1. Jaffray DA. Image-guided radiotherapy: from current concept to future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012; 9:688–99.

2. Herrera FG, Bourhis J, Coukos G. Radiotherapy combination opportunities leveraging immunity for the next oncology practice. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017; 67:65–85.

3. Postow MA, Callahan MK, Barker CA, Yamada Y, Yuan J, Kitano S, et al. Immunologic correlates of the abscopal effect in a patient with melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:925–31.

4. Siva S, Callahan J, MacManus MP, Martin O, Hicks RJ, Ball DL. Abscopal [corrected] effects after conventional and stereotactic lung irradiation of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013; 8:e71.
5. Stamell EF, Wolchok JD, Gnjatic S, Lee NY, Brownell I. The abscopal effect associated with a systemic anti-melanoma immune response. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013; 85:293–5.

6. Wersäll PJ, Blomgren H, Pisa P, Lax I, Kalkner KM, Svedman C. Regression of non-irradiated metastases after extracranial stereotactic radiotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2006; 45:493–7.

7. Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J. The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012; 12:298–306.

8. Son CH, Bae JH, Shin DY, Lee HR, Jo WS, Yang K, et al. Combination effect of regulatory T-cell depletion and ionizing radiation in mouse models of lung and colon cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015; 92:390–8.

9. Golden EB, Chhabra A, Chachoua A, Adams S, Donach M, Fenton-Kerimian M, et al. Local radiotherapy and granulocyte- macrophage colony-stimulating factor to generate abscopal responses in patients with metastatic solid tumours: a proof-of-principle trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:795–803.
10. Deng L, Liang H, Burnette B, Beckett M, Darga T, Weichselbaum RR, et al. Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J Clin Invest. 2014; 124:687–95.

11. Park SS, Dong H, Liu X, Harrington SM, Krco CJ, Grams MP, et al. PD-1 restrains radiotherapy-induced abscopal effect. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015; 3:610–9.

12. Tian S, Quan H, Xie C, Guo H, Lu F, Xu Y, et al. YN968D1 is a novel and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase with potent activity in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2011; 102:1374–80.

13. Li J, Zhao X, Chen L, Guo H, Lv F, Jia K, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of novel selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor YN968D1 in patients with advanced malignancies. BMC Cancer. 2010; 10:529.

14. Li J, Qin S, Xu J, Xiong J, Wu C, Bai Y, et al. Randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled phase iii trial of apatinib in patients with chemotherapy-refractory advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:1448–54.
15. Zhang L, Shi M, Huang C, Liu X, Xiong JP, Chen G, et al. A phase II, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial of apatinib in patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after two previous treatment regimens. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30(15 Suppl):7548.

16. Voron T, Marcheteau E, Pernot S, Colussi O, Tartour E, Taieb J, et al. Control of the immune response by pro-angiogenic factors. Front Oncol. 2014; 4:70.

17. Jiang XD, Dai P, Wu J, Song DA, Yu JM. Inhibitory effect of radiotherapy combined with weekly recombinant human endostatin on the human pulmonary adenocarcinoma A549 xenografts in nude mice. Lung Cancer. 2011; 72:165–71.

18. Zheng B, Ren T, Huang Y, Guo W. Apatinib inhibits migration and invasion as well as PD-L1 expression in osteosarcoma by targeting STAT3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 495:1695–701.

19. Qiu MJ, He XX, Bi NR, Wang MM, Xiong ZF, Yang SL. Effects of liver-targeted drugs on expression of immune-related proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Clin Chim Acta. 2018; 485:103–5.

20. Liu Y, Dong Y, Kong L, Shi F, Zhu H, Yu J. Abscopal effect of radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J Hematol Oncol. 2018; 11:104.

21. Peng S, Zhang Y, Peng H, Ke Z, Xu L, Su T, et al. Intracellular autocrine VEGF signaling promotes EBDC cell proliferation, which can be inhibited by Apatinib. Cancer Lett. 2016; 373:193–202.

22. Liu K, Ren T, Huang Y, Sun K, Bao X, Wang S, et al. Apatinib promotes autophagy and apoptosis through VEGFR2/STAT3/ BCL-2 signaling in osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017; 8:e3015.
23. Sun C, Mezzadra R, Schumacher TN. Regulation and function of the PD-L1 checkpoint. Immunity. 2018; 48:434–52.

24. Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer: new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 4:97–105.
25. Chen J, Jiang CC, Jin L, Zhang XD. Regulation of PD-L1: a novel role of pro-survival signalling in cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016; 27:409–16.

26. Terme M, Pernot S, Marcheteau E, Sandoval F, Benhamouda N, Colussi O, et al. VEGFA-VEGFR pathway blockade inhibits tumor-induced regulatory T-cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2013; 73:539–49.

27. Ozao-Choy J, Ma G, Kao J, Wang GX, Meseck M, Sung M, et al. The novel role of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the reversal of immune suppression and modulation of tumor microenvironment for immune-based cancer therapies. Cancer Res. 2009; 69:2514–22.

28. Ziogas AC, Gavalas NG, Tsiatas M, Tsitsilonis O, Politi E, Terpos E, et al. VEGF directly suppresses activation of T cells from ovarian cancer patients and healthy individuals via VEGF receptor Type 2. Int J Cancer. 2012; 130:857–64.

29. Tian L, Goldstein A, Wang H, Ching Lo H, Sun Kim I, Welte T, et al. Mutual regulation of tumour vessel normalization and immunostimulatory reprogramming. Nature. 2017; 544:250–4.

30. Dewan MZ, Galloway AE, Kawashima N, Dewyngaert JK, Babb JS, Formenti SC, et al. Fractionated but not single-dose radiotherapy induces an immune-mediated abscopal effect when combined with anti-CTLA-4 antibody. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:5379–88.

