Introduction
Materials and Methods
1) Study design and subjects
2) Data collection
3) Statistical analysis
Results
1) Baseline characteristics
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Total (n = 236) | Survivor (n = 139) | Non-survivor (n = 97) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 69 (57–76) | 70 (58–77) | 67 (55–75) | 0.192 |
| Male sex | 144 (61.0) | 82 (59.0) | 62 (63.9) | 0.498 |
| ICU type | ||||
| Medical ICU | 86 (36.4) | 46 (33.1) | 40 (41.2) | 0.218 |
| Surgical ICU | 31 (31.1) | 14 (10.1) | 17 (17.5) | 0.117 |
| Cardio-stroke ICU | 32 (13.6) | 18 (12.9) | 14 (14.4) | 0.847 |
| Emergency ICU | 57 (24.2) | 13 (28.1) | 18 (18.6) | 0.122 |
| Neurosurgical ICU | 27 (11.4) | 19 (13.7) | 8 (8.2) | 0.219 |
| Trauma ICU | 3 (1.3) | 3 (1.3) | 0 | 0.271 |
| APACHE II score on ICU admission day | 23 (17–29) | 20 (15–26) | 26 (22–32) | <0.001 |
| SOFA score on ICU admission day | 7 (4–9) | 5 (3–8) | 9 (6–11) | <0.001 |
| qSOFA score at ICU admission time | 2 (0–3) | 1 (0–3) | 2 (0–3) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities, overlapped | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 69 (29.2) | 46 (33.1) | 23 (23.7) | 0.146 |
| Hemato-oncological disease | 55 (23.3) | 21 (15.1) | 34 (35.1) | 0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 34 (14.4) | 20 (14.4) | 14 (14.4) | >0.999 |
| Heart failure | 34 (14.4) | 21 (15.1) | 13 (13.4) | 0.851 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 25 (10.6) | 14 (10.1) | 11 (11.3) | 0.831 |
| Biliary disease | 21 (8.9) | 16 (11.5) | 5 (5.2) | 0.107 |
| Chronic liver disease | 19 (8.1) | 9 (6.5) | 10 (10.3) | 0.335 |
| Neuromuscular disease | 13 (5.5) | 11 (7.9) | 2 (2.1) | 0.079 |
| Chronic lung diseasea | 12 (8.9) | 12 (8.6) | 9 (9.3) | >0.999 |
| Source of infection | ||||
| Pneumonia | 91 (38.6) | 49 (35.3) | 42 (43.3) | 0.224 |
| Intra-abdominal | 61 (25.8) | 37 (26.6) | 24 (24.7) | 0.765 |
| Urinary tract | 25 (10.6) | 19 (13.7) | 6 (6.2) | 0.085 |
| Musculoskeletal | 41 (17.4) | 28 (20.1) | 13 (13.4) | 0.222 |
| Catheter-related | 22 (9.3) | 14 (10.1) | 8 (8.2) | 0.821 |
| Neutropenia | 13 (5.5) | 2 (1.4) | 11 (11.3) | 0.002 |
| Infectious endocarditis | 11 (4.7) | 5 (3.6) | 6 (6.2) | 0.366 |
| Organism | ||||
| Gram-positive bacteremia | 138 (58.5) | 92 (66.2) | 46 (47.4) | 0.005 |
| Gram-negative bacteremia | 84 (35.6) | 42 (30.2) | 42 (43.3) | 0.053 |
| Multidrug-resistant bacteremiab | 60 (25.4) | 33 (23.7) | 27 (27.8) | 0.544 |
| Fungemia | 24 (10.2) | 10 (7.2) | 14 (14.4) | 0.082 |
| Polymicrobialc | 27 (11.4) | 14 (10.1) | 13 (13.4) | 0.534 |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%).
ICU: intensive care unit; APACHE: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; qSOFA: quick Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment.
b Including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, extended-spectrum ß-lactamase-producing Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae), carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative rods (Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa), and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium;
2) qSOFA score and patient outcomes
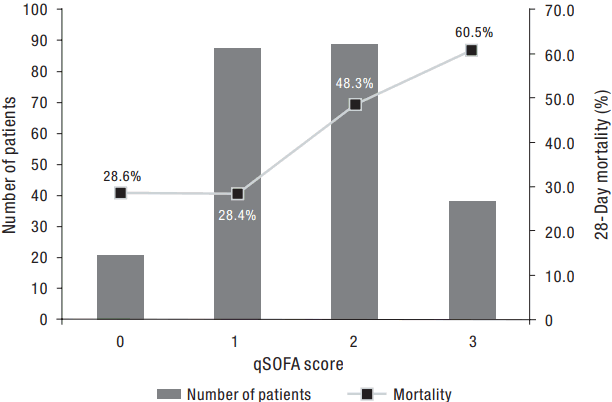 | Figure 1.The number of patients for each qSOFA level (left Y axis) and the corresponding mortality (right Y axis). qSOFA: quick Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment. |
Table 2.
