Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Table 3.
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Notes
Disclosure
Mayank Goyal: consultant (Medtronic, Stryker, Microvention, GE Healthcare, Mentice). Michael Hill: grants from Stryker, Medtronic, NoNO Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim. Bijoy Menon: patent (system/method for decision making/triaging in acute stroke). Johanna Ospel: research scholarships from the University of Basel Research Foundation, Julia Bangerter Rhyner Foundation and “Freiwillige Akademische Gesellschaft Basel.” The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
References
Figure 1.
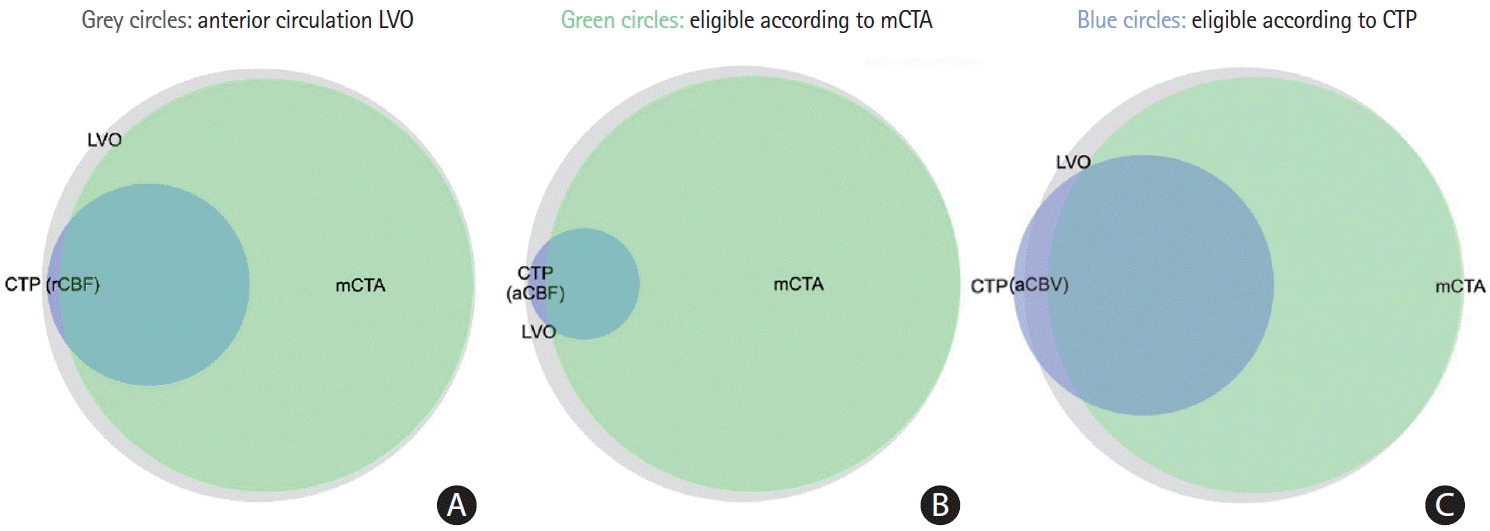
Figure 2.
