INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Participants and Design
Measurements
RESULTS
Table 1.
| Patient no. | Age (yr) | Sex | BMI (kg/m2) |
Symptom |
Neck circumference (cm) | STOP-Bang score | Comorbidity | APACHE II score | Duration of mechanical ventilation (day) | Reason for mechanical ventilation | In-hospital outcome | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDS | Nonrestorative sleep | Fatigue | Insomnia | Snoring | Witnessed apnea | |||||||||||
| 1a | 77 | M | 21.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | HTN, DM, multiple myeloma | 35 | 7 | Sepsis | Died 14 days after ICU discharge |
| 2 | 56 | F | 21.7 | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | 37.0 | 2 | DM, post-lung TPL | 21 | 2 | Pneumonia | Survived |
| 3 | 58 | M | 26.2 | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | 39.0 | 3 | Sarcoma | 22 | 8 | Pneumonia | Survived |
| 4 | 80 | M | 27.4 | No | No | No | No | No | No | 42.0 | 3 | DM, CHF, CVD, AF, lung cancer | 13 | 6 | Pneumonia | Survived |
| 5 | 67 | M | 20.8 | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | 38.5 | 3 | CHF, AF, COPD, LC | 25 | 6 | CHF | Survived |
| 6 | 83 | M | 14.3 | No | No | No | No | No | No | 38.0 | 2 | NTM-PD | 18 | 4 | Pneumonia | Died 237 days after ICU discharge |
| 7 | 70 | M | 28.7 | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 43.0 | 6 | Post-lung TPL | 15 | 3 | Post-lung TPL | Survived |
| 8 | 75 | M | 25.5 | No | No | No | No | No | No | 45.0 | 3 | IPF, vasculitis | 35 | 8 | Pneumonia | Died 13 days after ICU discharge |
| 9 | 69 | F | 24.9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 40.0 | 5 | OSA, asthma | 20 | 5 | Acute exacerbation of asthma | Survived |
| 10 | 74 | M | 22.5 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | 38.0 | 3 | Asthma, COPD, CKD, leiomyosarcoma | 30 | 3 | Pneumonia | Died 19 days after ICU discharge |
BMI: body mass index; EDS: excessive daytime sleepiness; STOP-Bang: snoring, tiredness, observed apnea, high blood pressure, body mass index, age, neck circumference, and gender; APACHE: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; HTN: hypertension; DM: diabetes mellitus; ICU: intensive care unit; TPL: transplantation; CHF: congestive heart failure; CVD: cardiovascular disease; AF: atrial fibrillation; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; LC: liver cirrhosis; NTM-PD: nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease; IPF: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; OSA: obstructive sleep apnea; CKD: chronic kidney disease.
Table 2.
| Variable | All patients (n=10) | Patient with an REI <5/hr (n=7) | Patient with an REI ≥5/hr (n=3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 72 (67–77) | 74 (67–77) | 69 (56–83) |
| Male sex | 8 (80) | 7 (100) | 1 (33) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.7 (21.7–26.2) | 25.5 (21.7–27.4) | 21.7 (14.3–24.9) |
| Neck circumference (cm)a | 39 (38–42) | 41 (39–43) | 38 (37–40) |
| STOP-Bang score ≥3a | 7 (70) | 6 (86) | 1 (33) |
| Charlson comorbidity index | 5 (3–8) | 6 (5–8) | 2 (0–3) |
| Hypertension | 1 (10) | 1 (14) | 0 |
| Diabetes | 3 (30) | 2 (29) | 1 (33) |
| Congestive heart failure | 2 (20) | 2 (29) | 0 |
| COPD | 2 (20) | 2 (29) | 0 |
| APACHE II score | 22 (18–30) | 25 (15–35) | 20 (18–21) |
| SOFA score | 6 (5–10) | 9 (4–10) | 5 (5–7) |
| SAPS II | 48 (32–66) | 54 (32–68) | 46 (30–50) |
| Failure during the first intubation attempt | 4 (40) | 3 (43) | 1 (33) |
| Internal diameter of the endotracheal tubes (mm) | 7.5 (7.5–7.5) | 7.5 (7.5–7.5) | 7.5 (7.0–7.5) |
| Duration of mechanical ventilation (day) | 6 (3–7) | 6 (3–8) | 4 (2–5) |
| Reason for mechanical ventilation | |||
| Pneumonia | 6 (60) | 4 (57) | 2 (67) |
| Acute exacerbation of asthma | 1 (10) | 0 | 1 (33) |
| Heart failure | 1 (10) | 1 (14) | 0 |
| Sepsis | 1 (10) | 1 (14) | 0 |
| Post-lung transplantation | 1 (10) | 1 (14) | 0 |
| Total drug equivalent dose administered 48 hours prior to extubation | |||
| Remifentanyl (mg) | 7.4 (4.2–10.6) | 9.6 (4.2–22.1) | 4.8 (1.8–9.6) |
| Propofol (mg) | 0 (0–1,344) | 0 (0–1,728) | 0 (0–1,344) |
| Dexmedetomidine (mg) | 1.1 (0.04–3.0) | 0.8 (0.04–3.6) | 1.5 (0–3.0) |
| Methylprednisolone (mg) | 78 (0–120) | 60 (0–160) | 100 (0–120) |
| Method of oxygen delivery during the night of respiratory polygraphy | |||
| Low-flow oxygen therapy via nasal prong | 5 (50) | 2 (29) | 3 (100) |
| High-flow nasal cannula | 5 (50) | 5 (71) | 0 |
| FiO2 | 0.4 (0.3–0.5) | 0.4 (0.4–0.6) | 0.3 (0.3–0.4) |
| Flow (L/min) | 23 (2–60) | 40 (4–60) | 2 (2–6) |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%).
