A 76-year-old woman presented with complaints of pruritus and painless jaundice. She had undergone radical resection of a stage IIB retinal melanoma followed by chemotherapy and immunotherapy 5 years before and is free of disease in last 3 years.
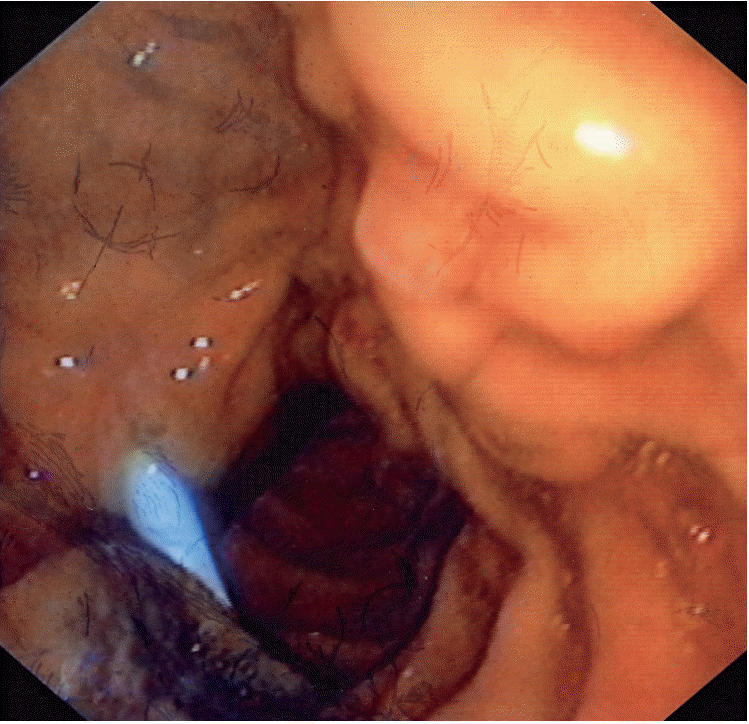
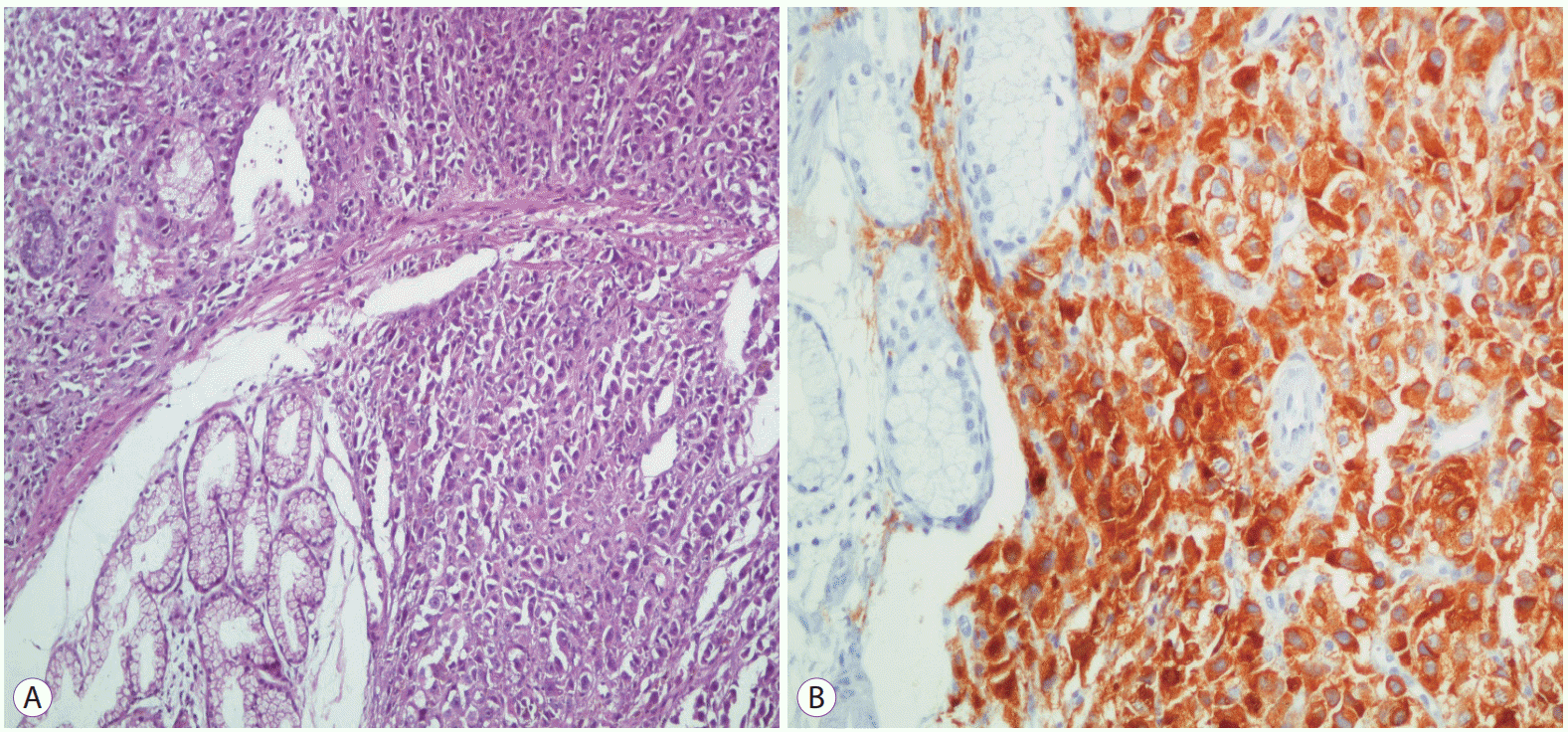
On admission, she had a total bilirubin level of 9.6 mg/dL (direct, 6.3 mg/dL) and highly elevated cholestatic enzymes. An abdominal computed tomography revealed dilation of the intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary systems, as well as the main pancreatic duct up to the level of the major papilla. No evidence of metastases to the liver or other organs were observed. An endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography image demonstrated a swollen major papilla with a blackish hue at the periampullary area and a black volcano-like lesion near the major papilla (Fig. 1). Conventional cannulation of the common bile duct was impossible. Therefore, a suprapapillary sphincterotomy was performed. Many biopsy specimens were taken through sphincterotomy, from the volcano-like lesion. A palliative 10-Fr, 7-cm plastic stent was placed (Fig. 1). Histological examination of the biopsies with hematoxylin-eosin staining revealed spindle-shaped cells with cytoplasmic brightness and nuclear atypia consistent with the diagnosis of melanoma (Fig. 2). Immunohistochemistry was positive for melan-A protein antigen, confirming the diagnosis of metastatic malignant melanoma (Fig. 2). An outpatient positron emission tomography scan showed numerous areas from the chest to the abdomen with hypermetabolic activity indicating neoplasia. She underwent palliative chemotherapy but died 6 months later.
Malignant melanoma is among the most threatening malignancies and a highly metastatic cancer [1]. Gastrointestinal tract metastases involve mostly the small intestine and colon [2]. Cholestatic jaundice due to major papilla or periampullary area metastases is rare [3].
The endoscopic findings of melanomas metastases frequently comprise a black volcano-like lesion or infiltrates in the submucosa and extend for variable depths into the wall [4]. Amelanotic lesions with variable appearance are rare entities [2,4]. The diagnosis of malignancy is established by immunohistochemical analysis of biopsy specimens; the tumor marker S-100 protein positivity ranges from 30% to 100%, melan-A protein antigen has high specificity (100%), and HMB-45 protein displays high specificity (100%) and sensitivity of 80%–90% [1].




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download