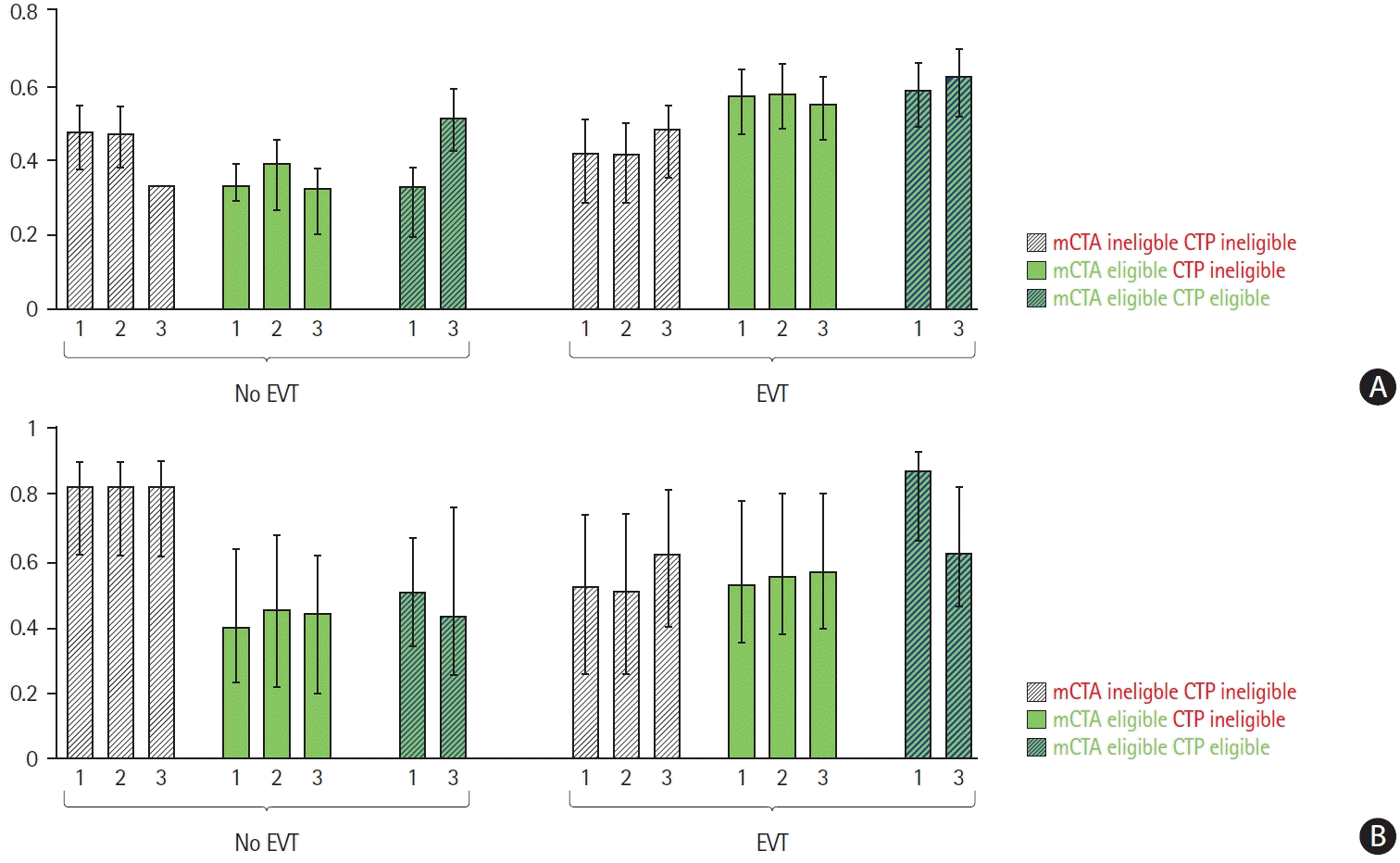
Table 1.
Values are presented as median (interquartile range), number (%), or mean±standard deviation.
TIA, transient ischemic attack; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; CT, computed tomography; ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; NCCT, non-contrast head computed tomography; CTA, computed tomography angiography; ICA, internal carotid artery.
Table 2.
| Variable | AIC | BIC | C statistic (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical models* | ||||
| Model 1. Baseline model (simplest)† | 611.57 | 640.54 | 0.664 (0.614–0.713) | |
| Model 2. Baseline model+CTP based eligibility for EVT (rCBF) | 611.36 | 640.32 | 0.670 (0.621–0.719) | |
| Model 3. Baseline model+CTP based eligibility for EVT (aCBF) | 612.57 | 641.54 | 0.665 (0.616–0.714) | |
| Model 4. Baseline model+CTP based eligibility for EVT (CBV) | 610.44 | 639.41 | 0.671 (0.622–0.720) | |
| Model 5. Baseline model+mCTA based eligibility for EVT | 610.52 | 639.48 | 0.665 (0.616–0.714) | |
| Baseline model†+mCTA criteria vs. additional CTP criteria | ||||
| Model 6. Model 5+CTP based EVT eligibility (rCBF) | 609.51 | 642.61 | 0.670 (0.621–0.719) | |
| Model 7. Model 5+CTP based EVT eligibility (aCBF) | 612.49 | 645.60 | 0.664 (0.615–0.713) | |
| Model 8. Model 5+CTP based EVT eligibility (CBV) | 611.20 | 644.30 | 0.669 (0.621–0.718) | |
NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; AIC, Akaike information criterion; BIC, Bayesian information criterion; CI, confidence interval; CTP, computed tomography perfusion; EVT, endovascular treatment; rCBF, relative cerebral blood flow; aCBF, absolute cerebral blood flow; CBV, cerebral blood volume; mCTA, multi-phase computed tomography angiography.
