1. Yao JC, Eisner MP, Leary C, et al. Population-based study of islet cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007; 14:3492–500.

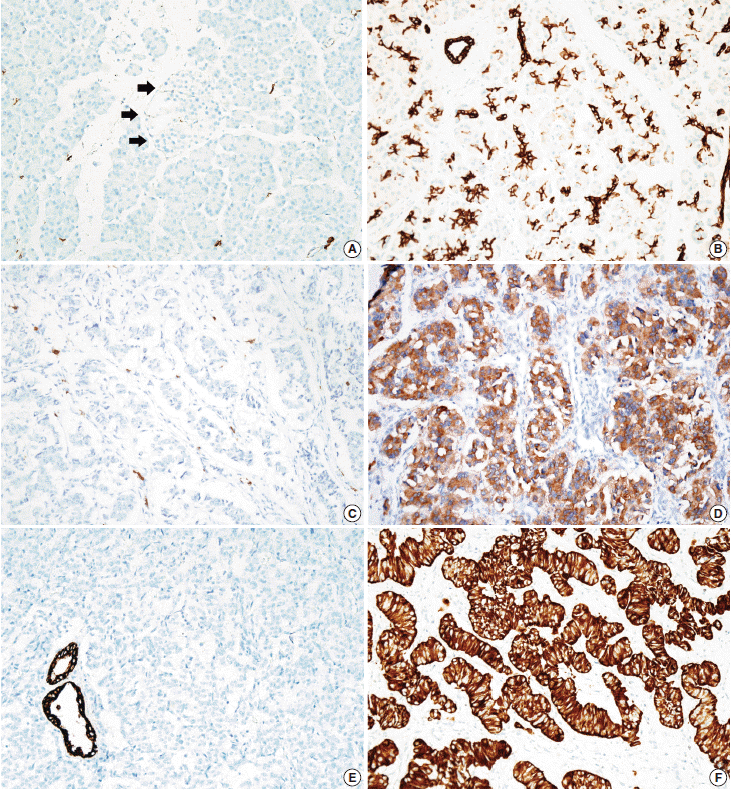
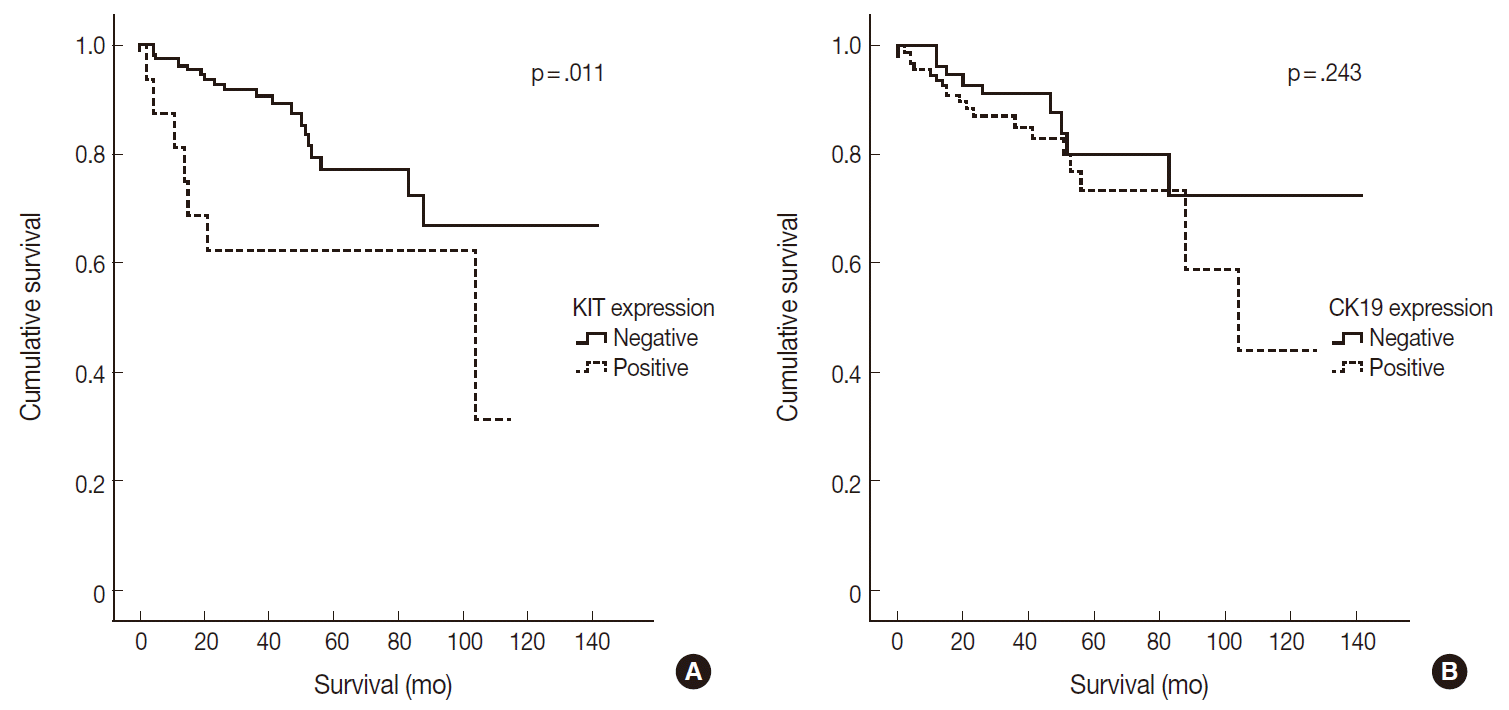
2. Han X, Zhao J, Ji Y, Xu X, Lou W. Expression of CK19 and KIT in resectable pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Tumour Biol. 2013; 34:2881–9.

