This article has been
cited by other articles in ScienceCentral.
Abstract
Background
Data on severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) delta variant virulence are insufficient. We retrospectively compared the clinical features of adult coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients without risk factors for severe COVID-19 who entered residential treatment centers (RTCs) before and after the delta variant outbreak.
Methods
We collected medical information from two RTCs in South Korea. On the basis of nationwide delta variant surveillance, we divided the patients into two groups: 1) the delta-minor group (diagnosed from December 2020–June 2021, detection rate < 10%) and 2) the delta-dominant group (diagnosed during August 2021, detection rate > 90%). After propensity-score matching, the incidences of pneumonia, hospital transfer and need for supplemental oxygen were compared between the groups. In addition, risk factors for hospital transfer were analysed.
Results
A total of 1,915 patients were included. The incidence of pneumonia (14.6% vs. 9.2%, P = 0.009), all-cause hospital transfer (10.4% vs. 6.3%, P = 0.020) and COVID-19-related hospital transfer (7.5% vs. 4.8%, P = 0.081) were higher in the delta-dominant group than those in the delta-minor group. In the multivariate analysis, the delta-dominant group was an independent risk factor for all-cause (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.91; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.16–3.13; P = 0.011) and COVID-19-related hospital transfer (aOR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.04–3.32; P = 0.036).
Conclusion
Hospitalization rates were increased in the adult COVID-19 patients during the delta variant nationwide outbreak. Our results showed that the delta variant may be more virulent than previous lineages.
Keywords: COVID-19, Delta Variant, Virulence, Hospitalization, South Korea
INTRODUCTION
Since severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) B.1.617.2 (delta) variant was first detected in December 2020, it has become the dominant variant in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) global pandemic.
1 South Korea (Republic of Korea) was no exception to this global trend; the detection rate of the delta variant was only 1.4% in April 2021 but has since increased sharply to 90% in August 2021.
23 Regarding the delta variants’ high transmissibility,
4 this increased prevalence of the delta variant is thought to be contributing to the new nationwide COVID-19 outbreak of South Korea (the so-called ‘fourth wave’) that began in July 2021.
The virulence of the delta variant is another important concern. It is estimated that this variant is associated with a poorer prognosis—increased hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission and mortality—than that of earlier variants.
5678 These studies have very important implications for individual patients but also for the field of public health because increased severity of COVID-19 can lead to faster depletion of medical resources. However, because these studies used data from only a few countries (Scotland, USA, Canada, and Singapore), additional data on the severity of the delta variant are needed.
Because all patients diagnosed with COVID-19 should be hospitalized regardless of symptoms in South Korea, asymptomatic to moderate COVID-19 patients without risk factors for severe disease are isolated in residential treatment centers (RTCs) to cope with the shortage of hospital beds. This approach allows health care workers to closely observe the change or progression of patients’ initial symptoms and signs. Therefore, we conducted a retrospective observational study to compare the clinical features of adult South Korean COVID-19 patients before and after the national ‘fourth wave’ delta variant outbreak.
METHODS
Nationwide surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 variants in South Korea
The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency regularly updates the status of COVID-19 variants by analyzing > 20% of daily confirmed cases in South Korea through random sampling. According to the report, from December 2020 to March 2021, the wild-type accounted for > 90% of SARS-CoV-2 viruses, and no delta variants were seen. From April 2021, the delta variant started to be detected at a rate of 1.4%, and it continued to increase to 4.2% in May, 18.7% in June, and 53.7% in July when the fourth nationwide outbreak began. In August 2021, the detection rate of the delta variant exceeded 90%, indicating that delta was the dominant lineage in South Korea.
239
Study patients and group definition
From December 2020 to August 2021, a total of 2,478 COVID-19 patients were isolated in two RTCs located in Gyeongsangnam-do, South Korea. Although most of the patients had no risk factors for severe COVID-19, only patients who had acceptable medical conditions, such as well-controlled hypertension, diabetes, or mental illness, were allowed to enter the RTC. After the fourth COVID-19 outbreak, the criteria for RTC admission were maintained without modification during the study period.
