INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
Outcome measures
GAS and the standard GAS score
Questionnaires for therapists
Data analysis
RESULTS
Patient characteristics
Table 1.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
The study hospital began the Wee-FIM assessment from 2015 and included only the results for 58 patients. The sum of the manual muscle test by Medical Research Council score was divided into 6 muscle groups including shoulder abductor of the weaker side, elbow flexor, wrist extensor, hip flexor, knee extensor, and ankle dorsiflexor. It ranges from 0 (totally hemiplegic) to 30 (normal strength).
MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; FMA, Fugl-Meyer Assessment; MFT, Manual Function Test; MBI, Modified Barthel Index; FIM, Functional Independence Measurement; MMT, Manual Muscle Test; BBS, Berg Balance Scale; TIS, Trunk Impairment Scale; FAC, Functional Ambulatory Category.
Age and post-stroke duration were compared by independent t-test. Evaluation scores were compared by Mann-Whitney U-test. Number of each group was compared by chi-square test. There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics of patients during both periods.
Effect on rehabilitation outcomes
Table 2.
| Assessments (range) |
2014–2015 (n=121) |
2016–2018 (n=141) |
p-value (between groups) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Follow-up | Change | p-value (within groups) | Baseline | Follow-up | Change | p-value (within groups) | |||
| MMSE score (0–30) | 15.2±8.9 | 21.1±8.2 | 5.9±5.1 | <0.01 | 15.6±8.6 | 21.2±7.9 | 5.6±4.4 | <0.01 | 0.55 | |
| FMA score (0–66) | 30.8±25.2 | 38.4±25.3 | 7.6±11.1 | <0.01 | 31.0±24.1 | 38.3±25.4 | 7.3±10.3 | <0.01 | 0.63 | |
| MFT score (0–100) | 35.3±35.2 | 47.7±37.2 | 12.4±13.5 | <0.01 | 36.3±34.1 | 49.1±38.1 | 12.8±15.3 | <0.01 | 0.84 | |
| MBI score (0–100) | 34.2±23.9 | 53.5±27.2 | 19.3±13.3 | <0.01 | 35.9±23.8 | 55.2±27.6 | 19.3±13.4 | <0.01 | 0.73 | |
| FIM score | ||||||||||
| Cognition (0–35) | 16.9±8.6a) | 20.9±9.0a) | 4.0±4.0a) | <0.01 | 18.8±8.4 | 22.5±8.3 | 3.7±3.7 | <0.01 | 0.54 | |
| Motor (0–91) | 32.4±15.6a) | 46.2±22.9a) | 13.8±10.6a) | <0.01 | 36.5±17.4 | 50.5±21.1 | 14.0±10.2 | <0.01 | 0.40 | |
| MMT score (0–30) | 12.0±6.1 | 14.4±6.1 | 2.4±2.8 | <0.01 | 12.2±5.3 | 14.6±5.8 | 2.4±2.5 | <0.01 | 0.39 | |
| BBS score (0–56) | 16.7±17.8 | 30.3±20.4 | 13.6±12.8 | <0.01 | 17.7±18.2 | 31.4±20.5 | 13.7±11.6 | <0.01 | 0.82 | |
| TIS score (0–23) | 8.22±6.02 | 12.47±6.32 | 4.25±3.56 | <0.01 | 8.35±6.61 | 12.84±6.77 | 4.49±3.82 | <0.01 | 0.48 | |
| FAC (0–5) | 1.20±1.27 | 2.31±1.57 | 1.11± 0.92 | <0.01 | 1.27±1.27 | 2.42±1.60 | 1.15±0.94 | <0.01 | 0.65 | |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation.
The study hospital began the Wee-FIM assessment from 2015 and included only the results for 58 patients. The sum of the manual muscle test by Medical Research Council score was divided into 6 muscle groups including shoulder abductor of the weaker side, elbow flexor, wrist extensor, hip flexor, knee extensor, and ankle dorsiflexor. It ranges from 0 (totally hemiplegic) to 30 (normal strength).
MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; FMA, Fugl-Meyer Assessment; MFT, Manual Function Test; MBI, Modified Barthel Index; FIM, Functional Independence Measurement; MMT, Manual Muscle Test; BBS, Berg Balance Scale; TIS, Trunk Impairment Scale; FAC, Functional Ambulatory Category.
Each score of baseline and follow-up within same group was compared by paired t-test. The independent t-test was used to compare changes in each score (score at follow-up minus score at admission) between both periods. There was no significant difference in all assessments between both periods.
Quality check for goal setting
Fig. 1.
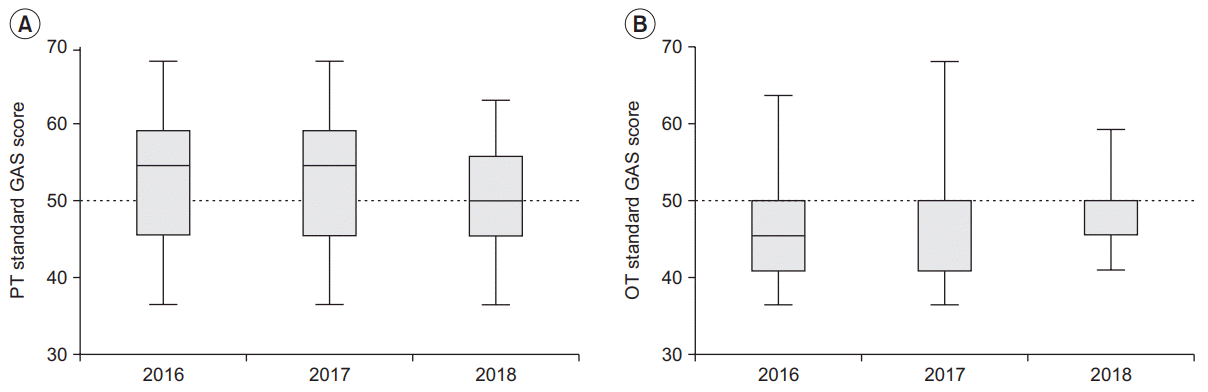
GAS scores
Table 3.
