1. Rosen PP, Groshen S, Kinne DW, Norton L. Factors influencing prognosis in node-negative breast carcinoma: analysis of 767 T1N0M0/T2N0M0 patients with long-term follow-up. J Clin Oncol. 1993; 11:2090–2100. PMID:
8229123.

2. Fisher B, Bauer M, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Fisher ER, Cruz AB, et al. Relation of number of positive axillary nodes to the prognosis of patients with primary breast cancer: an NASABP update. Cancer. 1983; 52:1551–1557. PMID:
6352003.
3. Consensus statement treatment of early-stage breast cancer. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Panel. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1992; 11:1–5.
4. NIH Consensus Conference, Treatment of early-stage breast cancer. JAMA. 1991; 265:391–395. PMID:
1984541.
5. Davies GC, Millis RR, Hayward JL. Assessment of axillary lymph node status. Ann Surg. 1980; 192:148–151. PMID:
7406568.

6. Kang HS, Noh DY, Youn YK, Oh SK, Choe KJ. The predictors of axillary node metastasis in 2 cm or less breast cancer univariate and multivaritate analysis. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 1999; 2:7–13.

7. Nemoto T, Vana J, Bedwani RN, Baker HW, McGregor FH, Murphy GP. Management and survival of female breast cancer: results of a national survey by the American college of surgeons. Cancer. 1980; 45:2917–2924. PMID:
7388735.

8. Ernst MF, Voogd AC, Balder W, Klinkenbijl JH, Roukema JA. Early and late morbidity associated with axillary levels I-III dissection in breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2002; 79:151–155. PMID:
11870664.

9. Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Dixon JM, et al. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: the ALMANAC Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006; 98:599–609. PMID:
16670385.

10. Frederick LG, David LP, Irvin DF, April F, Charles MB, Daniel GH, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual/American Joint Committee on Cancer. Breast. 2002. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;p. 223–240.
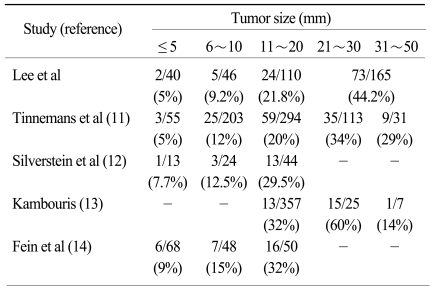
11. Tinnemans JG, Wobbes T, Holland R, Hendriks JH, Van der Sluis RF, De Boer HH. Treatment and survival of female patients with nonpalpable breast carcinoma. Ann Surg. 1989; 209:249–253. PMID:
2537064.

12. Silverstein MJ, Skinner KA, Lomis TJ. Predicting axillary nodal positivity in 2282 patients with breast carcinoma. World J Surg. 2001; 25:767–772. PMID:
11376414.

13. Kambouris AA. Axillary node metastases in relation to size and location of breast cancers: analysis of 147 patients. Am Surg. 1996; 62:519–524. PMID:
8651544.
14. Fein DA, Fowble BL, Hanlon AL, Hooks MA, Hoffman JP, Sigurdson ER, et al. Identification of women with T1-T2 breast cancer at low risk of positive axillary nodes. J Surg Oncol. 1997; 65:34–39. PMID:
9179265.

15. Cetinas SK, Kurt M, Ozkan L, Engin K, Gökgöz S, Tasdelen I. Factors influencing axillary node metastasis in breast cancer. Tumori. 2006; 92:416–422. PMID:
17168435.

16. Jonjic N, Mustac E, Dekanic A, Marijic B, Gaspar B, Kolic I, et al. Predicting sentinel lymph node metastases in infiltrating breast carcinoma with vascular invasion. Int J Surg Pathol. 2006; 14:306–311. PMID:
17041193.

17. Bevilacqua J, Cody H 3rd, MacDonald KA, Tan LK, Borgen PI, Van Zee KJ. A prospective validated model for predicting axillary node metastases based on 2000 sentinel node procedures: the role of tumor location [corrected]. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002; 28:490–500. PMID:
12217300.
18. Colleoni M, Rotmensz N, Maisonneuve P, Sonzogni A, Pruneri G, Casadio C, et al. Prognostic role of the extent of peritumoral vascular invasion in operable breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2007; 18:1632–1640. PMID:
17716986.

19. Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006; 295:2492–2502. PMID:
16757721.

20. Onitilo AA, Engel JM, Greenlee RT, Mukesh BN. Breast cancer subtypes based on ER/PR and Her2 expression: comparison of clinicopathologic features and survival. Clin Med Res. 2009; 7:4–13. PMID:
19574486.

21. Bader AA, Tio J, Petru E, Bühner M, Pfahlberg A, Volkholz H, et al. T1 breast cancer: identification of patients at low risk of axillary lymph node metastases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2002; 76:11–17. PMID:
12408371.

22. Chua B, Ung O, Taylor R, Boyages J. Frequency and predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in invasive breast cancer. ANZ J Surg. 2001; 71:723–728. PMID:
11906387.

23. Martelli G, Boracchi P, De Palo M, Pilotti S, Oriana S, Zucali R, et al. A randomized trial comparing axillary dissection to no axillary dissection in older patients with T1N0 breast cancer: results after 5 years of follow-up. Ann Surg. 2005; 242:1–6. PMID:
15973094.
24. Kim HJ, Chang MA, Hong SJ, Lee JS, Jung MS, Kim MJ, et al. Result of sentinel lymph node biopsy using radioisotope in clinically lymph node negative breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2007; 10:141–146.

25. Harden SP, Neal AJ, Al-Nasiri N, Ashley S, Querci della Rovere G. Predicting axillary lymph node metastases in patients with T1 infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. Breast. 2001; 10:155–159. PMID:
14965577.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download