Introduction
Anatomy and physiology of leptomeningeal collaterals
Anatomy
Physiology
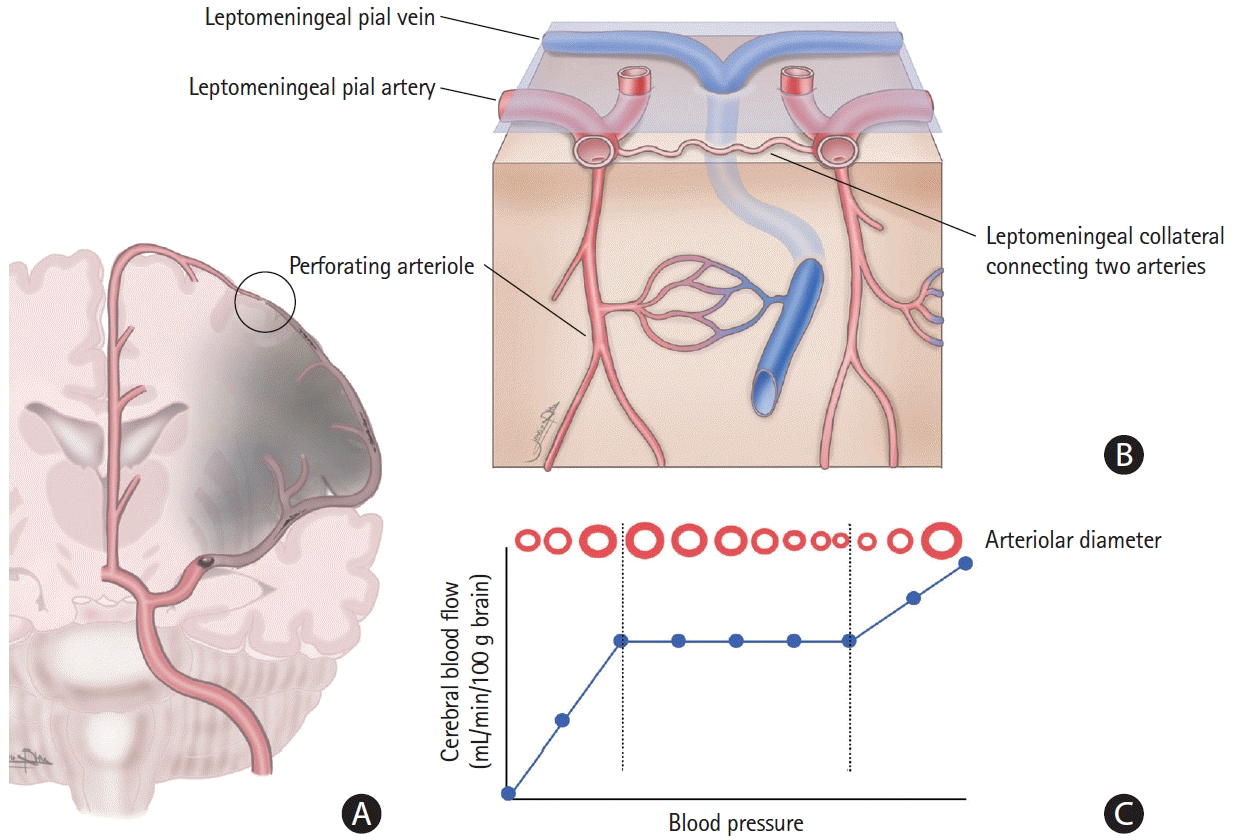 | Figure 1.Overview of leptomeningeal collaterals and cerebral autoregulation. (A) When a perfusion pressure gradient develops after large vessel occlusion, leptomeningeal collaterals are instantaneously recruited to provide cerebral perfusion to the ischemic territory within the functional capacity of cerebral autoregulation. (B) Microscopically, leptomeningeal collateral channels utilize pre-existing arterial tubular structures between the pial arteries, arterioles, or proximal branches. (C) The recruitment of leptomeningeal channels depends primarily on the myogenic dilatation of the pial arteries responsive to decreased local perfusion pressure (i.e., cerebral autoregulation). |
Leptomeningeal collateral perfusion and systemic blood pressure after large vessel occlusion
Levels and variabilities of blood pressure in peri-endovascular treatment and stroke outcomes
Table 1.