Factors affecting the standard GAS score
Table 4.
| Independent variable |
Dependent variable |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | p-value | OR | 95% CI | |
| Physical therapy | |||||
| Age | -0.027 | 0.019 | 0.167 | 0.974 | 0.937 to 1.011 |
| Post-stroke duration (day) | -0.021 | 0.010 | 0.032* | 0.979 | 0.959 to 0.998 |
| Stroke etiology | -0.160 | 0.535 | 0.765 | 0.852 | -0.197 to 1.900 |
| Stroke recurrence | -0.409 | 1.336 | 0.759 | 0.664 | -1.955 to 3.283 |
| Laterality | 0.274 | 0.451 | 0.543 | 1.315 | 0.431 to 2.199 |
| Location | 19.916 | 1.213×104 | 0.999 | 4.461×108 | -4.461×108 to 4.461×108 |
| MBI | 0.016 | 1.757 | 0.185 | 1.016 | -2.428 to 4.460 |
| Occupational therapy | |||||
| Age | -0.017 | 0.016 | 0.291 | 0.983 | 0.951 to 1.014 |
| Post-stroke duration (day) | -0.016 | 0.009 | 0.091 | 0.984 | 0.966 to 1.001 |
| Stroke etiology | 0.242 | 0.448 | 0.589 | 1.274 | 0.396 to 2.152 |
| Stroke recurrence | -0.895 | 1.295 | 0.490 | 0.409 | -2.129 to 2.947 |
| Laterality | -0.181 | 0.389 | 0.642 | 0.835 | 0.073 to 1.597 |
| Location | 1.293 | 0.849 | 0.128 | 3.644 | 1.965 to 5.323 |
| MBI | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.252 | 1.011 | 0.991 to 1.031 |
Goal attainment was assessed as having a standard GAS score ≥50 in each department (physical therapy or occupational therapy). Etiology of stroke was classified into cerebral infarction and intracerebral hemorrhage. The stroke laterality was classified as right, left and both sides. The table shows the OR of the left side for the right side. Stroke location was classified as cerebral hemisphere lesion and brainstem or cerebellar lesion.
B, regression coefficient; SE, standard error; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; MBI, Modified Barthel Index; GAS, goal attainment scaling.
Table 5.
| Group with MMSE <20 (n=85) | Group with MMSE ≥20 (n=56) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 64.0±12.9 | 54.0±13.5 | <0.01** |
| Sex | 0.10 | ||
| Male | 46 | 38 | |
| Female | 39 | 18 | |
| Etiology | 0.06 | ||
| Cerebral infarction | 30 (35.3) | 29 (51.8) | |
| Intracerebral hemorrhage | 55 (64.7) | 27 (48.2) | |
| Lesion | 0.04* | ||
| Right hemisphere | 37 (43.5) | 32 (57.1) | |
| Left hemisphere | 35 (41.2) | 19 (33.9) | |
| Bilateral hemispheres | 3 (3.5) | 5 (9.0) | |
| Cerebellum | 2 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Brainstem | 8 (9.4) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Post-stroke duration (day) | 40.4±25.2 | 25.5±12.9 | <0.01** |
| Recurred stroke | 2 (2.4) | 1 (1.8) | 0.82 |
| MMSE score | 10.2±6.9 | 23.7±2.8 | <0.01** |
| FMA score | 26.2±22.9 | 38.4±24.4 | <0.01** |
| MFT score | 28.9±31.7 | 47.7±34.8 | <0.01** |
| MBI score | 26.3±19.9 | 50.8±22.2 | <0.01** |
| FIM score | |||
| Cognition | 14.0±6.4 | 26.2±5.1 | <0.01** |
| Motor | 28.9±13.2 | 48.0±17.2 | <0.01** |
| MMT score | 11.0±5.3 | 14.0±4.8 | <0.01** |
| BBS score | 13.2±16.0 | 24.6±19.7 | <0.01** |
| TIS score | 6.27±6.18 | 11.50±6.04 | <0.01** |
| FAC | 0.91±1.03 | 1.80±1.44 | <0.01** |
| Standard GAS score | |||
| Physical therapy | 49.1±8.0 | 54.3±6.8 | <0.01** |
| Occupational therapy | 47.1±6.9 | 49.0±6.4 | 0.04* |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
The sum of the manual muscle test by Medical Research Council score was divided into 6 muscle groups including shoulder abductor of the weaker side, elbow flexor, wrist extensor, hip flexor, knee extensor, and ankle dorsiflexor. It ranges from 0 (totally hemiplegic) to 30 (normal strength).
MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; FMA, Fugl-Meyer Assessment; MFT, Manual Function Test; MBI, Modified Barthel Index; FIM, Functional Independence Measurement; MMT, Manual Muscle Test; BBS, Berg Balance Scale; TIS, Trunk Impairment Scale; FAC, Functional Ambulatory Category; GAS, goal attainment scaling.
Number of each group was compared by chi-square test. Other characteristics and evaluation scores were compared by Mann-Whitney U-test.
Fig. 2.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download