Abstract
Objective
To introduce a systematic classification of diaphragmatic surgery in patients with ovarian cancer based on disease spread and surgical complexity.
Methods
For all consecutive patients who underwent diaphragmatic surgery during Visceral-Peritoneal debulking (VPD) in the period 2009–2017, we extracted: initial surgical finding, extent of liver mobilization and type of procedure. Combining these features, we aimed to classify the surgical procedures necessary to tackle different presentation of diaphragmatic disease. We also report histology, intra- and post-operative specific complication rate based on the classification.
Results
A total of 170 patients were included in this study, 110 (64.7%) had a peritonectomy, while 60 (35.3%) had a full thickness resection with pleurectomy. We identified 3 types of surgical procedures. Type I treated 28 out of 170 patients (16.5%) who only had anterior diaphragm disease, needed no liver mobilization, included peritonectomy and had no morbidity recorded. Type II pertained to 105 out of 170 patients (61.7%) who had anterior and posterior disease, needed partial and sometimes full liver mobilization, had a mix of peritonectomy and full thickness resection, and experienced 10% specific morbidity. Type III included 37 out of 170 patients (21.7%) who needed full mobilization of the liver, always had full thickness resection, and suffered 30% specific morbidity.
Conclusion
Diaphragmatic surgery can be classified in 3 types. The adoption of this classification can facilitate standardization of the surgery, comparison of data and define the expertise required. Finally, this classification can be a benchmark to establish the training required to treat diaphragmatic disease.
Go to : 
References
1. Vergote I, Tropé CG, Amant F, Kristensen GB, Ehlen T, Johnson N, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary surgery in stage IIIC or IV ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:943–53.

2. Chi DS, Liao JB, Leon LF, Venkatraman ES, Hensley ML, Bhaskaran D, et al. Identification of prognostic factors in advanced epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2001; 82:532–7.

3. Winter WE 3rd, Maxwell GL, Tian C, Carlson JW, Ozols RF, Rose PG, et al. Prognostic factors for stage III epithelial ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:3621–7.

4. Bristow RE, Tomacruz RS, Armstrong DK, Trimble EL, Montz FJ. Survival effect of maximal cytoreductive surgery for advanced ovarian carcinoma during the platinum era: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:1248–59.

5. Chi DS, Eisenhauer EL, Lang J, Huh J, Haddad L, Abu-Rustum NR, et al. What is the optimal goal of primary cytoreductive surgery for bulky stage IIIC epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC)? Gynecol Oncol. 2006; 103:559–64.

6. Deppe G, Malviya VK, Boike G, Hampton A. Surgical approach to diaphragmatic metastases from ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1986; 24:258–60.

7. Montz FJ, Schlaerth JB, Berek JS. Resection of diaphragmatic peritoneum and muscle: role in cytoreductive surgery for ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 1989; 35:338–40.

8. Tozzi R, Giannice R, Cianci S, Tardino S, Campanile RG, Gubbala K, et al. Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy does not increase the rate of complete resection and does not significantly reduce the morbidity of Visceral-Peritoneal Debulking (VPD) in patients with stage IIIC–IV ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2015; 138:252–8.

9. Soleymani Majd H, Ferrari F, Manek S, Gubbala K, Campanile RG, Hardern K, et al. Diaphragmatic peritonectomy vs. full thickness resection with pleurectomy during Visceral-Peritoneal Debulking (VPD) in 100 consecutive patients with stage IIIC–IV ovarian cancer: a surgical-histological analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2016; 140:430–5.

10. Tsolakidis D, Amant F, Leunen K, Cadron I, Neven P, Vergote I. Comparison of diaphragmatic surgery at primary or interval debulking in advanced ovarian carcinoma: an analysis of 163 patients. Eur J Cancer. 2011; 47:191–8.

11. Einenkel J, Ott R, Handzel R, Braumann UD, Horn LC. Characteristics and management of diaphragm involvement in patients with primary advanced-stage ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2009; 19:1288–97.

12. Fanfani F, Fagotti A, Gallotta V, Ercoli A, Pacelli F, Costantini B, et al. Upper abdominal surgery in advanced and recurrent ovarian cancer: role of diaphragmatic surgery. Gynecol Oncol. 2010; 116:497–501.

13. Chéreau E, Ballester M, Selle F, Cortez A, Pomel C, Darai E, et al. Pulmonary morbidity of diaphragmatic surgery for stage III/IV ovarian cancer. BJOG. 2009; 116:1062–8.

