Abstract
Objective
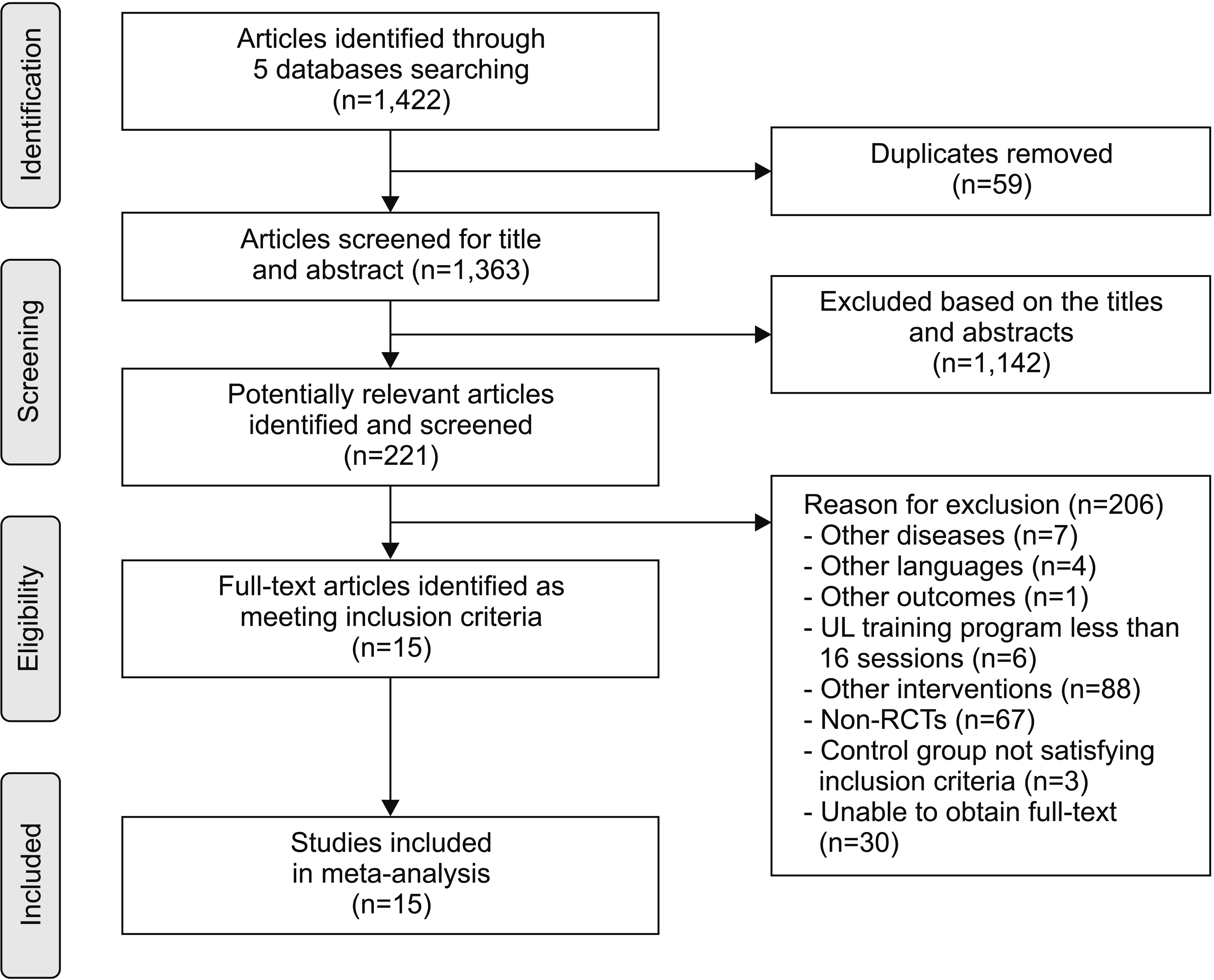
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Notes
Conceptualization: Kruapanich C, Tantisuwat A, Mathiyakom W. Methodology: Kruapanich C, Ubolnuar N, Tantisuwat A. Formal analysis: Kruapanich C, Lertmaharit S. Funding acquisition: Tantisuwat A. Project administration: Tantisuwat A. Writing – original draft: Kruapanich C. Writing – review and editing: Kruapanich C, Tantisuwat A, Mathiyakom W, Thaveeratitham P. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
REFERENCES
Fig. 3.