Among those patients, those who met the following criteria were included in this study: 1) adult patients (≥ 18 years of age), 2) diagnosed from December 2020 to June 2021 (period of the delta variant detection rate < 10% = the delta-minor group) or during August 2021 (period of the delta variant detection rate > 90% = the delta-dominant group). Patients diagnosed during July 2021 were excluded because of inconclusive detection rates of the delta variant (53.7%).
Patient management in the RTC
On the admission day, all patients underwent initial chest X-ray (CXR) examinations. If pneumonic infiltration was found in the initial CXR or fever/respiratory symptoms did not improve, CXR was repeated within 2 to 3 days. The patients measured their vital signs (blood pressure, body temperature, SpO2) twice a day and informed the medical staff of the results. In addition, the patients reported their symptoms every day through a standardized mobile phone application. This medical information was stored in a web-based RTC health care support system. At our RTCs, only symptomatic therapy is provided.
To maintain the number of spare hospital beds, we limited the criteria for hospital transfer as follows: 1) progression of COVID-19 severity: decreased SpO2 < 95%, progression of dyspnea, or increased pneumonic infiltration on CXR, 2) physical symptoms not controlled by over-the-counter medications, and 3) psychiatric symptoms.
Data collection
We collected age, sex, underlying disease, COVID-19 symptoms, hospital transfer and radiologic evidence of pneumonia from the web-based RTC health care support system. For more detailed comparisons, we divided hospital transfer into two categories: 1) COVID-19-related transfer (progression of COVID-19 severity, deterioration of the general condition or uncontrolled other COVID-19-related symptoms) and 2) not COVID-19-related transfer (uncontrolled symptoms other than COVID-19, psychiatric problems or non-medical causes). For those who transferred to a hospital, additional outcomes (oxygen supply, ICU admission and death) were extracted from the electronic medical records of the relevant hospitals.
Statistical analysis
For comparison of clinical characteristics and outcomes between the delta-dominant group and delta-minor group, we used propensity-score (PS) modelling to reduce selection bias and potential confounding factors. After calculation of PSs by using age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypothyroidism, period from the diagnosis to admission day, presence of fever/pneumonia/COVID-19 symptoms on the admission day, the two groups were matched according to the PSs at a 1:1 ratio. With PS-matched cohort, we compared clinical characteristics and outcomes between the delta-dominant and the delta-minor group. Subgroup analysis according to the presence or absence of symptoms on the admission day was also performed in both the delta-dominant and the delta-minor group, respectively. To identify independent risk factors for all-cause and COVID-19-related hospital transfer, variables with P values < 0.1 in the univariate analysis were included in a multivariate analysis using a multiple logistic regression model. Subsequent statistical analysis was performed by using the χ2 test or two-tailed Fisher’s exact test for binary variables. For continuous variables, Student’s t-test was used. R software version 4.1.1 (2021; The R Foundation, Vienna, Austria) and SPSS version 24.0 (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) were used for statistical analyses.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital (No. 2021-09-023). Informed consent was waived by the board.
RESULTS
Patients’ characteristics
A total of 1,915 adult patients were enrolled in our study cohort. Of these patients, 479 (25%) were in the delta-dominant group, and 1,436 (75%) were in the delta-minor group. For the unmatched cohort, the delta-dominant group was younger (mean age 39.9 vs. 44.9 years,
P < 0.001), had a larger proportion of males (58% vs. 49%,
P = 0.001) and had a lower proportion of patients with underlying diseases, such as diabetes (0.6% vs. 1.9%,
P = 0.047), hypertension (2.5% vs. 7.3%,
P < 0.001), and hyperlipidemia (1.3% vs. 2.7%,
P = 0.067) than those in the delta-minor group. After PS matching, these demographic differences were compensated to reduce their statistical significance (
Table 1).