* mCTA: EVT treatment decision (yes is indicated by presence of a large vessel occlusion and good or intermediate collaterals), CTP treatment decision (yes is indicated by an ischemic core volume [defined as rCBF <30% for model 2, a CBF <7 mL/100 g/min for model 3, CBV <2 mL/100 g for model 4]) <70 mL and absolute mismatch >15 mL and penumbra (defined as Tmax >6 seconds)/core mismatch ratio >1.8 (Endovascular Therapy Following Imaging Evaluation for Ischemic Stroke 3 [DEFUSE-3] criteria6);
† Adjustment was performed for the following pre-specified baseline variables: age, baseline stroke severity as measured by the NIHSS, time from stroke symptom onset to baseline non-contrast head computed tomography (NCCT), baseline Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) (11 point ordinal scale) on NCCT, occlusion location (anterior circulation large vessel occlusion vs. not) and treatment type (EVT vs. not). Since large vessel occlusion presence was part of the mCTA and CTP-based treatment decision rules, it was not incorporated as an independent variable in models 2–8.
Table 3.
| Variable | AIC | BIC | C statistic (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical models* | ||||
| Model 1. Baseline model (simplest)† | 490.95 | 519.91 | 0.808 (0.769–0.847) | |
| Model 2. Baseline model+CTP based EVT eligibility (rCBF) | 491.09 | 520.05 | 0.808 (0.769–0.847) | |
| Model 3. Baseline model+CTP based EVT eligibility (aCBF) | 486.60 | 515.56 | 0.812 (0.774–0.851) | |
| Model 4. Baseline model+CTP based EVT eligibility (CBV) | 491.02 | 519.98 | 0.808 (0.769–0.847) | |
| Model 5. Baseline model+mCTA treatment decision | 490.99 | 519.96 | 0.808 (0.769–0.847) | |
| Baseline model†+mCTA criteria vs. additional CTP criteria | ||||
| Model 6. Model 5+CTP based EVT eligibility (rCBF) | 492.95 | 526.05 | 0.808 (0.769–0.847) | |
| Model 7. Model 5+CTP based EVT eligibility (aCBF) | 488.55 | 521.66 | 0.813 (0.774–0.851) | |
| Model 8. Model 5+CTP based EVT eligibility (CBV) | 492.94 | 526.05 | 0.808 (0.769–0.847) | |
AIC, Akaike information criterion; BIC, Bayesian information criterion; CI, confidence interval; CTP, computed tomography perfusion; EVT, endovascular treatment; rCBF, relative cerebral blood flow; aCBF, absolute cerebral blood flow; CBV, cerebral blood volume; mCTA, multi-phase computed tomography angiography.
* mCTA: EVT treatment decision (yes is indicated by presence of a large vessel occlusion and good or intermediate collaterals), CTP treatment decision (yes is indicated by an ischemic core volume [defined as rCBF <30% for model 2, a CBF <7 mL/100 g/min for model 3, CBV <2 mL/100 g for model 4]) <70 mL and absolute mismatch >15 mL and penumbra (defined as Tmax >6 seconds)/core mismatch ratio >1.8 (DEFUSE-3 criteria6);
† Adjustment was performed for the following pre-specified baseline variables: age, baseline stroke severity as measured by the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, time from stroke symptom onset to baseline non-contrast head computed tomography (NCCT), baseline Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) (11 point ordinal scale) on NCCT, occlusion location (anterior circulation large vessel occlusion vs. not) and treatment type (EVT vs. not). Since large vessel occlusion presence was part of the mCTA and CTP-based treatment decision rules, it was not incorporated as an independent variable in models 2–8.
Table 4.
Net reclassification index and integrated discrimination improvement for a statistical model that included additional CTP eligibility criteria compared to a statistical model that included pre-specified baseline variables* and multi-phase computed tomography angiography based eligibility criteria (cut-off probability 50%, dependent variables: major clinical improvement, defined as National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale [NIHSS] drop at 24 hours compared to baseline >50%, and good outcome, defined as modified Rankin Scale 0–2 at 90 days). The analysis was conducted in the entire patient sample.
NRI, net reclassification index; IDI, incremental discrimination improvement; CTP, computed tomography perfusion; rCBF, relative cerebral blood flow; aCBF, absolute cerebral blood flow; CBV, cerebral blood volume.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download