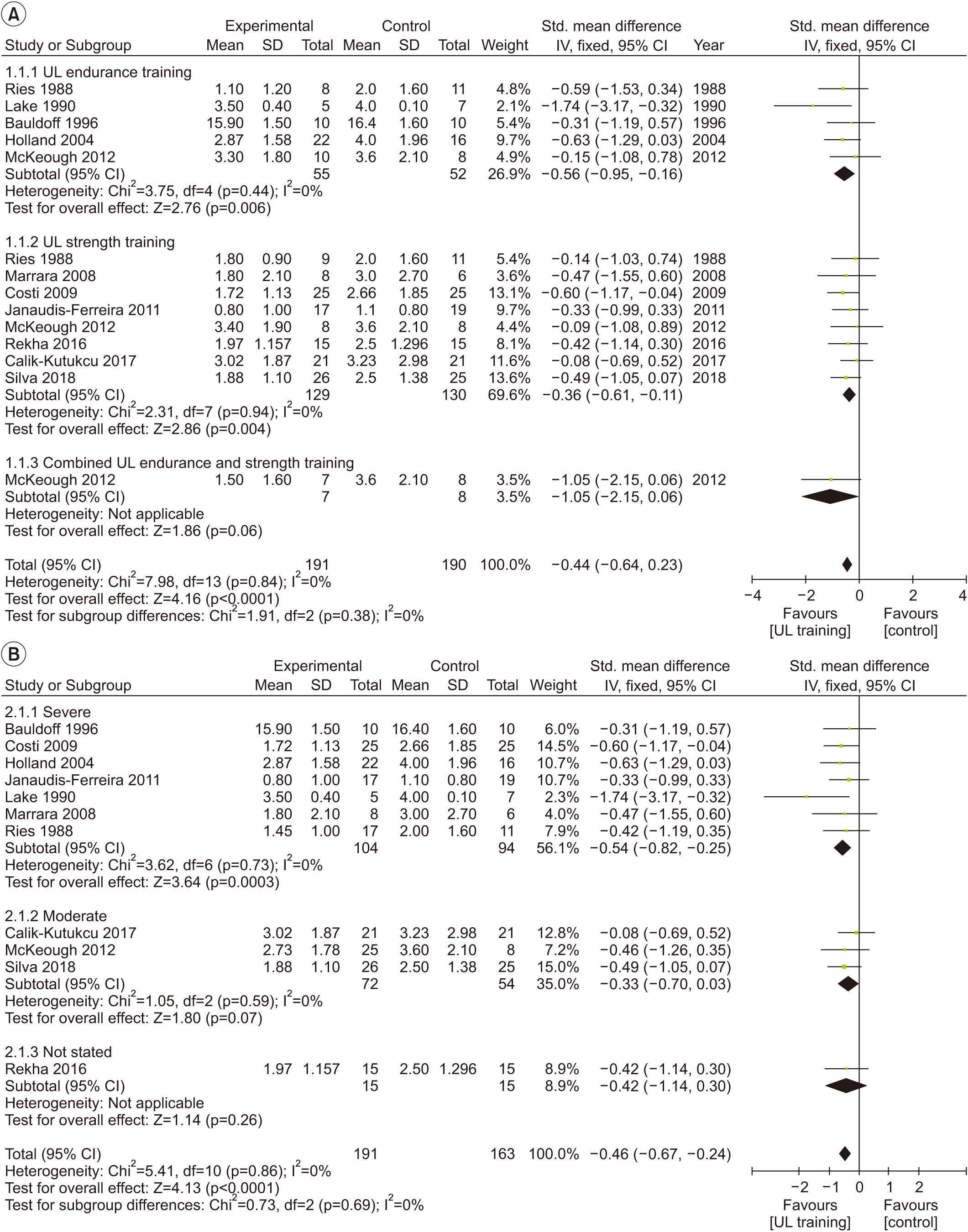
Fig. 4.
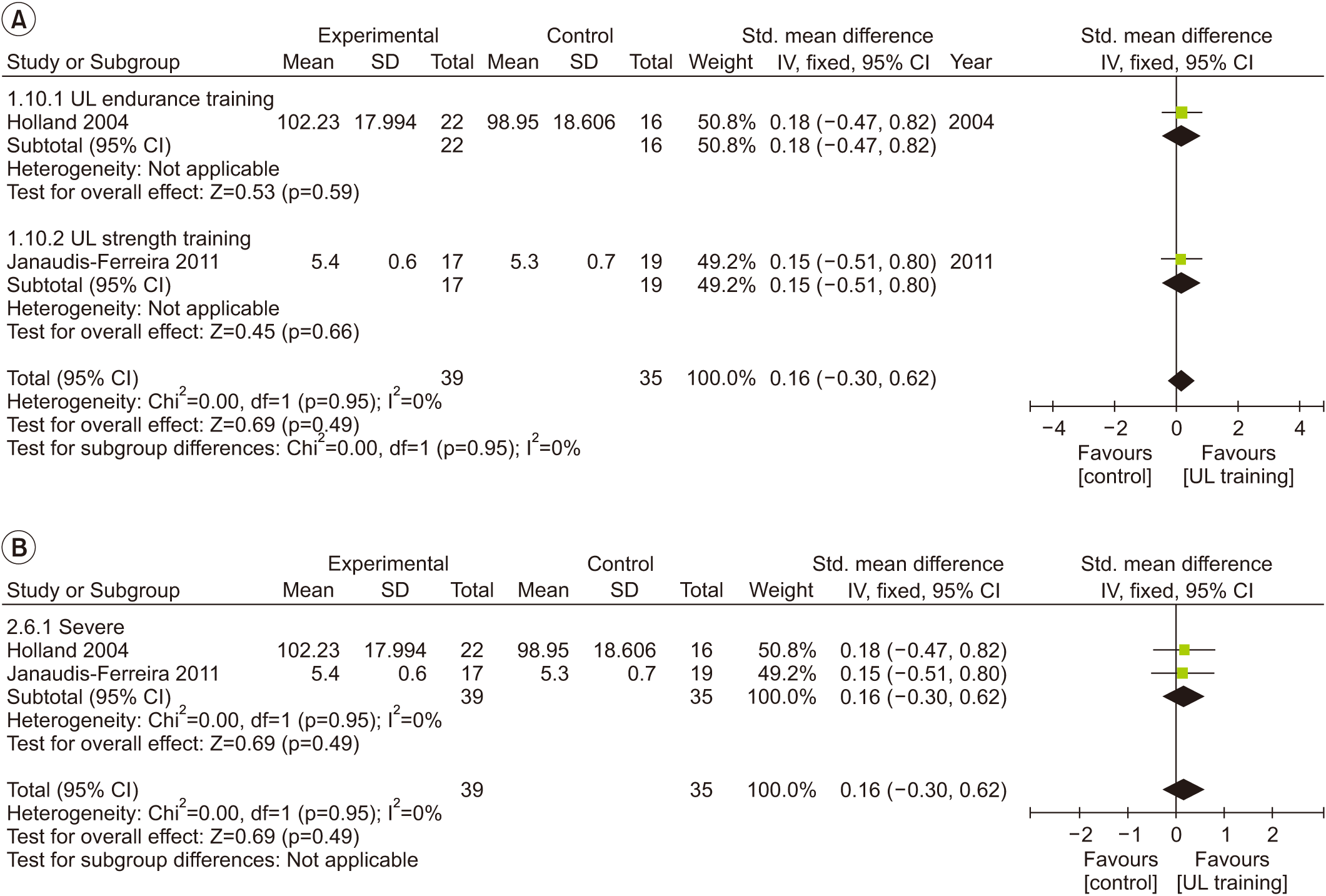
Fig. 5.