3. Reichert M, Rustgi AK. Pancreatic ductal cells in development, regeneration, and neoplasia. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121:4572–8.

4. Strosberg JR, Cheema A, Weber J, Han G, Coppola D, Kvols LK. Prognostic validity of a novel American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Classification for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3044–9.

5. Jiao Y, Shi C, Edil BH, et al. DAXX/ATRX, MEN1, and mTOR pathway genes are frequently altered in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Science. 2011; 331:1199–203.
6. Krausch M, Raffel A, Anlauf M, et al. Loss of PTEN expression in neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors. Horm Metab Res. 2011; 43:865–71.

7. Marinoni I, Kurrer AS, Vassella E, et al. Loss of DAXX and ATRX are associated with chromosome instability and reduced survival of patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:453–60.
8. Bosnan FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2010.
9. Ali A, Serra S, Asa SL, Chetty R. The predictive value of CK19 and CD99 in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006; 30:1588–94.

10. Jonkers YM, Claessen SM, Perren A, et al. DNA copy number status is a powerful predictor of poor survival in endocrine pancreatic tumor patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007; 14:769–79.

11. La Rosa S, Rigoli E, Uccella S, Novario R, Capella C. Prognostic and biological significance of cytokeratin 19 in pancreatic endocrine tumours. Histopathology. 2007; 50:597–606.

12. Schmitt AM, Anlauf M, Rousson V, et al. WHO 2004 criteria and CK19 are reliable prognostic markers in pancreatic endocrine tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:1677–82.

13. Zhang L, Smyrk TC, Oliveira AM, et al. KIT is an independent prognostic marker for pancreatic endocrine tumors: a finding derived from analysis of islet cell differentiation markers. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1562–9.
14. Lennartsson J, Rönnstrand L. Stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit: from basic science to clinical implications. Physiol Rev. 2012; 92:1619–49.

15. Li J, Quirt J, Do HQ, et al. Expression of c-Kit receptor tyrosine kinase and effect on beta-cell development in the human fetal pancreas. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 293:E475–83.
16. Ashman LK. The biology of stem cell factor and its receptor C-kit. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999; 31:1037–51.

17. Feng ZC, Li J, Turco BA, Riopel M, Yee SP, Wang R. Critical role of c-Kit in beta cell function: increased insulin secretion and protection against diabetes in a mouse model. Diabetologia. 2012; 55:2214–25.

18. Kaligin MS, Gumerova AA, Titova MA, Andreeva DI, Sharipova ÉI, Kiiasov AP. C-kit is a marker of human pancreatic endocrinocyte stem cells. Morfologiia. 2011; 140:32–7.
19. Liu W, Chen L, Zhu J, Rodgers GP. The glycoprotein hGC-1 binds to cadherin and lectins. Exp Cell Res. 2006; 312:1785–97.

20. Kimura W, Ma J, Takeshita A, et al. Analysis of c-kit protein expression in pancreatic neoplasms and its implication for prognosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007; 54:2203–8.
21. Ohike N, Sato M, Hisayuki T, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of nestin and c-kit and their significance in pancreatic tumors. Pathol Int. 2007; 57:589–93.

22. Yasuda A, Sawai H, Takahashi H, et al. The stem cell factor/c-kit receptor pathway enhances proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2006; 5:46.
23. Sammarco I, Capurso G, Coppola L, et al. Expression of the protooncogene c-KIT in normal and tumor tissues from colorectal carcinoma patients. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2004; 19:545–53.

24. Heinzelmann-Schwarz VA, Nixdorf S, Valadan M, et al. A clinicopathological review of 33 patients with vulvar melanoma identifies c-KIT as a prognostic marker. Int J Mol Med. 2014; 33:784–94.

25. Kurokawa Y, Matsuura N, Kawabata R, et al. Prognostic impact of major receptor tyrosine kinase expression in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21 Suppl 4:S584–90.

26. Hong SM, Hwang I, Song DE, Choi J, Yu E. Clinical and prognostic significances of nuclear and cytoplasmic KIT expressions in extrahepatic bile duct carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 2007; 20:562–9.

27. Scobie JV, Acs G, Bandera CA, et al. C-kit immunoreactivity in endometrial adenocarcinomas and its clinicopathologic significance. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2003; 22:149–55.

28. Chung CY, Yeh KT, Hsu NC, et al. Expression of c-kit protooncogene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2005; 217:231–6.

29. Krams M, Parwaresch R, Sipos B, Heidorn K, Harms D, Rudolph P. Expression of the c-kit receptor characterizes a subset of neuroblastomas with favorable prognosis. Oncogene. 2004; 23:588–95.

30. Piper K, Brickwood S, Turnpenny LW, et al. Beta cell differentiation during early human pancreas development. J Endocrinol. 2004; 181:11–23.

31. Bouwens L, Lu WG, De Krijger R. Proliferation and differentiation in the human fetal endocrine pancreas. Diabetologia. 1997; 40:398–404.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download