1. García-Pagán JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J. Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:458–461.

2. Garcia-Tsao G, Bosch J. Management of varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:823–832.

3. de Franchis R, Primignani M. Natural history of portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2001; 5:645–663.

4. de Franchis R. Revising consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno V consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2010; 53:762–768.

5. Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology. 2017; 65:310–335.

6. de Franchis R. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno VI consensus workshop: stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2015; 63:743–752.
7. Cheung J, Soo I, Bastiampillai R, Zhu Q, Ma M. Urgent vs. non-urgent endoscopy in stable acute variceal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:1125–1129.

8. Hsu YC, Chung CS, Tseng CH, et al. Delayed endoscopy as a risk factor for in-hospital mortality in cirrhotic patients with acute variceal hemorrhage. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 24:1294–1299.

9. Chen PH, Chen WC, Hou MC, et al. Delayed endoscopy increases re-bleeding and mortality in patients with hematemesis and active esophageal variceal bleeding: a cohort study. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:1207–1213.

10. Garcia-Tsao G, Sanyal AJ, Grace ND, Carey W. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2007; 46:922–938.

11. de Franchis R, Primignani M. Endoscopic treatments for portal hypertension. Semin Liver Dis. 1999; 19:439–455.

12. Hashizume M, Ohta M, Ueno K, Tanoue K, Kitano S, Sugimachi K. Endoscopic ligation of esophageal varices compared with injection sclerotherapy: a prospective randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 39:123–126.

13. Lo GH, Lai KH, Cheng JS, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of sclerotherapy versus ligation in the management of bleeding esophageal varices. Hepatology. 1995; 22:466–471.

14. Poza Cordon J, Froilan Torres C, Burgos García A, Gea Rodriguez F, Suárez de Parga JM. Endoscopic management of esophageal varices. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 4:312–322.
15. Cárdenas A. Management of acute variceal bleeding: emphasis on endoscopic therapy. Clin Liver Dis. 2010; 14:251–262.

16. Soehendra N, Binmoeller KF. Is sclerotherapy out? Endoscopy. 1997; 29:283–284.

17. Azoulay D, Castaing D, Majno P, et al. Salvage transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for uncontrolled variceal bleeding in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2001; 35:590–597.

18. Bureau C, Garcia Pagan JC, Layrargues GP, et al. Patency of stents covered with polytetrafluoroethylene in patients treated by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term results of a randomized multicentre study. Liver Int. 2007; 27:742–747.

19. Yang Z, Han G, Wu Q, et al. Patency and clinical outcomes of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stents versus bare stents: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:1718–1725.

20. Panés J, Terés J, Bosch J, Rodés J. Efficacy of balloon tamponade in treatment of bleeding gastric and esophageal varices. Results in 151 consecutive episodes. Dig Dis Sci. 1988; 33:454–459.
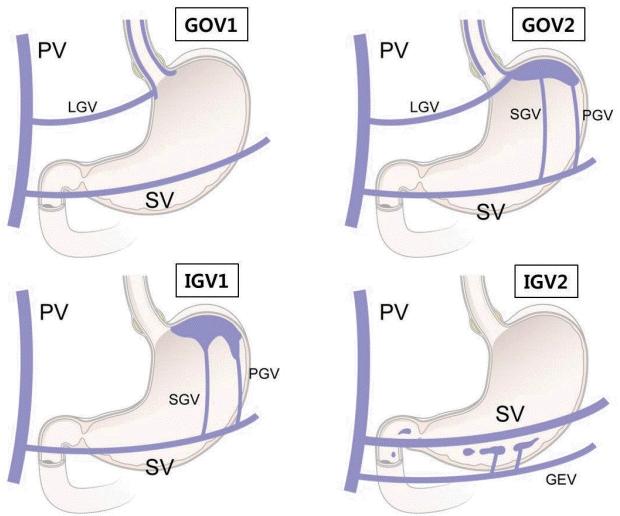
21. Sarin SK, Lahoti D, Saxena SP, Murthy NS, Makwana UK. Prevalence, classification and natural history of gastric varices: a long-term follow-up study in 568 portal hypertension patients. Hepatology. 1992; 16:1343–1349.

22. Sarin SK. Long-term follow-up of gastric variceal sclerotherapy: an eleven-year experience. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997; 46:8–14.

23. Watanabe K, Kimura K, Matsutani S, Ohto M, Okuda K. Portal hemodynamics in patients with gastric varices. A study in 230 patients with esophageal and/or gastric varices using portal vein catheterization. Gastroenterology. 1988; 95:434–440.
24. Ryan BM, Stockbrugger RW, Ryan JM. A pathophysiologic, gastroenterologic, and radiologic approach to the management of gastric varices. Gastroenterology. 2004; 126:1175–1189.

25. Maruyama H, Okugawa H, Yoshizumi H, Kobayashi S, Yokosuka O. Hemodynamic features of gastrorenal shunt: a Doppler study in cirrhotic patients with gastric fundal varices. Acad Radiol. 2008; 15:1148–1154.
26. Greenwald BD, Caldwell SH, Hespenheide EE, et al. N-2-butyl-cyanoacrylate for bleeding gastric varices: a United States pilot study and cost analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:1982–1988.

27. Kim MY, Um SH, Baik SK, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of gastric variceal bleeding: retrospective Korean multicenter data. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013; 19:36–44.