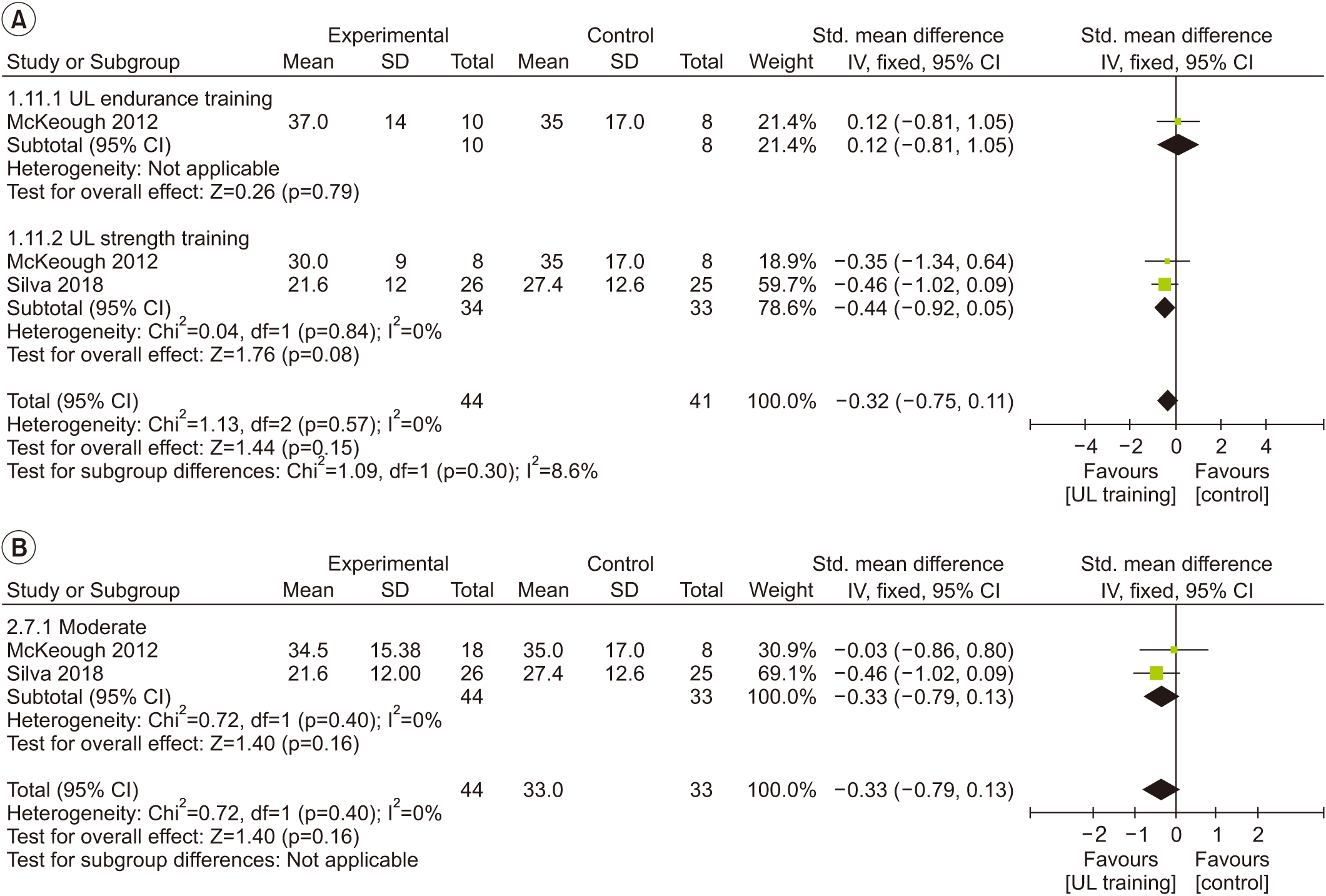
Fig. 6.