| Study | Year | Study subjects | Major BP indices | Major findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nogueira et al. [36] | 2009 | 305 LVO patients included in the MERCI and multi-MERCI trials | BP on admission | Higher SBP on admission associated with unfavorable outcomes but an independent predictor of successful recanalization |
| Maier et al. [38] | 2017 | 1,042 LVO patients with EVT from ETIS registry | BP on admission | Admission SBP showed J- or U-shaped association with mortality, with the inflection point at SBP 157 mm Hg |
| Mulder et al. [37] | 2017 | 500 LVO patients included in the MR CLEAN trial | BP at baseline, before EVT (for EVT group) or stroke unit admission (for the no-EVT group) | Baseline SBP showed U-shape association with functional outcome |
| High SBP associated with mortality and symptomatic hemorrhage | ||||
| No interaction between SBP level and EVT | ||||
| Goyal et al. [41] | 2017 | 116 LVO patients with EVT | SBP on admission | Admission SBP correlated with final infarct volume |
| Higher admission SBP associated with mRS 0–2 | ||||
| Schonenberger et al. [40]* | 2018 | 150 EVT cases randomized to GA or CS from the SIESTA trial | BP measurements were divided into 4 phases: pre-EVT, pre-recanalization, post- recanalization, and post-EVT | No association between the difference in SBP, DBP, and MAP from baseline to the different phases of intervention with 24-hour NIHSS |
| No association of BP drop with a change in mRS | ||||
| Anadani et al. [42] | 2020 | 381 EVT cases from the ASTER trial | Baseline BP prior to randomization | No association between admission BP with mRS or successful revascularization |
| van den Berg et al. [39] | 2020 | 3180 EVT patients from the MR CLEAN registry | BP on admission | J-shaped association with mRS and mortality with inflection points at 150 and 81 mm Hg |
| Higher SBP associated with poor mRS and mortality |
BP, blood pressure; EVT, endovascular treatment; LVO, large vessel occlusion; MERCI, Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia Trial; Multi-MERCI, Multi Mechanical Embolus Removal in Cerebral Ischemia Trial; SBP, systolic blood pressure; ETIS, endovascular treatment in ischemic stroke follow-up evaluation study; MR CLEAN, Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial of Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke in the Netherlands; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; GA, general anesthesia; CS, conscious sedation; SIESTA, Sedation vs. Intubation for Endovascular Stroke Treatment trial; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; ASTER, Contact Aspiration vs. Stent Retriever For Successful Revascularization trial.
Table 2.
