MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study place and study duration
Study population
Immunohistochemistry
DNA extraction and polymerase chain reaction
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
RESULTS
Clinical findings
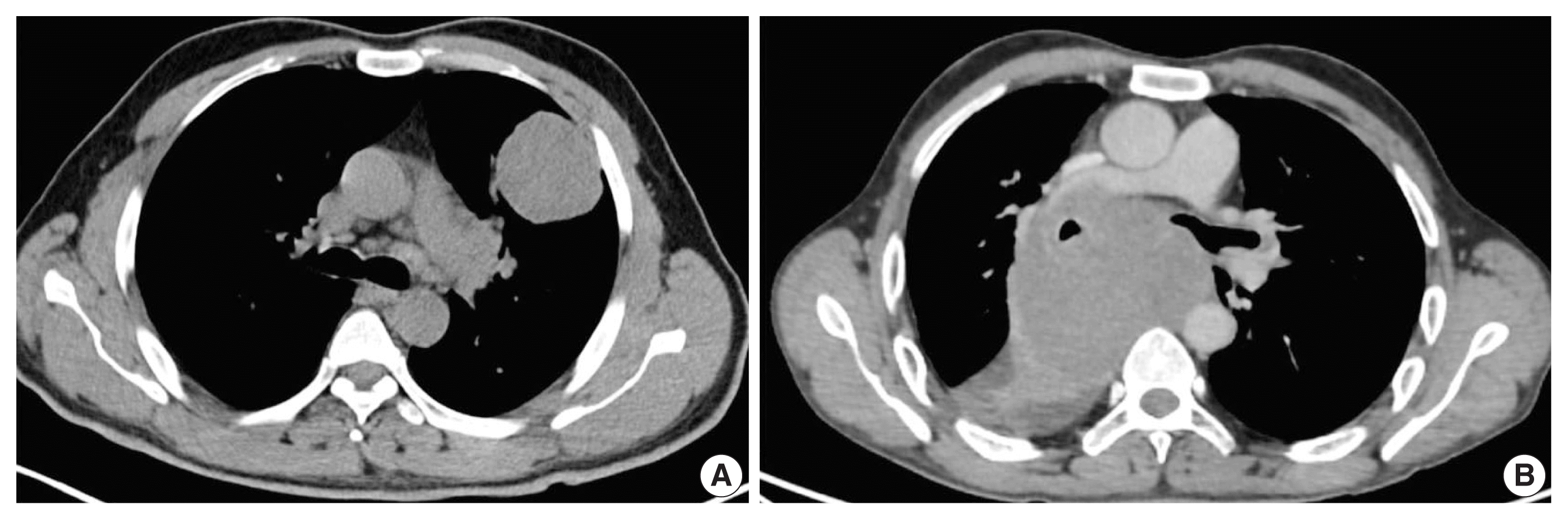 | Fig. 1Axial computed tomography images of SMARCA4/BRG1 protein–deficient thoracic sarcoma (SD-TS). (A) Case No. 7 showed well defined intra-pulmonary mass on the left side, abutting the pleural margin. (B) Case No. 8 showed a well defined heterogeneously enhancing mediastinal-based mass splaying the carina and abutting the right pulmonary artery, encasing the right main bronchus without invasion. |
Table 1
Pathological findings in SD-LUAD
 | Fig. 2Histology and immunohistochemistry images of SMARCA4/BRG1 protein–deficient lung adenocarcinoma (SD-LUAD). (A) Scanner view of SD-LUAD. Note the solid pattern of growth with a sieved appearance. (B) The dry high-power view exhibits large cells with sharp margins and scattered large signet ring cells that are regularly observed in this tumor type. Also note the bubbly cytoplasm of many cells with indented nuclei. (C) The second case of SD-LUAD exhibited tumor cells arranged in an Indian file pattern. (D) The third case of SD-LUAD showed with highly inflamed background and a solid growth pattern comprised of large rhabdoid cells. (E) Tumor cells showed intra-cytoplasmic mucin (arrow) highlighted by mucicarmine. (F, G) Tumor cells showed strong cytokeratin (CK) and CK7 immunoreactivity, respectively. (H) SD-LUAD expressed BerEp4, supporting the adenocarcinomatous histogenesis. (I) All SD-LUAD expressed varying degrees of Hep Par 1. (J) Transcription termination factor 1 was universally absent. (K, L) No SD-LUAD exhibited BRG1 nuclear expression. Note the strong nuclear reactivity for BRG1 in the inflammatory cells. |
Table 2
Table 3
Pathological findings in SD-TS
 | Fig. 3Histology images of cases. (A–C) Case No. 8 of SMARCA4/BRG1 protein–deficient thoracic sarcoma (SD-TS) showed a diffuse growth pattern. The constituent cells are large, and some have clear cytoplasm. Nuclei are irregular. (D, E) The stroma is inflamed in SD-TS. (E, F) Two cases (cases No. 7 and 9) revealed tumors with diffuse growth but obvious rhabdoid morphology of spheroidal cytoplasm, eccentric nuclei, and globoid inclusions. |
 | Fig. 4Immunophenotype of SMARCA4/BRG1 protein–deficient thoracic sarcoma (SD-TS). (A) Weak expression of pan-cytokeratin (CK) was observed in all cases of SD-TS. (B) Weak CK7 immunoreactivity was noted in case No. 7. (C) Focal strong CK7 staining is seen in case No. 8. (D) Case No. 7 expressed weak and focal Hep Par 1. (E–G) Expression of stemness markers of SALL4, SOX2, and CD34, respectively. (H) Expression of synaptophysin in case No. 7 of SD-TS. (I) Lack of nuclear expression of BRG1 defining BRG1 loss. Note the intense staining of stromal and inflammatory cells. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download