INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
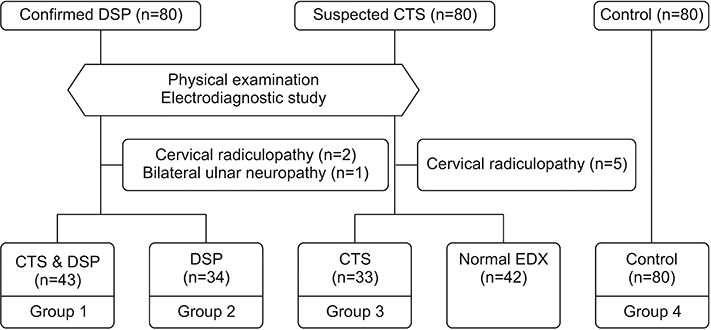
Participants
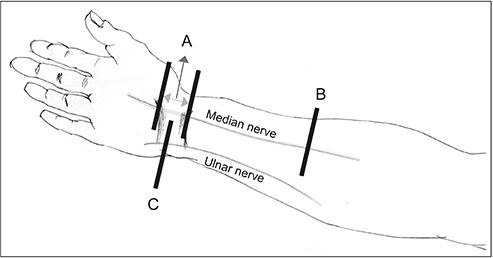
Ultrasonography
Electrodiagnostic evaluation
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Table 1.
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of hands | 43 | 34 | 33 | 80 | |
| Age (yr) | 63.3±9.4 | 61.0±10.1 | 59.9±6.3 | 61.2±5.9 | 0.29a) |
| Sex, female | 24 (55.8) | 15 (44.1) | 19 (57.6) | 50 (62.5) | 0.44b) |
| Height (cm) | 161.1±6.4 | 164.3±10.1 | 160.3±6.9 | 160.6±6.2 | 0.07a) |
| Weight (kg) | 59.0±8.7 | 62.0±10.1 | 60.0±9.5 | 59.2±8.6 | 0.43a) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.7±3.0 | 23.3±5.0 | 23.3±2.6 | 22.9±2.6 | 0.82a) |
| Diabetes duration (yr) | 17.2±8.7 | 16.2±8.4 | NA | NA | 0.61c) |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.7±1.2 | 6.3±0.9 | NA | NA | 0.12c) |
| CTS grades | 0.11b) | ||||
| Mild to moderate | 16 (37.2) | NA | 18 (54.5) | NA | |
| Severe to extreme | 27 (62.8) | NA | 15 (45.5) | NA |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
BMI, body mass index; CTS, carpal tunnel syndrome; DSP, diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy; NA, not applicable; Group 1, patients with CTS and DSP; Group 2, patients with DSP; Group 3, patients with CTS only; Group 4, healthy controls.
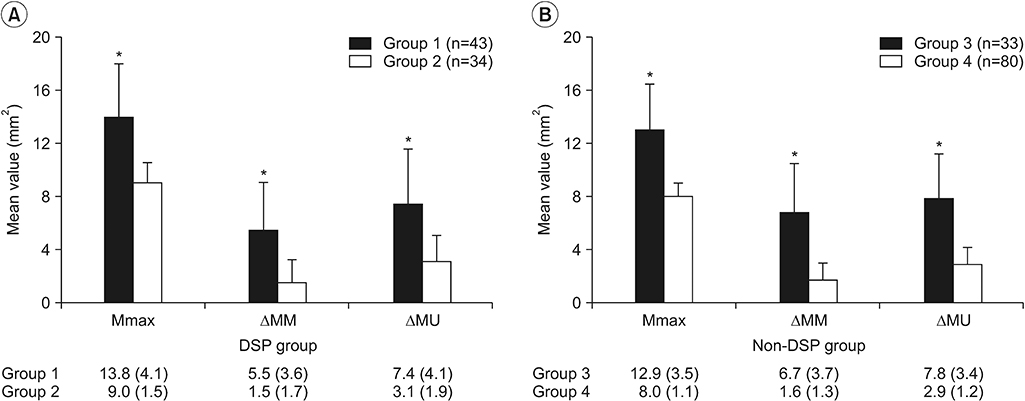 | Fig. 3.The mean sonographic values were compared between patients with CTS and those without CTS, according to the presence of DSP: (A) DSP group and (B) non-DSP group. Data are expressed as mean±standard deviation. CTS, carpal tunnel syndrome; DSP, diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy; Mmax, maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel; ΔMM, difference between maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel and the