1. Morson B. President’s address. The polyp-cancer sequence in the large bowel. Proc R Soc Med. 1974; 67(6 Pt 1):451–457.
2. Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:687–696.

3. Lieberman D, Moravec M, Holub J, Michaels L, Eisen G. Polyp size and advanced histology in patients undergoing colonoscopy screening: implications for CT colonography. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:1100–1105.

4. Rex DK, Overhiser AJ, Chen SC, Cummings OW, Ulbright TM. Estimation of impact of American College of Radiology recommendations on CT colonography reporting for resection of high-risk adenoma findings. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:149–153.

5. Butterly LF, Chase MP, Pohl H, Fiarman GS. Prevalence of clinically important histology in small adenomas. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:343–348.

6. Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Five-year colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:1077–1085.

7. Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. Gastroenterology. 2008; 134:1570–1595.

8. Kessler WR, Imperiale TF, Klein RW, Wielage RC, Rex DK. A quantitative assessment of the risks and cost savings of forgoing histologic examination of diminutive polyps. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:683–691.

9. Hassan C, Pickhardt PJ, Rex DK. A resect and discard strategy would improve cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:865–869. 869.e1-e3.

10. Gellad ZF, Voils CI, Lin L, Provenzale D. Clinical practice variation in the management of diminutive colorectal polyps: results of a national survey of gastroenterologists. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108:873–878.

11. von Renteln D, Bouin M, Barkun AN, et al. Patients’ willingness to defer resection of diminutive polyps: results of a multicenter survey. Endoscopy. 2018; 50:221–229.

12. Ponugoti PL, Cummings OW, Rex DK. Risk of cancer in small and diminutive colorectal polyps. Dig Liver Dis. 2017; 49:34–37.

13. ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Thosani N, et al. ASGE Technology Committee systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting real-time endoscopic assessment of the histology of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:502.e1–e502.e16.

14. Brenner H, Altenhofen L, Stock C, Hoffmeister M. Natural history of colorectal adenomas: birth cohort analysis among 3.6 million participants of screening colonoscopy. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013; 22:1043–1051.

15. Mizuno K, Suzuki Y, Takeuchi M, Kobayashi M, Aoyagi Y. Natural history of diminutive colorectal polyps: long-term prospective observation by colonoscopy. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26 Suppl 2:84–89.

16. Hofstad B, Vatn MH, Andersen SN, et al. Growth of colorectal polyps: redetection and evaluation of unresected polyps for a period of three years. Gut. 1996; 39:449–456.

17. Machida H, Sano Y, Hamamoto Y, et al. Narrow-band imaging in the diagnosis of colorectal mucosal lesions: a pilot study. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:1094–1098.

18. Apel D, Jakobs R, Schilling D, et al. Accuracy of high-resolution chromoendoscopy in prediction of histologic findings in diminutive lesions of the rectosigmoid. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:824–828.

19. Tischendorf JJ, Wasmuth HE, Koch A, Hecker H, Trautwein C, Winograd R. Value of magnifying chromoendoscopy and narrow band imaging (NBI) in classifying colorectal polyps: a prospective controlled study. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:1092–1096.

20. De Palma GD, Rega M, Masone S, et al. Conventional colonoscopy and magnified chromoendoscopy for the endoscopic histological prediction of diminutive colorectal polyps: a single operator study. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:2402–2405.
21. Wilson AI, Saunders BP. New paradigms in polypectomy: resect and discard, diagnose and disregard. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2015; 25:287–302.
22. Su MY, Hsu CM, Ho YP, Chen PC, Lin CJ, Chiu CT. Comparative study of conventional colonoscopy, chromoendoscopy, and narrow-band imaging systems in differential diagnosis of neoplastic and nonneoplastic colonic polyps. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:2711–2716.

23. Chiu HM, Chang CY, Chen CC, et al. A prospective comparative study of narrow-band imaging, chromoendoscopy, and conventional colonoscopy in the diagnosis of colorectal neoplasia. Gut. 2007; 56:373–379.

24. Ignjatovic A, East JE, Guenther T, et al. What is the most reliable imaging modality for small colonic polyp characterization? Study of white-light, autofluorescence, and narrow-band imaging. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:94–99.

25. Longcroft-Wheaton GR, Higgins B, Bhandari P. Flexible spectral imaging color enhancement and indigo carmine in neoplasia diagnosis during colonoscopy: a large prospective UK series. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 23:903–911.
26. Kudo S, Tamura S, Nakajima T, Yamano H, Kusaka H, Watanabe H. Diagnosis of colorectal tumorous lesions by magnifying endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:8–14.

