INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Patients
Table 1
Clinical-pathologic characteristics of the patients in the present study (n = 26)
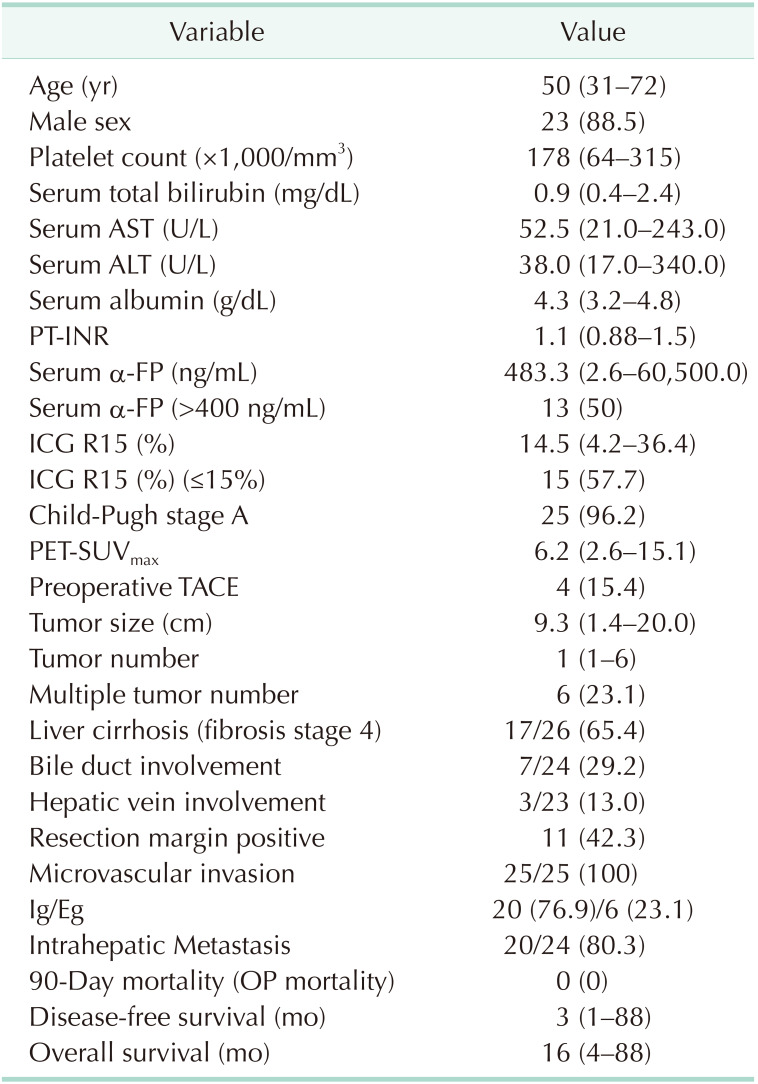
Values are presented as median (range) or number (%).
PT-INR, prothrombin time-international normalized ratio; ICG R15, indocyanine green retention rate at 15 min; PET-SUVmax, positron emission tomography-the maximum standard uptake value; TACE, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; OP, operation.