cross-sectional area of the median nerve at the forearm level; ΔMU, difference between maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel and the cross-sectional area of the ulnar nerve at the pisiform level. *p<0.001, using Student t-test to compare the 2 means (group 1, patients with CTS and DSP; group 2, patients with DSP; group 3, patients with CTS only; group 4, healthy controls). |
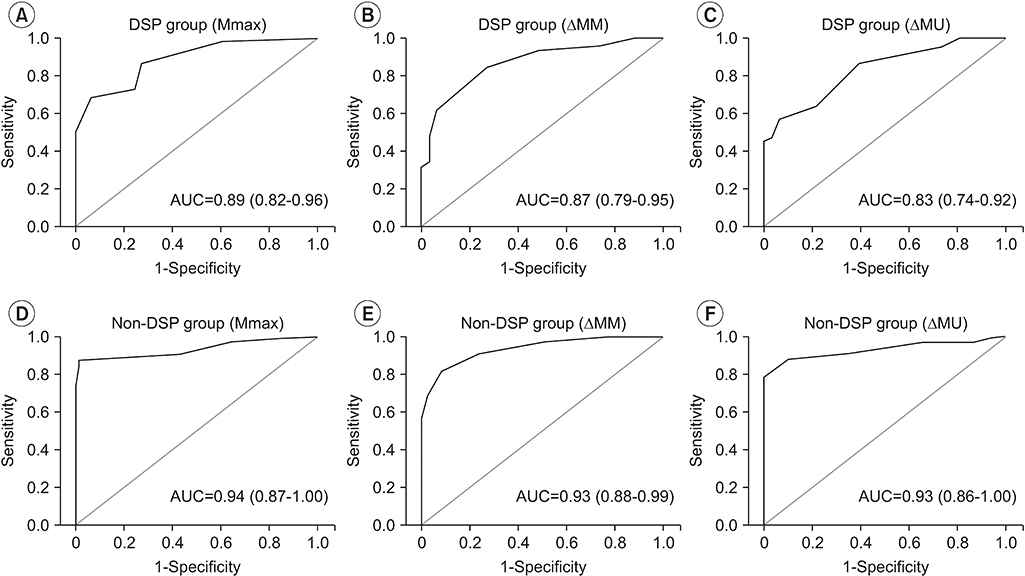 | Fig. 4.The ROC curves of the ultrasound parameters (Mmax, ΔMM, and ΔMU) were measured in the DSP group and non-DSP group: (A) ROC curve of Mmax in the DSP group, (B) ROC curve of ΔMM in the DSP group, (C) ROC curve of ΔMU in the DSP group, (D) ROC curve of Mmax in the non-DSP group, (E) ROC curve of ΔMM in the non-DSP group, and (F) ROC curve of ΔMU in the non-DSP group. ROC, receiver operating characteristic; DSP, diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy; Mmax, maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel; ΔMM, difference between maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel and the cross-sectional area of the median nerve at the forearm level; ΔMU, difference between maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel and the cross-sectional area of the ulnar nerve at the pisiform level; AUC, area under the curve. |
Table 2.
DSP, diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy; Mmax, maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel; ΔMM, difference between maximal cross-sectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel and cross-sectional area of the median nerve at the forearm level; ΔMU, difference between maximal crosssectional area of the median nerve throughout the carpal tunnel and cross-sectional area of the ulnar nerve at the pisiform level.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download