MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients and tissue samples
Table 1.
| Adjuvant chemotherapy regimen | No. of patients |
|---|---|
| Anthracycline-based | 164 |
| FAC | 132 |
| AC | 10 |
| FEC | 21 |
| EC | 1 |
| Taxane-anthracycline-based | 51 |
| AC →paclitaxel and/or docetaxel | 50 |
| FEC →paclitaxel | 1 |
| CMF | 65 |
| Change of regimen | 1a |
| Unknown | 2 |
| Total | 283 |
TMA construction and IHC
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 in TNBC tissues
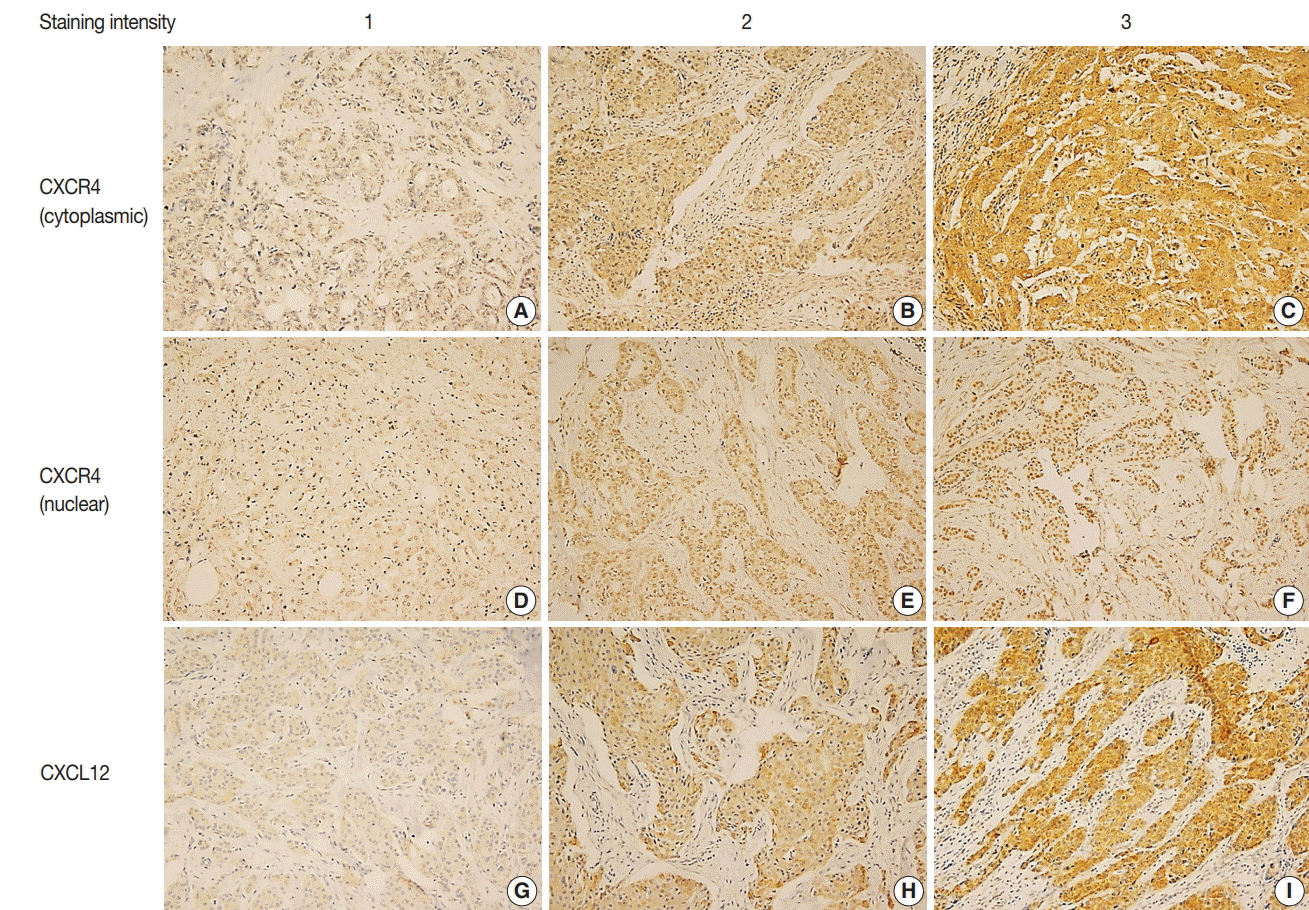 | Fig. 1.Immunohistochemistry for CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and CXC motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12). Representative immunohistochemistry images of cytoplasmic CXCR4 (A–C), nuclear CXCR4 (D–F), and CXCL12 (G–I) in order of staining intensity. CXCR4 and CXCL12 expression are mainly observed in tumor cells. CXCR4 shows cytoplasmic and nuclear staining, and CXCL12 shows cytoplasmic staining. |
Clinicopathologic characteristics and expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12
Table 2.
