INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND MEHTODS
Subjects
Methods
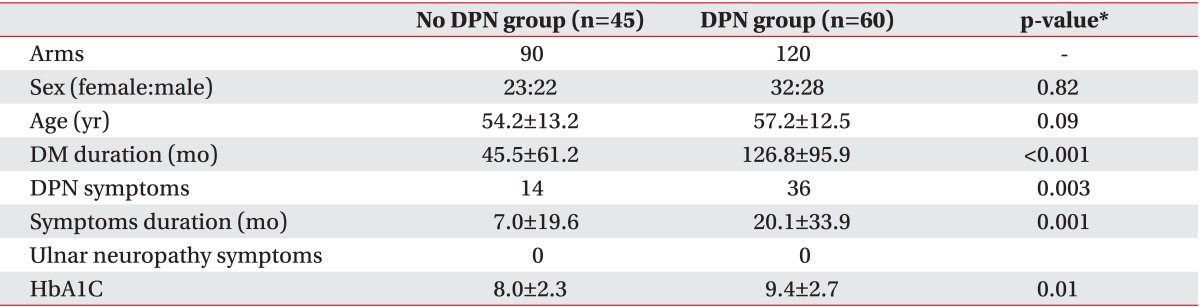
Table 1
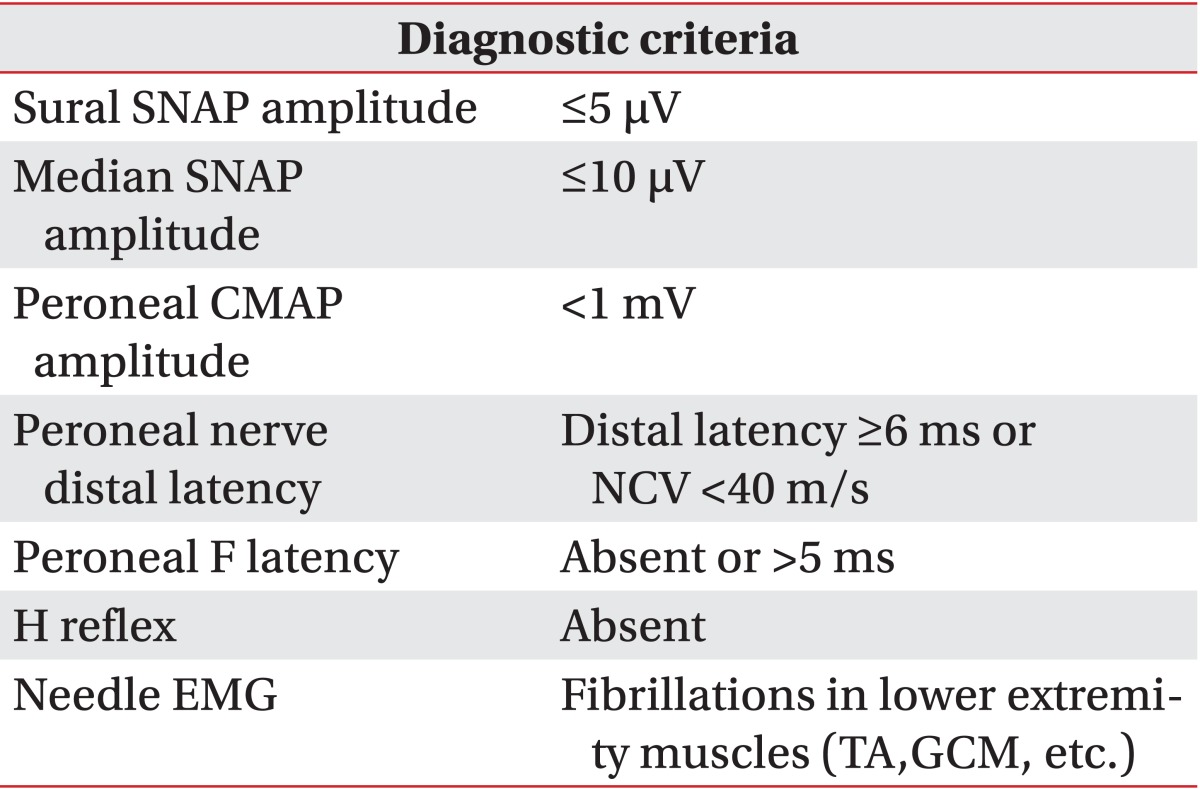
SNAP, sensory nerve action potential; CMAP, compound muscle action potential; NCV, nerve conduction velocity; EMG, electromyography; TA, tibialis anterior muscle; GCM, gastrocnemius medialis muscle; suspected DPN, sural plus at least two of above list; probable DPN, suspected plus two of above list; definite DPN, probable plus any of above list; DPN, diabetic polyneuropathy.
