J Oncol. 2014; 45:426–38.

16. Hsiao PJ, Chiou HC, Jiang HJ, Lee MY, Hsieh TJ, Kuo KK. Pioglitazone enhances cytosolic lipolysis, beta-oxidation and autophagy to ameliorate hepatic steatosis. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:9030.

18. Lutgendorf SK, Cole S, Costanzo E, Bradley S, Coffin J, Jabbari S, et al. Stress-related mediators stimulate vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by two ovarian cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:4514–21.
19. Srivastava N, Kollipara RK, Singh DK, Sudderth J, Hu Z, Nguyen H, et al. Inhibition of cancer cell proliferation by PPARgamma is mediated by a metabolic switch that increases reactive oxygen species levels. Cell Metab. 2014; 20:650–61.
20. Ushio-Fukai M. Redox signaling in angiogenesis: role of NADPH oxidase. Cardiovasc Res. 2006; 71:226–35.
21. Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH. starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014; 42:D92–7.

22. Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45:W98–102.

23. Qin J, Liu H, Li Y, Liu B, Ni H. Effect of hormones from adrenal gland on breast cancer metastasis in mice. Cancer Res Prev Treat. 2016; 43:1013–7.
24. Nasir A, Bullo MM, Ahmed Z, Imtiaz A, Yaqoob E, Jadoon M, et al. Nutrigenomics: epigenetics and cancer prevention: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020; 60:1375–87.

25. Hill EM, Watkins K. Women with ovarian cancer: examining the role of social support and rumination in posttraumatic growth, psychological distress, and psychological well-being. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2017; 24:47–58.

26. Botteri E, Munzone E, Rotmensz N, Cipolla C, De Giorgi V, Santillo B, et al. Therapeutic effect of beta-blockers in triple-negative breast cancer postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 140:567–75.
27. Wallukat G. The beta-adrenergic receptors. Herz. 2002; 27:683–90.
28. Chen HY, Liu Q, Salter AM, Lomax MA. Synergism between cAMP and PPARgamma signalling in the initiation of UCP1 gene expression in HIB1B brown adipocytes. PPAR Res. 2013; 2013:476049.
29. Luz AL, Kassotis CD, Stapleton HM, Meyer JN. The high-production volume fungicide pyraclostrobin induces triglyceride accumulation associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, and promotes adipocyte differentiation independent of PPARgamma activation, in 3T3-L1 cells. Toxicology. 2018; 393:150–9.
30. Pineda-Belmontes CP, Hernandez-Ramirez RU, Hernandez-Alcaraz C, Cebrian ME, Lopez-Carrillo L. Genetic polymorphisms of PPAR gamma, arsenic methylation capacity and breast cancer risk in Mexican women. Salud Publica Mex. 2016; 58:220–7.

31. Giaginis C, Politi E, Alexandrou P, Sfiniadakis J, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S. Expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) in human non-small cell lung carcinoma: correlation with clinicopathological parameters, proliferation and apoptosis related molecules and patients' survival. Pathol Oncol Res. 2012; 18:875–83.
32. Lee EJ, Park JS, Lee YY, Kim DY, Kang JL, Kim HS. Antiinflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of an MMP-8 inhibitor in lipoteichoic acid-stimulated rat primary astrocytes: involvement of NF-kappaB, Nrf2, and PPAR-gamma signaling pathways. J Neuroinflammation. 2018; 15:326.

33. Amor S, Iglesias-de la Cruz MC, Ferrero E, Garcia-Villar O, Barrios V, Fernandez N, et al. Peritumoral adipose tissue as a source of inflammatory and angiogenic factors in colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2016; 31:365–75.

34. Yoshizaki T, Motomura W, Tanno S, Kumei S, Yoshizaki Y, Tanno S, et al. Thiazolidinediones enhance vascular endothelial growth factor expression and induce cell growth inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 29:22.

35. Chiu M, McBeth L, Sindhwani P, Hinds TD. Deciphering the roles of thiazolidinediones and PPARgamma in bladder cancer. PPAR Res. 2017; 2017:4810672.