| Variable | Total (n = 259) |
CXCR4 (cytoplasmic) |
CXCR4 (nuclear) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n = 65) | High (n = 194) | p-value | Low (n=144) | High (n = 115) | p-value | ||
| Age (yr) | .008 | .524 | |||||
| ≤ 50 | 152 | 29 (19.1) | 123 (80.9) | 82 (53.9) | 70 (46.1) | ||
| > 50 | 107 | 36 (33.6) | 71 (66.4) | 62 (57.9) | 45 (42.1) | ||
| Histologic grade | .007 | .310 | |||||
| I, II | 47 | 19 (40.4) | 28 (59.6) | 23 (48.9) | 24 (51.1) | ||
| III | 212 | 46 (21.7) | 166 (78.3) | 121 (57.1) | 91 (42.9) | ||
| Size (cm) | .131a | .957 | |||||
| ≤ 5 | 243 | 58 (23.9) | 185 (76.1) | 135 (55.6) | 108 (44.4) | ||
| > 5 | 16 | 7 (43.8) | 9 (56.3) | 9 (56.3) | 7 (43.8) | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | .473 | .476 | |||||
| Negative | 165 | 39 (23.6) | 126 (76.4) | 89 (53.9) | 76 (46.1) | ||
| Positive | 94 | 26 (27.7) | 68 (72.3) | 55 (58.5) | 39 (41.5) | ||
| Stage | .045 | .087 | |||||
| I, II | 216 | 49 (22.7) | 167 (77.3) | 115 (53.2) | 101 (46.8) | ||
| III | 43 | 16 (37.2) | 27 (62.8) | 29 (67.4) | 14 (32.6) | ||
| Histologic type | .992 | .144 | |||||
| IDC | 239 | 60 (25.1) | 179 (74.9) | 136 (56.9) | 103 (43.1) | ||
| Otherb | 20 | 5 (25.0) | 15 (75.0) | 8 (40.0) | 12 (60.0) | ||
| Adjuvant chemotherapy regimenc | .009 | .538 | |||||
| Anthracycline-based | 149 | 27 (18.1) | 122 (81.9) | 79 (53.0) | 70 (47.0) | ||
| Taxane-anthracycline-based | 49 | 14 (28.6) | 35 (71.4) | 30 (61.2) | 19 (38.8) | ||
| CMF | 58 | 22 (37.9) | 36 (62.1) | 34 (58.6) | 24 (41.4) | ||
| Radiation therapyd | .506 | .975 | |||||
| No | 84 | 23 (27.4) | 61 (72.6) | 47 (56.0) | 37 (44.0) | ||
| Yes | 174 | 41 (23.6) | 133 (76.4) | 97 (55.7) | 77 (44.3) | ||
Values are presented as number (%).
CXCR4, CXC chemokine receptor type 4; IDC, Invasive ductal carcinoma; CMF, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil.
Table 3.
| Variable | Total (n = 238) |
CXCL12 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n = 123) | High (n = 115) | p-value | ||
| Age (yr) | .721 | |||
| ≤ 50 | 140 | 71 (50.7) | 69 (49.3) | |
| > 50 | 98 | 52 (53.1) | 46 (46.9) | |
| Histologic grade | .155 | |||
| I, II | 43 | 18 (41.9) | 25 (58.1) | |
| III | 195 | 105 (53.8) | 90 (46.2) | |
| Size (cm) | .045 | |||
| ≤ 5 | 223 | 119 (53.4) | 104 (46.6) | |
| > 5 | 15 | 4 (26.7) | 11 (73.3) | |
| Lymph node metastasis | .005 | |||
| Negative | 158 | 92 (58.2) | 66 (41.8) | |
| Positive | 80 | 31 (38.8) | 49 (61.3) | |
| Stage | .017 | |||
| I, II | 202 | 111 (55.0) | 91 (45.0) | |
| III | 36 | 12 (33.3) | 24 (66.7) | |
| Histologic type | .931 | |||
| IDC | 219 | 113 (51.6) | 106 (48.4) | |
| Othera | 19 | 10 (52.6) | 9 (47.4) | |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy regimenb | .117 | |||
| Anthracycline-based | 144 | 82 (56.9) | 62 (43.1) | |
| Taxane-anthracycline-based | 38 | 15 (39.5) | 23 (60.5) | |
| CMF | 53 | 25 (47.2) | 28 (52.8) | |
| Radiation therapyc | .408 | |||
| No | 79 | 38 (48.1) | 41 (51.9) | |
| Yes | 158 | 85 (53.8) | 73 (46.2) | |
Values are presented as number (%).
CXCL12, CXC motif chemokine 12; IDC, Invasive ductal carcinoma; CMF, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil.
