Abstract
Objective
Ovarian needle aspiration and biopsy (ONAB) may be employed for pretreatment diagnosis of ovarian malignancies or intraoperatively to facilitate removal of ovarian masses. However, there is reluctance to utilize this procedure due to potential cyst rupture or seeding of malignant cells. The objective of this study was to examine the efficacy of ONAB over a 13-year period at our institution.
Methods
Between 2000 and 2013, all ONAB specimens were identified from the Queen's Medical Center Pathology Department database. All cytologic specimens were reviewed and correlated with histopathologic findings. A retrospective chart review was conducted to retrieve data on clinical course and treatment.
Results
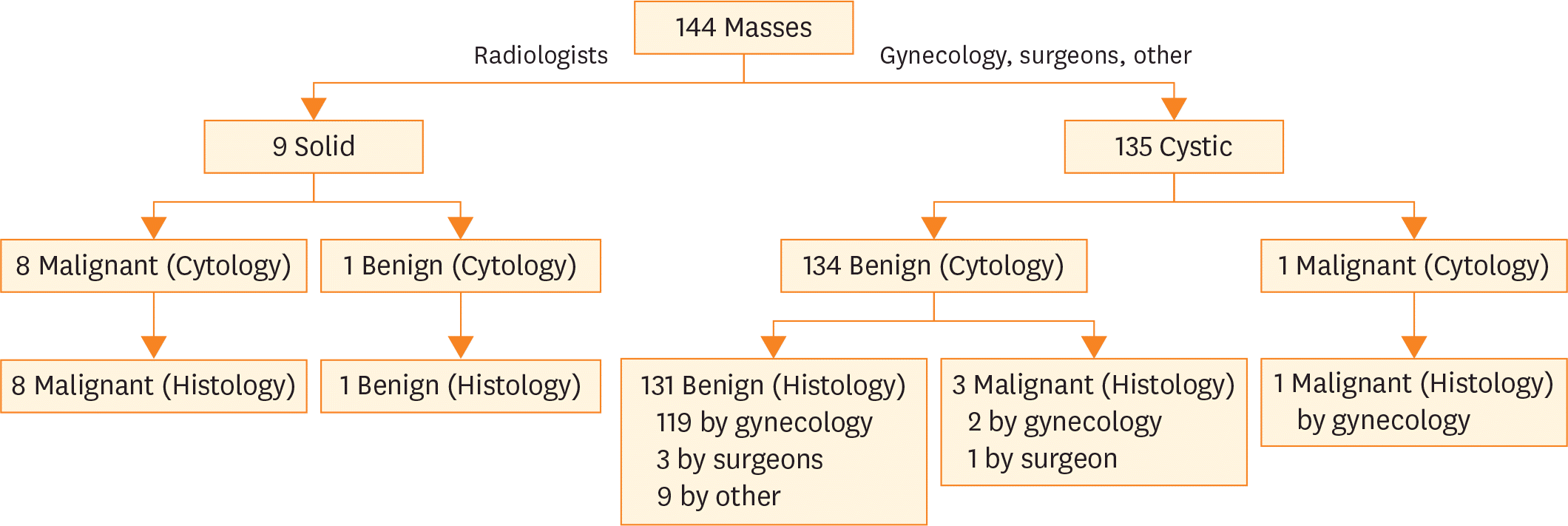
This study identified 144 cases of ovarian masses sampled by aspiration or needle biopsy between 2000 and 2013. Ninety-two (64%) cases had corresponding histopathology, 84 (91%) of which were obtained concomitantly. On histology, 12 (13%) cases were malignant and 80 (87%) benign. Three false negative cases were noted; 2 serous borderline tumors and 1 mucinous cystadenocarcinoma. These were sampling errors; no diagnostic tumor cells were present in the aspirates. Sensitivity and specificity of ONAB in the detection of malignancy were 75% and 100%, respectively. The positive and negative predictive values were 100% and 96%, respectively.
References
1. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Practice Bulletin. Management of adnexal masses. Obstet Gynecol. 2007; 110:201–14.
2. van Zante A, Ljung BM. Fine-needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy: reconsidering the evidence of superiority. Cancer. 2016; 124:853–6.

3. Cole L, Mount S, Nuzzo E, Wong C. Aspiration cytology of ovarian cystic masses: histologic correlation and review of the literature. Acta Cytol. 2011; 55:19–25.

5. Moran O, Menczer J, Ben-Baruch G, Lipitz S, Goor E. Cytologic examination of ovarian cyst fluid for the distinction between benign and malignant tumors. Obstet Gynecol. 1993; 82:444–6.
6. Dordoni D, Zaglio S, Zucca S, Favalli G. The role of sonographically guided aspiration in the clinical management of ovarian cysts. J Ultrasound Med. 1993; 12:27–31.