36. Moloney JN, Cotter TG. ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018; 80:50–64.

37. Majumder A, Singh M, George AK, Behera J, Tyagi N, Tyagi SC. Hydrogen sulfide improves postischemic neoangiogenesis in the hind limb of cystathionine-beta-synthase mutant mice via PPAR-gamma/VEGF axis. Physiol Rep. 2018; 6:e13858.
Fig. 1.
Effect of chronic stress alone or in combination with pioglitazone (PioG) on tumor progression in a mouse model. (A) To establish the animal model, 4T1 cells were injected into the mice. On the same day, chronic stress was induced for 4 weeks. After 7 days, mice were treated with PioG for 3 weeks. (B) Tumor representative images from mice in control, chronic stress, PioG and chronic stress+PioG group (4-5 mice per group). Tumor growth curves (C) and average tumor weight (D) was measured on day 28 (4-5 tumors per group). (E) Representative images and calculated graph of lung nodules on day 28 (n=4 lungs per group). (F) H&E staining images of lung issues section from difference groups. Values are presented as mean±standard error of mean. #p < 0.05 vs. control group, *p < 0.05 vs. chronic stress+PioG group on day 28.
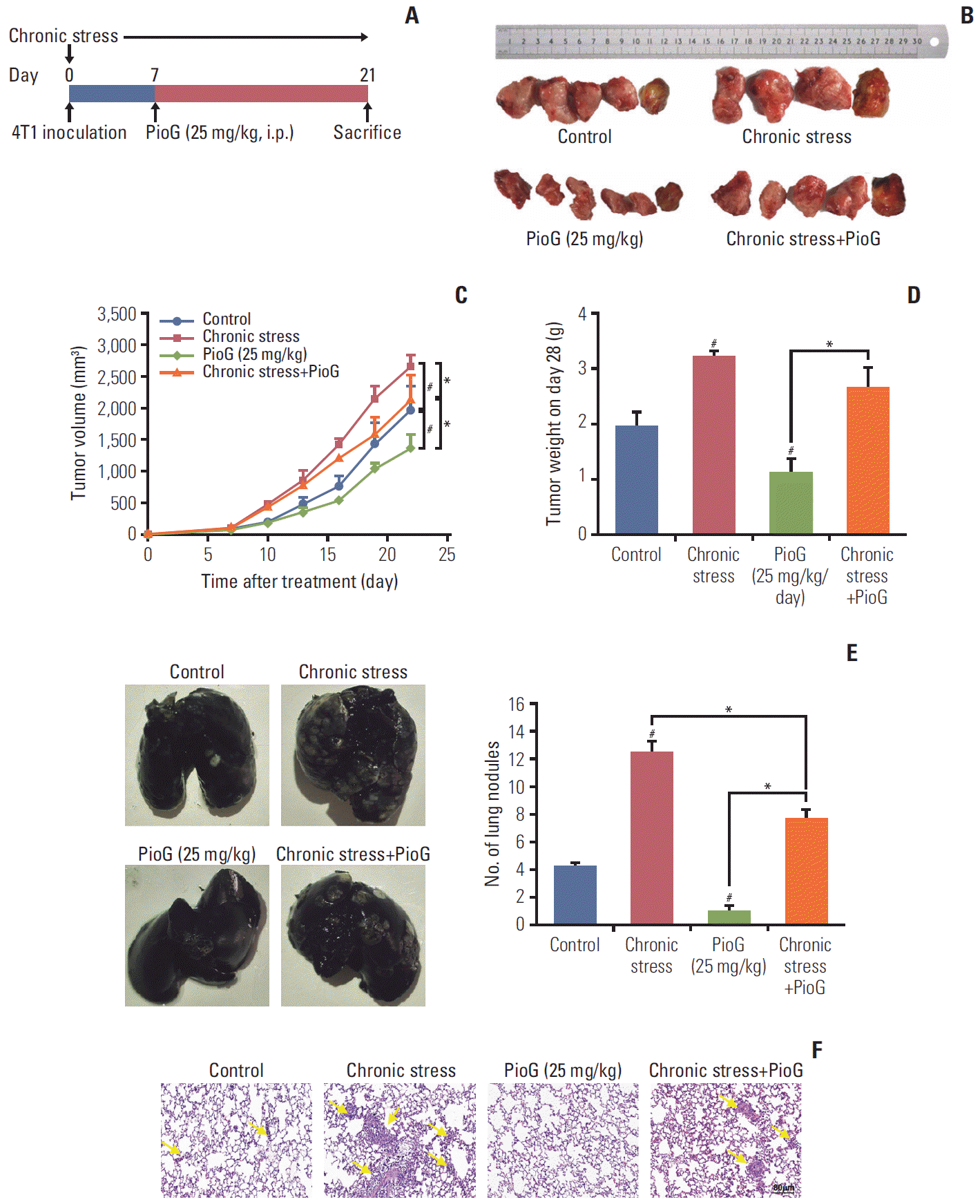
Fig. 2.