Statistics
RESULTS
Demographic data
Electrophysiologic data
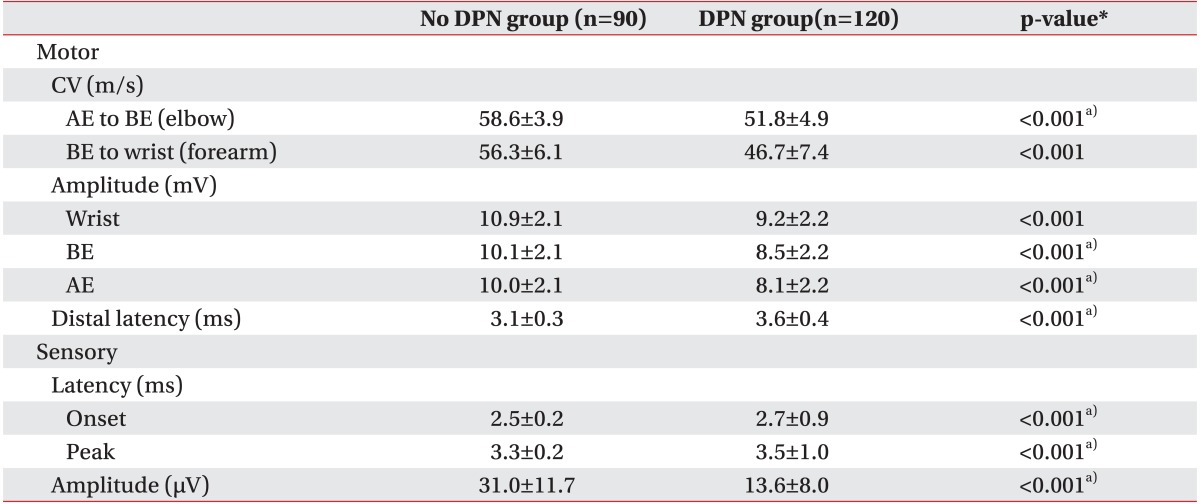
Table 4
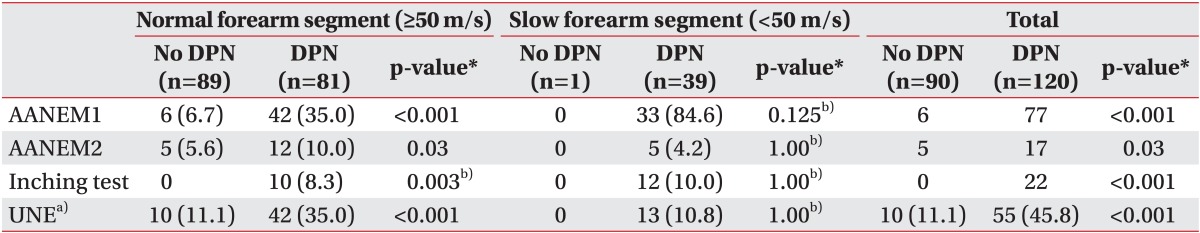
Values are presented as number (%).
DPN, diabetic polyneuropathy; MCV, motor conduction velocity; AANEM1, absolute MCV from above elbow (AE) to below elbow (BE) of less than 50 m/s; AANEM2, an AE-to-BE segment greater than 10 m/s slower than the BE-to-wrist segment; forearm, motor conduction velocity of below elbow to wrist.
*p<0.05, significant differences exists between DPN group and no DPN group.
a)Ulnar neuropathy was diagnosed by AANEM1 or AANEM2 or inching test in subgroup with normal forearm segment (≥50 m/s), but diagnosed by AANEM2 or inching test in subgroup with slow forearm segment (<50 m/s). b)Fisher exact test was done: the number of cells which expected frequency is less than 5 were 25% or more.