Operating procedure and portal vein thrombectomy
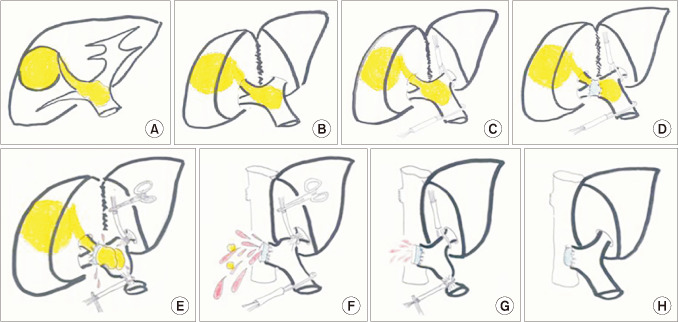 | Fig. 1The surgical procedures for thrombectomy. (A) Schema showing a right liver hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and HCC-derived portal vein tumor thrombous (PVTT) extending to the main portal vein. (B) Exposure the hilar structure after the liver parenchyma divided. (C) Extra fascial access to tape the main and the left glissonean pedicle. (D) The hepatic artery and the bile duct were ligated and divided separately. (E) While clamping the main and left portal glissonean pedicle, the anterior wall of the portal vein was transversely incised. The PVTT was peeling off from the portal lumen. (F) The lumen was flushed with heparinized saline and main portal bleeding to remove potentially cancerous residual tissue. (G) Left portal back-bleeding to remove potentially cancerous residual tissue. (H) The posterior wall of the portal vein was dissected by scalpel and the stump was closed with 6/0 prolene by continuous suture. |
Follow-up strategy, recurrence, and treatment pattern
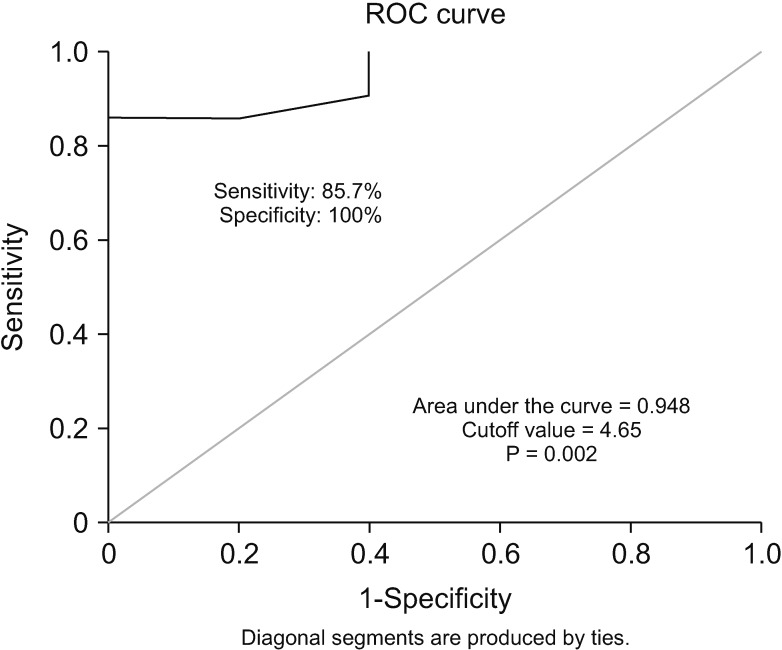
18F-FDG PET/CT acquisition, analysis, and the determination of the optimal cutoff value of SUVmax
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
The characteristics of HCC patients complicated by mPVTT
Survival outcomes and characteristics of patients with long-term survivals
