1. Jang JY. The past, present, and future of image-enhanced endoscopy. Clin Endosc. 2015; 48:466–475.

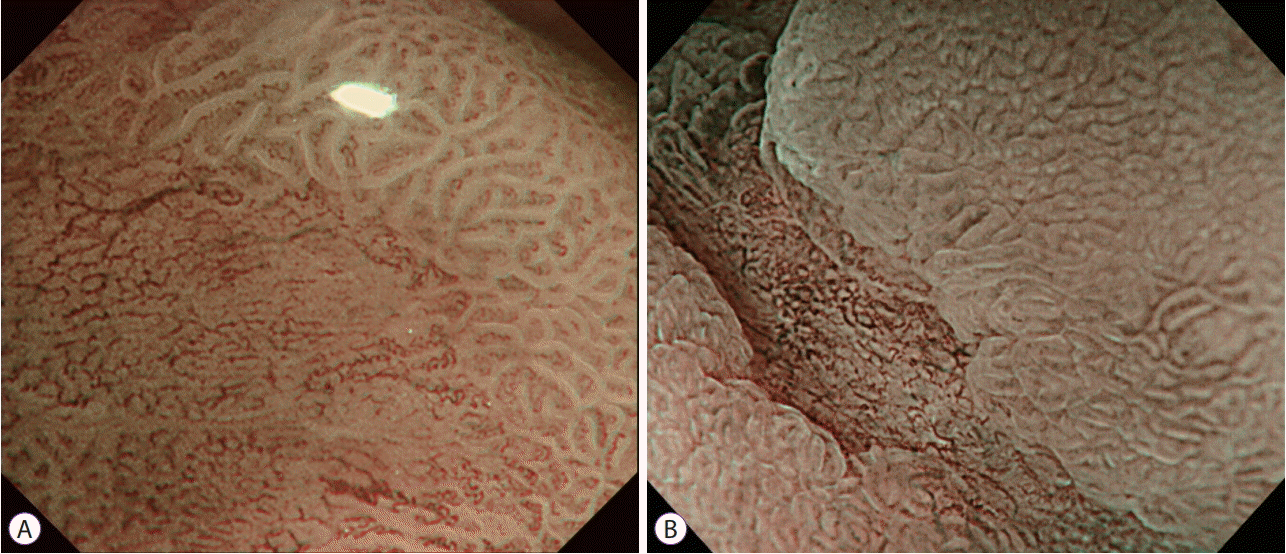
2. Kudo S, Hirota S, Nakajima T, et al. Colorectal tumours and pit pattern. J Clin Pathol. 1994; 47:880–885.

3. Oka S, Tanaka S, Kaneko I, et al. Advantage of endoscopic submucosal dissection compared with EMR for early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:877–883.

4. Asada-Hirayama I, Kodashima S, Sakaguchi Y, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging is more accurate for determination of horizontal extent of early gastric cancers than chromoendoscopy. Endosc Int Open. 2016; 4:E690–E698.

5. Nagahama T, Yao K, Uedo N, et al. Delineation of the extent of early gastric cancer by magnifying narrow-band imaging and chromoendoscopy: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2018; 50:566–576.

6. Yao K, Anagnostopoulos GK, Ragunath K. Magnifying endoscopy for diagnosing and delineating early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:462–467.

7. Kikuchi D, Iizuka T, Hoteya S, et al. Usefulness of magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging for determining tumor invasion depth in early gastric cancer. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2013; 2013:217695.

8. Nagahama T, Yao K, Maki S, et al. Usefulness of magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging for determining the horizontal extent of early gastric cancer when there is an unclear margin by chromoendoscopy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1259–1267.

9. Kiyotoki S, Nishikawa J, Satake M, et al. Usefulness of magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging for determining gastric tumor margin. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:1636–1641.

10. Kobara H, Mori H, Fujihara S, et al. Prediction of invasion depth for submucosal differentiated gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging. Oncol Rep. 2012; 28:841–847.