27. Fu KI, Sano Y, Kato S, et al. Chromoendoscopy using indigo carmine dye spraying with magnifying observation is the most reliable method for differential diagnosis between non-neoplastic and neoplastic colorectal lesions: a prospective study. Endoscopy. 2004; 36:1089–1093.

28. Konishi K, Kaneko K, Kurahashi T, et al. A comparison of magnifying and nonmagnifying colonoscopy for diagnosis of colorectal polyps: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:48–53.

29. Togashi K, Konishi F. Magnification chromo-colonoscopy. ANZ J Surg. 2006; 76:1101–1105.

30. Togashi K, Konishi F, Ishizuka T, Sato T, Senba S, Kanazawa K. Efficacy of magnifying endoscopy in the differential diagnosis of neoplastic and non-neoplastic polyps of the large bowel. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999; 42:1602–1608.

31. Kato S, Fu KI, Sano Y, et al. Magnifying colonoscopy as a non-biopsy technique for differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic and neoplastic lesions. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:1416–1420.

32. East JE, Suzuki N, Saunders BP. Comparison of magnified pit pattern interpretation with narrow band imaging versus chromoendoscopy for diminutive colonic polyps: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:310–316.

33. Konerding MA, Fait E, Gaumann A. 3D microvascular architecture of pre-cancerous lesions and invasive carcinomas of the colon. Br J Cancer. 2001; 84:1354–1362.

34. Sano Y, Ikematsu H, Fu KI, et al. Meshed capillary vessels by use of narrow-band imaging for differential diagnosis of small colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:278–283.

35. Hirata M, Tanaka S, Oka S, et al. Evaluation of microvessels in colorectal tumors by narrow band imaging magnification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:945–952.

36. Hewett DG, Kaltenbach T, Sano Y, et al. Validation of a simple classification system for endoscopic diagnosis of small colorectal polyps using narrow-band imaging. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143:599–607. e1.

37. Gupta N, Bansal A, Rao D, et al. Accuracy of in vivo optical diagnosis of colon polyp histology by narrow-band imaging in predicting colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:494–502.

38. East JE, Suzuki N, Bassett P, et al. Narrow band imaging with magnification for the characterization of small and diminutive colonic polyps: pit pattern and vascular pattern intensity. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:811–817.

39. Hirata M, Tanaka S, Oka S, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging for diagnosis of colorectal tumors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:988–995.

40. van den Broek FJ, Reitsma JB, Curvers WL, Fockens P, Dekker E. Systematic review of narrow-band imaging for the detection and differentiation of neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions in the colon (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:124–135.

41. East JE, Tan EK, Bergman JJ, Saunders BP, Tekkis PP. Meta-analysis: narrow band imaging for lesion characterization in the colon, oesophagus, duodenal ampulla and lung. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 28:854–867.

42. Schachschal G, Mayr M, Treszl A, et al. Endoscopic versus histological characterisation of polyps during screening colonoscopy. Gut. 2014; 63:458–465.

43. Longcroft-Wheaton G, Brown J, Cowlishaw D, Higgins B, Bhandari P. High-definition vs. standard-definition colonoscopy in the characterization of small colonic polyps: results from a randomized trial. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:905–910.

44. Ladabaum U, Fioritto A, Mitani A, et al. Real-time optical biopsy of colon polyps with narrow band imaging in community practice does not yet meet key thresholds for clinical decisions. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:81–91.

45. Kominami Y, Yoshida S, Tanaka S, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of colorectal polyp histology by using a real-time image recognition system and narrow-band imaging magnifying colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83:643–649.

46. Misawa M, Kudo SE, Mori Y, et al. Characterization of colorectal lesions using a computer-aided diagnostic system for narrow-band imaging endocytoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150:1531–1532. e3.

47. McKenna MT, Wang S, Nguyen TB, Burns JE, Petrick N, Summers RM. Strategies for improved interpretation of computer-aided detections for CT colonography utilizing distributed human intelligence. Med Image Anal. 2012; 16:1280–1292.

48. Tulum G, Bolat B, Osman O. A CAD of fully automated colonic polyp detection for contrasted and non-contrasted CT scans. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2017; 12:627–644.

49. Byrne MF, Chapados N, Soudan F, et al. Real-time differentiation of adenomatous and hyperplastic diminutive colorectal polyps during analysis of unaltered videos of standard colonoscopy using a deep learning model. Gut. 2019; 68:94–100.