14. Eisenhauer EL, D'Angelica MI, Abu-Rustum NR, Sonoda Y, Jarnagin WR, Barakat RR, et al. Incidence and management of pleural effusions after diaphragm peritonectomy or resection for advanced mullerian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2006; 103:871–7.

15. Chi DS, Abu-Rustum NR, Sonoda Y, Chen SW, Flores RM, Downey R, et al. The benefit of video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery before planned abdominal exploration in patients with suspected advanced ovarian cancer and moderate to large pleural effusions. Gynecol Oncol. 2004; 94:307–11.

16. Eisenkop SM, Spirtos NM. What are the current surgical objectives, strategies, and technical capabilities of gynecologic oncologists treating advanced epithelial ovarian cancer? Gynecol Oncol. 2001; 82:489–97.

17. Chéreau E, Rouzier R, Gouy S, Ferron G, Narducci F, Bergzoll C, et al. Morbidity of diaphragmatic surgery for advanced ovarian cancer: retrospective study of 148 cases. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2011; 37:175–80.

18. Dowdy SC, Loewen RT, Aletti G, Feitoza SS, Cliby W. Assessment of outcomes and morbidity following diaphragmatic peritonectomy for women with ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2008; 109:303–7.

19. Aletti GD, Dowdy SC, Podratz KC, Cliby WA. Surgical treatment of diaphragm disease correlates with improved survival in optimally debulked advanced stage ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2006; 100:283–7.

20. Diaz JP, Abu-Rustum NR, Sonoda Y, Downey RJ, Park BJ, Flores RM, et al. Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) evaluation of pleural effusions in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian carcinoma can influence the primary management choice for these patients. Gynecol Oncol. 2010; 116:483–8.

