Abstract
We report a rare case of a gastric plasmacytoma treated with endoscopic resection and oral thalidomide therapy. A 70-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with indigestion. He had no specific medical history and unremarkable laboratory results. Gastroendoscopic findings revealed a focal, erythematous, flat elevated lesion in the anterior wall of the stomach antrum. A biopsy revealed atypical lymphocytes. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) with an insulation-tipped knife was performed 45 days after diagnosis. Radiological and hematological evaluations, including a bone marrow biopsy, were performed and showed no involvement of other organs. The patient was diagnosed with extramedullary gastric plasmacytoma. Follow-up gastroendoscopy was performed three times during a 2-year period and showed nonspecific ESD scarring. The patient's condition was found to be stable.
Extramedullary plasmacytomas (EMPs) are uncommon and occur almost exclusively in the head, neck, and upper respiratory tract; EMPs in gastrointestinal organs are rare.1 The next most frequent site of mass lesion occurrence is the stomach; however, this is also extremely rare, accounting for less than 5% of all EMPs.2 EMPs of the head and neck are more sensitive to radiotherapy than to surgery.2,3 Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is a less invasive therapeutic approach for early gastric cancer and has been accepted as a standard therapeutic approach for early gastric cancers limited to the mucosa.4 Here, we report the successful treatment via ESD of a patient with a solitary gastric EMP confined to the mucosa.
A 70-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with the complaint of dyspepsia. He had no previous specific medical history and unremarkable laboratory results. We performed gastroscopy and observed a flat lesion with focal erythematous changes in the anterior wall of the antrum (Fig. 1). There were no specific serum and urine immunoelectrophoresis or immunofixation findings. A biopsy revealed poorly differentiated neoplastic cells and atypical lymphocytes, consistent with metastatic carcinoma. A Giemsa stain indicated Helicobacter pylori negativity. To rule out cancer and systemic diseases such as lymphoma, we performed a bone marrow aspiration, biopsy, and peripheral blood smear. There was no evidence of clonal marrow or peripheral plasmacytosis. We also performed abdominal and pelvic computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography/CT scans; these yielded unremarkable results, particularly with regard to lymph node and bone lesions. Regarding the gastric focal lesion, we performed an endoscopic procedure to confirm the previous endoscopic biopsy result as well as for therapeutic reasons using an insulation-tipped knife (KD-610L; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) (Fig. 2). After successful ESD, the acquired specimen revealed plasma cell infiltration into the lamina propria; however, these cells did not extend deeply into the submucosal layer. The lesion was confined to the mucosa and had a clear resection margin. Numerous plasma cells with atypical hyperchromatic nuclei were observed to infiltrate the gastric mucosa. The neoplastic cells were positive for CD138 (Fig. 3).
We finally diagnosed the patient with gastric EMP. Because EMPs are systemic, the patient was treated with additional oral thalidomide and dexamethasone. Later, we performed three endoscopic follow-up exams during a 2-year period and confirmed nonspecific ESD scarring. We found the patient's condition to be stable (Fig. 4).
Plasma cell neoplasms are classified into four types: solitary myeloma (bone plasmacytoma), multiple myeloma (bone marrow and other systemic involvements), extramedullary (soft tissue) plasmacytoma, and plasmablastic sarcoma.5 EMP is defined as an immunoproliferative, monoclonal, plasma cell tumor that develops in an extramedullary organ; gastric plasmacytomas are a very rare form of EMP. Gastric tumors account for 2% to 5% of all EMPs and tend to be identified at a late stage if an endoscopic examination is not performed.6 Gastric plasmacytomas can be classified into infiltrative, nodular, ulcerative, and polypoid types, of which the nodular type is most common. Most gastric plasmacytomas are large, deeply infiltrating tumors with ulceration; however, tumor cells are limited to the mucosal and submucosal layers in the early stage.7 Almost all patients with EMPs are treated with radiation therapy, surgery, or combination therapy (surgery and/or chemotherapy or irradiation). However, no general treatment guidelines have been established for gastric EMPs. Additionally, the invasiveness of these initial therapeutic approaches precludes their recommendation for EMPs of the head and neck.2,3
We also considered the possibility of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma in the present case, although the endoscopic findings suggested a reduced likelihood of MALT lymphoma. Extranodal lymphomas mainly occur in the stomach, whereas MALT lymphomas mainly occur in the digestive tract. MALT lymphomas arise in the mucosa and are related to the glandular epithelium. Further, H. pylori infection correlates with MALT lymphoma, and MALT lymphomas express B-cell lineage markers.8 However, in the present case CD138 immunostaining was positive and a Giemsa stain was negative. Some studies have reported the complete regression of EMPs after treatment for H. pylori.6,9,10 However, there is insufficient data to demonstrate a relationship between gastric plasmacytoma and H. pylori.11
Endoscopic mucosal resection has been established as a reliable therapeutic approach for early gastric cancers limited to the mucosa, but ESD has limited efficacy for infiltrative diseases. In this case, ESD was performed to treat a solitary gastric EMP confined to the mucosa. ESD has the advantages of being less invasive and less expensive and also has a lower incidence of side effects than surgery or radiotherapy.4 In addition, confinement of an EMP to the mucosa can be confirmed using endoscopic ultrasonography.10 In this case, plasma cells did not extend deeply into the submucosal layer. However, we administered additional thalidomide and dexamethasone to this patient because EMPs are systemic and a combination therapy with thalidomide and dexamethasone is known to be highly effective.12,13 Although other similar case reports have been published,10,13 further study is needed to confirm the results of solitary gastric EMP treatment via ESD. Nevertheless, our case report suggests that ESD can be an alternative therapeutic option for solitary gastric EMPs confined to the mucosa.
References
1. Weber DM. Solitary bone and extramedullary plasmacytoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2005; 2005:373–376. PMID: 16304406.