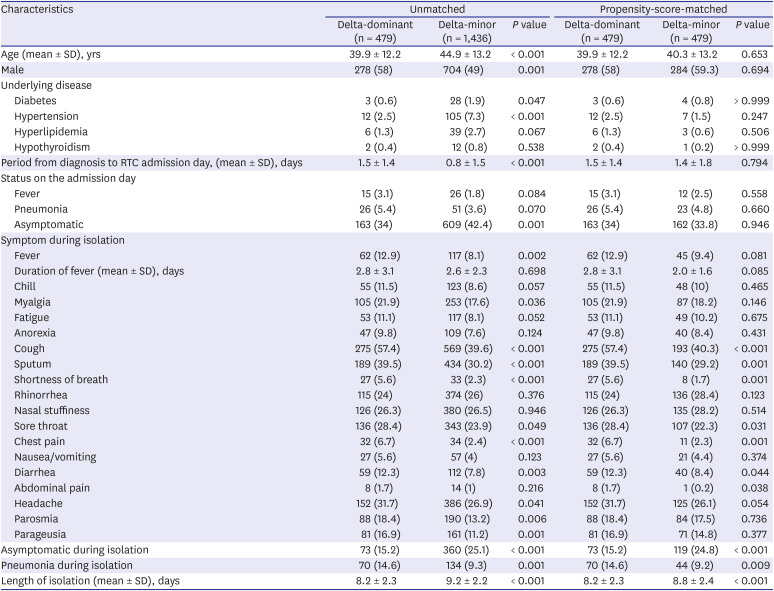
Table 1
Characteristics of adult COVID-19 patients in the RTCs
|
Characteristics |
Unmatched |
Propensity-score-matched |
|
Delta-dominant (n = 479) |
Delta-minor (n = 1,436) |
P value |
Delta-dominant (n = 479) |
Delta-minor (n = 479) |
P value |
|
Age (mean ± SD), yrs |
39.9 ± 12.2 |
44.9 ± 13.2 |
< 0.001 |
39.9 ± 12.2 |
40.3 ± 13.2 |
0.653 |
|
Male |
278 (58) |
704 (49) |
0.001 |
278 (58) |
284 (59.3) |
0.694 |
|
Underlying disease |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diabetes |
3 (0.6) |
28 (1.9) |
0.047 |
3 (0.6) |
4 (0.8) |
> 0.999 |
|
Hypertension |
12 (2.5) |
105 (7.3) |
< 0.001 |
12 (2.5) |
7 (1.5) |
0.247 |
|
Hyperlipidemia |
6 (1.3) |
39 (2.7) |
0.067 |
6 (1.3) |
3 (0.6) |
0.506 |
|
Hypothyroidism |
2 (0.4) |
12 (0.8) |
0.538 |
2 (0.4) |
1 (0.2) |
> 0.999 |
|
Period from diagnosis to RTC admission day, (mean ± SD), days |
1.5 ± 1.4 |
0.8 ± 1.5 |
< 0.001 |
1.5 ± 1.4 |
1.4 ± 1.8 |
0.794 |
|
Status on the admission day |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fever |
15 (3.1) |
26 (1.8) |
0.084 |
15 (3.1) |
12 (2.5) |
0.558 |
|
Pneumonia |
26 (5.4) |
51 (3.6) |
0.070 |
26 (5.4) |
23 (4.8) |
0.660 |
|
Asymptomatic |
163 (34) |
609 (42.4) |
0.001 |
163 (34) |
162 (33.8) |
0.946 |
|
Symptom during isolation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fever |
62 (12.9) |
117 (8.1) |
0.002 |
62 (12.9) |
45 (9.4) |
0.081 |
|
Duration of fever (mean ± SD), days |
2.8 ± 3.1 |
2.6 ± 2.3 |
0.698 |
2.8 ± 3.1 |
2.0 ± 1.6 |
0.085 |
|
Chill |
55 (11.5) |
123 (8.6) |
0.057 |
55 (11.5) |
48 (10) |
0.465 |
|
Myalgia |
105 (21.9) |
253 (17.6) |
0.036 |
105 (21.9) |
87 (18.2) |
0.146 |
|
Fatigue |
53 (11.1) |
117 (8.1) |
0.052 |
53 (11.1) |
49 (10.2) |
0.675 |
|
Anorexia |
47 (9.8) |
109 (7.6) |
0.124 |
47 (9.8) |
40 (8.4) |
0.431 |
|
Cough |
275 (57.4) |
569 (39.6) |
< 0.001 |
275 (57.4) |
193 (40.3) |
< 0.001 |
|
Sputum |
189 (39.5) |
434 (30.2) |
< 0.001 |
189 (39.5) |
140 (29.2) |
0.001 |
|
Shortness of breath |
27 (5.6) |
33 (2.3) |
< 0.001 |
27 (5.6) |
8 (1.7) |
0.001 |
|
Rhinorrhea |