REI: respiratory event index; BMI: body mass index; STOP-Bang: snoring, tiredness, observed apnea, high blood pressure, body mass index, age, neck circumference, and gender; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; APACHE: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; SAPS: Simplified Acute Physiology Score; FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen.
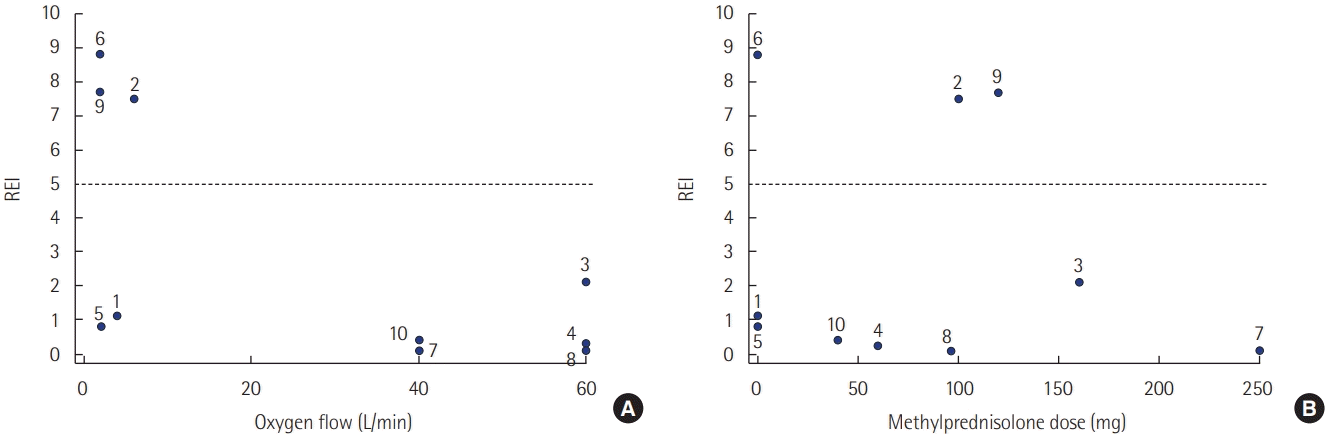
Table 3.
| Patient no. |
Total drug equivalent dose administered 48 hours prior to extubation |
Method of oxygen delivery during the night of respiratory polygraphy |
REI (/hr) | Mean SpO2 (%) | Lowest SpO2 (%) | Time spent (%) with SpO2 <90% | ODI (/hr) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Remifentanyl (mg) | Propofol (mg) | Dexmedetomidine (mg) | Methylprednisolone (mg)a | Device | Flow rate (L/min) | FiO2 of HFNC | ||||||
| 1 | 5.3 | 0 | 2.9 | 0 | Low-flow via nasal prong | 4 | – | 1.1 | 92 | 83 | 5.9 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 1.8 | 0 | 3.0 | 100 | Low-flow via nasal prong | 6 | – | 7.5 | 97 | 74 | 1.0 | 8.1 |
| 3 | 10.6 | 0 | 0.7 | 160 | HFNC | 60 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 93 | 85 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| 4 | 9.6 | 0 | 2.0 | 60 | HFNC | 60 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 93 | 86 | 4.4 | 0.3 |
| 5 | 2.0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0 | Low-flow via nasal prong | 2 | – | 0.8 | 98 | 86 | 0.2 | 1.8 |
| 6 | 4.8 | 0 | 1.5 | 0 | Low-flow via nasal prong | 2 | – | 8.8 | 97 | 87 | 0.3 | 5.0 |
| 7 | 22.1 | 4,722 | 0.8 | 250 | HFNC | 40 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 93 | 87 | 1.8 | 0.1 |
| 8 | 26.4 | 0 | 3.6 | 96 | HFNC | 60 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 94 | 88 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| 9 | 9.6 | 1,344 | 0 | 120 | Low-flow via nasal prong | 2 | – | 7.7 | 92 | 75 | 13.3 | 14.7 |
| 10 | 4.2 | 1,728 | 0 | 40 | HFNC | 40 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 90.8 | 82 | 19.4 | 1.5 |
FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen; HFNC: high-flow nasal cannula; REI: respiratory event index; SpO2: oxygen saturation; ODI: oxygen desaturation index.
a Six of the seven patients who were treated with corticosteroids received methylprednisolone intravenously. Patient 10 received 50 mg hydrocortisone intravenously four times for 48 hours prior to extubation. Five of the seven patients who received corticosteroids were treated with long-term corticosteroid therapy. The remaining two patients, patients 4 and 10, were treated with corticosteroids for 15 days and 2 days, respectively.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download