Clinical outcome and pattern of recurrence after adjuvant chemotherapy
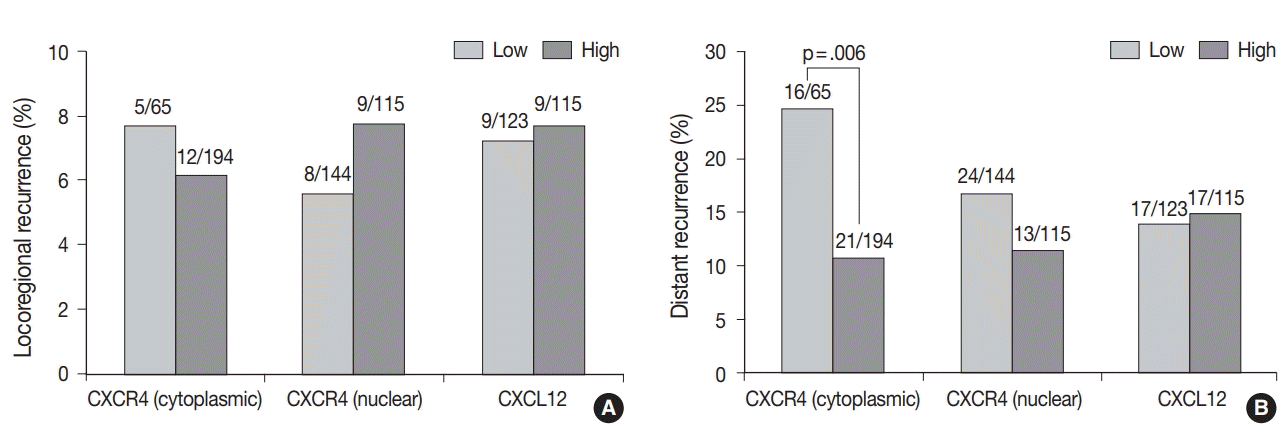 | Fig. 2.The pattern of recurrence after adjuvant chemotherapy according to CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and CXC motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12) expression. CXCR4 and CXCL12 expression do not show a significant association with locoregional recurrence (A), while high cytoplasmic CXCR4 expression is significantly associated with lower distant recurrence (B). Figures above each bar refer to the number of recurrences/the number of patients in each group. |
Table 4.
RFS and OS after adjuvant chemotherapy
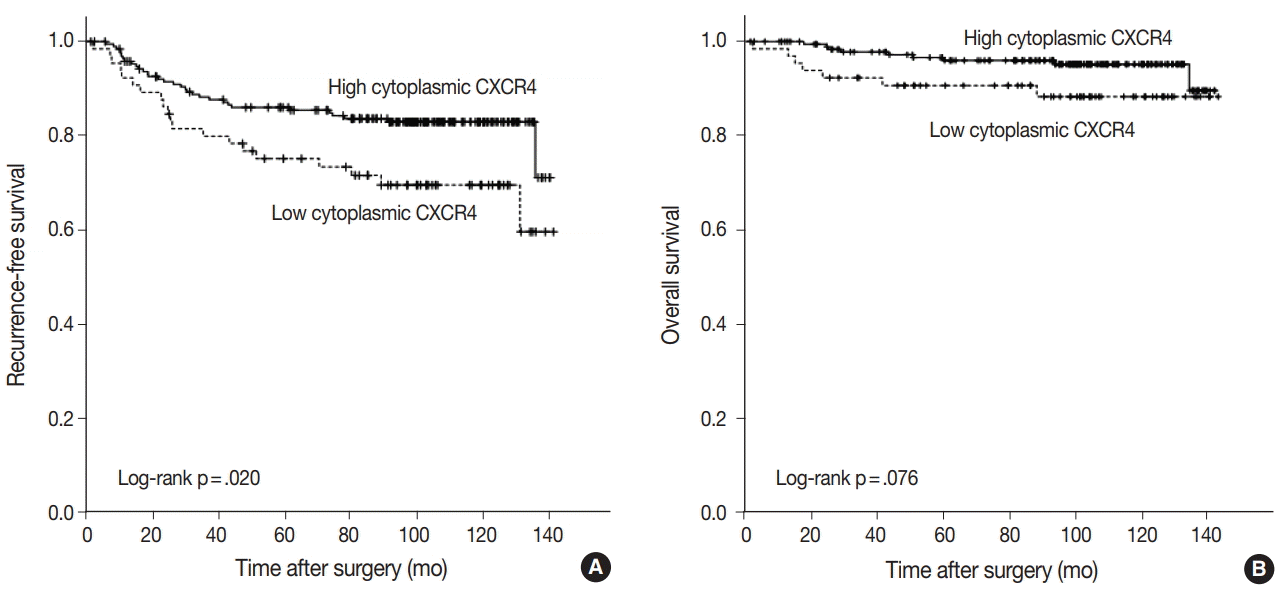 | Fig. 3.Recurrence-free and overall survival after adjuvant chemotherapy according to cytoplasmic CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) expression. Recurrence-free survival is significantly better in the high cytoplasmic CXCR4 group (A), but the difference in overall survival is not significant between high and low cytoplasmic CXCR4 groups (B). |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download