50. Nagata K, Endo S, Honda T, et al. Accuracy of CT colonography for detection of polypoid and nonpolypoid neoplasia by gastroenterologists and radiologists: a nationwide multicenter study in Japan. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017; 112:163–171.

51. Chen PJ, Lin MC, Lai MJ, Lin JC, Lu HH, Tseng VS. Accurate classification of diminutive colorectal polyps using computer-aided analysis. Gastroenterology. 2018; 154:568–575.

52. Tamai N, Saito Y, Sakamoto T, et al. Effectiveness of computer-aided diagnosis of colorectal lesions using novel software for magnifying narrow-band imaging: a pilot study. Endosc Int Open. 2017; 5:E690–E694.

53. Repici A, Ciscato C, Correale L, et al. Narrow-band imaging international colorectal endoscopic classification to predict polyp histology: REDEFINE study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 84:479–486. e3.

54. Bisschops R, Hassan C, Bhandari P, et al. BASIC (BLI Adenoma Serrated International Classification) classification for colorectal polyp characterization with blue light imaging. Endoscopy. 2018; 50:211–220.

55. Corley DA, Jensen CD, Marks AR, et al. Adenoma detection rate and risk of colorectal cancer and death. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370:1298–1306.

56. Bird-Lieberman E, East JE. Diminutive polyps and future colorectal cancer risk perception: how low do we need to go? Endoscopy. 2018; 50:197–199.

57. Sakata S, Lee AHS, Kheir AO, et al. Patient acceptance of the optical diagnosis and misdiagnosis of diminutive colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86:372–375. e2.
58. Rex DK, Patel NJ, Vemulapalli KC. A survey of patient acceptance of resect and discard for diminutive polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:376–380. e1.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



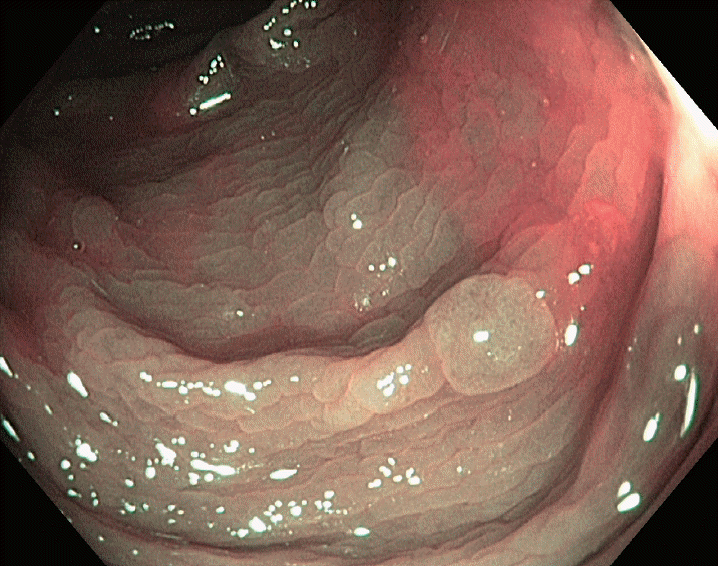
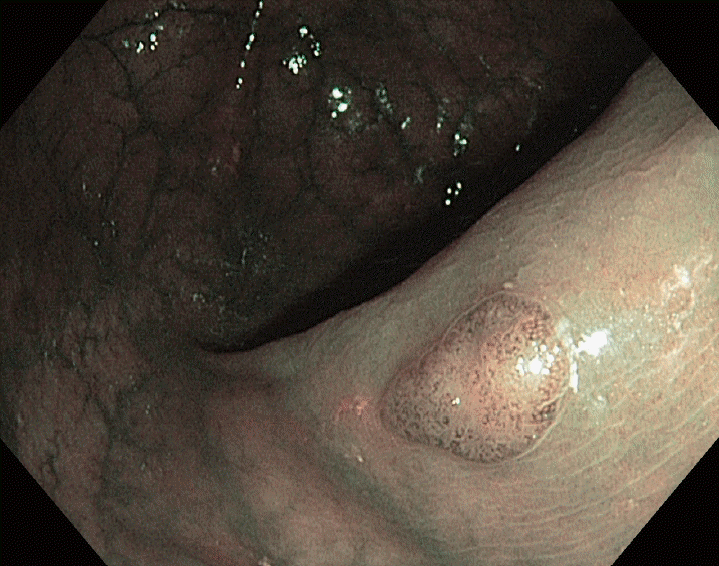
 XML Download
XML Download