INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Patients and data collection
Negative or positive final neck findings: definitions and outcomes
The no zone approach with hard signs
Statistical analyses
RESULTS
Clinical characteristics
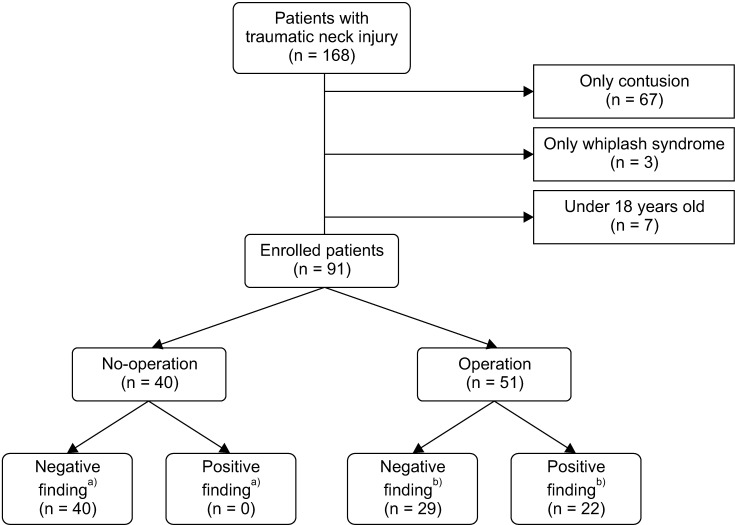 | Fig. 1Flowchart of study design. a)Internal organ injuries confirmed by CT scan. b)Internal organ injuries confirmed by an operation. |
Table 1
Clinical characteristic and patients outcomes (n = 91)
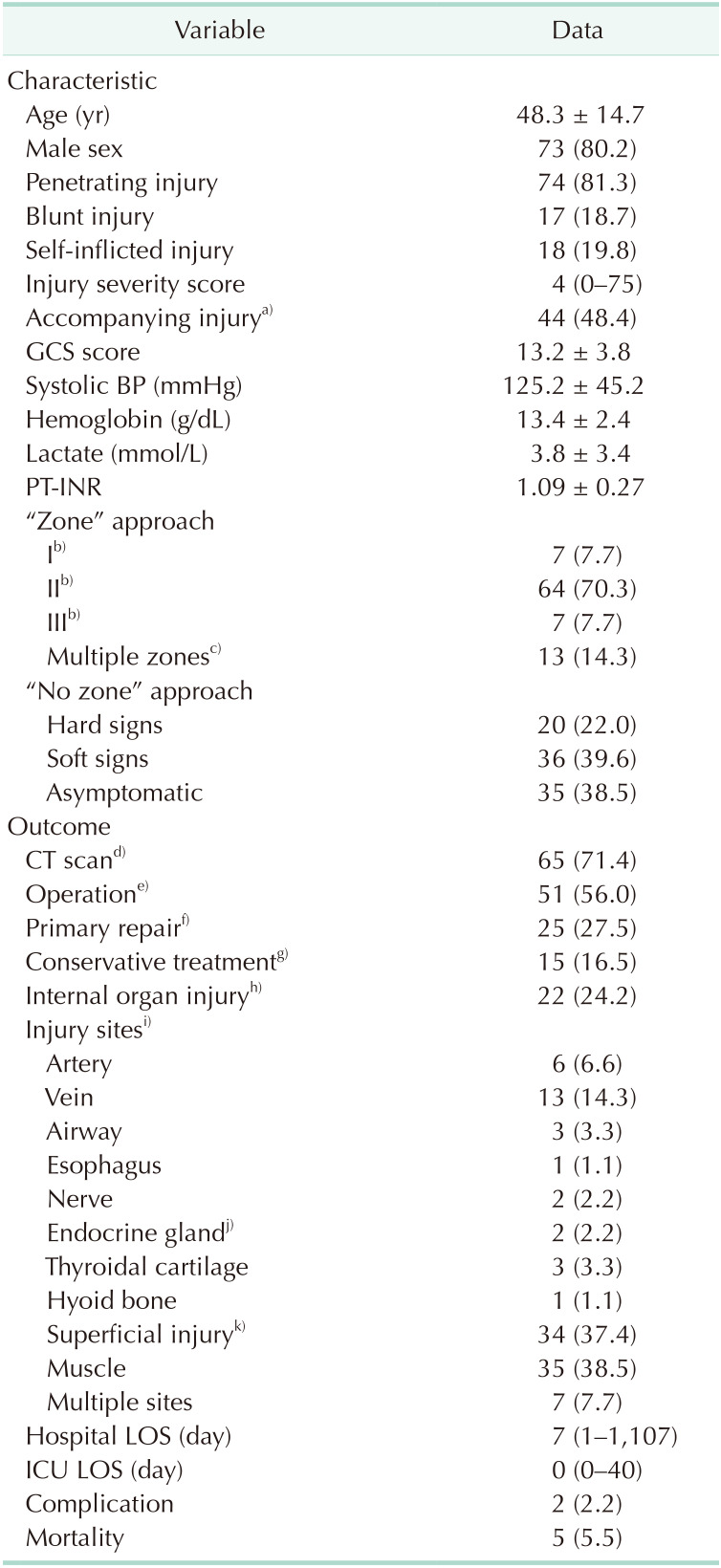
Values are presented as number (%), mean ± standard deviation, or median (range).