2. Alexiou C, Kau RJ, Dietzfelbinger H, et al. Extramedullary plasmacytoma: tumor occurrence and therapeutic concepts. Cancer. 1999; 85:2305–2314. PMID: 10357398.
3. Dimopoulos MA, Hamilos G. Solitary bone plasmacytoma and extramedullary plasmacytoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2002; 3:255–259. PMID: 12057071.

4. Gotoda T. Endoscopic resection of early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2007; 10:1–11. PMID: 17334711.

5. Kaler AK, Shankar A, Jena M. Extramedullary plasmacytoma of soft tissues and gingiva. Online J Health Allied Sci. 2012; 11:1–3.
6. Nolan KD, Mone MC, Nelson EW. Plasma cell neoplasms. Review of disease progression and report of a new variant. Surg Oncol. 2005; 14:85–90. PMID: 15993050.
7. Morita T, Tamura S, Yokoyama Y, et al. A case of early-stage gastric plasmacytoma. J Gastroenterol. 2002; 37:398–401. PMID: 12051542.

8. Wang L, Liu Y, Lin XY, et al. A case of enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (type I) arising in stomach without refractory celiac disease. Diagn Pathol. 2012; 7:172. PMID: 23217032.

9. Krishnamoorthy N, Bal MM, Ramadwar M, Deodhar K, Mohandas KM. A rare case of primary gastric plasmacytoma: an unforeseen surprise. J Cancer Res Ther. 2010; 6:549–551. PMID: 21358099.
10. Park CH, Lee SM, Kim TO, et al. Treatment of solitary extramedullary plasmacytoma of the stomach with endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gut Liver. 2009; 3:334–337. PMID: 20431772.

11. Shapiro M, Kimchi NA, Herbert M, Scapa E. Gastric plasmacytoma and Helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 39:56–57. PMID: 15599212.
12. Sekiguchi Y, Asahina T, Shimada A, et al. A case of extramedullary plasmablastic plasmacytoma successfully treated using a combination of thalidomide and dexamethasone and a review of the medical literature. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2013; 53:21–28. PMID: 23801130.

13. Kim JW, Kim HS, Lee JH, et al. Complete endoscopic resection of very early stage gastric plasmacytoma. Gut Liver. 2010; 4:547–550. PMID: 21253307.

Fig. 1
(A, B) Endoscopy showed a focal, erythematous, flat elevated lesion in the anterior wall of the stomach antrum.
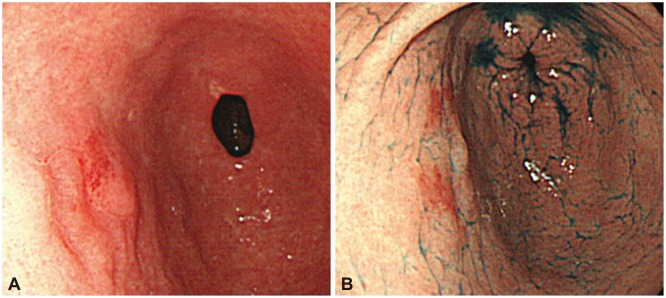
Fig. 2
(A) The lesion was resected using endoscopic submucosal dissection with an insulation-tipped knife. (B) The resected tumor was 40×35 mm in size.
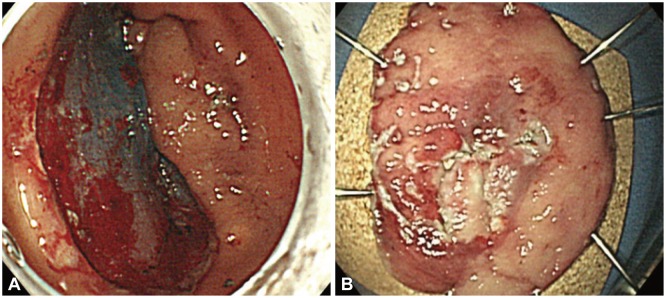
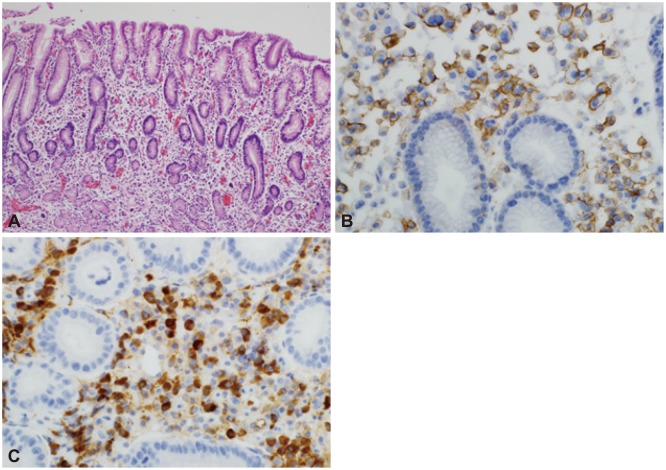
Fig. 3
(A) Numerous plasma cells were observed to infiltrate the gastric mucosa. Some of these cells contained atypical hyperchromatic nuclei (H&E stain, ×100). (B) The neoplastic cells were positive for CD138 (immunostaining, ×400). (C) The neoplastic cells were also positive for κ light chain (immunostaining, ×400).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download