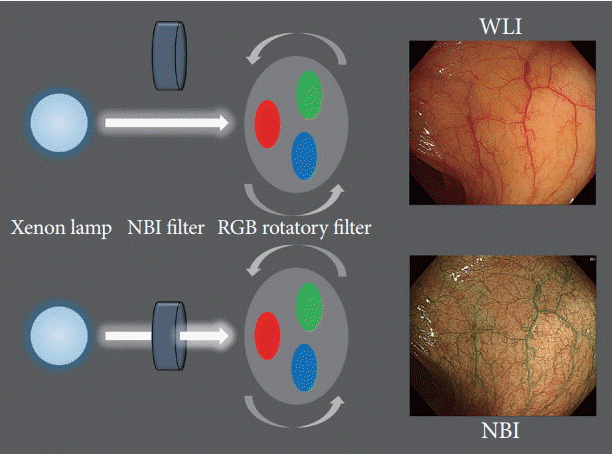
11. Gono K. Narrow band imaging: technology basis and research and development history. Clin Endosc. 2015; 48:476–480.

12. Gono K, Obi T, Yamaguchi M, et al. Appearance of enhanced tissue features in narrow-band endoscopic imaging. J Biomed Opt. 2004; 9:568–577.

13. Sano Y. New diagnostic method based on color imaging using narrow-band imaging (NBI) system for gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:AB125.
14. Muto M, Horimatsu T, Ezoe Y, Morita S, Miyamoto S. Improving visualization techniques by narrow band imaging and magnification endoscopy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:1333–1346.

15. Nakagawa S, Kato M, Shimizu Y, et al. Relationship between histopathologic gastritis and mucosal microvascularity: observations with magnifying endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:71–75.

16. Tajiri H, Doi T, Endo H, et al. Routine endoscopy using a magnifying endoscope for gastric cancer diagnosis. Endoscopy. 2002; 34:772–777.

17. Kim S, Harum K, Ito M, Tanaka S, Yoshihara M, Chayama K. Magnifying gastroendoscopy for diagnosis of histologic gastritis in the gastric antrum. Dig Liver Dis. 2004; 36:286–291.

18. Guelrud M, Herrera I, Essenfeld H, Castro J, Antonioli DA. Intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia: a prospective study with enhanced magnification endoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:584–589.

19. Yao K, Takaki Y, Matsui T, et al. Clinical application of magnification endoscopy and narrow-band imaging in the upper gastrointestinal tract: new imaging techniques for detecting and characterizing gastrointestinal neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2008; 18:415–433, vii-viii.

20. Yao K. Clinical application of magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging in the stomach. Clin Endosc. 2015; 48:481–490.

21. Yagi K, Nakamura A, Sekine A, Umezu H. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging for early differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma. Dig Endosc. 2008; 20:115–122.

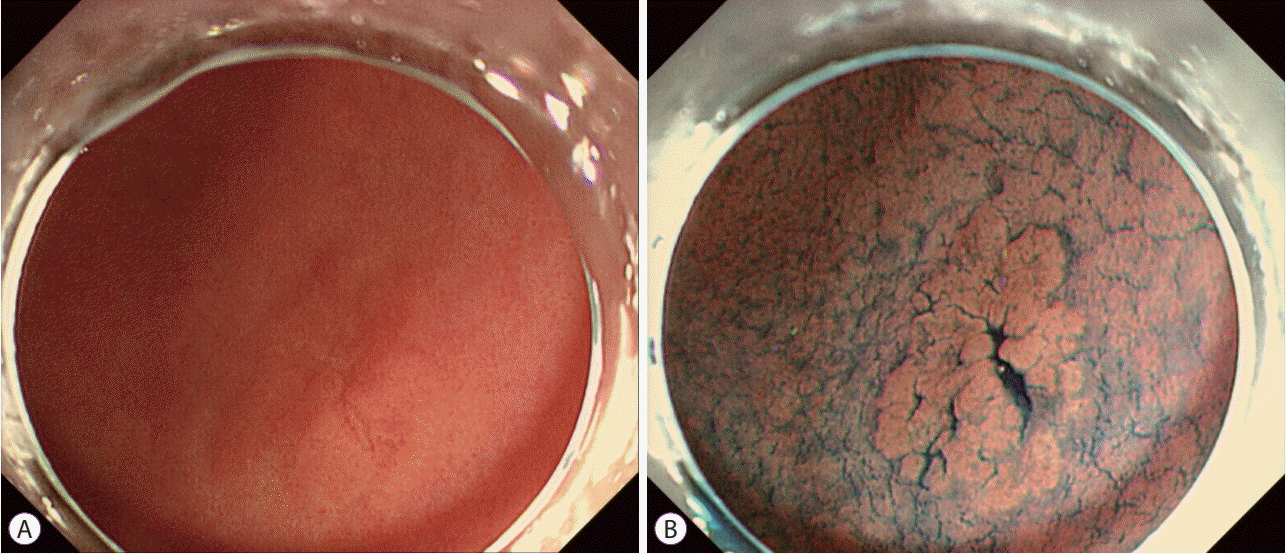
22. Nakayoshi T, Tajiri H, Matsuda K, Kaise M, Ikegami M, Sasaki H. Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow band imaging system for early gastric cancer: correlation of vascular pattern with histopathology (including video). Endoscopy. 2004; 36:1080–1084.