Effect of chronic stress alone or in combination with pioglitazone (PioG) on angiogenesis in vivo. (A, B) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) mRNA expression by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) in the tumor tissue from different groups. (C) PPARγ protein bands (left panel) and bar graph (right panel) in the tumor tissue from different groups. (D) Representative images of Matrigel plugs and newly formed blood vessels in the Matrigel (left panel) and hemoglobin (Hgb) content in the Matrigel matrix (right panel) in which we excised the Matrigel plugs and used them for quantification of angiogenesis. (E) Microvascular density was measured (left panel) and images of tumor section CD31 immunohistochemistry staining (right panel). (F) Quantitative vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) mRNA expression in tumor tissues detected by qPCR. (G) VEGF and FGF2 protein levels in tumor tissues were detected by western blot (WB). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Values are presented as mean±standard error of mean. *p < 0.05.
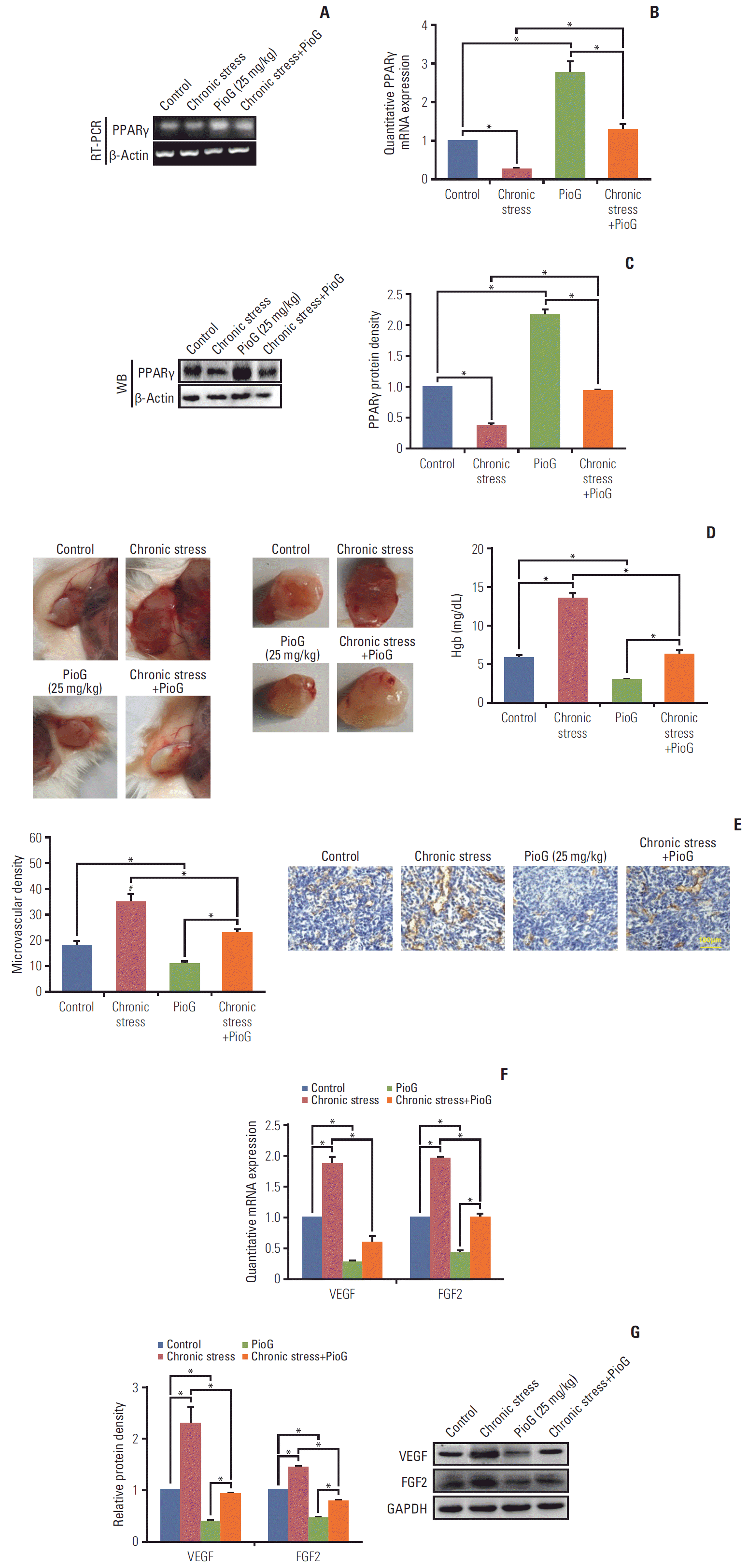
Fig. 3.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) inhibition induced by norepinephrine (NE) improves viability and proliferation of 4T1 cells. (A-C) PPARγ mRNA expression in 4T1 cells treated with different concentrations of NE (0, 1, 10, and 100 μM) for different times (0 minute, 10 minutes, 1 hour, 3 hours, and 12 hours) by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (A) and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. (B, C). *p < 0.05 vs. control group. (D) PPARγ expression in 4T1 cells detected by cell fluorescence staining. PE, phycoerythrin. (E) Cell viability measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay in 4T1 cells. PioG, pioglitazone. (F) Proliferation ability evaluated by soft agar colony formation assay in 4T1 cells. Values are presented as mean±standard error of mean. #p < 0.05 vs. control, *p < 0.05 vs. NE+PioG group.
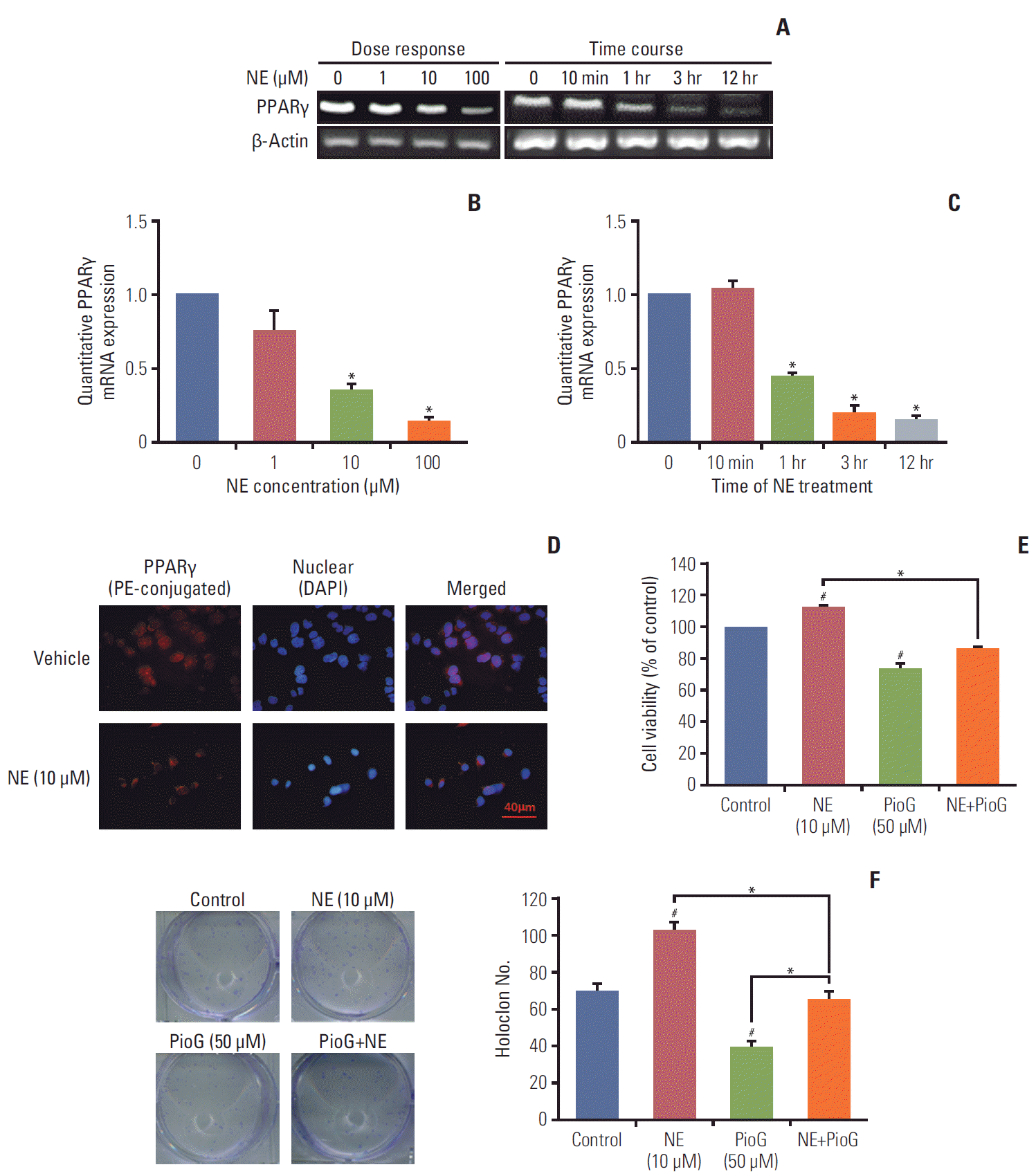
Fig. 4.