| Study | Year | Study subjects | Major BP indices | Major findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Davis et al. [43] | 2012 | 96 EVT cases (48 GA and 48 LA) | SBP, DBP, and MAP (minimum and maximum values for each) in LA and GA groups | Higher rates of mRS 0–2 in LA groups; lower SBP levels in GA group |
| Hendén et al. [53] | 2015 | 108 EVT cases | Fall in MAP of >40% compared to the baseline under GA | Fall in MAP of >40% from baseline associated with poor neurological recovery |
| John et al. [54] | 2015 | 147 EVT during 2008–2012 | Levels of BP during the EVT procedure under GA | Lower maximum intraprocedural SBP associated with mRS 0–2 |
| Jagani et al. [44] | 2016 | 99 EVT with CS or GA | Maximum or minimum values of SBP, DBP, and MAP | GA associated with lower BP levels and poor outcome |
| Whalin et al. [55] | 2017 | 255 Anterior circulation occlusions with mTICI ≥2b with monitored anesthesia care | MAP level during the procedure with monitored anesthesia care | 10% MAP drop associated with poor functional outcome |
| Athiraman et al. [56] | 2018 | 88 EVTs under GA | Episodes or durations of SBP lower than specific thresholds | Lower SBP levels associated with poor outcome |
| Pikija et al. [46] | 2018 | 164 EVT cases under GA | In-procedure SBP and MAP excursions to >120%/80% of the reference value and the reference BP/weighted in-procedure mean BP | High in-procedure SBP/MAP excursion to >120% associated with lower infarct volume and mRS 0–2 |
| Higher in-procedure mean SBP/MAP associated with lower rates of hemorrhage | ||||
| Rasmussen et al. [45] | 2018 | 128 EVT patients randomized to GA or CS from the GOLIATH trial | Levels and durations of SBP or MAP lower than specific thresholds | Higher MAP or SBP levels in CS group |
| No significant difference in the association between BP parameters and mRS | ||||
| Schonenberger et al. [40]* | 2018 | 150 EVT cases randomized to GA or CS from the SIESTA trial | BP measurements were divided into 4 phases: pre-EVT, pre-recanalization, post-recanalization, and post-EVT | No association between the difference in SBP, DBP, and MAP from baseline to the different phases of intervention with 24 hours NIHSS |
| No association of BP drop (magnitude of changes) with a change in mRS | ||||
| Treurniet et al. [57] | 2018 | 60 EVT under GA in the MR CLEAN trial | Levels and changes of SBP, DBP, and MAP during the procedure | Greater MAP reduction associated with worse functional outcome |
| Petersen et al. [47] | 2019 | 390 EVTs from two comprehensive stroke centers | Intraprocedural MAP, delta MAP (baseline MAP–lowest MAP during EVT procedures before recanalization) | MAP reduction noted in 87% of cases during EVT Delta-MAP associated with infarct growth and |
| infarct volume; Delta-MAP correlated with higher mRS at discharge | ||||
| Pikija et al. [58] | 2019 | 39 BAO with EVT | BP levels and variability indices; difference of peak and trough values, SD, CV, ARV; reference SBP calculated as a median of the first five procedural measurements | Shorter procedural duration of SBP <140 associated with successful recanalization |
| Higher SBP and longer duration of SBP over 180 mm Hg associated with hemorrhage | ||||
| Fandler-Hofler et al. [59] | 2020 | 115 Anterior circulation occlusion patients with EVT under GA | Peri-interventional BP levels and reduction | Single BP drop associated with poor outcome |
