INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
Study process
Identification of duties, tasks, and task elements
Verification of the appropriateness and significance of the tasks and task elements
Survey for job analysis
Sampling: Surveys were conducted with a total of 418 care helpers working in 48 nursing facilities and community senior service facilities across the country including the provinces of Seoul, Gyeongi, Gangwon, Chungchung, Gyeongsang, Jeolla, and Jeju. The number of samples was determined in proportion to the number of nursing facilities and community senior service facilities and the number of registered care helpers by region and a convenience sampling method was used to select facilities agreeing to participate in this study.
Data collection: Official letters were sent to the facilities to explain the purpose, intent, subject, and method of this study. Only among those facilities in which a facility representative understood the study purpose and agreed to participate, did each region’s interviewers, who were educated about the guidelines and things to note, visit participants to fill out the questionnaire in person. The questionnaire consisted of tasks and task elements from the results of the DACUM workshop. A mail survey method was used for facilities which allowed the survey but were difficult to visit. The job components and the frequency of tasks were measured on a five-point scale (0, no; 1, 1 time a week or less; 2, 2 or 3 times a week; 3, once a day; 4, 2 to 3 times a day; 5, 4 times or above). To prevent the convergence toward the center that a five-point scale tends to produce, job components and the difficulty of tasks were measured by a four-point scale (1, very easy; 2, easy; 3, difficult; 4, very difficult). If the score was three or above, it was considered a difficult task.
Data analysis: The collected data were analyzed using PASW ver. 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive statistics were utilized for determining frequencies, percentages, and means.
RESULTS
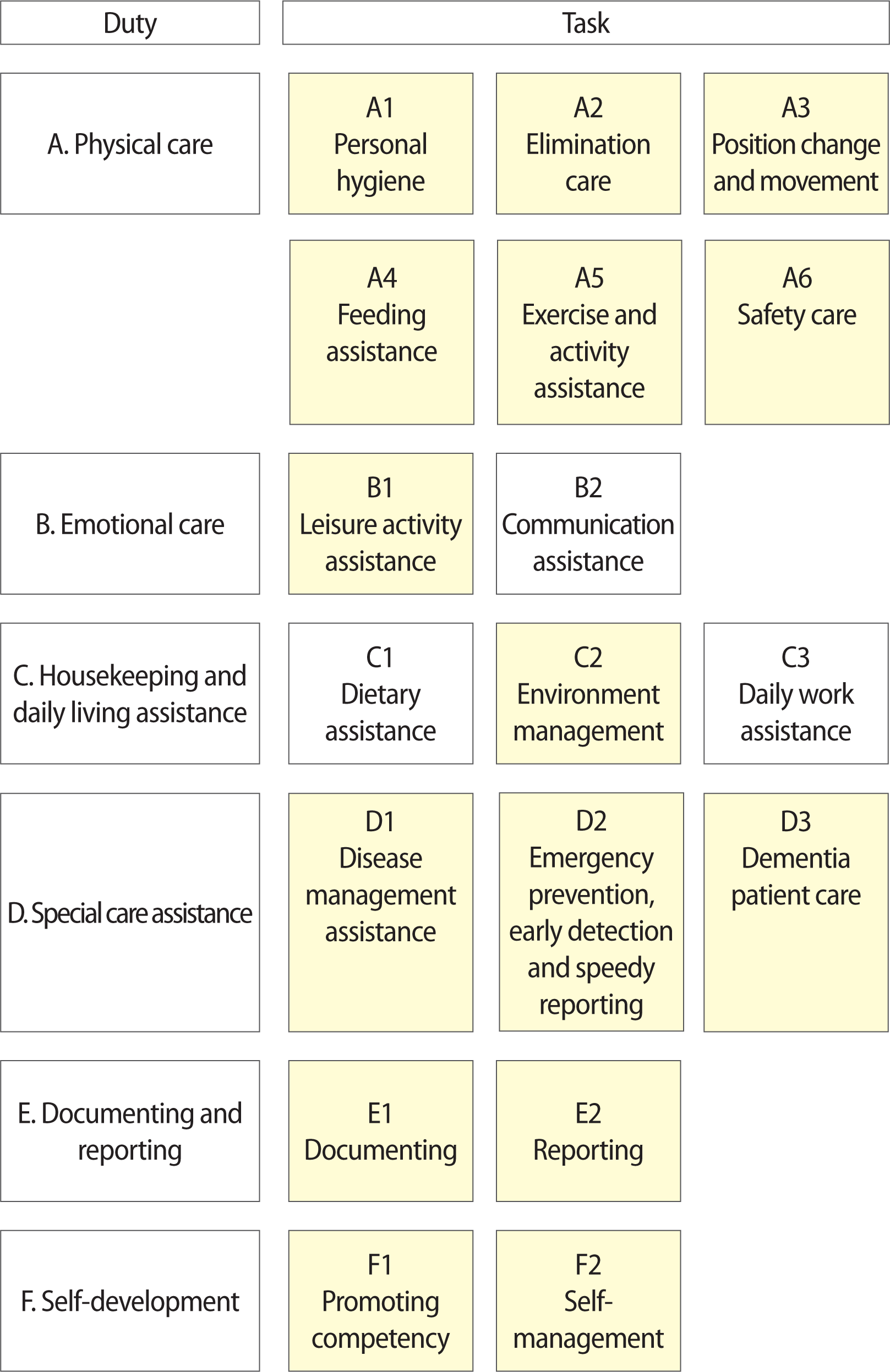
Job model
Appropriateness and significance of tasks and task elements
Table 1
Frequency and difficulty of tasks and task elements
General characteristics of the surveyed participants
Table 2
| Variables | No. (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Work site | Long term care facilities | 284 (67.9) |
| Client's home | 134 (32.1) | |
| Gender | Male | 25 (6.1) |
| Female | 388 (93.9) | |
| Missing | 5 | |
| Age (yr) | 20–29 | 13 (3.4) |
| 30–29 | 32 (8.2) | |
| 40–49 | 146 (37.6) | |
| 50–59 | 162 (41.8) | |
| ≥ 60 | 35 (9.0) | |
| Missing | 30 | |
| Educational status | Elementary | 19 (4.9) |
| Middle | 66 (17.1) | |
| High | 224 (58.0) | |
| College | 47 (12.2) | |
| University | 27 (7.0) | |
| Graduate | 3 (0.8) | |
| Missing | 32 | |
| Career (mo) | < 6 | 42 (10.7) |
| 6–12 | 70 (17.9) | |
| 13–24 | 149 (38.0) | |
| ≥ 25 | 131 (33.4) | |
| Missing | 26 | |
| Certification or license* | Care helper class 1 | 405 (96.9) |
| Care helper class 2 | 12 (2.9) | |
| Social worker class 2 | 42 (10.0) | |
| Nurse aid | 17 (4.1) | |
| Nurse | 2 (0.5) | |
| Caregiver | 60 (14.4) | |
| Others | 21 (5.0) |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download