Effect of norepinephrine (NE) alone or in combination with pioglitazone (PioG) on proangiogenic factors expression in vitro. (A) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) mRNA expression in 4T1 cells treated with NE (10 μM) alone or in combination with PioG (50 μM) by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. #p < 0.05 vs. control, *p < 0.05 vs. NE+PioG group. (B) PPARγ, VEGF, and FGF2 protein expression by western blot in the same condition. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (C) PPARγ, VEGF, and FGF2 mRNA expression in 4T1 cells treated with NE (10 μM) alone or in combination with αR inhibitor phent (1 μM) or βR inhibitor propranolol (PPL, 1 μM). *p < 0.05. (D) PPARγ, VEGF, and FGF2 mRNA expression in 4T1 cells treated with NE (10 μM) alone or in combination with β1R inhibitor metoprolol (1 μM) or β2R inhibitor ICI118551 (1 μM). *p < 0.05.
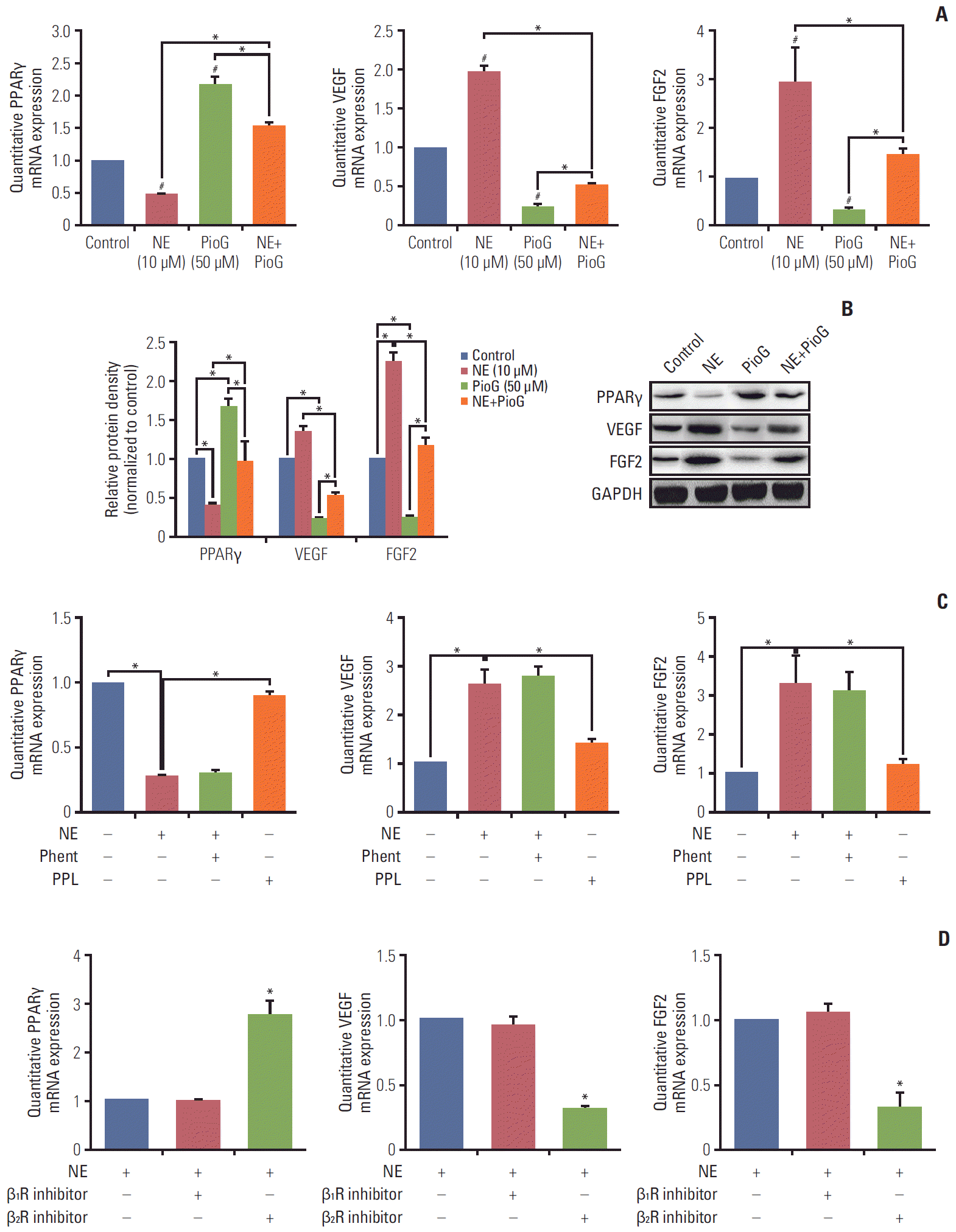
Fig. 5.
β2-adrenergic receptor (β2R) is involved in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) inhibition and angiogenesis induced by norepinephrine (NE) in vitro. (A) PPARγ expression in 4T1 cells after β2R inhibitor treatment by flow cytometry analysis. (B) PPARγ expression detected by western blot in 4T1 cells transfected with siCtrl or siβ2R(1). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (C) PPARγ expression detected by cell fluorescence staining in 4T1 cells transfected with siCtrl or siβ2R(1). (D) PPARγ, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), or fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) mRNA expression analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in 4T1 cells treated by adenylyl cyclase activator forskolin (10 μM). *p < 0.05; NS, no significance. (E) VEGF expression detected by western blot in 4T1 cells transfected with siPPARγ. (F) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels determined by flow cytometry in 4T1 cells with different treatment. (G, H) VEGF expression detected by western blot in 4T1 cells with different treatments, H2O2 (250 μmol/L) used to induce ROS (G), N-acetylcysteine (NAC, 5 mmol/L) used to eliminate ROS (H). *p < 0.05; NS, no significance.