28. Seo YS. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2018; 24:20–42.

29. Lim YS. Practical approach to endoscopic management for bleeding gastric varices. Korean J Radiol. 2012; 13 Suppl 1:S40–S44.

30. Cheng LF, Wang ZQ, Li CZ, Lin W, Yeo AE, Jin B. Low incidence of complications from endoscopic gastric variceal obturation with butyl cyanoacrylate. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:760–766.

31. Kim JW, Baik SK, Kim KH, et al. [Effect of endoscopic sclerotherapy using N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in patients with gastric variceal bleeding]. Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12:394–403.
32. Paik CN, Kim SW, Lee IS, et al. The therapeutic effect of cyanoacrylate on gastric variceal bleeding and factors related to clinical outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008; 42:916–922.

33. Jun CH, Kim KR, Yoon JH, et al. Clinical outcomes of gastric variceal obliteration using N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate in patients with acute gastric variceal hemorrhage. Korean J Intern Med. 2014; 29:437–444.
34. Qiao W, Ren Y, Bai Y, Liu S, Zhang Q, Zhi F. Cyanoacrylate injection versus band ligation in the endoscopic management of acute gastric variceal bleeding: meta-analysis of randomized, controlled studies based on the PRISMA statement. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e1725.
35. Park SW, Seo YS, Lee HA, et al. Changes in cardiac varices and their clinical significance after eradication of esophageal varices by band ligation. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 2016:2198163.

36. Takeuchi M, Nakai Y, Syu A, Okamoto E, Fujimoto J. Endoscopic ligation of gastric varices. Lancet. 1996; 348:1038.

37. Toubia N, Sanyal AJ. Portal hypertension and variceal hemorrhage. Med Clin North Am. 2008; 92:551–574. , viii.

38. Lo GH, Lin CW, Perng DS, et al. A retrospective comparative study of histoacryl injection and banding ligation in the treatment of acute type 1 gastric variceal hemorrhage. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:1198–1204.

39. Tan PC, Hou MC, Lin HC, et al. A randomized trial of endoscopic treatment of acute gastric variceal hemorrhage: N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate injection versus band ligation. Hepatology. 2006; 43:690–697.

40. El Amin H, Abdel Baky L, Sayed Z, et al. A randomized trial of endoscopic variceal ligation versus cyanoacrylate injection for treatment of bleeding junctional varices. Trop Gastroenterol. 2010; 31:279–284.
41. Mahadeva S, Bellamy MC, Kessel D, Davies MH, Millson CE. Cost-effectiveness of N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (histoacryl) glue injections versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the management of acute gastric variceal bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98:2688–2693.

42. Procaccini NJ, Al-Osaimi AM, Northup P, Argo C, Caldwell SH. Endoscopic cyanoacrylate versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for gastric variceal bleeding: a single-center U.S. analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:881–887.

43. Chau TN, Patch D, Chan YW, Nagral A, Dick R, Burroughs AK. “Salvage” transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: gastric fundal compared with esophageal variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 1998; 114:981–987.

44. Barange K, Péron JM, Imani K, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the treatment of refractory bleeding from ruptured gastric varices. Hepatology. 1999; 30:1139–1143.

45. Sahagun G, Benner KG, Saxon R, et al. Outcome of 100 patients after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for variceal hemorrhage. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997; 92:1444–1452.
46. Sanyal AJ, Freedman AM, Luketic VA, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts for patients with active variceal hemorrhage unresponsive to sclerotherapy. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:138–146.

47. Imai Y, Nakazawa M, Ando S, Sugawara K, Mochida S. Long-term outcome of 154 patients receiving balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for gastric fundal varices. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 31:1844–1850.

48. Jang SY, Kim GH, Park SY, et al. Clinical outcomes of balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration for the treatment of gastric variceal hemorrhage in Korean patients with liver cirrhosis: a retrospective multicenter study. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2012; 18:368–374.

49. Park JK, Saab S, Kee ST, et al. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO) for treatment of gastric varices: review and meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2015; 60:1543–1553.

50. Wang YB, Zhang JY, Gong JP, Zhang F, Zhao Y. Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration versus transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for treatment of gastric varices due to portal hypertension: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 31:727–733.

51. Gwon DI, Kim YH, Ko GY, et al. Vascular plug-assisted retrograde transvenous obliteration for the treatment of gastric varices and hepatic encephalopathy: a prospective multicenter study. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015; 26:1589–1595.

52. Ibrahim M, El-Mikkawy A, Abdel Hamid M, et al. Early application of haemostatic powder added to standard management for oesophagogastric variceal bleeding: a randomised trial. Gut. 2019; 68:844–853.

53. Escorsell À, Pavel O, Cárdenas A, et al. Esophageal balloon tamponade versus esophageal stent in controlling acute refractory variceal bleeding: a multicenter randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology. 2016; 63:1957–1967.

54. Boustière C, Dumas O, Jouffre C, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography classification of gastric varices in patients with cirrhosis. Comparison with endoscopic findings. J Hepatol. 1993; 19:268–272.

55. Bhatia V. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) for esophageal and gastric varices: how can it improve the outcomes and reduce complications of glue injection. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2012; 2:70–74.

56. Bhat YM, Weilert F, Fredrick RT, et al. EUS-guided treatment of gastric fundal varices with combined injection of coils and cyanoacrylate glue: a large U.S. experience over 6 years (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:1164–1172.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download