115 (24) |
374 (26) |
0.376 |
115 (24) |
136 (28.4) |
0.123 |
|
Nasal stuffiness |
126 (26.3) |
380 (26.5) |
0.946 |
126 (26.3) |
135 (28.2) |
0.514 |
|
Sore throat |
136 (28.4) |
343 (23.9) |
0.049 |
136 (28.4) |
107 (22.3) |
0.031 |
|
Chest pain |
32 (6.7) |
34 (2.4) |
< 0.001 |
32 (6.7) |
11 (2.3) |
0.001 |
|
Nausea/vomiting |
27 (5.6) |
57 (4) |
0.123 |
27 (5.6) |
21 (4.4) |
0.374 |
|
Diarrhea |
59 (12.3) |
112 (7.8) |
0.003 |
59 (12.3) |
40 (8.4) |
0.044 |
|
Abdominal pain |
8 (1.7) |
14 (1) |
0.216 |
8 (1.7) |
1 (0.2) |
0.038 |
|
Headache |
152 (31.7) |
386 (26.9) |
0.041 |
152 (31.7) |
125 (26.1) |
0.054 |
|
Parosmia |
88 (18.4) |
190 (13.2) |
0.006 |
88 (18.4) |
84 (17.5) |
0.736 |
|
Parageusia |
81 (16.9) |
161 (11.2) |
0.001 |
81 (16.9) |
71 (14.8) |
0.377 |
|
Asymptomatic during isolation |
73 (15.2) |
360 (25.1) |
< 0.001 |
73 (15.2) |
119 (24.8) |
< 0.001 |
|
Pneumonia during isolation |
70 (14.6) |
134 (9.3) |
0.001 |
70 (14.6) |
44 (9.2) |
0.009 |
|
Length of isolation (mean ± SD), days |
8.2 ± 2.3 |
9.2 ± 2.2 |
< 0.001 |
8.2 ± 2.3 |
8.8 ± 2.4 |
< 0.001 |

For COVID-19-related symptoms in the PS-matched cohort, there were more patients who complained of fever and lower respiratory symptoms (cough, sputum, shortness of breath and chest pain) in the delta-dominant group than those in the delta-minor group. The number of asymptomatic patients was lower in the delta-dominant group than in the delta-minor group (15.2% vs. 24.3%, P < 0.001). More patients showed radiologic evidence of pneumonia in the delta-dominant group than in the delta-minor group (14.6% vs. 9.2%, P = 0.009).
In the subgroup analysis, the delta-dominant group showed higher frequencies of lower respiratory symptoms and pneumonia during the isolation period than the delta-minor group did, regardless of the presence of symptoms on the admission day. The asymptomatic persistence rate during isolation of patients who were asymptomatic at the admission day was significantly lower in the delta-dominant group than in the delta-minor group (44.8% vs. 73.5%,
P < 0.001) (
Supplementary Table 1).
