Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Study design and patients
2. Survival outcomes
3. ASCT procedure
4. Assessment of transplantation-related outcomes
5. Statistical analysis
Results
1. Patients’ characteristics
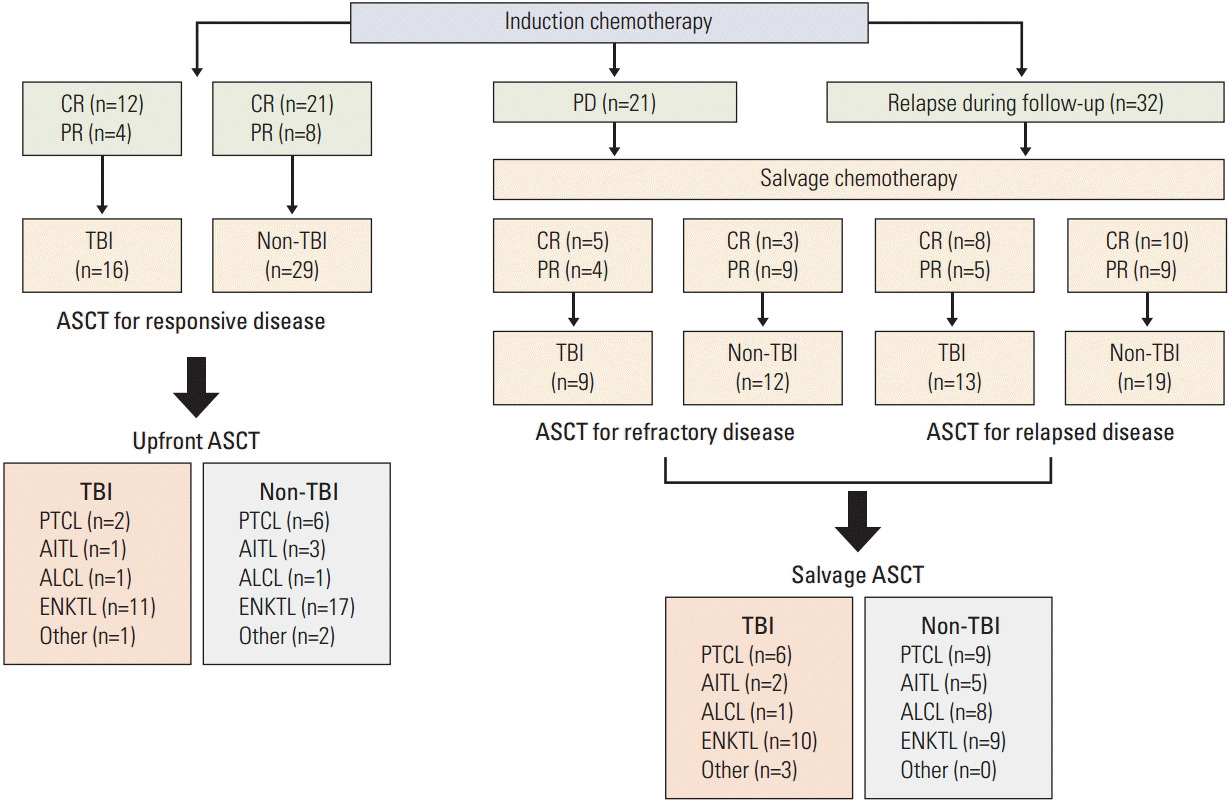 | Fig. 1.Classification of patients according to response to induction treatment and time of autologous stem cell transplantation. CR, complete response; PR, partial response; PD, progressive disease; TBI, total body irradiation; ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; PTCL, peripheral T-cell lymphoma; AITL, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma; ALCL, anaplastic large cell lymphoma; ENKTL, extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. |
Table 1.
Values are presented as number (%). TBI, total body irradiation; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PTCL-NOS, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not-otherwise specified; AITL, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma; ALCL, anaplastic large cell lymphoma; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; EATL, enteropathy associated T-cell lymphoma; HSTL, hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma; SPTL, subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma; ENKTL, extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma; PET, positron emission tomography.
2. Toxicities of TBI and non-TBI–based conditioning for ASCT
Table 2.