| Maïer et al. [51] | 2020 | 381 Patients from the ASTER trial | Dynamic BP parameter, CV; steady BP parameter, hypotension time of SBP <140 or MAP <90 | BP variability parameter associated with poor outcomes regardless of collateral status |
| Hypotension time associated with poor outcomes only in patients with poor collaterals | ||||
| Petersen et al. [52] | 2020 | 90 EVTs for anterior circulation occlusions | Optimal ranges of MAP based on an autoregulatory index calculated by a real-time NIRS in response to changes in MAP | Percent time of MAP greater than the upper limit of the optimal range associated with worse 90- day outcomes and trends in hemorrhage |
| Rasmussen et al. [49] | 2020 | 368 EVT patient’s data from SIESTA, ANSTROKE, GOLIATH trials (CS vs. GA) | Levels and durations of MAP greater or less than thresholds | Cumulative hypo- (MABP <70 mm Hg for >10 minutes) and hypertension (MABP >90 mm Hg for >45 minutes) associated with poor functional outcomes |
| Valent et al. [48] | 2020 | 371 EVT cases under GA or CS | Baseline BP; BP measured in the interventional suite immediately before the induction | The time below 90% of the reference value associated with mRS ≥3 |
| Duration of arterial hypotension (below the baseline BP) | ||||
| Samuels et al. [50] | 2021 | 440 EVT patients from the MR CLEAN registry, under CS or LA | Changes and duration of MAP levels | Lower MAP levels in CS; worse outcome in CS |
| Xu et al. [60] | 2021 | 131 EVT patients after LVO under GA | Delta MAP; MAP every 5 minutes–baseline MAP | Longer duration delta MAP associated with poor outcome, but only documented in mild reduction group |
| Cumulated time and the longest continuous episode of delta MAP <10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 mm Hg | ||||
| Chen et al. [61] | 2021 | 139 EVT cases with successful recanalization | Procedural BPs categorized into baseline, pre-recanalization, postrecanalization, and post-intervention | High pre-recanalization BPs associated with poor outcomes; protocol-based BP lowering during EVT not associated with outcomes |
BP, blood pressure; EVT, endovascular treatment; GA, general anesthesia; LA, local anesthesia; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; CS, conscious sedation; mTICI, modified treatment in cerebral ischemia; GOLIATH, General or Local Anesthesia in Intra-arterial Therapy trial; SIESTA, Sedation vs. Intubation for Endovascular Stroke Treatment trial; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; MR CLEAN, Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial of Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke in the Netherlands; BAO, basilar artery occlusion; SD, standard deviation; CV, coefficient of variation; ARV, average real variation; ASTER, Contact Aspiration vs. Stent Retriever For Successful Revascularization trial; NIRS, near-infrared spectroscopy; ANSTROKE, Anesthesia During Stroke trial; MABP, mean arterial blood pressure; LVO, large vessel occlusion.
Table 3.
| Study | Year | Study subjects | Major BP indices | Major findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Martins et al. [79] | 2016 | 674 IVT or EVT cases | BP every 2 hours for 24 hours after admission | SBP showed J-shape in non-recanalized group but linear association in recanalized group |
| Mistry et al. [80] | 2017 | 228 EVT from three hospitals | BP (max, min, and average) in the first 24 hours after EVT | High peak SBP correlated with worse functional outcome and hemorrhagic complications |