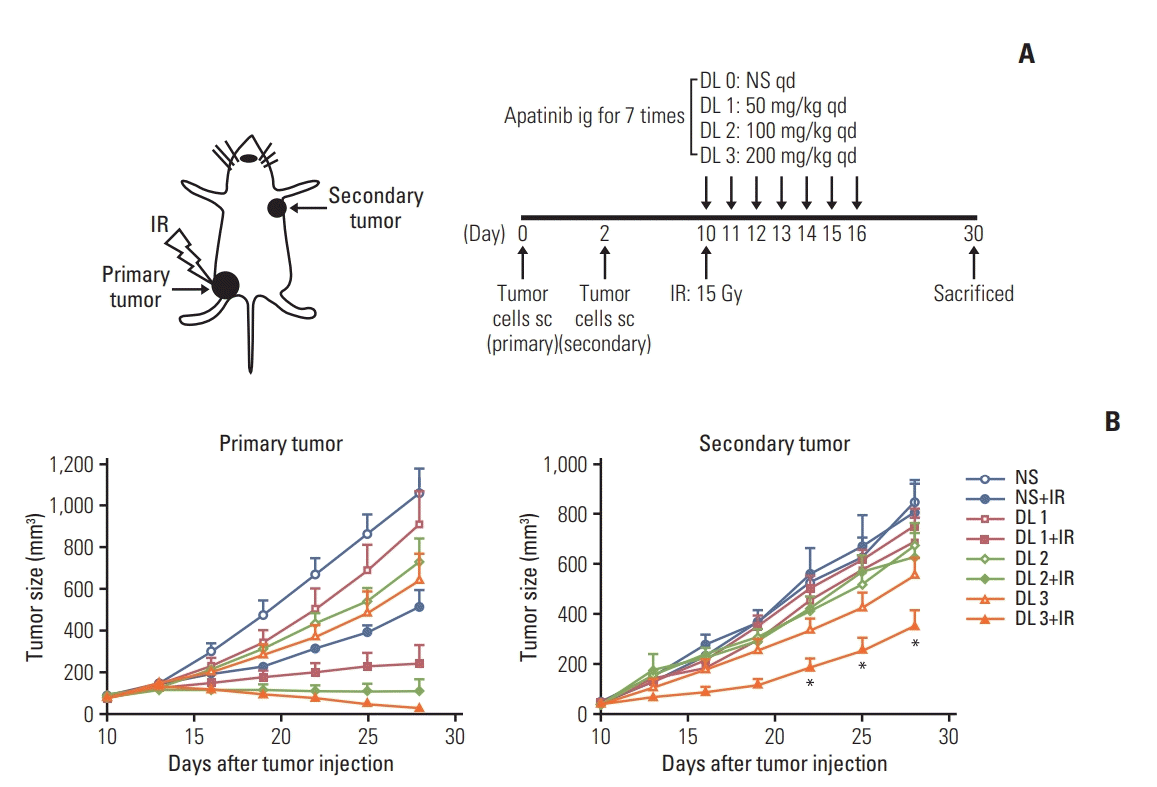
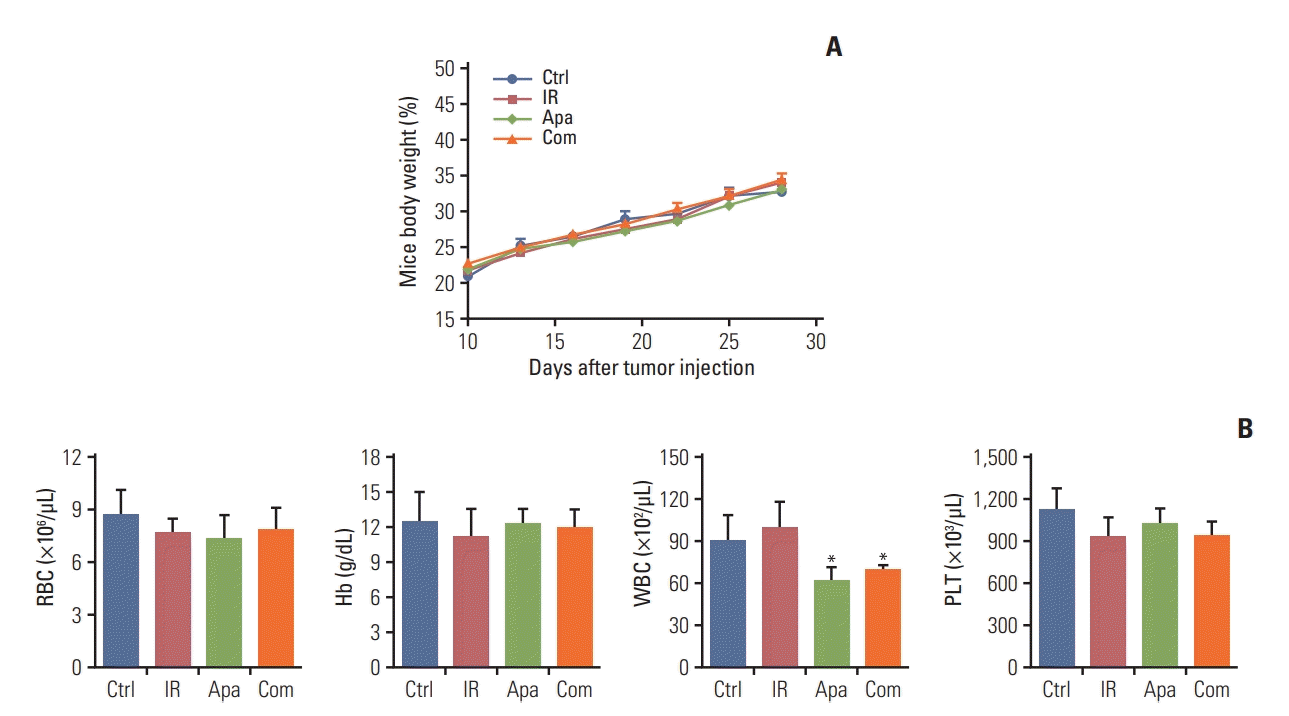