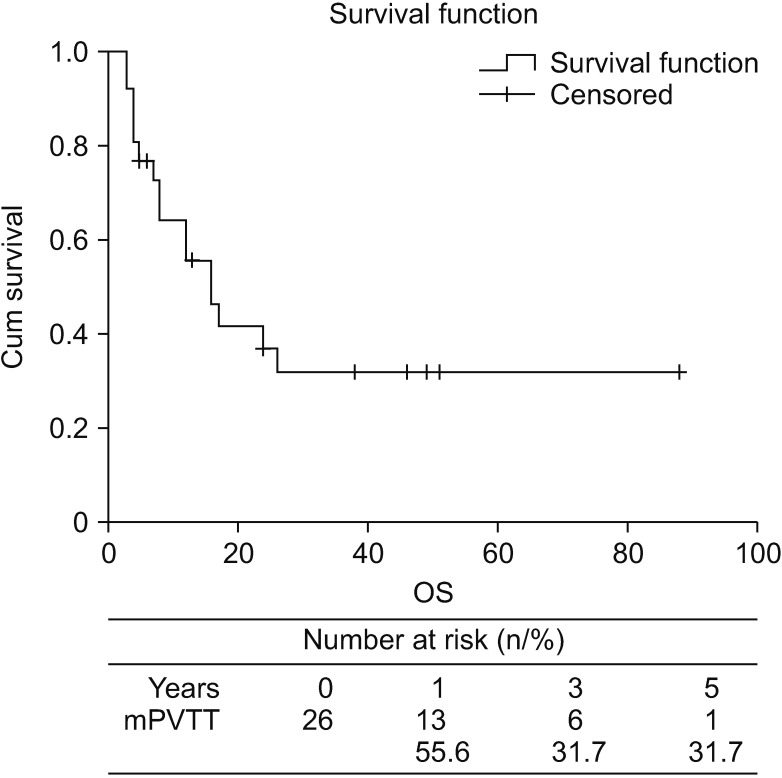 | Fig. 3Kaplan-Meier survival analysis shows the overall survival cure of the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with major portal vein tumor thrombosis (mPVTT) in the present study. The 5-year overall survival (OS) of the patients with mPVTT in this study was 31.7%. |
Table 2
The characteristics for the patients with long-term survival more than 3 years (n = 6)
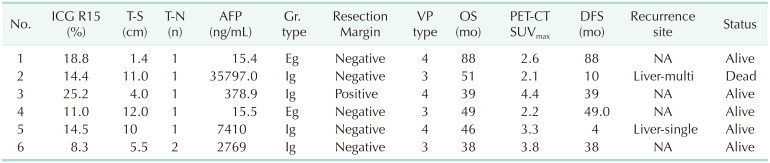
ICG R15, indocyanine green retention rate at 15 min; T-S, tumor size; T-N, tumor number; Gr. type, growth type; VP type, portal vein thrombosis type; OS, overall survival; PET-SUVmax, positron emission tomography-the maximum standard uptake value; DFS, disease-free survival; Eg, expanding type; Ig, infiltrate growth type.
The survival analysis of low and high SUVmax groups
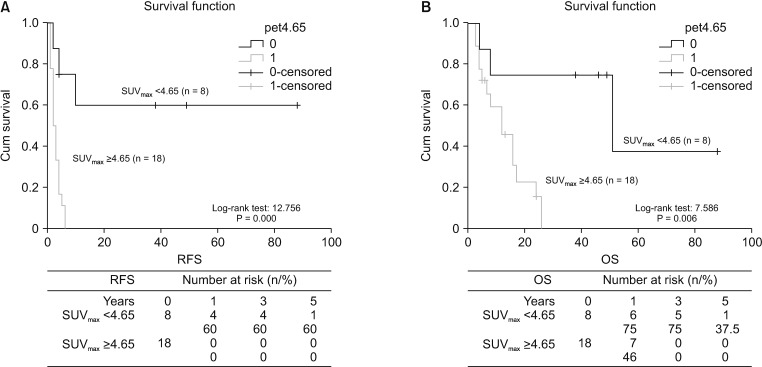 | Fig. 4Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with regard to SUVmax. (A) Patients with low SUVmax (<4.65) showed significantly longer disease-free survival than those with high SUVmax (≥4.65). (B) Patients with low SUVmax (<4.65) showed significantly longer overall survival than those with high SUVmax (≥4.65). SUVmax, maximum standard uptake value. RFS, recurrence-free survival; OS, overall survival. |
Analysis of risk factors for mPVTT patients
Table 3
Comparison of clinical-pathologic characteristic between patients with high and low SUVmax
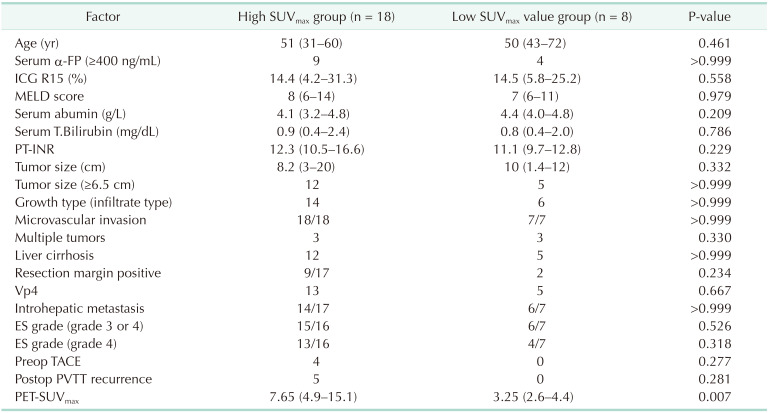
Values are presented as median (range) or number.