| Goyal et al. [65] | 2017 | 217 LVO with EVT with hourly BP | BP goals post EVT; permissive hypertension (<220 or 185), moderate BP control (<160), intensive BP control (<140) | Higher SBPmax associated with mortality |
| Intensive BP target (<140/90 mm Hg) associated with higher rates of mRS 0–2 | ||||
| Bennett et al. [71] | 2018 | 182 LVO patients with EVT | Post-procedural BP variability indices; SD, CV, and SV | High BPV associated with high mRS |
| Chang et al. [81] | 2018 | 303 LVO patients with EVT | Post-procedural BP variability indices; SD, CV, and VIM | High BPV associated with poor functional recovery and low successful recanalization |
| Maier et al. [67] | 2018 | 168 Anterior circulation occlusions with successful recanalization after EVT | Mean, max, and peak SBP for the first 24 hours after successful EVT | High mean SBP and maximum SBP associated with unfavorable outcome |
| Martins et al. [82] | 2018 | 674 IVT or EVT | Standard deviations of SBP and DBP during the first 24 hours after stroke | A differential effect from SD of SBP on mRS by recanalization status; significant only in non-recanalized patients |
| Schonenberger et al. [40]* | 2018 | 150 EVT cases randomized to GA or CS from the SIESTA trial | BP measurements were divided into 4 phases: pre-EVT, pre-recanalization, post-recanalization, and post-EVT | No association between the difference in SBP, DBP, and MAP from baseline to the different phases of intervention and NIHSS change after 24 hours |
| No association of BP drops with a change in mRS | ||||
| Cernik et al. [66] | 2019 | 690 EVT patients | Levels of SBP and DBP | Low BP levels associated with better functional recovery or recanalization |
| Chang et al. [83] | 2019 | 90 EVT with mTICI ≥2b | BP variability indices | BP variability associated with poor mRS only in patients with poor collaterals at baseline |
| Cho et al. [84] | 2019 | 378 EVTs | Levels and variability indices during the first 24 hours after admission | Higher mean SBP and SV of SBP associated with poor mRS; the effect of SV modified by recanalization status |
| Choi et al. [85] | 2019 | 1,540 AIS patients after IVT or EVT | BP ≤130/80 mm Hg | Lower BP levels associated with mRS 0–2 |
| Kim et al. [73] | 2019 | 211 EVT with mTICI ≥2b | Levels, excursions, variability indices, and time rate of BP variation | BP variability indices associated with higher rates of SICH |
| Mistry et al. [70] | 2019 | 485 Consecutive EVT patients from 12 centers | All SBP values within 24 hours post EVT | Peak SBP <158 mm Hg associated with good functional outcome |
| Overall, SBP showed a U-shape association with outcome | ||||
| Higher BP levels after EVT associated with poor outcome | ||||
| Zhang et al. [86] | 2019 | 72 LVOs with EVT | Post-procedural BP variability indices; SD, CV, and SV | Higher SV of SBP correlated with mRS at 3 months |
| Anadani et al. [87] | 2020 | 1,361 EVT cases from an international multicenter study | SBP reduction in the first 24 hours after EVT | SBP reduction associated with a good outcome only in patients with complete reperfusion (mTICI, 3) |
| Anadani et al. [88] | 2020 | 433 EVT cases from the BEST study [70] | SBP reduction, the absolute difference between admission SBP and mean SBP in the first 24 hours | No association between SBP with poor outcome or death |