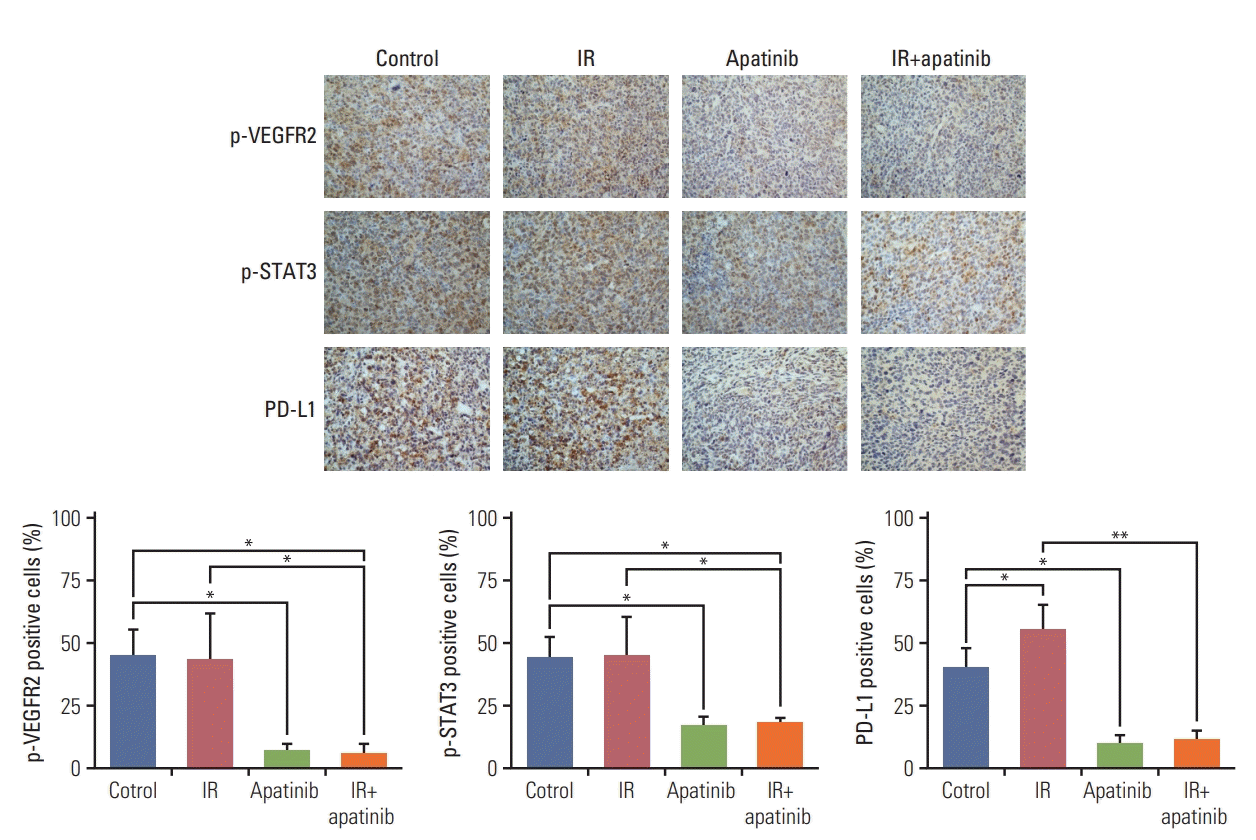
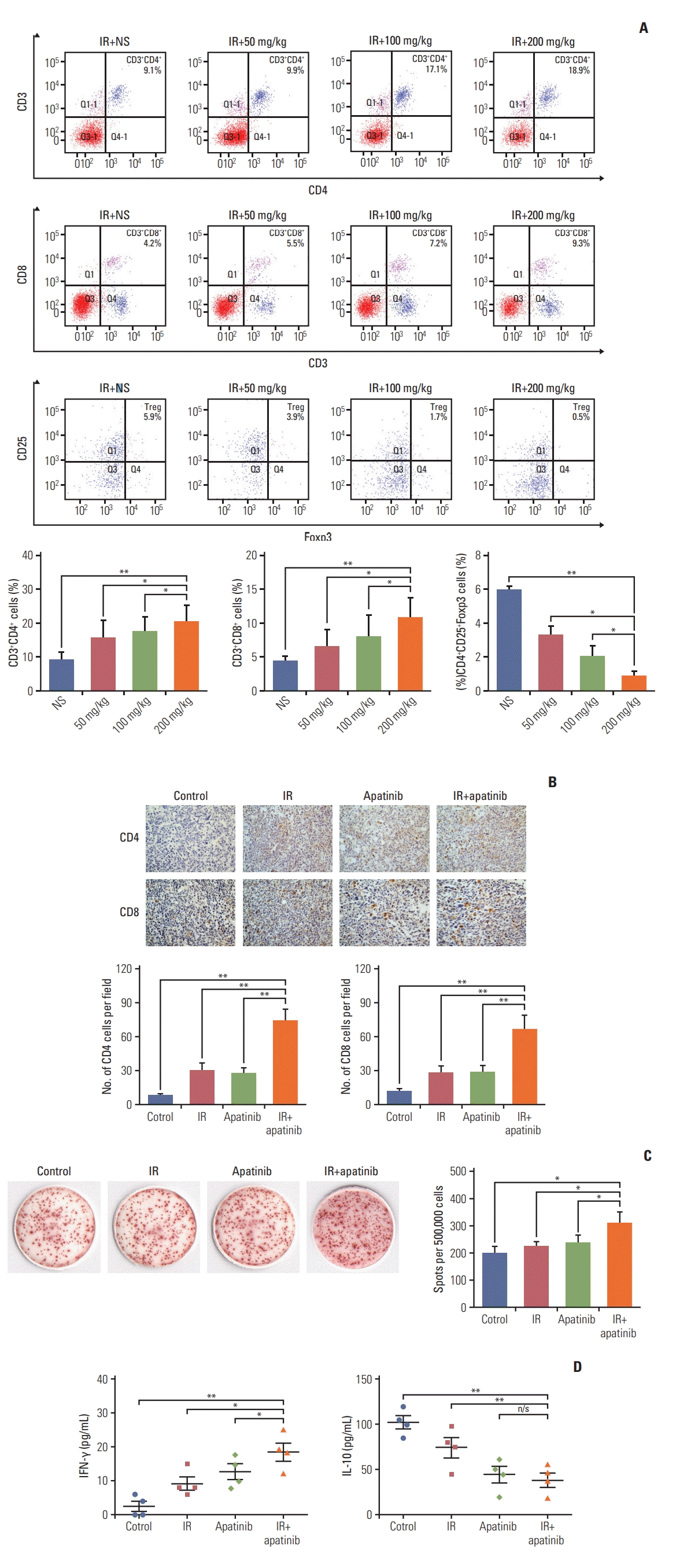
