1. Herath NI, Boyd AW. The role of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010; 126:2003–11.

2. Pasquale EB. Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010; 10:165–80.

3. Janes PW, Adikari S, Lackmann M. Eph/ephrin signalling and function in oncogenesis: lessons from embryonic development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008; 8:473–9.

4. Lackmann M, Boyd AW. Eph, a protein family coming of age: more confusion, insight, or complexity? Sci Signal. 2008; 1:re2.

5. Boyd AW, Bartlett PF, Lackmann M. Therapeutic targeting of EPH receptors and their ligands. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13:39–62.

6. Tang XX, Zhao H, Robinson ME, et al. Implications of EPHB6, EFNB2, and EFNB3 expressions in human neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000; 97:10936–41.

7. Fox BP, Kandpal RP. Invasiveness of breast carcinoma cells and transcript profile: Eph receptors and ephrin ligands as molecular markers of potential diagnostic and prognostic application. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 318:882–92.

8. Kinch MS, Moore MB, Harpole DH Jr. Predictive value of the EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase in lung cancer recurrence and survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:613–8.
9. Nakamura R, Kataoka H, Sato N, et al. EPHA2/EFNA1 expression in human gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2005; 96:42–7.

10. Guan M, Xu C, Zhang F, Ye C. Aberrant methylation of EphA7 in human prostate cancer and its relation to clinicopathologic features. Int J Cancer. 2009; 124:88–94.
11. Herath NI, Spanevello MD, Sabesan S, et al. Over-expression of Eph and ephrin genes in advanced ovarian cancer: ephrin gene expression correlates with shortened survival. BMC Cancer. 2006; 6:144.

12. Batlle E, Bacani J, Begthel H, et al. EphB receptor activity suppresses colorectal cancer progression. Nature. 2005; 435:1126–30.

13. Hafner C, Becker B, Landthaler M, Vogt T. Expression profile of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in human skin and downregulation of EphA1 in nonmelanoma skin cancer. Mod Pathol. 2006; 19:1369–77.

14. Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, et al. Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem. 2004; 50:490–9.

15. Batlle E, Henderson JT, Beghtel H, et al. Beta-catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell. 2002; 111:251–63.
16. Kim JH, Kim KJ, Rhee YY, et al. Expression status of wild-type HSP110 correlates with HSP110 T17 deletion size and patient prognosis in microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. Mod Pathol. 2014; 27:443–53.
17. Bae JM, Kim JH, Cho NY, Kim TY, Kang GH. Prognostic implication of the CpG island methylator phenotype in colorectal cancers depends on tumour location. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109:1004–12.

18. Merlos-Suárez A, Barriga FM, Jung P, et al. The intestinal stem cell signature identifies colorectal cancer stem cells and predicts disease relapse. Cell Stem Cell. 2011; 8:511–24.