| Anadani et al. [76] | 2020 | 1,019 Anterior circulation occlusion patients with EVT from eight comprehensive stroke centers | Post-EVT BP target, <140, <160, and <180 | Lower SBP goal (<140 or <160, compared to <180) associated with good outcome |
| However, mean achieved SBP levels tended to overlap | ||||
| Cheng et al. [68] | 2020 | 124 Anterior circulation occlusion patients with EVT | Two BP measurements immediately after successful recanalization | Higher BP associated with PH2 hemorrhagic transformation |
| Chu et al. [89] | 2019 | 166 EVT patients | Hourly BP after EVT, by 1–6, 7–12, 13–18, and 19–24 hours | Lower mean, max, SD of SBP, and DBP associated with functional independence, in <6 hours |
| Dias et al. [90] | 2020 | 458 EVT cases | Median SBP within the first hour after EVT | Lower median SBP associated with NIHSS reduction by 8 or ≤2 at 24 hours |
| Ding et al. [91] | 2020 | 262 EVT cases | Maximum SBP and DBP for 24 hours after the EVT | Max SBP associated with poor mRS and parenchymal hemorrhage (hyper attenuated lesion on immediate CT, cannot distinguish from contrast staining) |
| Matusevicius et al. [69] | 2020 | 3,631 EVT cases from the SITS-ISTR | Mean 24-hour SBP after EVT | Higher SBP associated with poor functional recovery in successful recanalization patients and with SICH in all recanalization |
| McCarthy et al. [92] | 2020 | 212 EVT patients | Daily peak SBP and DBP | Higher peak 24-hour SBP associated with SICH and poor outcome |
| Higher peak SBP at day 2 and day 3 associated with poor outcome | ||||
| Mistry et al. [72] | 2020 | 443 EVT cases from the BEST study [70] | Systolic BPV (SD, CV, ARV, SV, and rSD) during 24 hours after EVT | Higher BP variability associated with poor outcome and mortality |
| Anadani et al. [74] | 2021 | 5,835 EVT patients from the SITS-ISTR registry | Delta SBP (SBP–baseline SBP) 0–2/2–4/4–12/12–24 hours | SBP elevation after EVT associated with poor functional outcome |
| Gigliotti et al. [93] | 2021 | 117 EVT cases | SBP for 24 hours after EVT | SBP ≥180 associated with poor function at discharge but not at 3 months |
| SBP ≥160 associated with malignant cerebral edema with lower symptomatic hemorrhage | ||||
| Han et al. [94] | 2021 | 187 BAO with EVT | Levels of SBP, MAP, and DBP | Maximum SBP and maximum MAP associated with mortality |
| Huang et al. [95] | 2021 | 502 Anterior circulation LVO patients with EVT | Levels and variability indices of SBP and DBP | High BP variability associated with poor functional recovery and hemorrhagic complications, differentiated by recanalization status, not by baseline collaterals |
| Liu et al. [77] | 2021 | 596 LVO patients with EVT (GA in 37%) | BP for 24 hours after EVT | Higher mean SBP levels, mean SBP >140, and SD of SBP associated with the unfavorable outcome only in poor collaterals subgroup |
| Mazighi et al. [75] | 2021 | 324 LVO patients with EVT (BP-TARGET trial) | Randomized to intensive SBP target (100–129) vs. standard SBP target (130–185) for 24 hours | No difference in the primary outcome (any hemorrhage or hypotensive event) |
| Castro et al. [78] | 2021 | 146 Anterior circulation LVO with successful recanalization | Spectral analysis of 5-minute recordings of beat-to-beat BP | High frequency BP variability associated with cerebral edema and unfavorable functional outcomes |