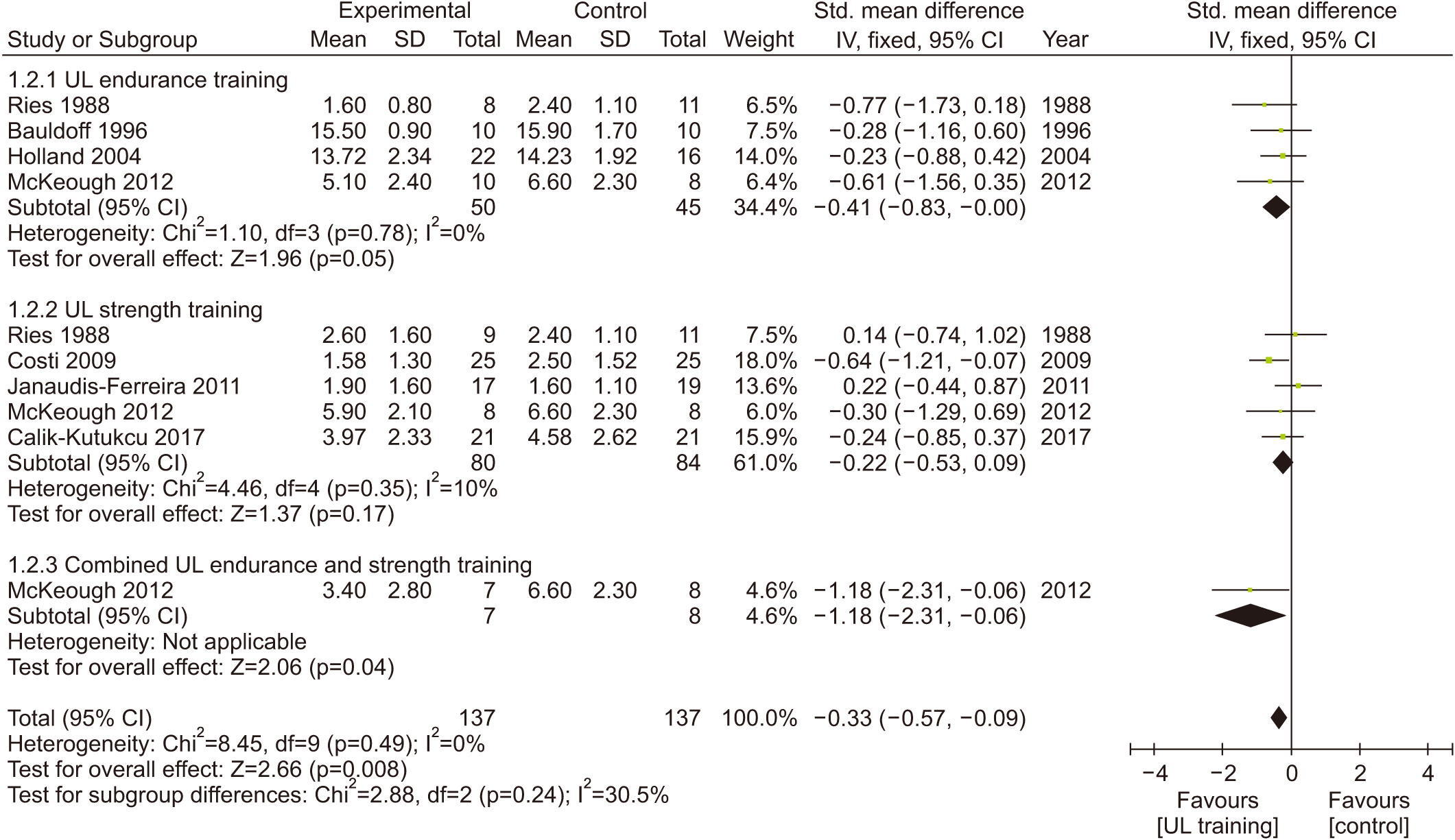
Fig. 7.
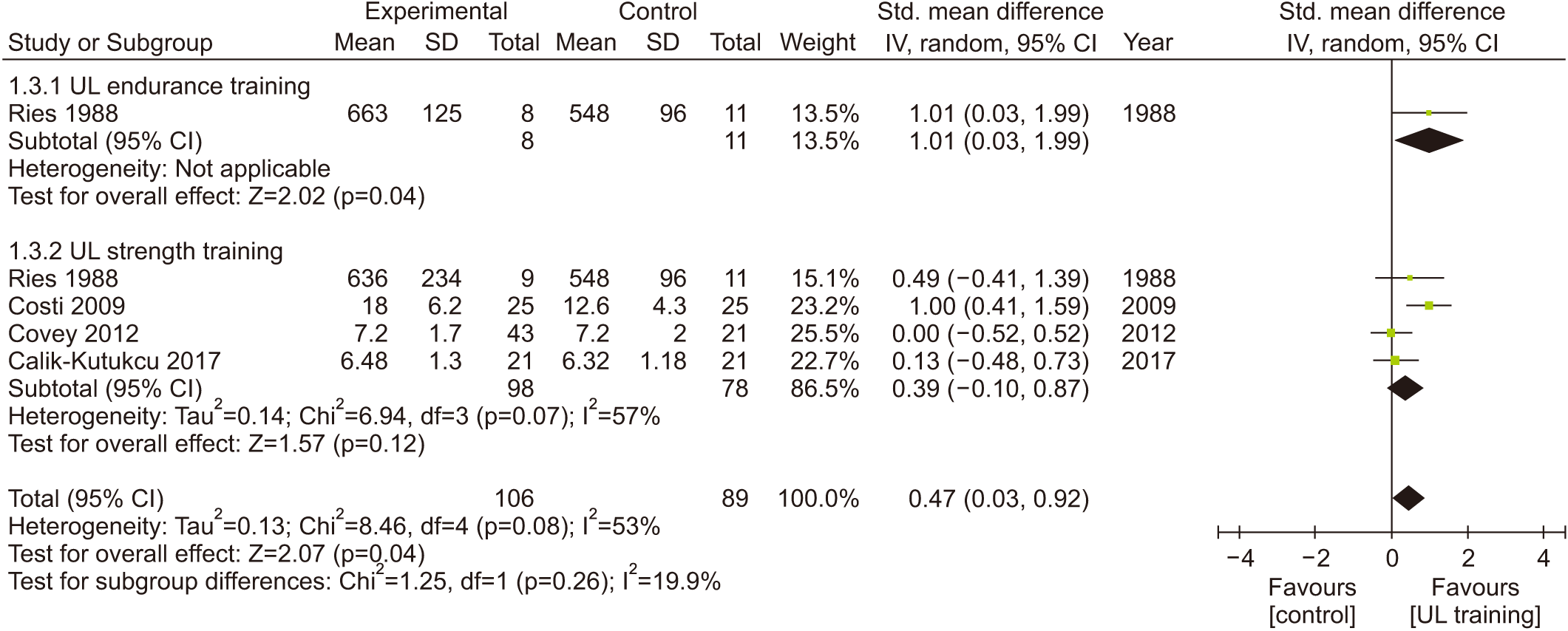
Fig. 8.
