A 76-year-old man was referred from a local clinic and admitted to our hospital for colonic ESD for a large polypoid mass. His history included PLA 4 years prior and a cystectomy for a bladder tumor. He denied any other medical history. Initially, his vital signs, physical examination results, laboratory tests, and plain abdominal films were normal. During colonoscopy, a 5-cm mass was seen in the cecum (
Fig. 1A). The mass was identified as a tubular adenoma and focal high-grade dysplasia on a preprocedural evaluation. ESD was performed using a J-type knife (FINEMEDIX Co., Daegu, Korea) connected to an electrosurgical unit (VIO®300D; ERBE, Tübingen, Germany). The injection material was 0.4% sodium hyaluronate solution (Endo-Mucoup; BMI Korea Co., Jeju, Korea). The total procedure time was 120 min. Because of massive bleeding that occurred during ESD, a piecemeal
en-bloc resection was performed. No immediate complications were noted (
Fig. 1B). Four days after the procedure, the patient complained of myalgia and abdominal discomfort. His blood pressure was 128/78 mm Hg, and his body temperature was 38.2℃. Palpation of the abdomen showed tenderness and mild rebound tenderness on the epigastric and right upper quadrant areas. Laboratory tests indicated a leukocyte count of 12,450/mL (normal range, 4,000–10,800/mL), hemoglobin level of 11.6 g/dL (normal range, 11–17 g/dL), aspartate aminotransferase level of 27 IU/L (normal range, <37 IU/L), alanine aminotransferase level of 33 IU/L (normal range, <41 IU/L), total bilirubin level of 1.07 mg/dL (normal range, 0.3–1.2 mg/dL), alkaline phosphatase level of 120 U/L (normal range, 40–129 U/L), and C-reactive protein level of 19.2 mg/dL (normal range, <0.3 mg/dL). Computed tomography (CT) revealed a 5.4-cm, newly developed PLA in the right lobe of the liver, in contrast to the previous CT that was obtained 14 days before (
Fig. 2A,
B). After blood cultures were collected, antibiotics (third-generation cephalosporin and metronidazole) were administered. Next, a drainage catheter was placed with radiologic and ultrasonographic guidance (
Fig. 3). From the drainage catheter, about 25 mL of turbid yellow pus was obtained. On microscopic examination, there were many leukocytes in pus. However, cultures from blood and pus were negative for bacterial growth. As the antimicrobial therapy continued, the patient’s clinical symptoms resolved. The drainage catheter was removed, and he was discharged 2 weeks after the procedure. Two months after discharge, serial CT scans showed complete resolution of the PLA (
Fig. 4). The pathologic diagnosis of the ESD specimen was colon adenocarcinoma. However, as ESD was performed through piecemeal
en-bloc resection, the pathologic report could not exclude submucosal invasion of the adenocarcinoma. Consequently, the patient underwent an additional surgery. The final pathologic report indicated no residual tumor at the endoscopic resection site. During follow-up, he complained of no PLA-related symptoms.
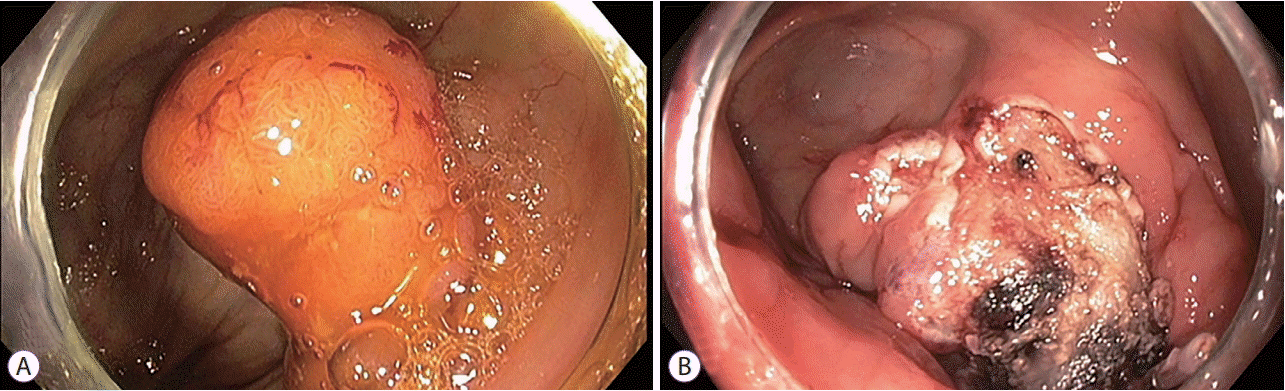 | Fig. 1.(A) Colonoscopy image showing a 5-cm polypoid mass at the cecum. (B) The mass was removed be means of endoscopic submucosal dissection. 