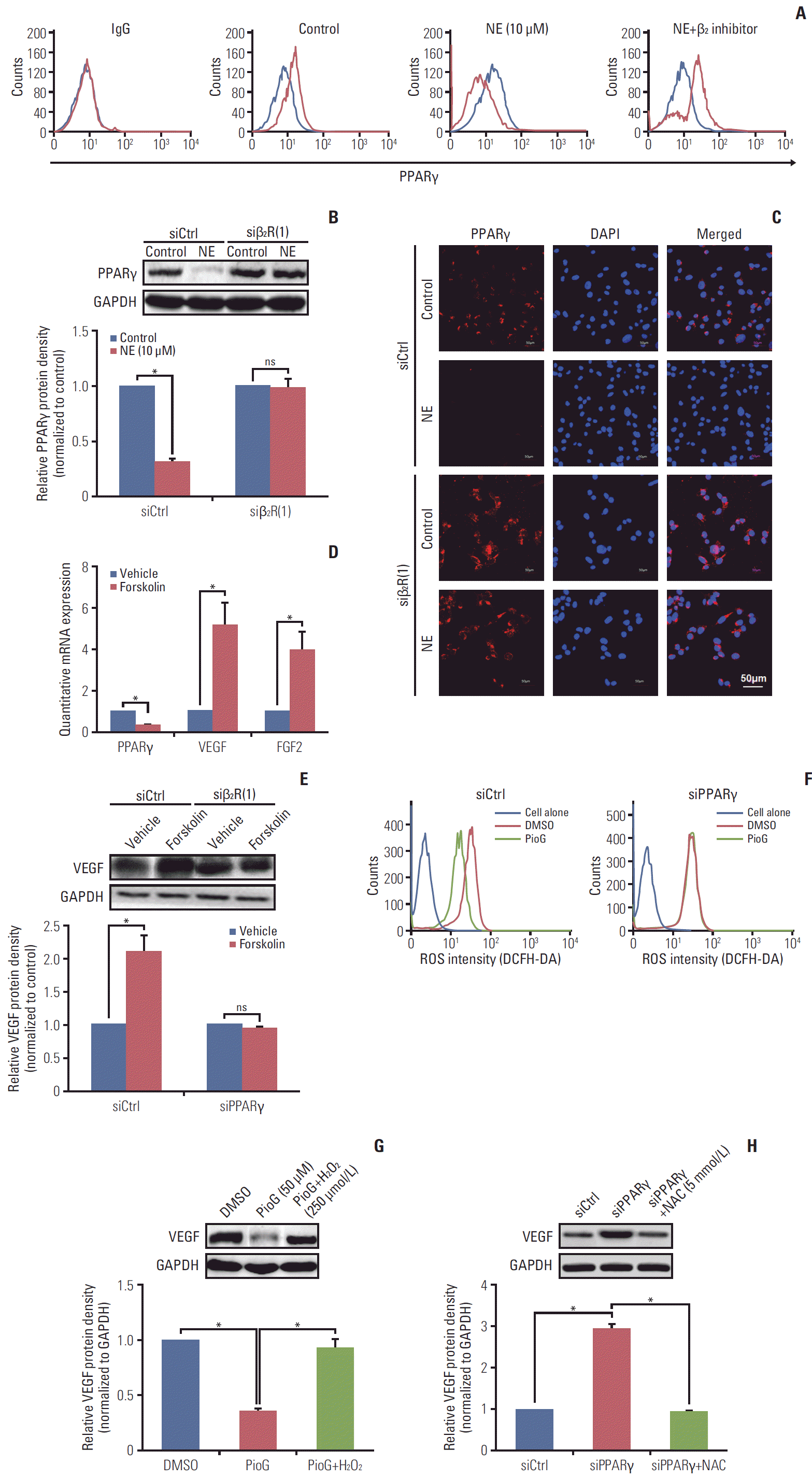
Fig. 6.
β2 receptor activation and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) inhibition is involved in chronic stress-induced tumor angiogenesis in vivo. (A) Representative tumor images from mice in control (n=4), ICI118551 (n=4) and GW9662 group (n=5). (B) Tumor growth curves. (C) Average tumor weight was measured on day 28. *p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. chronic stress. (D, E) PPARγ, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) mRNA expression in tumor tissues by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (D) and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (E). *p < 0.05. (F) PPARγ, VEGF, and FGF2 protein expression in tumor tissues by western blot. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (G) Representative images (left panel) and bar graph (right panel) of PPARγ expression detected in tumor tissue paraffin sections by immunohistochemistry staining. *p < 0.05. (H) Images of tumor section CD31 immunohistochemistry staining (left panel) and microvascular density was measured (right panel). *p < 0.05 vs. control, #p < 0.05 vs. chronic stress.