7. Ganjei P, Dickinson B, Harrison T, Nassiri M, Lu Y. Aspiration cytology of neoplastic and non-neoplastic ovarian cysts: is it accurate? Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1996; 15:94–101.
8. Balat O, Sarac K, Sonmez S. Ultrasound guided aspiration of benign ovarian cysts: an alternative to surgery? Eur J Radiol. 1996; 22:136–7.

9. Caspi B, Goldchmit R, Zalel Y, Appelman Z, Insler V. Sonographically guided aspiration of ovarian cyst with simple appearance. J Ultrasound Med. 1996; 15:297–300.

10. Higgins RV, Matkins JF, Marroum MC. Comparison of fine-needle aspiration cytologic findings of ovarian cysts with ovarian histologic findings. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 180:550–3.

11. Allias F, Chanoz J, Blache G, Thivolet-Bejui F, Vancina S. Value of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in the management of ovarian and paraovarian cysts. Diagn Cytopathol. 2000; 22:70–80.

12. Martínez-Onsurbe P, Ruiz Villaespesa A, Sanz Anquela JM, Valenzuela Ruiz PL. Aspiration cytology of 147 adnexal cysts with histologic correlation. Acta Cytol. 2001; 45:941–7.

13. Roy M, Bhattacharya A, Roy A, Sanyal S, Sangal MK, Dasgupta S, et al. Fine needle aspiration cytology of ovarian neoplasms. J Cytol. 2003; 20:31–5.
14. Papathanasiou K, Giannoulis C, Dovas D, Tolikas A, Tantanasis T, Tzafettas JM. Fine needle aspiration cytology of the ovary: is it reliable? Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2004; 31:191–3.
15. Hemalatha AL, Divya P, Mamatha R. Image-directed percutaneous FNAC of ovarian neoplasms. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2005; 48:305–9.
16. Uguz A, Ersoz C, Bolat F, Gokdemir A, Vardar MA. Fine needle aspiration cytology of ovarian lesions. Acta Cytol. 2005; 49:144–8.

17. Kadivar M, Karamvandi M. Fine needle aspiration cytology of ovarian lesions: Is it reliable? Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2008; 4:143–8.

18. Khan N, Afroz N, Aqil B, Khan T, Ahmad I. Neoplastic and nonneoplastic ovarian masses: diagnosis on cytology. J Cytol. 2009; 26:129–33.

19. Sood T, Handa U, Mohan H, Goel P. Evaluation of aspiration cytology of ovarian masses with histopathological correlation. Cytopathology. 2010; 21:176–85.

20. Mehdi G, Maheshwari V, Afzal S, Ansari HA, Ansari M. Image-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology of ovarian tumors: an assessment of diagnostic efficacy. J Cytol. 2010; 27:91–5.

21. Goel S, Agarwal D, Goel N, Naim M, Khan T. Ekrammulah. Ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration cytology in ovarian neoplasms: an assessment of diagnostic accuracy and efficacy and role in clinical management. Internet J Pathol. 2010; 11:1–6.
22. Gupta N, Rajwanshi A, Dhaliwal LK, Khandelwal N, Dey P, Srinivasan R, et al. Fine needle aspiration cytology in ovarian lesions: an institutional experience of 584 cases. Cytopathology. 2012; 23:300–7.

23. Bandyopadhyay A, Chakraborty J, Chowdhury AR, Bhattacharya A, Bhattachrya P, Chowdhury M. Fine needle aspiration cytology of ovarian tumors with histological correlation. J Cytol. 2012; 29:35–40.

24. Garady C, Boerner SL. Does cytological examination of ovarian cyst fluids obtained during oophorectomy add useful information? Mod Pathol. 2013; 26:A369.
25. Ray S, Gangopadhyay M, Bandyopadhyay A, Majumdar K, Chaudhury N. USG guided FNAC of ovarian mass lesions: a cyto-histopathological correlation, with emphasis on its role in pre-operative management guidelines. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2014; 15:6–12.

26. Pal S, Chakrabarti S, Deuoghuria D, Phukan JP, Sinha A, Mondal PK. Evaluation of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology of ovarian masses with histopathological correlation. Acta Cytol. 2015; 59:149–55.