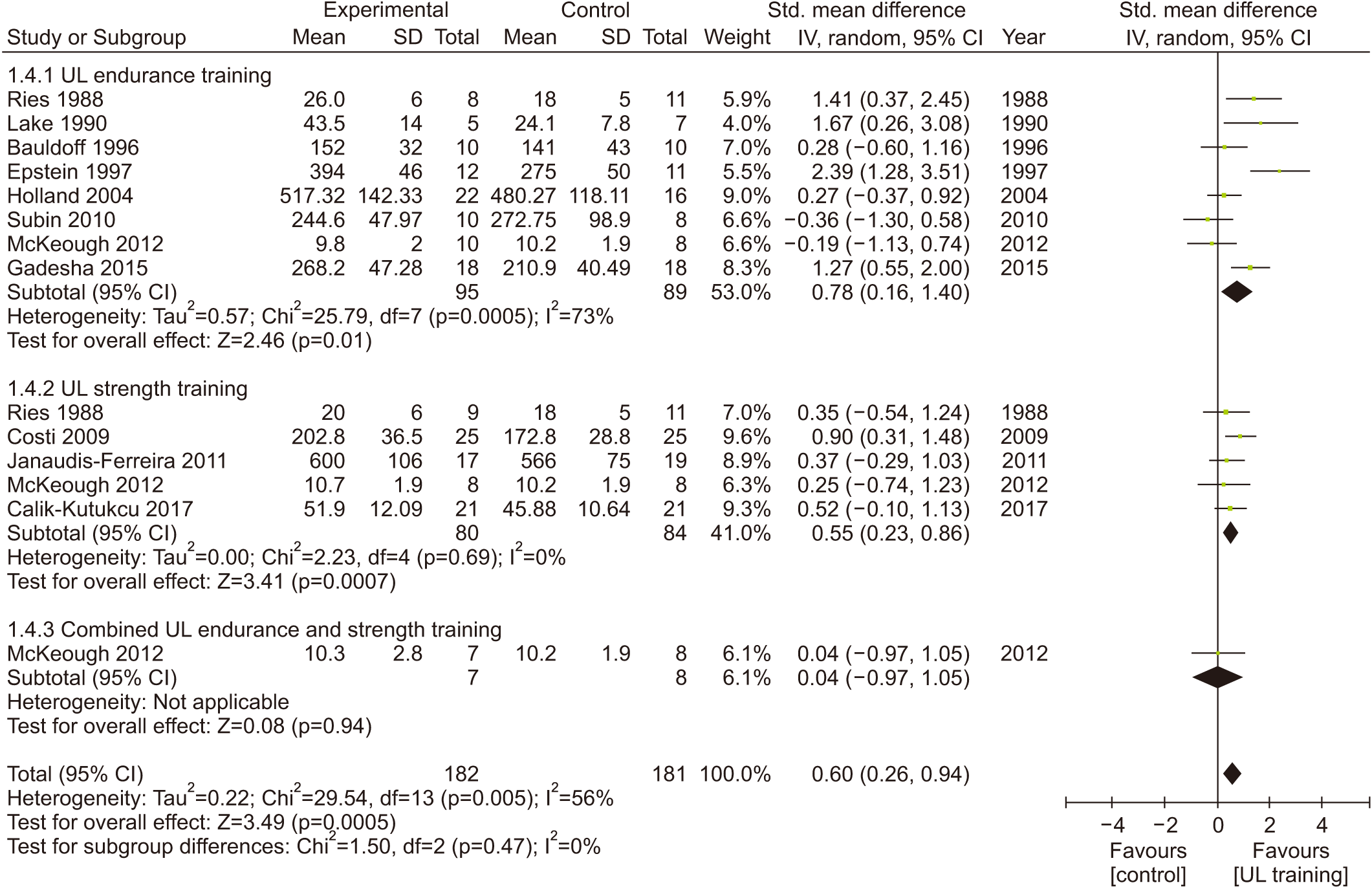
Table 1.