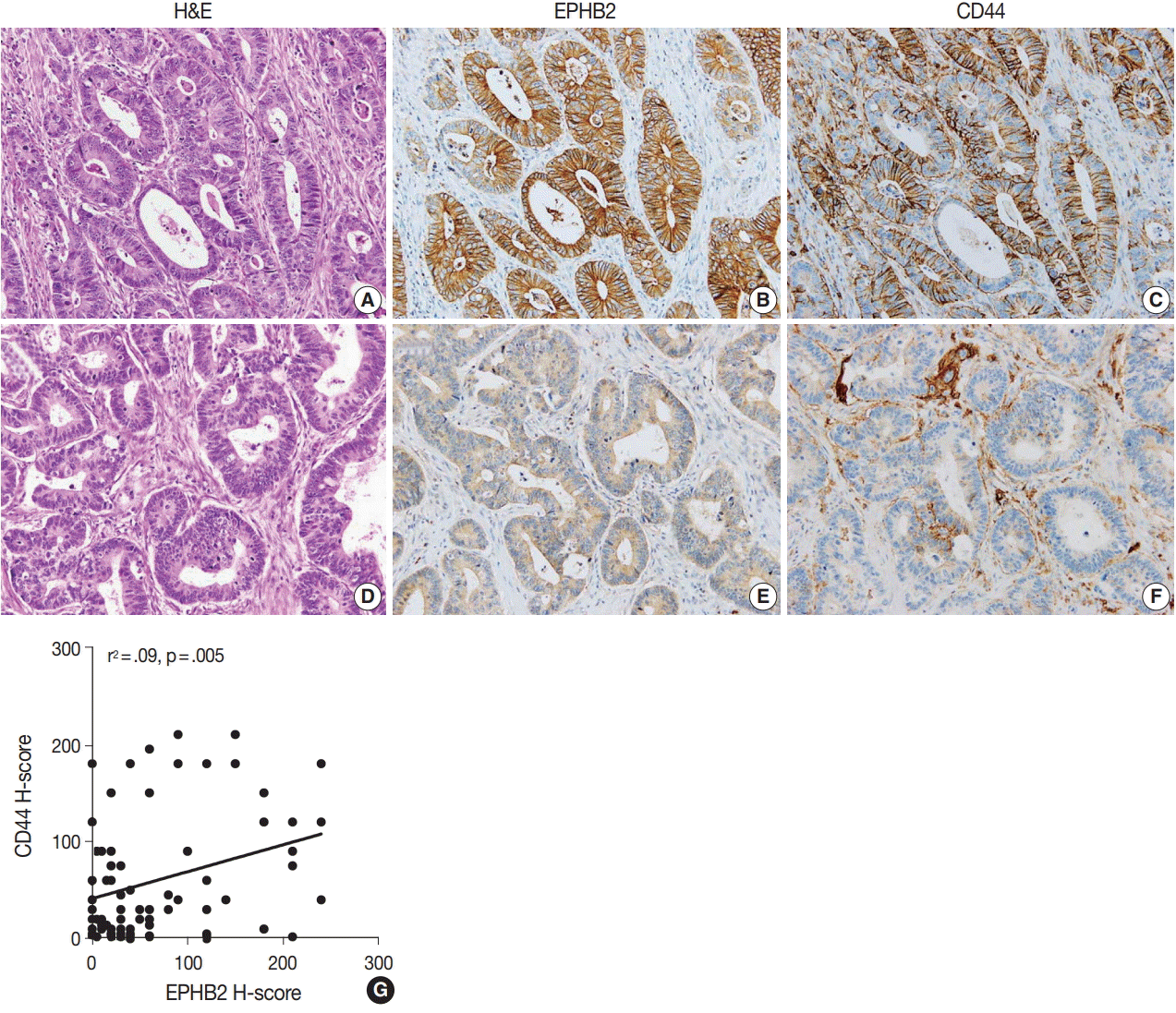
19. Guo DL, Zhang J, Yuen ST, et al. Reduced expression of EphB2 that parallels invasion and metastasis in colorectal tumours. Carcinogenesis. 2006; 27:454–64.

20. Lugli A, Spichtin H, Maurer R, et al. EphB2 expression across 138 human tumor types in a tissue microarray: high levels of expression in gastrointestinal cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:6450–8.

21. Kumar SR, Scehnet JS, Ley EJ, et al. Preferential induction of EphB4 over EphB2 and its implication in colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2009; 69:3736–45.

22. Alazzouzi H, Davalos V, Kokko A, et al. Mechanisms of inactivation of the receptor tyrosine kinase EPHB2 in colorectal tumors. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:10170–3.

23. Jubb AM, Zhong F, Bheddah S, et al. EphB2 is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11:5181–7.

24. Cortina C, Palomo-Ponce S, Iglesias M, et al. EphB-ephrin-B interactions suppress colorectal cancer progression by compartmentalizing tumor cells. Nat Genet. 2007; 39:1376–83.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download