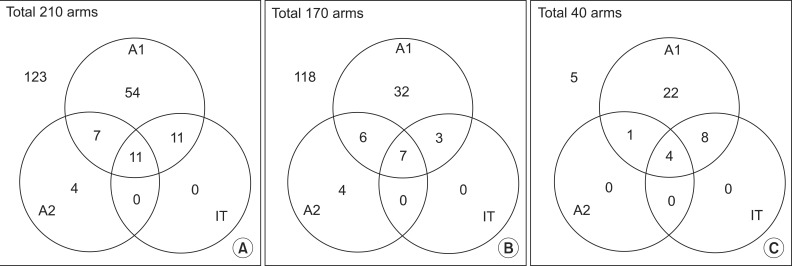 | Fig. 1Overlapping patients who satisfy each diagnostic criterion of ulnar neuropathy out of (A) all diabetic patients, in (B) the subgroup with the normal forearm segment (≥50 m/s) and (C) the subgroup with the slow forearm segment (<50 m/s). A1, AANEM1; A2, AANEM2; IT, inching test. |
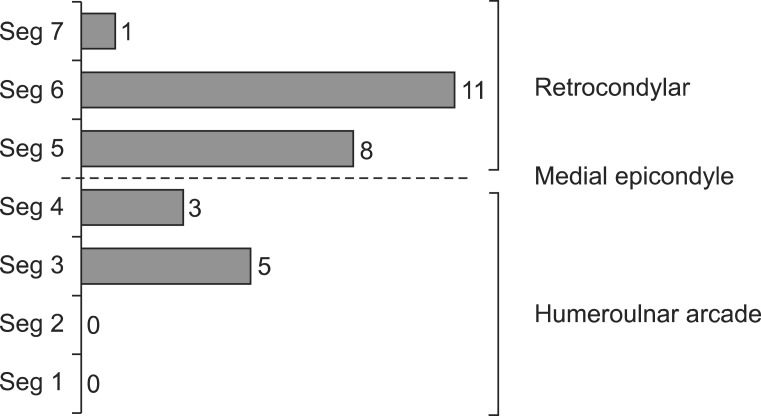 | Fig. 2Ulnar neuropathy lesion site which identified by the inching test. The most common lesion site was the retrocondylar groove (20 arms, 69.6%), and the second common site was the humeroulnar arcade (8 arms, 21.8%). Dual lesions including the retrocondylar and humeroulnar arcade lesions were found in 2 arms (8.7%). Seg1, segment between 3 and 4 cm distal to the medial epicondyle (ME); Seg2, segment between 2 and 3 cm distal to ME; Seg3, segment between 1 and 2 cm distal to ME; Seg4, segment between ME and 1 cm distal to ME; Seg5, segment between ME and 1 cm proximal to ME; Seg6, segment between 1 and 2 cm proximal to ME; Seg7, segment between 2 and 3 cm proximal to ME. |
Table 5
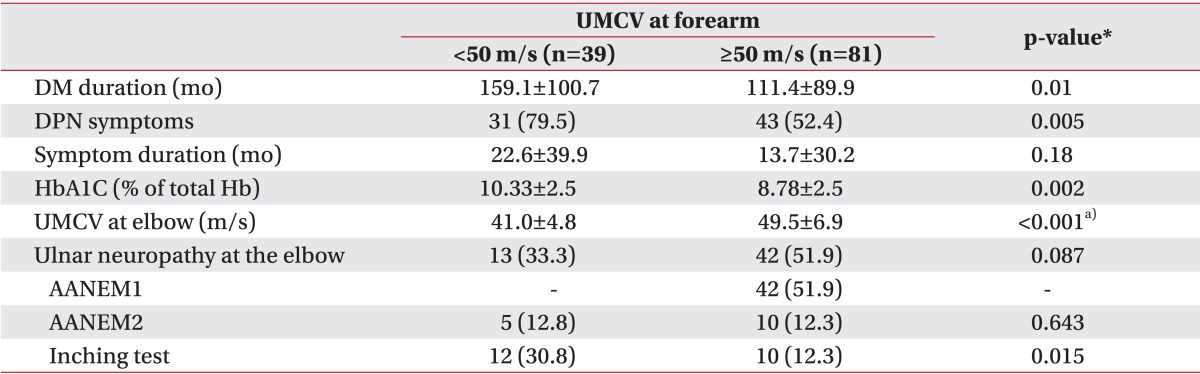
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
UMCV, ulnar motor conduction velocity; DM, diabetes mellitus; DPN, diabetic polyneuropathy; HbA1C, glycosylated hemoglobin; AANEM1, absolute MCV from above elbow (AE) to below elbow (BE) of less than 50 m/s; AANEM2, an AE-to-BE segment greater than 10 m/s slower than the BE-to-wrist segment.
*p<0.05, significant differences exists between DPN group and no DPN group.
a)Mann-Whitney test was done because normal distribution cannot be assumed.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download