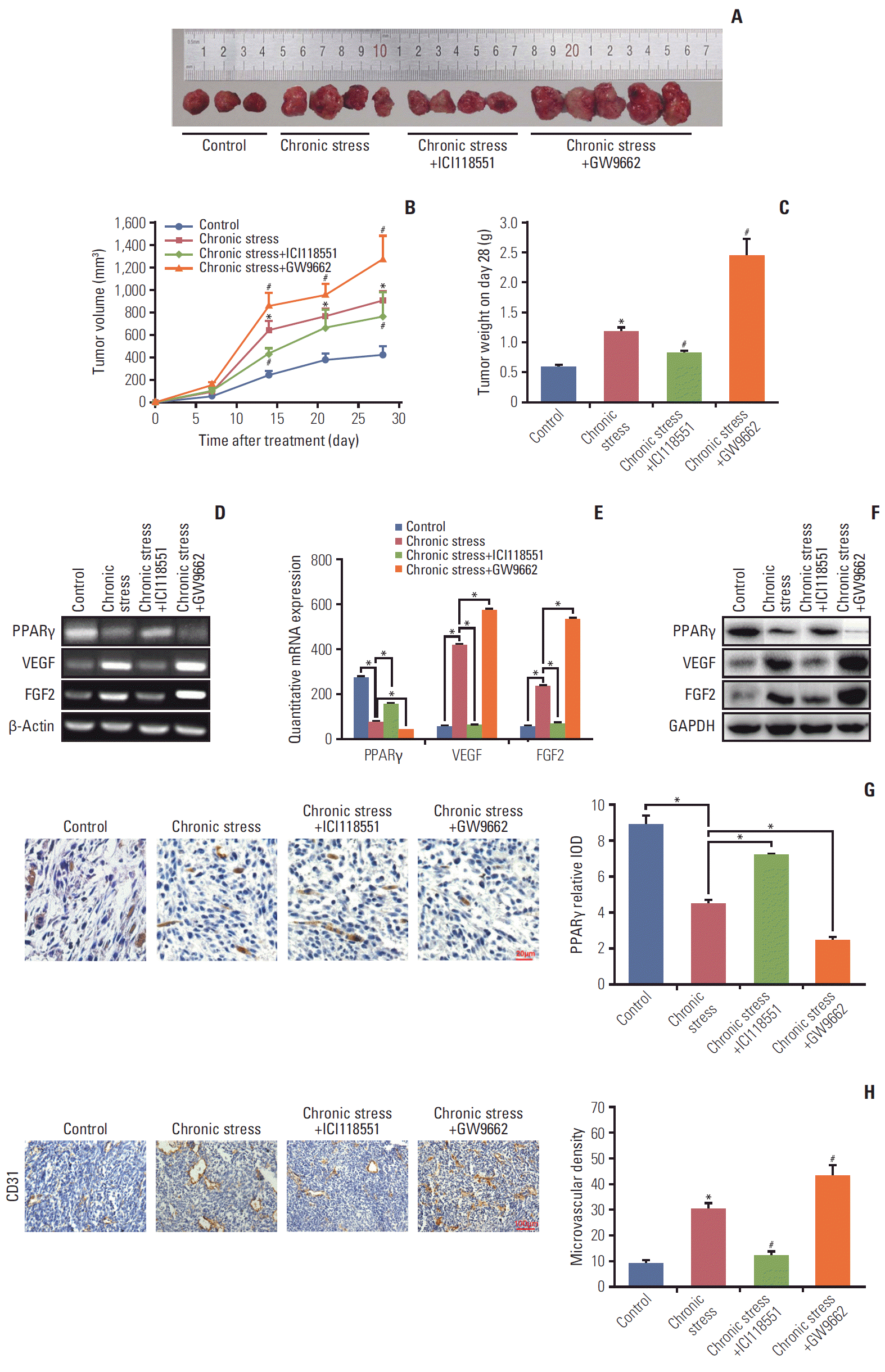
Fig. 7.
Bioinformatics analysis of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in breast invasive carcinoma (BRCA). (A, B) Higher PPARγ expression in normal tissue and lower PPARγ expression in BRCA tissue. Data from StarBase database (A) and data from GEPIA database (B). *p < 0.05. (C) High PPARγ expression is associated with longer overall survival (OS) compared to low PPARγ expression, according to StarBase v3.0 data (p=0.039). (D) High PPARγ expression is associated with longer relapse-free survival compared to low PPARγ expression, according to online database data (http://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=breast) (p < 0.001). HR, hazard ratio. (E) Study model schematic. β2 receptor activation induced by chronic stress enables breast cancer progression by inactivating PPARγ and enhancing reactive oxygen species (ROS)–VEGF/fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2)–mediated angiogenesis.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download