GCS, Glasgow coma scale; BP, blood pressure; INR, international normalized ratio; LOS, length of stay; ICU, intensive care unit.
a)Injury of head, chest, abdomen, and extremities. b)Injury isolated to the zone. c)Zone II was included in all cases. d)Neck contrast CT or neck angiography CT. e)Surgery performed under general anesthesia. f)Simple wound closure without internal organ injury under local anesthesia. g)Surgical observation without any therapeutic procedures. h)Injury to need surgical treatment confirmed by CT scan or operation. i)Variable duplicated. j)Thyroid gland or submandibular gland. k)Non-invasion of the platysma muscle.
Patient outcomes
Complications and mortalities
Zone I or III with hard signs and zone II without hard signs
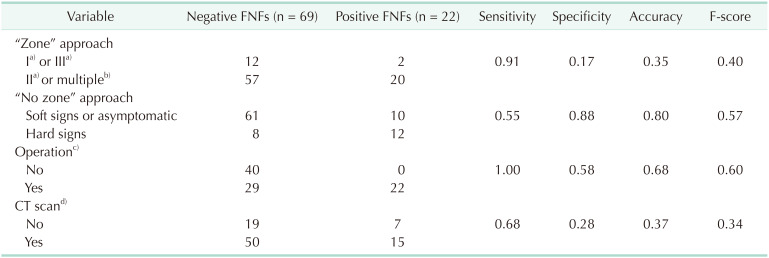
Analysis of the final neck findings of total number of patients
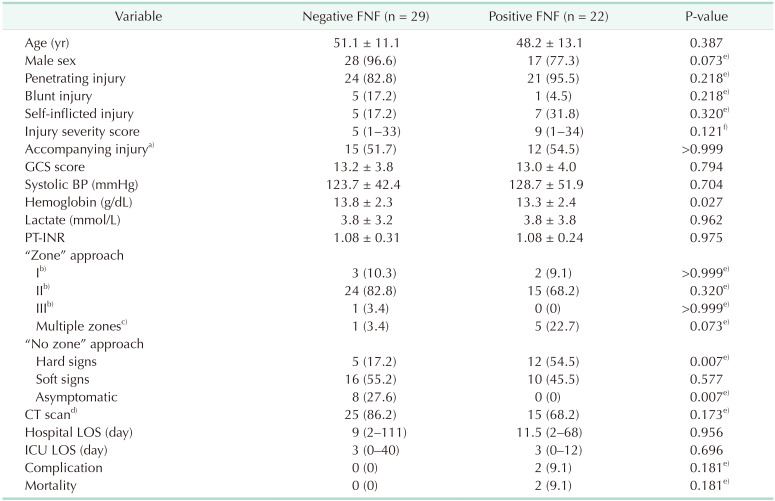
Table 3
Comparison between negative and positive FNFs in total patients
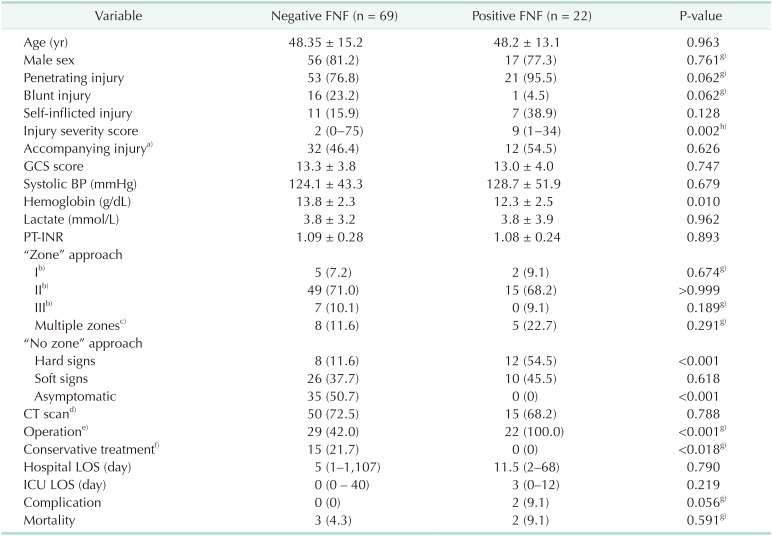
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation, number (%), or median (range).