Go to : 
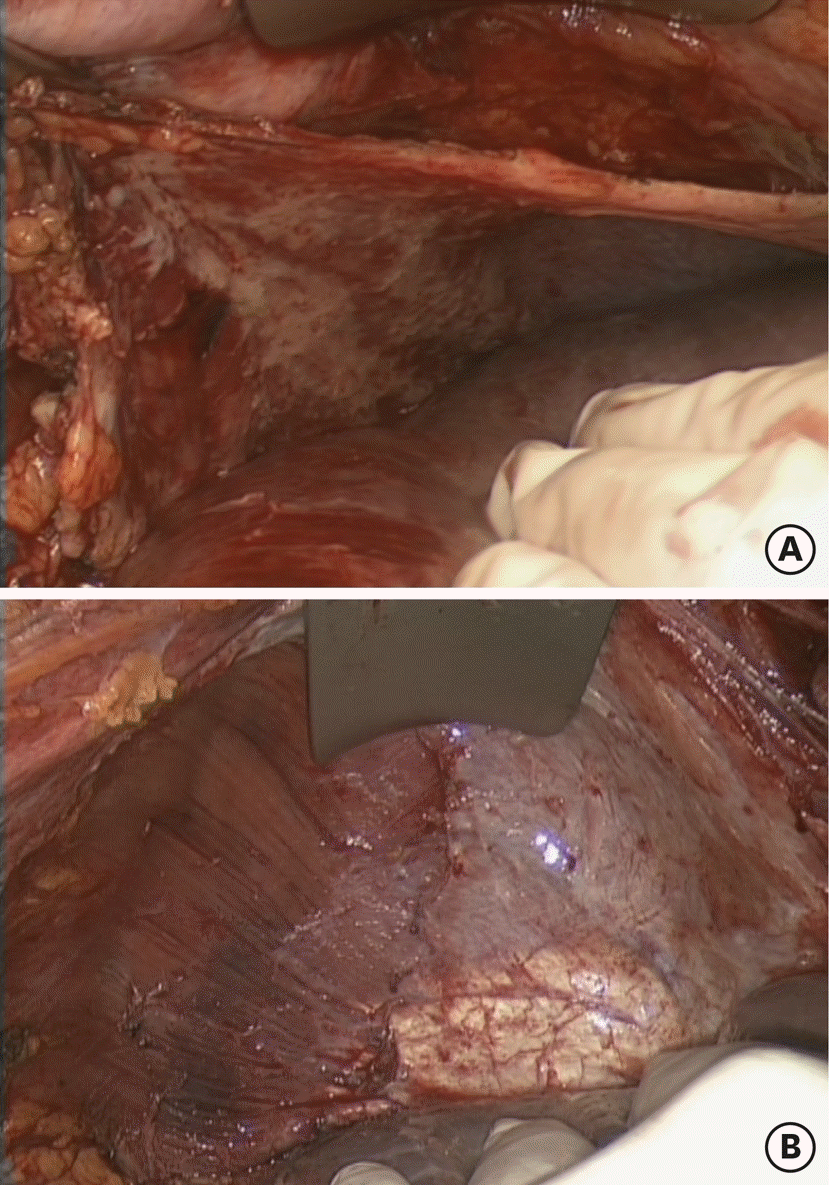 | Fig. 1.Type I diaphragmatic surgery according to Tozzi classification, initial finding (A) and final outcome (B). |
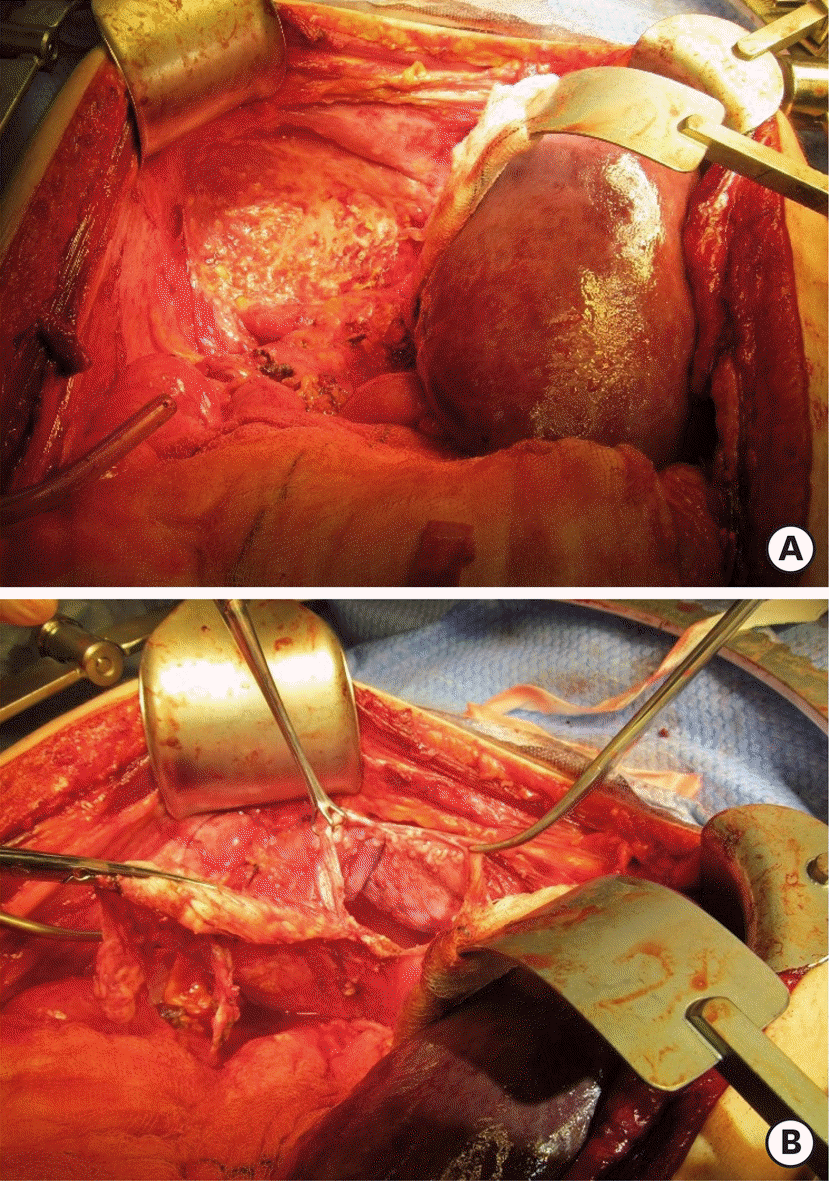 | Fig. 2.Type II diaphragmatic surgery according to Tozzi classification, initial finding (A) and open diaphragm (B). |
Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for VPD
Table 2.
Eleven steps of diaphragmatic surgery in patients with stage IIIC–IV ovarian cancer according to Tozzi classification
Table 3.
Patients and tumor characteristics in group 1 (primary VPD) and group 2 (neo-adjuvant VPD)
Table 4.
Tozzi classification of diaphragmatic surgery based on disease findings, liver mobilization and procedure with size of specimen and morbidity rate




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download