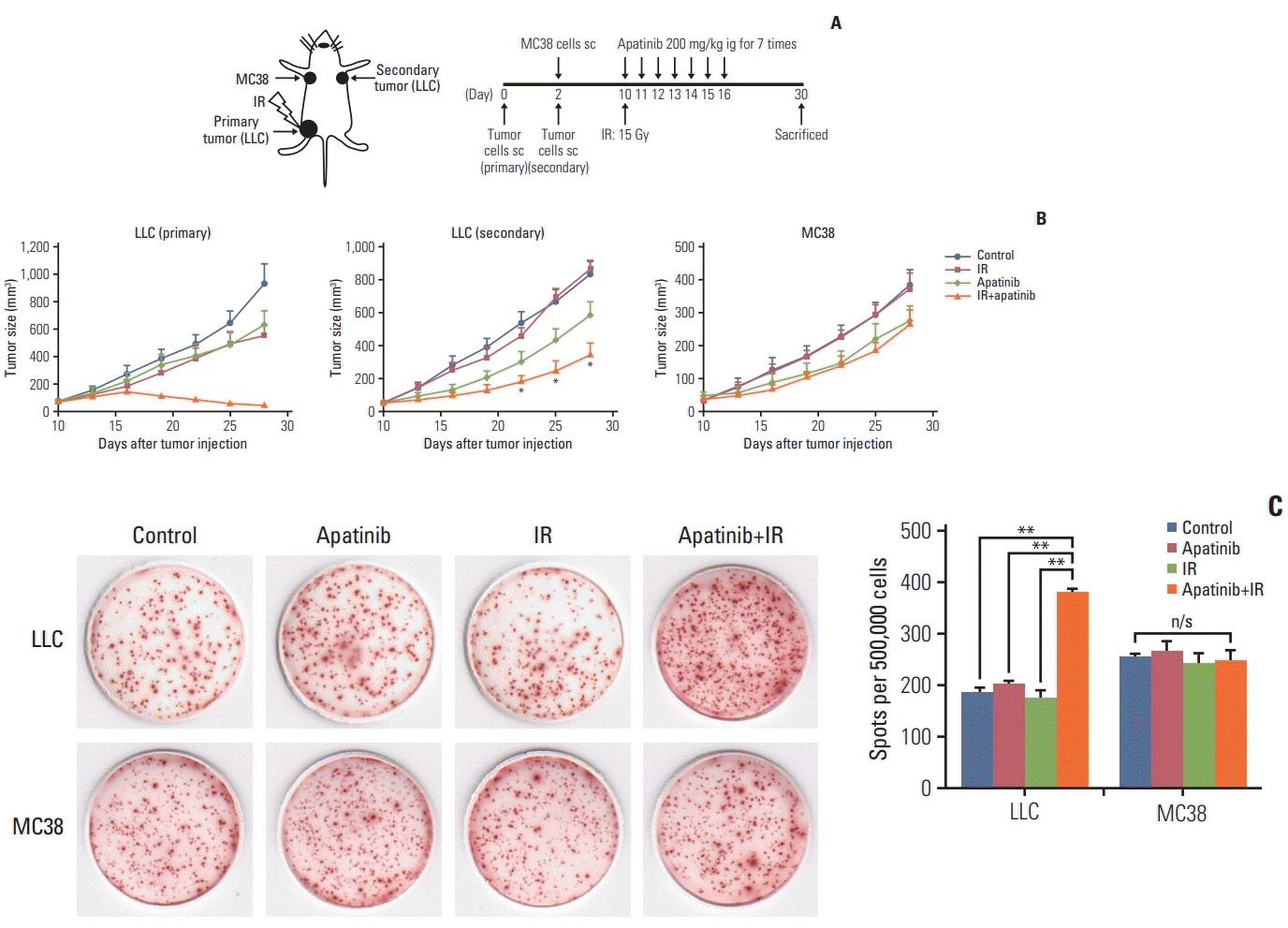
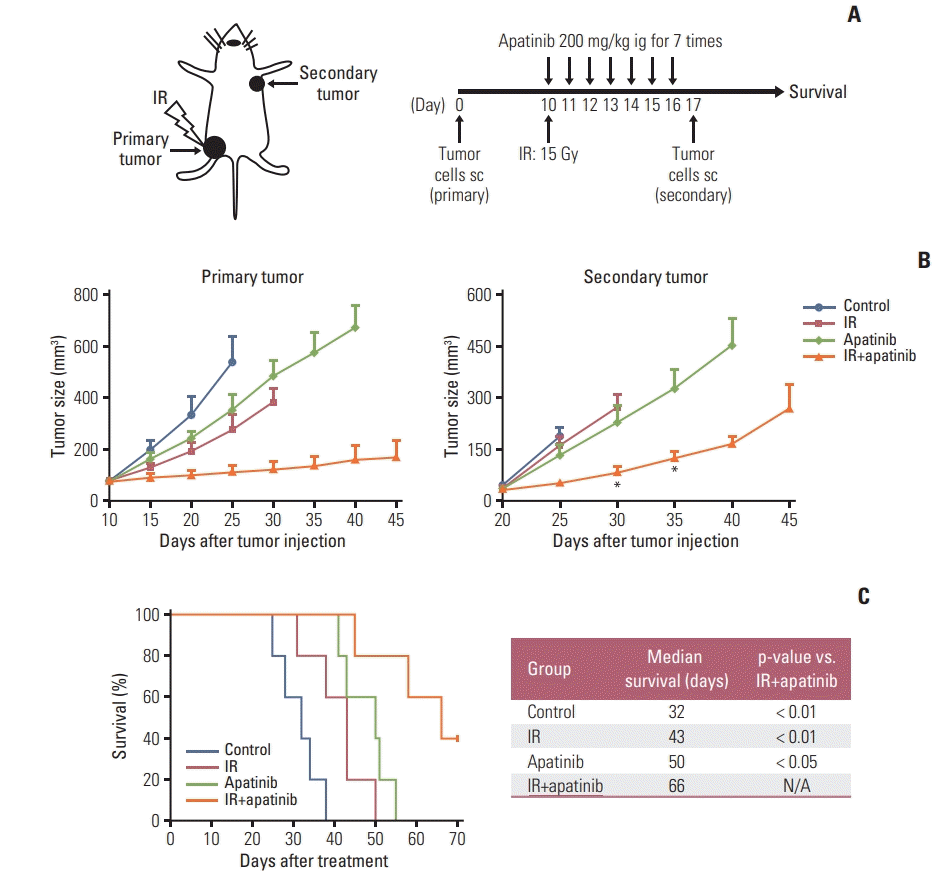




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download