Outcomes
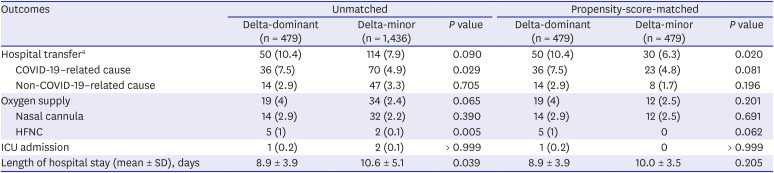
In the PS-matched cohort, all-cause transfer (10.4% vs. 6.3%,
P = 0.020) and COVID-19-related transfer to hospital (7.5% vs. 4.8%,
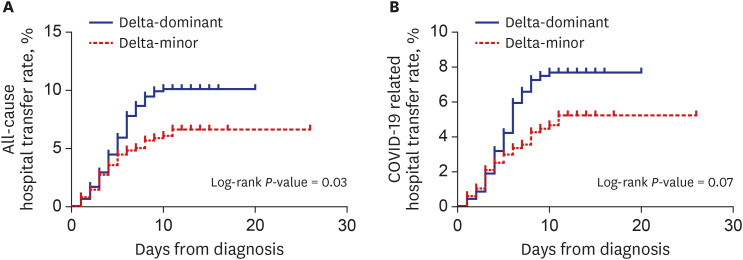
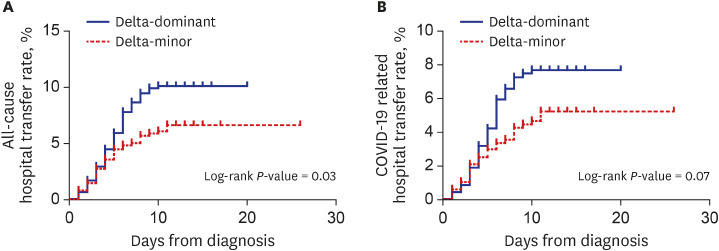
P = 0.081) were more frequent in the delta-dominant group than in the delta-minor group. Kaplan-Meier curves in
Fig. 1 visualized these outcomes. Except for those who were transferred to the hospital, all patients recovered and returned home.
Fig. 1
Kaplan-Meier curves for all-cause (A) and COVID-19-related hospital transfer (B) in the propensity-score-matched cohort.
COVID-19 = coronavirus disease 2019.

There was no statistical difference in the proportion of patients requiring supplemental oxygen between the two groups (4% vs. 2.5%, P = 0.201). Among oxygen-therapy types, there was a tendency for greater use of a high-flow nasal cannula in the delta-dominant group (1% vs. 0%, P = 0.062).
There was no significant difference in the number of ICU admissions (0.2% vs. 0%,
P > 0.999) and the length of hospital stay (mean 8.9 vs. 10.0 days,
P = 0.205) between the two groups (
Table 2). In-hospital mortality was not observed in either group.
Table 2
Outcomes of adult COVID-19 patients
|
Outcomes |
Unmatched |
Propensity-score-matched |
|
Delta-dominant (n = 479) |
Delta-minor (n = 1,436) |
P value |
Delta-dominant (n = 479) |
Delta-minor (n = 479) |
P value |
|
Hospital transfera
|
50 (10.4) |
114 (7.9) |
0.090 |
50 (10.4) |
30 (6.3) |
0.020 |
|
COVID-19-related cause |
36 (7.5) |
70 (4.9) |
0.029 |
36 (7.5) |
23 (4.8) |
0.081 |
|
Non-COVID-19-related cause |
14 (2.9) |
47 (3.3) |
0.705 |
14 (2.9) |
8 (1.7) |
0.196 |
|
Oxygen supply |
19 (4) |
34 (2.4) |
0.065 |
19 (4) |
12 (2.5) |
0.201 |
|
Nasal cannula |
14 (2.9) |
32 (2.2) |
0.390 |
14 (2.9) |
12 (2.5) |
0.691 |
|
HFNC |
5 (1) |
2 (0.1) |
0.005 |
5 (1) |
0 |
0.062 |
|
ICU admission |
1 (0.2) |
2 (0.1) |
> 0.999 |
1 (0.2) |
0 |
> 0.999 |
|
Length of hospital stay (mean ± SD), days |
8.9 ± 3.9 |
10.6 ± 5.1 |
0.039 |
8.9 ± 3.9 |
10.0 ± 3.5 |
0.205 |

In the subgroup analysis, all-cause hospital transfer rate of the delta-dominant group patients who were asymptomatic on the admission day was significantly higher than that of the delta-minor group patients (7.4% vs. 2.5%,
P = 0.041). For the symptomatic patients on the admission day, there was no significant difference in hospitalization rates between the two groups (
Supplementary Table 2).