3. Comparison of PFS between TBI and non-TBI group
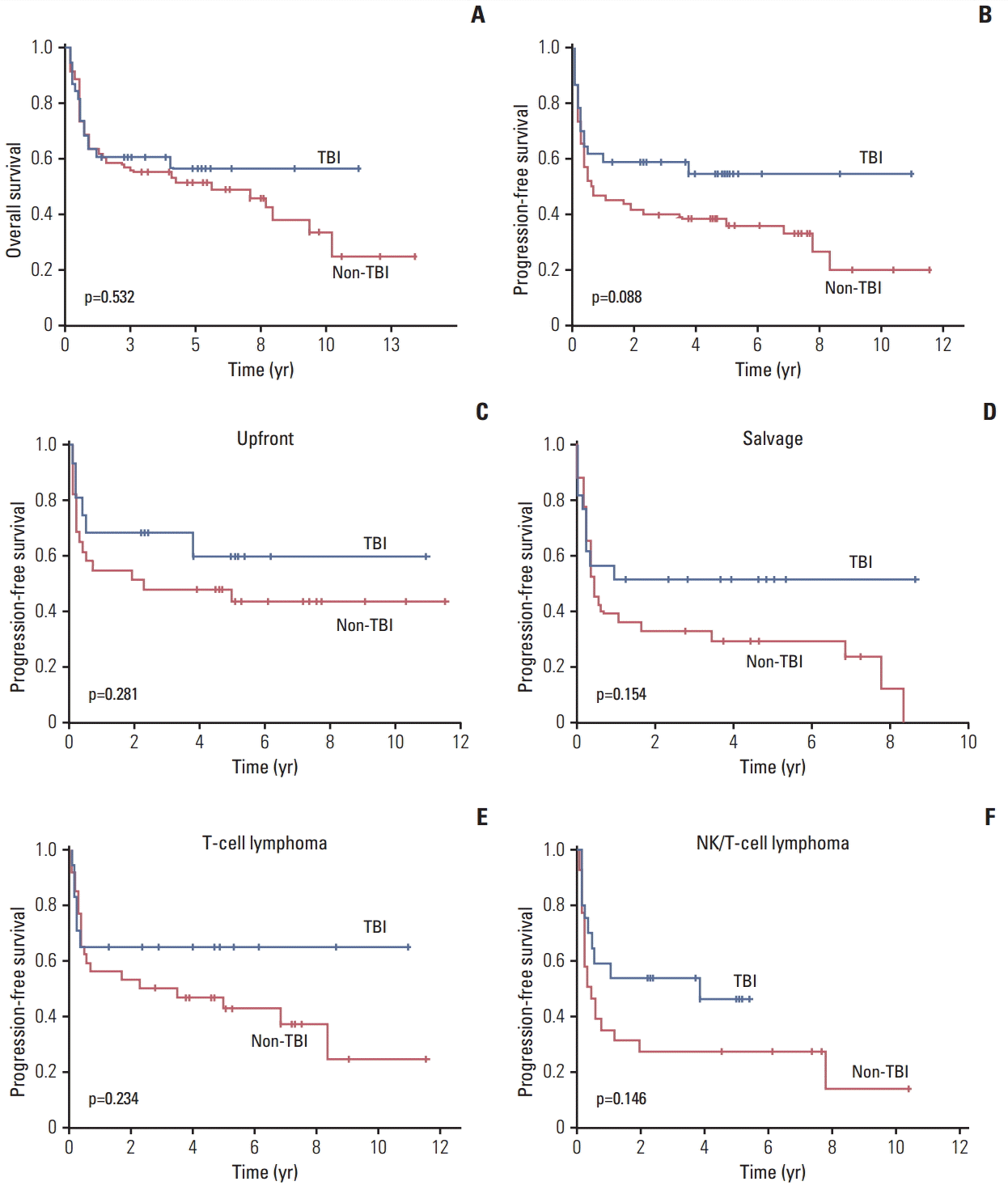 | Fig. 2.(A, B) Comparison of overall and progression-free survival according to the use of total body irradiation (TBI). (C, D) Comparison of progression-free survival between TBI and non-TBI group in upfront and salvage autologous stem cell transplantation. (E, F) Comparison of progression-free survival between TBI and non-TBI group in T-cell lymphomas and extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma. |
4. Pre-transplantation disease status and outcomes of ASCT
 | Fig. 3.(A, B) Comparison of progression-free survival between patients with pre-transplantation complete response (CR) and partial response (PR) in the total body irradiation (TBI) and non-TBI group. (C, D) Association of pre-transplantation CR assessed by