| Variable | qSOFA ≥2 (n = 127) | qSOFA <2 (n = 109) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 69 (57–76) | 68 (57–76) | 0.505 |
| Male sex | 79 (62.2) | 65 (59.6) | 0.691 |
| APACHE II score | 25 (19–31) | 21 (15–26) | <0.001 |
| SOFA score | 9 (6–11) | 5 (3–7) | <0.001 |
| Hospital LOS (d) | 24 (15–42) | 27 (13–57) | 0.355 |
| ICU LOS (d) | 11 (5–19) | 9 (4–18) | 0.540 |
| Source of infection | |||
| Pneumonia | 58 (45.7) | 33 (30.3) | 0.016 |
| Intra-abdominal | 36 (28.3) | 25 (22.9) | 0.373 |
| Urinary tract | 12 (9.4) | 13 (11.9) | 0.672 |
| Musculoskeletal | 17 (13.4) | 24 (22.0) | 0.088 |
| Catheter-related | 11 (8.7) | 11 (10.1) | 0.823 |
| Neutropenia | 11 (8.7) | 2 (1.8) | 0.024 |
| Infective endocarditis | 4 (3.1) | 7 (6.4) | 0.354 |
| Organism | |||
| Gram-positive bacteria | 64 (50.4) | 74 (67.9) | 0.008 |
| Gram-negative bacteria | 56 (44.1) | 28 (25.7) | 0.004 |
| Requirement for hemodialysisa | 55 (43.3) | 29 (26.6) | 0.009 |
| Requirement for NMBAsa | 33 (26.0) | 16 (14.7) | 0.037 |
| Requirement for vasopressorsa | 93 (73.2) | 53 (48.6) | <0.001 |
| Ventilator carea | 76 (59.8) | 51 (46.8) | 0.050 |
| Thrombocytopeniaa,b | 102 (80.3) | 62 (56.9) | <0.001 |
| Lactic acid >2.0 mmol/L (n = 161)a | 80 (80.0) | 39 (63.9) | 0.028 |
| Septic shock (n = 161)a,c | 67 (67.0) | 29 (47.5) | 0.020 |
| 28-Day mortality | 66 (52.0) | 31 (28.4) | <0.001 |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range) or number (%).
qSOFA: quick Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment; APACHE: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; LOS: length of stay; ICU: intensive care unit; NMBA: neuromuscular blocking agent.
3) Comparison of qSOFA score with MEWS, SIRS, and SOFA
Table 3.
| Variable |
MEWS |
SIRS |
SOFA |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥5 (n = 175) | <5 (n = 61) | P-value | ≥2 (n = 228) | <2 | P-value | ≥7 (n = 125) | <7 (n = 111) | P-value | |
| Requirement for hemodialysisa | 71 (40.6) | 13 (21.3) | 0.008 | 81 (35.5) | 3 (37.5) | >0.999 | 59 (47.2) | 25 (22.5) | <0.001 |
| Requirement for NMBAsa | 45 (25.7) | 4 (6.6) | 0.001 | 49 (21.5) | 0 | 0.211 | 35 (28.0) | 14 (12.6) | 0.004 |
| Requirement for vasopressorsa | 129 (73.7) | 17 (27.9) | <0.001 | 141 (61.8) | 5 (62.5) | >0.999 | 100 (80.0) | 46 (41.4) | <0.001 |
| Ventilator carea | 113 (64.6) | 14 (23.0) | <0.001 | 123 (53.9) | 4 (50.0) | >0.999 | 81 (64.8) | 46 (41.4) | <0.001 |
| Thrombocytopeniaa,b | 131 (74.9) | 33 (54.1) | 0.004 | 160 (70.2) | 4 (50.0) | 0.252 | 113 (90.4) | 51 (45.9) | <0.001 |
| Lactic acid >2.0 mmol/L (n = 161)a | 105 (78.9) | 14 (50.0) | 0.004 | 115 (73.7) | 4 (80.0) | >0.999 | 81 (78.0) | 38 (65.5) | 0.002 |
| Septic shock (n = 161)a,c | 84 (65.4) | 9 (32.1) | 0.001 | 92 (59.0) | 4 (80.0) | 0.649 | 72 (64.9) | 24 (25.0) | <0.001 |
| 28-Day mortality | 84 (48.0) | 13 (21.3) | <0.001 | 134 (58.8) | 5 (62.5) | >0.999 | 69 (55.2) | 28 (25.2) | <0.001 |
Values are presented as number (%). The cutoff levels of MEWS and SIRS were used according to published data, and the cutoff value of SOFA score was determined by receiver operating characteristic curves using our data.
MEWS: Modified Early Warning score; SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; NMBA: Neuromuscular blocking agent.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download