| Study | No. of participants (male/female) | Participants | Severity | Intervention group | Control group | Exercise intensity | Exercise time and duration | Frequency (day/wk) | Exercise sessions | Outcomes measurement (tool) | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ries et al., [22], 1988 | 28 (NA) | Age (yr): NA | Severe | I1: Gravity resistance training | C: Walking training | I1: Five low-resistance and high-repetition exercises (level able achieve1 set of all exercises) and the load was increased by number of arm motions, number of sets, and hand weight | >15 min 6 wk | Every other day for 1 week and then once daily | 38-39 | UL exercise tolerance (unsupported UL exercise capacity test) | I1 vs I2=+ |
| I1, I2 vs C= | |||||||||||
| FEV1 (% pred): 36±14.47 | I2: Modified PNF training | Perceived breathlessness rating (modified Borg scale) | I1 vs I2=0 | ||||||||
| I1, I2 vs C= | |||||||||||
| Perceived exertion rating (modified Borg scale) | I1 vs I2=0 | ||||||||||
| I2: Three sets of 4 to 10 reps of each exercise/set (1–5 lb) | I1, I2 vs C= | ||||||||||
| UL function (ADL simulation test) | I1 vs I2=+ | ||||||||||
| I1, I2 vs C= | |||||||||||
| Lake et al., [23], 1990 | 26 (22/4) | Age (yr): 66.45±5.43 | Severe | I: Arm cycle ergo metry and unsupported UL training (throwing ball against wall, passing a bean bag, pulling on ropes and pulleys, and moving a ring) | C: No treatment | I: NA | 40 min 8 wk | 3 | 24 | UL exercise tolerance (arm ergometer test) | I vs C=+ |
| FEV1 (% pred): 32(NA) | Dyspnea (NA) | I vs C=+ | |||||||||
| Bauldoff et al. [24], 1996 | 20 (9/11) | Age (yr): 62±13.50 | Severe | I: UL training modified from PNF program | C: Contacted weekly by telephone to equalize attention from health care providers | I: One to 3 set of 6 reps at 6RM and the weight increment increases from no weight to a total of 4 lb | NA 8 wk | 5 | 40 | UL exercise tolerance (6-PBRT) | I vs C=0 |
| FEV1 (% pred): 32±17.02 | Perceptions of breathlessness (BFS) | I vs C=0 | |||||||||
| Perceptions of fatigue (BFS) | I vs C=+ | ||||||||||
| Epstein et al. [34], 1997 | 23 (21/2) | Age (yr): 65±2 | Severe | I: Unsupported UL training by weight dowel lifts | C: low intensity resistive breathing by using a threshold resistor device | I: 750 g dowel lifts and the weight was increased by 250 g every 3 sessions | 30 min 7-8 wk | 3 | 21-24 | UL exercise tolerance (UAEX) | I vs C=+ |
| FEV1 (L): 0.86±0.10 | |||||||||||
| Holland et al. [25], 2004 | 38 (24/14) | Age (yr): 68±7.70 | Severe | I: Incremental unsupported UL endurance training by weight dowel lifts | C: Sham training of a pegboard finger dexterity and LL endurance training | I: 500 g stick and the weight was increased by 0.5 kg increments to maintain RPE at 12-14 and dyspnea scores 3 | >15 min 6 wk | 7 | 42 | UL exercise tolerance (UULEX) | I vs C=+ |
| Dyspnea (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=0 | ||||||||||
| FEV1 (% pred): 37±10.28 | UL Fatigue (RPE) | I vs C=0 | |||||||||
| QoL (CRQ) | I vs C=0 | ||||||||||
| Marrara et al. [26], 2008 | 14 (14/0) | Age (yr): 66.50±10.05 | Severe | I: Six UL training by progressive training (elbow flexion-extension, shoulder abduction, horizontal shoulder adduction, primitive diagonal, functional diagonal) | C: Bronchial hygiene therapy along with diaphragmatic pattern breathing orientations and stretching of the cervical, UL and LL muscles | I: 10RM of 5 trials for each exercise and the load was increased 3 sets of 10 reps at 50%, 75%, and 100% of 10RM | ~60 min 6 wk | 3 | 18 | Dyspnea (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=0 |
| FEV1 (% pred): 43.50±11.54 | |||||||||||
| Costi et al. [27], 2009 | 50 (33/17) | Age (yr): 69.5±8.9 | Severe | I: 15 sessions of resistance UL training by using dumbbells | C: PR program that consisted of a minimum of 15 consecutive sessions of specific training for the LL and general exercises | I: 50% of 1RM of 3 series of 10 reps for each exercise and increase number of reps from 10-12 and 12-15 reps, and increase load by 500 g | NA 3 wk | 7 | 21 | UL exercise tolerance (6-MRT) | I vs C=+ |
| Dyspnea (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=0 | ||||||||||
| FEV1 (% pred): 40.90±15.5 | UL Fatigue (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=+ | |||||||||
| UL function (ADL field test) | I vs C=+ | ||||||||||
| Subin Rao et al. [28], 2010 | 18 (18/0) | Age (yr): 58±8 | Severe | I: Unsupported UL training (throwing ball against wall, passing a bean bag, pulling on ropes and pulleys, and moving a ring) | C: LL training by walking training | NA | ~15 min 4 wk | 5 | 20 | UL exercise tolerance (UULEX) | I vs C=0 |
| FEV1 (% pred): 44.50±8.55 | |||||||||||
| Janaudis-Ferreira et al. [29], 2011 | 36 (21/15) | Age (yr): 67±11 | Severe | I: Unsupported UL training by resistance training with free-weights | C: Sham training consisted of UL flexibility and stretching exercises | I: Loads equivalent to 10-12 reps maximum and the load was increased for both sets on 2 consecutive training sessions | NA 6 wk | 3 | 18 | UL exercise tolerance (UULEX) | I vs C=+ |
| Dyspnea (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=0 | ||||||||||
| FEV1 (% pred): 35.15±15.12 | UL Fatigue (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=0 | |||||||||
| QoL (CRQ) | I vs C=0 | ||||||||||
| Covey et al. [31], 2012 | 64 (52/12) | Age (yr): 70.76±8.35 | Severe | I: UL resistance training (by using a cable crossover system) with exercise-specific selfefficacy enhancing intervention/health education | C: Sham training (gentle chair exercise and stretching) with health education | I: eight lifts in shoulder shrug, modified latissimus dorsi pulldown overhead pulldown, front pulldown, front raise, upright row, biceps curl, and triceps extension of 2 set of 8-10 reps, at 70% of 1RM and intensity was increased at 80% of 1RM and the load was increased to 3 sets of 8-10 reps and maintain RPE at 12 for week 5-16 | NA 16 wk | 3 | 48 | UL function (UBFPT) | I vs C=0 |