BP, blood pressure; IVT, intravenous thrombolysis; EVT, endovascular treatment; SBP, systolic blood pressure; LVO, large vessel occlusion; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; SD, standard deviation; CV, coefficient of variation; SV, successive variation; BPV, BP variability; VIM, variation independent of the mean; GA, general anesthesia; CS, conscious sedation; SIESTA, Sedation vs. Intubation for Endovascular Stroke Treatment trial; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; mTICI, modified treatment in cerebral ischemia; AIS, acute ischemic stroke; SICH, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage; BEST, Blood Pressure after Endovascular Therapy for Ischemic Stroke study; CT, computed tomography; PH2, parenchymal hemorrhage type 2; SITS-ISTR, Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke International Stroke Thrombolysis Registry; ARV, average real variation; rSD, residual standard deviation; BAO, basilar artery occlusion; BP-TARGET, Blood Pressure target in Acute Stroke to Reduce Hemorrhage after Endovascular Therapy trial.
Summary of current evidence for clinical practice
Current clinical guidelines and summary of the literature on BP management during the peri-endovascular treatment period
A tentative suggestion for the BP management of patients with EVT
Pre-EVT period
Procedural BP
Post-recanalization period
Research perspective
Summary measures for BP
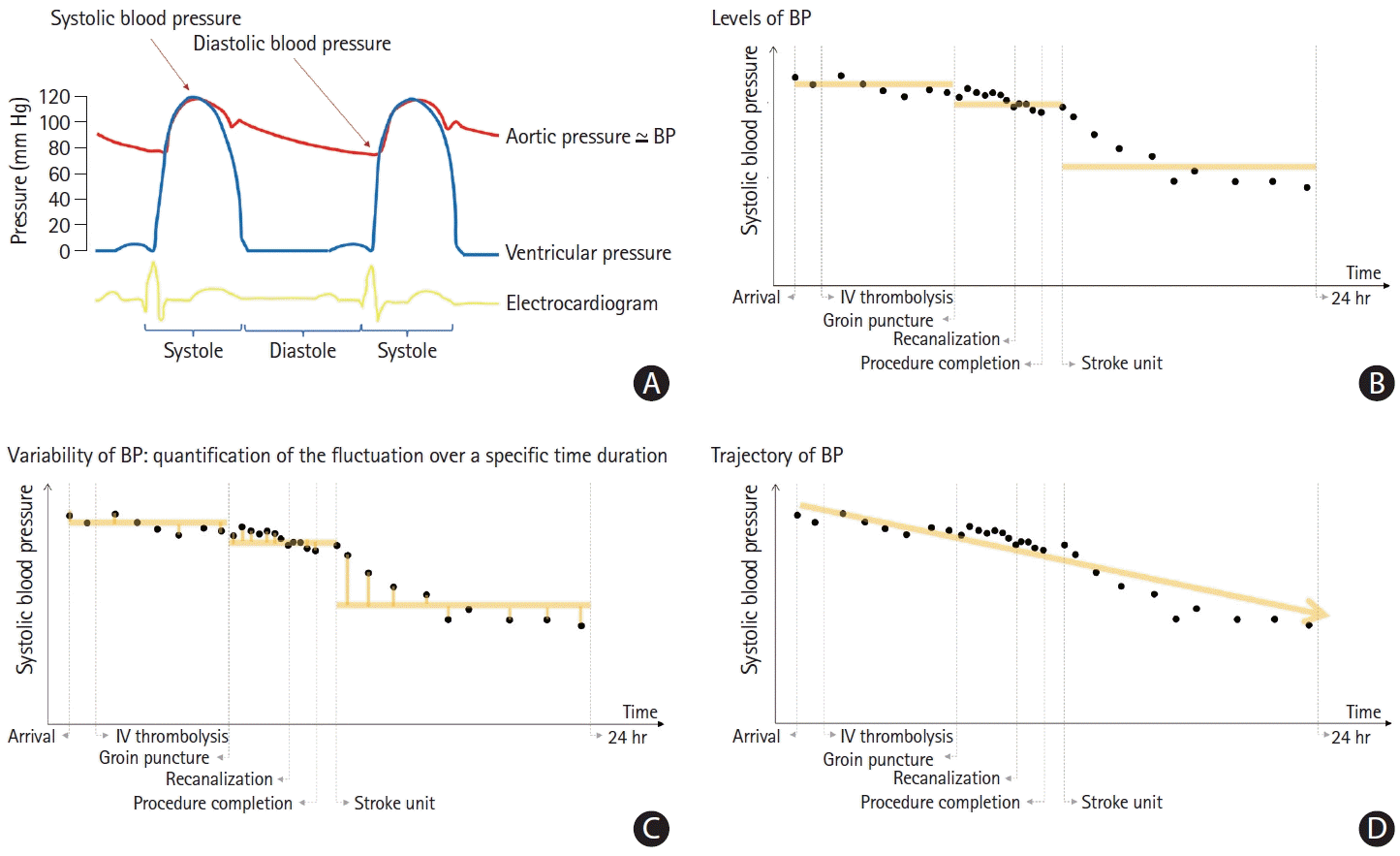 | Figure 2.Characteristics of blood pressure measurements and summary indices. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BP) is determined during every cardiac cycle. Intermittent measurements in routine clinical practice may capture only a fraction of the available BP measurements. BP measurements can be obtained repeatedly and exhibit constant fluctuations (A). The measurement density of BPs may be different throughout acute in-hospital care, that is, pre-endovascular treatment (EVT), during the procedure, as well as post-EVT. BP measurements can be summarized using means, as highlighted by the yellow line in the figure. The average BP level is intuitive and easy to calculate, but it does not reflect the variability and fluctuations in BP measurements that occur in a patient (B). Fluctuations of BP can be described by various variability measures, including standard deviations, coefficient of variations, maximum decrements, and average real variability, to name a few. In general, variability measures are calculated by taking the differences between each measurement or the differences between specific values (yellow lines). However, such variability measures do not provide information on the time intervals of the measurements. Thus, the absolute BP variability values may decrease during high measurement density periods such as during EVT procedures (C). The trajectory group describes the overall path (yellow line) of BP measurements over a certain period of time. By using a mixture model, clusters of patients with similar patterns of BP measurements over a period of time may be identified and grouped [104]. Five groups of acute BP trajectories were identified from a clinical registry of 8,000 stroke cases [103]. Trajectory groups are easy to recognize in clinical practice even before the measurement period is completed. However, the trajectory group estimation process depends on the characteristics of the source data and the modeling specification, and thus, the generalizability of the model is limited (D). IV, intravenous. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download