FNF, final neck finding; GCS, Glasgow coma scale; BP, blood pressure; INR, international normalized ratio; LOS, length of stay; ICU, intensive care unit.
a)Injury of head, chest, abdomen, and extremities. b)Injury isolated to the zone. c)Zone II was included in all cases. d)Neck contrast CT or neck angiography CT. e)Surgery performed under general anesthesia. f)Surgical observation without any therapeutic procedures. g)Fisher exact test. h)Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
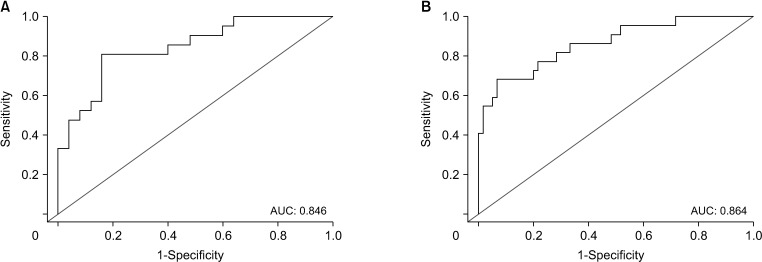 | Fig. 2A receiver operating characteristic curve and area under the curve (AUC) of multivariate logistic regression analysis for the final neck findings in total patients (A) and exploration group (B). |
Table 4
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis for negative and positive FNFs in total patient
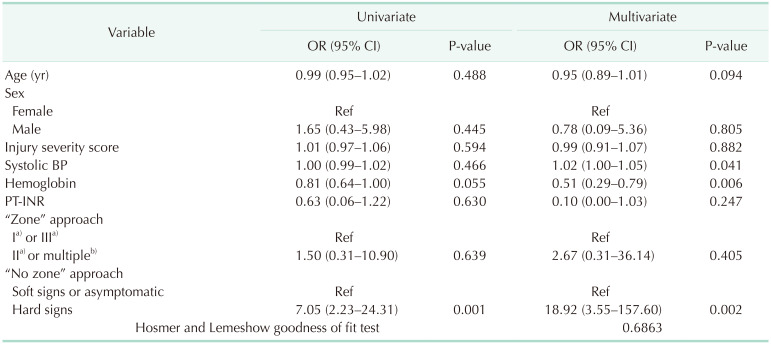
Compounding factor: age, sex, systolic BP, and PT-INR. Significant differences between the negative and positive FNFs: injury severity score and hemoglobin. Values to confirm: “zone” approach and “no zone” approach.
FNF, final neck finding; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; BP, blood pressure; INR, international normalized ratio.
a)Injury isolated to the zone. b)Zone II was included in all cases.
Analysis of the final neck findings of patients who underwent neck exploration
Table 5
Comparison between negative and positive FNFs in the exploration group
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation, number (%), or median (range).
FNF, final neck finding; GCS, Glasgow coma scale; BP, blood pressure; INR, international normalized ratio; LOS, length of stay; ICU, intensive care unit.
a)Injury of head, chest, abdomen, and extremities. b)Injury isolated to the zone. c)Zone II was included in all cases. d)Neck contrast CT or neck angiography CT. e)Fisher exact test. f)Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
Table 6
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis for negative and positive FNFs in the exploration group
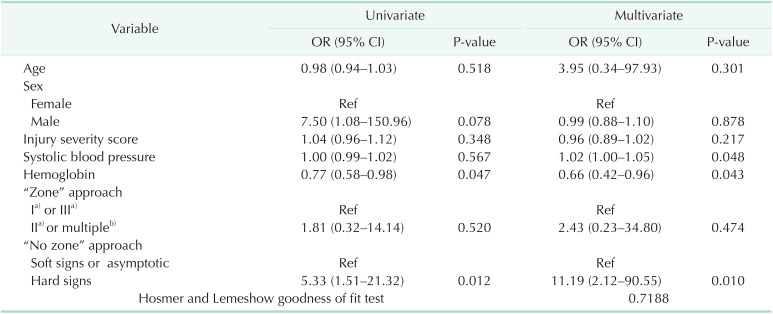
Compounding factor: age, sex, injury severity score, and systolic blood pressure. Significant differences between the negative and positive FNFs: hemoglobin. Values to confirm: “zone” approach and “no zone” approach.
FNF, final neck finding; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
a)Injury isolated to the zone. b)Zone II was included in all cases.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download