PET-SUVmax, positron emission tomography-the maximum standard uptake value; MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; T.Bilirubin, total bilirubin; ICG R15, indocyanine green retention rate at 15 min; Vp4, presence of a tumor thrombus in the main trunk of the portal vein or a portal vein branch contra lateral to the primarily involved lobe (or both); ES grade, Edmondson-Steiner grade; TACE, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization; PVTT, portal vein tumor thrumbosis; Preop, preoperative; Postop, postoperative.
Table 4
Cox proportional hazards model of risk factors for DFS in HCC patients with mPVTT
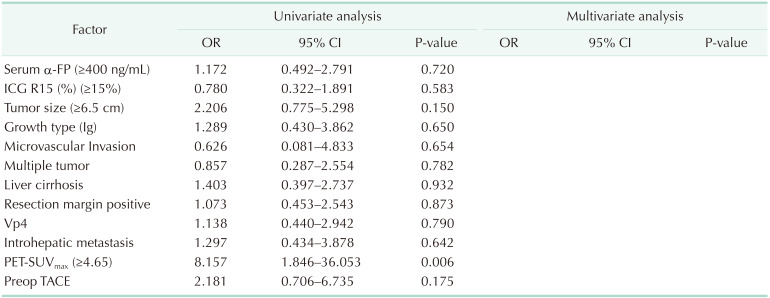
DFS, disease-free survival; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; mPVTT, major portal vein tumor thrombosis; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ICG R15, indocyanine green retention rate at 15 min; Ig, infiltrate growth type; Vp4, presence of a tumor thrombus in the main trunk of the portal vein or a portal vein branch contra lateral to the primarily involved lobe (or both); PET-SUVmax, positron emission tomography-the maximum standard uptake value; Preop, preoperative; TACE, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Table 5
Cox proportional hazards model of risk factors for OS in HCC patients with mPVTT
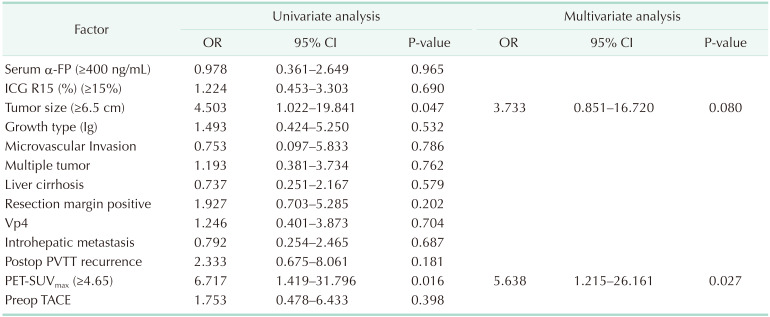
OS, overall survival; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; mPVTT, major portal vein tumor thrombosis; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ICG R15, indocyanine green retention rate at 15 min; Ig, infiltrate growth type; Vp4, presence of a tumor thrombus in the main trunk of the portal vein or a portal vein branch contra lateral to the primarily involved lobe (or both); PET-SUVmax, positron emission tomography-the maximum standard uptake value; Preop, preoperative; TACE, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download