Risk factors for hospital transfer
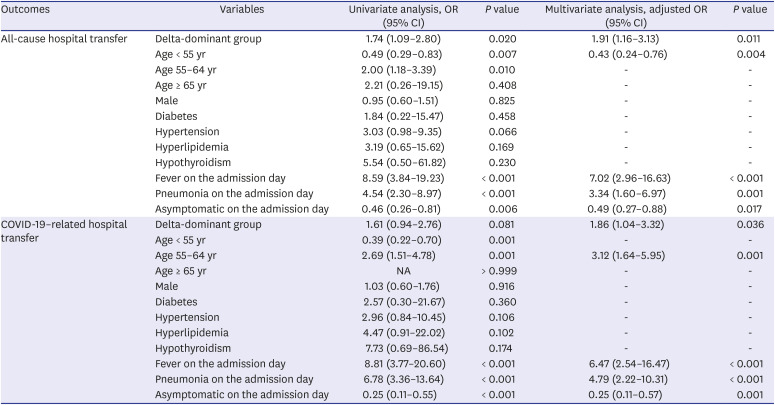
For all-cause hospital transfer, the delta-dominant group (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.91; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.16–3.13; P = 0.011), fever on the admission day (aOR, 7.02; 95% CI, 2.96–16.63; P < 0.001), and pneumonia on the admission day (aOR, 3.34; 95% CI, 1.60–6.97; P = 0.001) were independent risk factors. Age < 55 years (aOR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.24–0.76; P = 0.004) and asymptomatic on the admission day (aOR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.27–0.88; P = 0.017) were identified as independent protective factors.
For COVID-19-related hospital transfer, the delta-dominant group (aOR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.04–3.32;
P = 0.036), age 55–64 years (aOR, 3.12’ 95% CI, 1.64–5.95;
P = 0.001), fever on the admission day (aOR, 6.47; 95% CI, 2.54–16.47;
P < 0.001), and pneumonia on the admission day (aOR, 4.79; 95% CI, 2.22–10.31;
P < 0.001) were independent risk factors. Asymptomatic on the admission day (aOR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.11–0.57;
P = 0.001) was an independent factor reducing the risk of COVID-19-related hospital transfer (
Table 3).
Table 3
Risk factors for all-cause and COVID-19-related hospital transfer in the propensity-score-matched cohort
|
Outcomes |
Variables |
Univariate analysis, OR (95% CI) |
P value |
Multivariate analysis, adjusted OR (95% CI) |
P value |
|
All-cause hospital transfer |
Delta-dominant group |
1.74 (1.09–2.80) |
0.020 |
1.91 (1.16–3.13) |
0.011 |
|
Age < 55 yr |
0.49 (0.29–0.83) |
0.007 |
0.43 (0.24–0.76) |
0.004 |
|
Age 55–64 yr |
2.00 (1.18–3.39) |
0.010 |
- |
- |
|
Age ≥ 65 yr |
2.21 (0.26–19.15) |
0.408 |
- |
- |
|
Male |
0.95 (0.60–1.51) |
0.825 |
- |
- |
|
Diabetes |
1.84 (0.22–15.47) |
0.458 |
- |
- |
|
Hypertension |
3.03 (0.98–9.35) |
0.066 |
- |
- |
|
Hyperlipidemia |
3.19 (0.65–15.62) |
0.169 |
- |
- |
|
Hypothyroidism |
5.54 (0.50–61.82) |
0.230 |
- |
- |
|
Fever on the admission day |
8.59 (3.84–19.23) |
< 0.001 |
7.02 (2.96–16.63) |
< 0.001 |
|
Pneumonia on the admission day |
4.54 (2.30–8.97) |
< 0.001 |
3.34 (1.60–6.97) |
0.001 |
|
Asymptomatic on the admission day |
0.46 (0.26–0.81) |
0.006 |
0.49 (0.27–0.88) |
0.017 |
|
COVID-19-related hospital transfer |
Delta-dominant group |
1.61 (0.94–2.76) |
0.081 |
1.86 (1.04–3.32) |
0.036 |
|
Age < 55 yr |
0.39 (0.22–0.70) |
0.001 |
- |
- |
|
Age 55–64 yr |
2.69 (1.51–4.78) |
0.001 |
3.12 (1.64–5.95) |
0.001 |
|
Age ≥ 65 yr |
NA |
> 0.999 |
- |
- |
|
Male |
1.03 (0.60–1.76) |
0.916 |
- |
- |
|
Diabetes |
2.57 (0.30–21.67) |
0.360 |
- |
- |
|
Hypertension |
2.96 (0.84–10.45) |
0.106 |
- |
- |
|
Hyperlipidemia |
4.47 (0.91–22.02) |
0.102 |
- |
- |
|
Hypothyroidism |
7.73 (0.69–86.54) |
0.174 |
- |
- |
|
Fever on the admission day |
8.81 (3.77–20.60) |
< 0.001 |
6.47 (2.54–16.47) |
< 0.001 |
|
Pneumonia on the admission day |
6.78 (3.36–13.64) |
< 0.001 |
4.79 (2.22–10.31) |
< 0.001 |
|
Asymptomatic on the admission day |
0.25 (0.11–0.55) |
< 0.001 |
0.25 (0.11–0.57) |
0.001 |

DISCUSSION
Beginning with Scottish scholars who noted an increased hospitalization risk of the delta variant, reports on the augmented toxicity of this lineage began to be published around the world.