| FEV1 (% pred): 57.83±17.88 | |||||||||||
| McKeough et al. [30], 2012 | 38 (23/15) | Age (yr): 65.50±7.60 | Moderate | I1: UL endurance training (supported and unsupported UL exercises) | C: Standard LL endurance and strength training | I1: At 60% of peak work rate and the load was increased according to dyspnea and arm perceived exertion in order to maintain at score 3 | ~20 min 8 wk | 3 | 24 | UL exercise tolerance (UULEX) | I1 vs I2 vs I3 vs C=0 |
| Dyspnea (modified Borg scale) | I3 vs I1, I2, C=+ | ||||||||||
| FEV1 (% pred): 57±15.71 | I2: UL strength training by using weight machines | I2: Two sets of 10 reps at 60% of 1RM and the load was increased 3 sets at 80% of 1RM | UL Fatigue (RPE) | I3 vs I1, I2, C=+ | |||||||
| I3: Combined UL endurance and strength training | QoL (SGRQ) | I1 vs I2 vs I3 vs C=0 | |||||||||
| Rekha et al. [36], 2016 | 30 (NA) | Age (yr): NA | Unknown | I: UL resistance training by using 1 liter water bottle | C: Thoracic mobility exercise | I: One liter water bottle 3 sets of 8-10 reps and the load was increased by increments to maintain RPE and dyspnea scores 12-14 | 30 min 4 wk | 5 | 20 | Dyspnea (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=+ |
| FEV1 (% pred): NA | |||||||||||
| Gadesha & Bhise [35], 2015 | 36 (34/2) | Age (yr): 58.05±NA | Unknown | I: Unsupported UL training in shoulder flexion, abduction, horizontal adduction and abduction, elbow flexion and extension with PR program | C: PR program (treadmill, static cycling and stair climbing) | I: Three sets of 10 reps of each exercise and the load was increased by 10 to 12 to 15 reps, weight from 0.2 to 1.5 kg, and maintain RPE at 12 to 13 | NA 8 wk | 3 | 24 | UL exercise tolerance (UULEX) | I vs C=+ |
| FEV1 (% pred): NA | |||||||||||
| Calik-Kutukcu et al. [32], 2017 | 42 (27/15) | Age (yr): 59.04±9.30 | Moderate | I: Unsupported UL training by strength training with free-weights and breathing exercises | C: Breathing exercises | I: At 40-50% of 1RM 3 sets of 8-12 reps and increase number of reps in 2 consecutive training sessions and the load was increased by 250 or 500 g per week | NA 8 wk | 3 | 24 | UL exercise tolerance (arm ergometer test) | I vs C=0 |
| Dyspnea (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=+ | ||||||||||
| FEV1 (% pred): 51.85±15.73 | UL Fatigue (modified Borg scale) | I vs C=0 | |||||||||
| UL function (ADL simulation test) | I vs C=0 | ||||||||||
| Silva et al. [33], 2018 | 51 (21/30) | Age (yr): 67.5±7.87 | Moderate | I: UL resistance training with freeweight by using dumbbells in arm flexion-abduction and elbow flexionextension, and physical exercise routine (aerobic exercises, inspiratory muscle training, and stretching, followed by massage therapy) | C: Physical exercise routine (diagonal functional movements for UL and LL, inspiratory muscle training, UL stretching, and massage) | I: At 50% of maximum load 3 sets of 10 reps | 30-60 min 6 wk | 3 | 18 | Dyspnea (mMRC) | I vs C=+ |
| FEV1 (% pred): 56±21.71 | QoL (SGRQ) | I vs C=+ |
M/F, male/female; NA, not available; FEV1; forced expiratory volume in one second; UL, upper limb; LL, lower limb; PNF, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation; reps, repetitions; RM, repetition maximum; ADL, activities of daily living; PR, pulmonary rehabilitation; 6-PBRT, 6-minute pegboard and ring test; BFS, breathlessness and fatigue scale; UAEX, unsupported arm exercise test; UULEX, unsupported upper limb exercise test; RPE, rating of perceived exertion scale; 6-MRT, 6-minute ring test; QoL, quality of life; CRQ, Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire; SGRQ, St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; UB-FPT, upper-body functional performance test; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council dyspnea scale; I, intervention group; I1, intervention group 1; I2, intervention group 2; I3, intervention group 3; C, control group; positive (+), if the UL training was demonstrated to be statistically more effective than a control group; negative (-), if the UL training was demonstrated to be statistically less effective than a control group; neutral (0), if the UL training did not statistically differ from a control group.
Table 2.
| Outcomes |
Illustrative mean (95% CI) |
No. of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | ULE group | ||||
| Dyspnea | Mean dyspnea ranged across control group from 2.00–16.40 units | SMD dyspnea in the ULE group was -0.56 units (-0.95 to -0.16) | 107 (5 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Significant |
| Quality of life by using CRQ | Mean CRQ score was 98.95 units | SMD CRQ score in the ULE group was 0.18 units (-0.47 to 0.82) | 38 (1 RCT) | ⨁⨁○○ Low2,4 | Not significant |
| Quality of life by using SGRQ | Mean SGRQ score was 35 units | SMD SGRQ score in the ULE group was 0.12 units (-0.81 to 1.05) | 18 (1 RCT) | ⨁⨁○○ Low2,4 | Not significant |
| UL fatigue | Mean UL fatigue ranged across control group from 2.40–15.90 units | SMD UL fatigue in the ULE group was -0.41 units (-0.83 to -0.00) | 95 (4 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Significant |
| UL function | Mean UL function was 548 units | SMD UL function in the ULE group was 1.01 units (0.03 to 1.99) | 19 (1 RCT) | ⨁○○○ Very low1,2,4 | Significant |
| UL exercise tolerance | Mean UL exercise tolerance ranged across control group from 10.20–480.27 units | SMD UL exercise tolerance in the ULE group was 0.78 units (0.16 to 1.40) | 184 (8 RCTs) | ⨁○○○ Very low1,2,4 | Significant |
ULE, upper limb endurance training; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CI, confidence interval; GRADE, Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation; SMD, standardized mean difference; RCT, randomized clinical trial; CRQ, Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire; SGRQ, St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; UL, upper limb.