positron emission tomography (PET) computed tomography and progression-free survival in the TBI and non-TBI group. (E, F) Comparison of progression-free survival according to the response to induction treatment in the TBI and non-TBI group. |
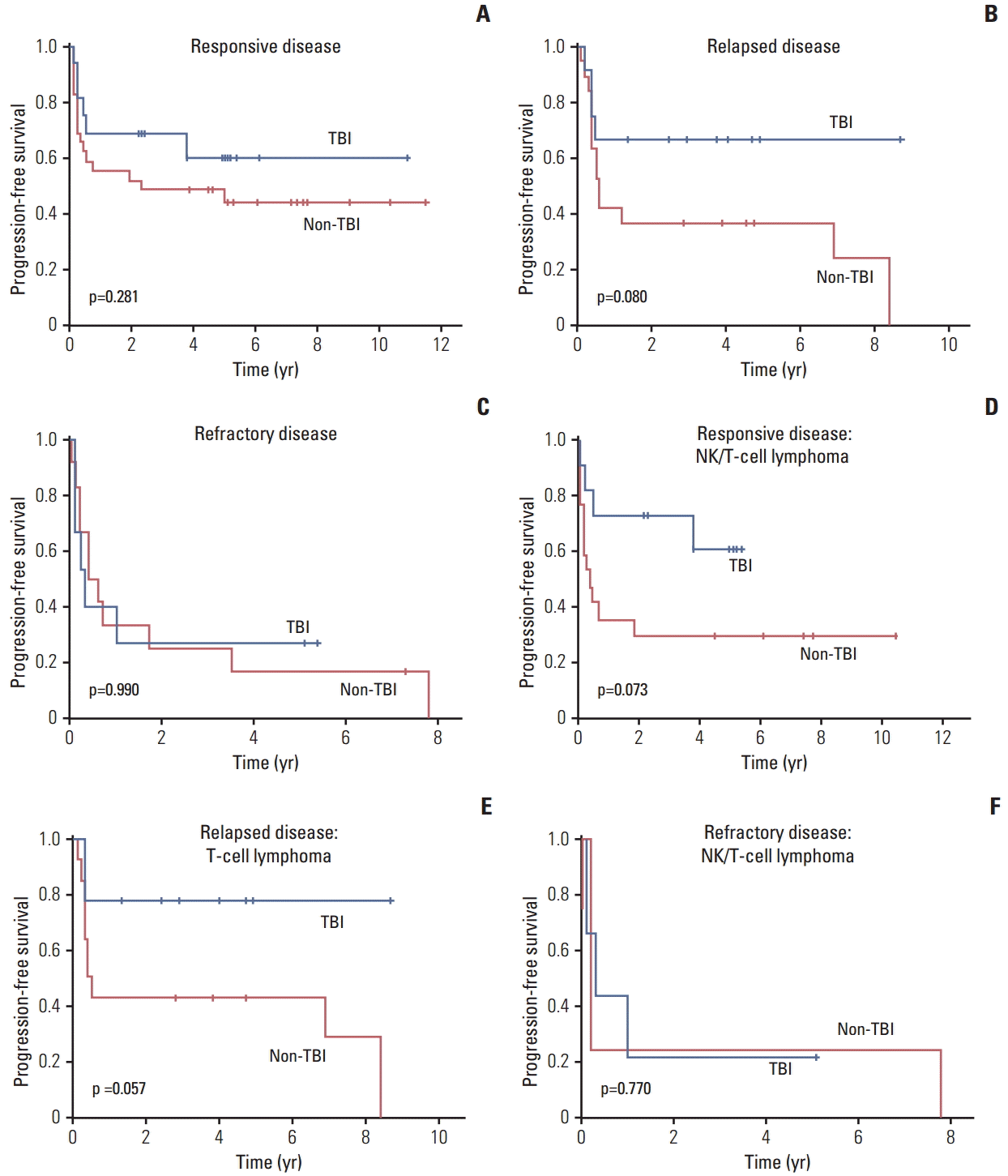 | Fig. 4.(A-C) Comparison of progression-free survival of patients with responsive, refractory, and relapsed disease between the total body irradiation (TBI) and non-TBI groups. (D, E) The TBI group showed a trend of better progression-free survival than the non-TBI group in extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma with responsive disease and T-cell lymphoma with relapsed disease. (F) No difference in progression-free survival of refractory disease was observed in patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download