|
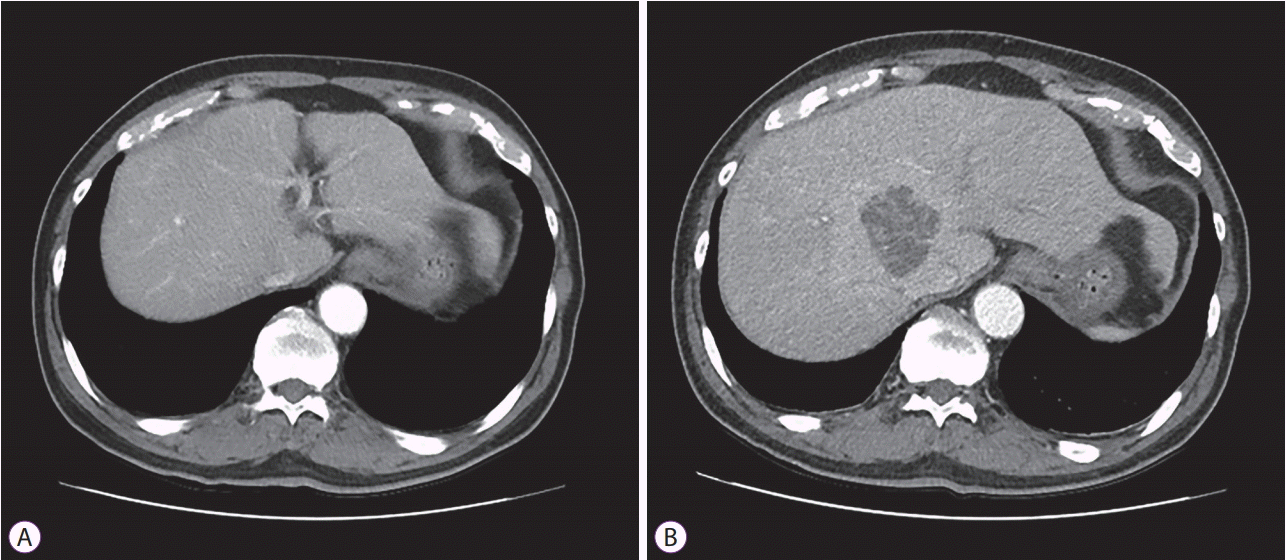 | Fig. 2.(A) Computed tomography (CT) scan showing normal findings 14 days before endoscopic submucosal dissection. (B) CT with intravenous contrast revealed a 5.4-cm pyogenic liver abscess in the right lobe of the liver. 
|
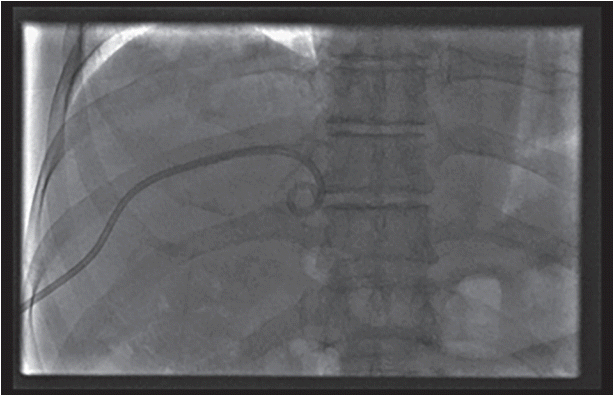 | Fig. 3.The drainage catheter was placed with radiologic and ultrasonographic guidance. 
|
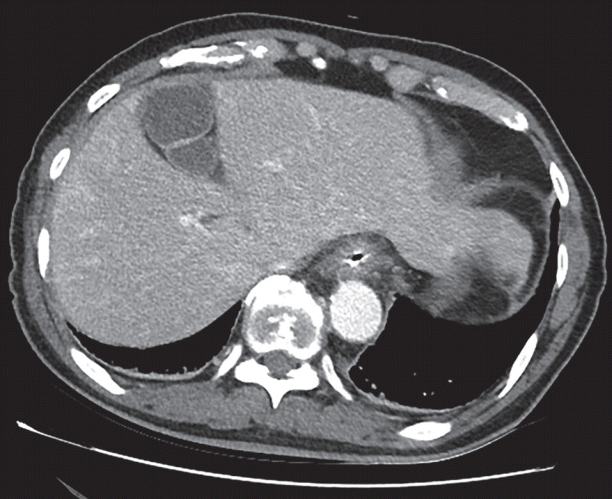 | Fig. 4.Two months after discharge, serial computed tomography scan showed complete resolution of pyogenic liver abscess. 
|