23. Ezoe Y, Muto M, Uedo N, et al. Magnifying narrowband imaging is more accurate than conventional white-light imaging in diagnosis of gastric mucosal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:2017–2025.e3.

24. Kato M, Kaise M, Yonezawa J, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging achieves superior accuracy in the differential diagnosis of superficial gastric lesions identified with white-light endoscopy: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:523–529.

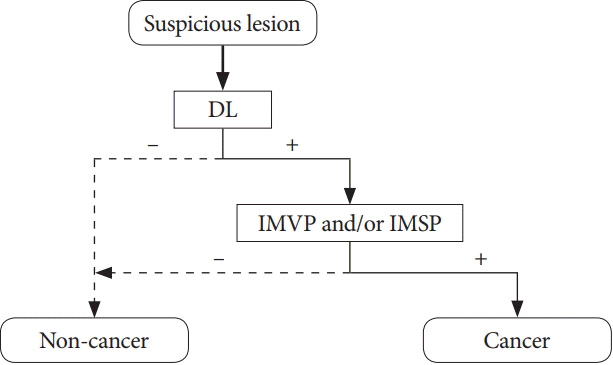
25. Muto M, Yao K, Kaise M, et al. Magnifying endoscopy simple diagnostic algorithm for early gastric cancer (MESDA-G). Dig Endosc. 2016; 28:379–393.

26. Choi J, Kim SG, Im JP, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS. Comparison of endoscopic ultrasonography and conventional endoscopy for prediction of depth of tumor invasion in early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:705–713.

27. Choi J, Kim SG, Im JP, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS. Endoscopic prediction of tumor invasion depth in early gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:917–927.

28. Yao K, Oishi T, Matsui T, Yao T, Iwashita A. Novel magnified endoscopic findings of microvascular architecture in intramucosal gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:279–284.

29. Tsujii Y, Kato M, Inoue T, et al. Integrated diagnostic strategy for the invasion depth of early gastric cancer by conventional endoscopy and EUS. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:452–459.

30. Iizuka T, Kikuchi D, Hoteya S, Yahagi N. The acetic acid + indigocarmine method in the delineation of gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:1358–1361.
31. Goda K, Dobashi A, Yoshimura N, et al. Dual-focus versus conventional magnification endoscopy for the diagnosis of superficial squamous neoplasms in the pharynx and esophagus: a randomized trial. Endoscopy. 2016; 48:321–329.

32. Goda K, Dobashi A, Tajiri H. Perspectives on narrow-band imaging endoscopy for superficial squamous neoplasms of the orohypopharynx and esophagus. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26 Suppl 1:1–11.

33. Singh R, Jayanna M, Navadgi S, Ruszkiewicz A, Saito Y, Uedo N. Narrow-band imaging with dual focus magnification in differentiating colorectal neoplasia. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25 Suppl 2:16–20.

34. Singh R, Shahzad MA, Tam W, et al. Preliminary feasibility study using a novel narrow-band imaging system with dual focus magnification capability in Barrett’s esophagus: is the time ripe to abandon random biopsies? Dig Endosc. 2013; 25 Suppl 2:151–156.

35. Wallace MB, Crook JE, Coe S, et al. Accuracy of in vivo colorectal polyp discrimination by using dual-focus high-definition narrow-band imaging colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:1072–1087.
36. Ikematsu H, Matsuda T, Osera S, et al. Usefulness of narrow-band imaging with dual-focus magnification for differential diagnosis of small colorectal polyps. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:844–850.

37. Bond A, Burkitt MD, Cox T, et al. Dual-focus magnification, high-definition endoscopy improves pathology detection in direct-to-test diagnostic upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2017; 26:19–24.

38. Li HY, Ge ZZ, Fujishiro M, Li XB. Current clinical applications of magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging in the stomach. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012; 2012:271914.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download