The risk in the intervention group (and 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and 95% CI).
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence: High quality: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. Moderate quality (We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different), Low quality (Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect), Very low quality (We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect).
Table 3.
| Outcomes |
Illustrative mean (95% CI) |
No. of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | ULE group | ||||
| Dyspnea | Mean dyspnea ranged across control group from 1.10-3.60 units | SMD dyspnea in the ULS group was -0.36 units (-0.61 to -0.11) | 259 (8 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Significant |
| Quality of life by using CRQ | Mean CRQ score was 5.30 units | SMD CRQ score in the ULE group was 0.15 units (-0.51 to 0.80) | 36 (1 RCT) | ⨁⨁○○ Low2,4 | Not significant |
| Quality of life by using SGRQ | Mean SGRQ score ranged across control group from 27.40–35.00 units | SMD SGRQ score in the ULS group was -0.44 units (-0.92 to 0.05) | 67 (2 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Not significant |
| UL fatigue | Mean UL fatigue ranged across control group from 1.60–6.60 units | SMD UL fatigue in the ULS group was -0.22 units (-0.53 to 0.09) | 164 (5 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Not significant |
| UL function | Mean UL function ranged across control group from 6.32–548.00 units | SMD UL function in the ULS group was 0.39 units (-0.10 to 0.87) | 176 (4 RCTs) | ⨁⨁○○ Low2,4 | Not significant |
| UL exercise tolerance | Mean UL exercise tolerance ranged across control group from 10.20–566.00 units | SMD UL exercise tolerance in the ULS group was 0.55 units (0.23 to 0.86) | 164 (5 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Significant |
ULS, upper limb strength training; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CI, confidence interval; GRADE, Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation; SMD, standardized mean difference; RCT, randomized clinical trial; CRQ, Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire; SGRQ, St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; UL, upper limb.
The risk in the intervention group (and 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and 95% CI).
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence: High quality (We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect), Moderate quality (We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different), Low quality (Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect), Very low quality (We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect).
Table 4.
| Outcomes |
Illustrative mean (95% CI) |
No. of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | ULE group | ||||
| Dyspnea | Mean dyspnea was 3.60 units | SMD dyspnea in the ULC group was -1.05 units (-2.15 to 0.06) | 15 (1 RCT) | ⨁⨁○○ Low2,4 | Not significant |
| UL fatigue | Mean UL fatigue was 6.60 units | SMD UL fatigue in the ULC group was -1.18 units (-2.31 to -0.06) | 15 (1 RCT) | ⨁⨁○○ Low2,4 | Significant |
| UL exercise | Mean UL exercise tolerance was 10.20 units | SMD UL exercise tolerance in the ULC group was 0.04 units (-0.97 to 1.05) | 15 (1 RCT) | ⨁⨁○○ Low2,4 | Not significant |
ULC, combined upper limb endurance and strength training; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CI, confidence interval; GRADE, Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation; SMD, standardized mean difference; RCT, randomized clinical trial; CRQ, Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire; SGRQ, St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; UL, upper limb.
The risk in the intervention group (and 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and 95% CI).
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence: High quality (We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect), Moderate quality (We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different), Low quality (Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect), Very low quality (We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect).
Table 5.
| Outcomes |
Illustrative mean (95% CI) |
No. of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | ULE group | ||||
| Dyspnea | Mean dyspnea ranged across control group from 1.10–16.40 units | SMD dyspnea in the UL training group was -0.44 units (-0.64 to -0.23) | 381 (14 RCTs) | ⨁⨁○○ Moderate4 | Significant |
| Quality of life by using CRQ | Mean CRQ score ranged across control group from 5.30–98.95 scores | SMD CRQ score in the UL training group was 0.16 scores (-0.30 to 0.62) | 74 (2 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Not significant |
| Quality of life by using SGRQ | Mean SGRQ score ranged across control group from 27.40–35.00 units | SMD SGRQ score in the UL training group was -0.32 units (-0.75 to 0.11) | 85 (3 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Not significant |
| UL fatigue | Mean UL fatigue ranged across control group from 1.60–15.90 units | SMD UL fatigue in the UL training group was -0.33 units (-0.57 to -0.09) | 274 (10 RCTs) | ⨁⨁⨁○ Moderate4 | Significant |
| UL function | Mean UL function ranged across control group from 6.32–548.00 units | SMD UL function in the UL training group was 0.47 units (0.03 to 0.92) | 195 (5 RCTs) | ⨁⨁○ Low2,4 | Significant |
| UL exercise tolerance | Mean UL exercise tolerance ranged across control group from 10.20–566.00 units | SMD UL exercise tolerance in the UL training group was 0.60 units (0.26 to 0.94) | 363 (14 RCTs) | ⨁○○○ Very low1,2,4 | Significant |
UL, upper limb; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CI, confidence interval; GRADE, Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation; SMD, standardized mean difference; RCT, randomized clinical trial; CRQ, Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire; SGRQ, St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire.
The risk in the intervention group (and 95% CI) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and 95% CI).
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence: High quality (We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect), Moderate quality (We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different), Low quality (Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect), Very low quality (We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download