5 The evidence for the greater toxicity included increased hospitalization or emergency department visits,
710 increased ICU admission or death,
678 and more frequent need for supplemental oxygen.
8 Consistent with these prior studies, our findings suggest that the delta variant contributed to deteriorated symptoms, development of pneumonia, and increased hospitalization. The reasons for the finding of enhanced virulence of the delta variant are as follows. The viral load was significantly higher for the delta variant than for other lineages,
11 and there is evidence that high SARS-CoV-2 levels are associated with worsening of severity and mortality. The delta variant has a higher degree of viremia and more active inflammatory response.
12 The delta variant has more efficient and more rapid cell infectivity,
13 which together with the increase in viral loads, leads to an enhanced inflammatory response and exacerbated toxicity.
Previously, India had been entering a period of reduced COVID-19 pandemic but then experienced a surge again as the delta variant spread rapidly. The explosive increase in patients led to depletion of hospital beds and medical oxygen supplies.
14 The precedent of India presents many challenges that other countries will experience. To combat the spread of the delta variant, sufficient medical resources must be prepared to accommodate the growing number of patients with severe disease. South Korea is solving this problem by making it mandatory to install beds for severe patients in medium-to-large hospitals and setting up RTCs for mild patients nationwidely.
In order to reduce the number of severe COVID-19 patients and make more efficient management of medical resources, South Korea's vaccination plan began with a focus on the elderly and essential social workers. As a result, people < 60 age had to wait for vaccinations, and the fourth wave outbreak began around this age group in South Korea. This suggests that most of the study patients who entered our RTCs during the in delta variant outbreak (mean age 39.9 years) were unvaccinated, and the impact of vaccination on our results is thought to be negligible.
Our study had several limitations. First, whole-genome sequencing was not performed to identify the SARS-CoV-2 variants in our patients. Instead, we established a study group based on the detection rate of the delta variants indirectly determined through random sampling. Second, patients with risk factors for severe COVID-19 were rarely included in our cohort. Hence, our results cannot be applied to those patients. Third, we could not access the patients’ vaccination records. Thus, the association between vaccination and the severity of the delta variant was difficult to be determined. However, given South Korea’s low vaccination rate in low-risk groups, the number of vaccinated patients was expected to be minimal until the study period.
Despite these limitations, our study had the following strength. We reviewed the medical information of adult COVID-19 patients without risk factors for severe disease from diagnosis to release from isolation. This approach provided a clearer understanding of the clinical course of asymptomatic to moderate COVID-19 patients than could be achieved in previous studies.
In conclusion, we found increased hospitalization in the adult COVID-19 patients diagnosed during the delta variant nationwide outbreak in South Korea. The incidence of pneumonia was higher and number of various COVID-19 symptoms was greater in the patients diagnosed during the delta variant outbreak than in those diagnosed earlier. Health care authorities should be aware of the greater toxicity of the delta variant. Appropriate countermeasures against pandemic of this variant are urgently required.







 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download