27. García-Tejedor A, Castellarnau M, Burdio F, Fernández E, Martí D, Pla MJ, et al. Ultrasound-guided aspiration of adnexal cysts with a low risk of malignancy: is it a recommendable option? J Ultrasound Med. 2015; 34:985–91.
Fig. 2.
Cytology of serous ovarian carcinoma with marked nuclear pleomorphism and prominent nucleoli (Diff-Quik, ×600).
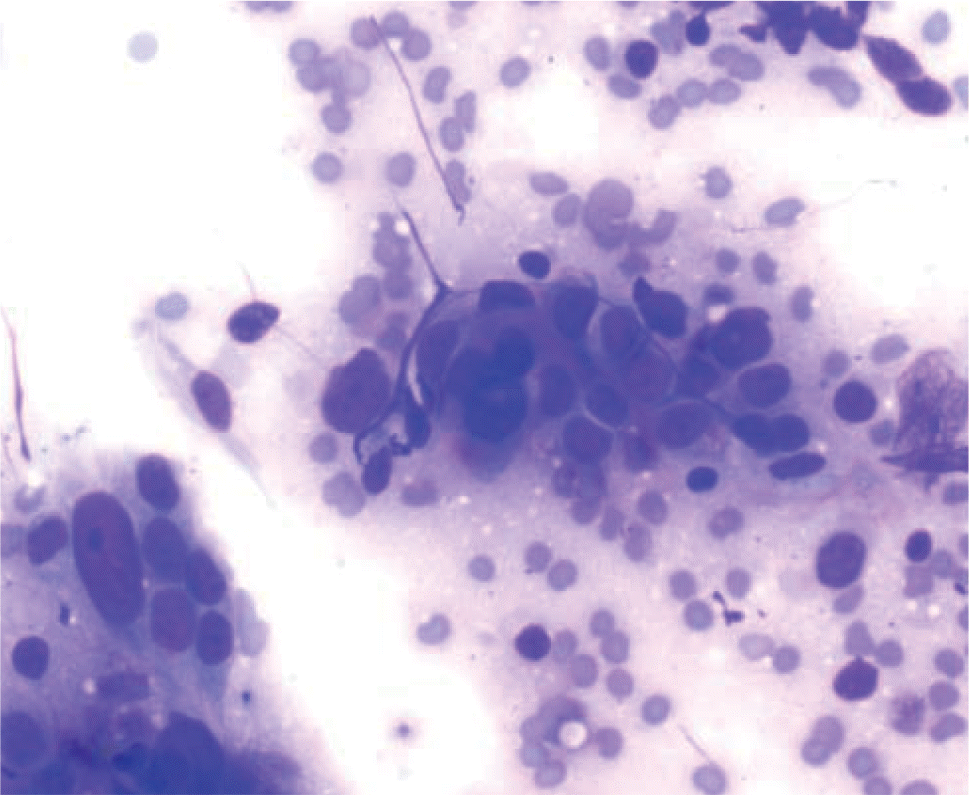
Fig. 3.
Cytology of mucinous borderline tumor showing honeycomb tumor sheets in a background of abundant mucin (Diff-Quik, ×200).
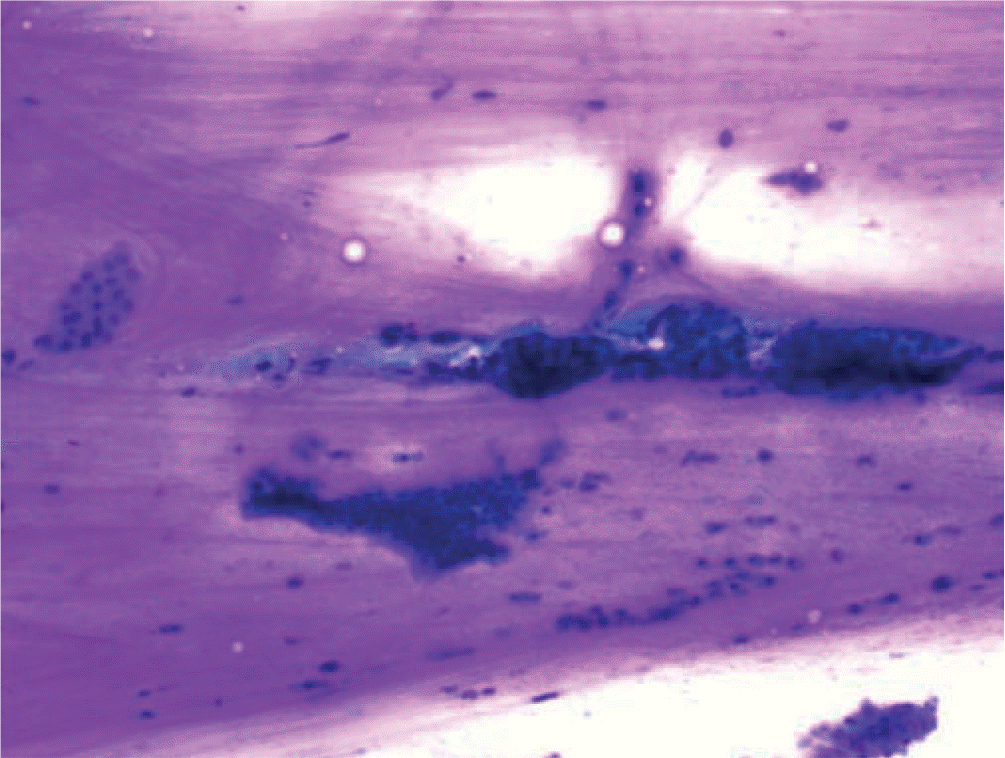
Fig. 4.
Cytology of clear cell ovarian carcinoma: 3-dimensional tumor cluster with enlarged vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and abundant clear cytoplasm (Pap, ×1,000).
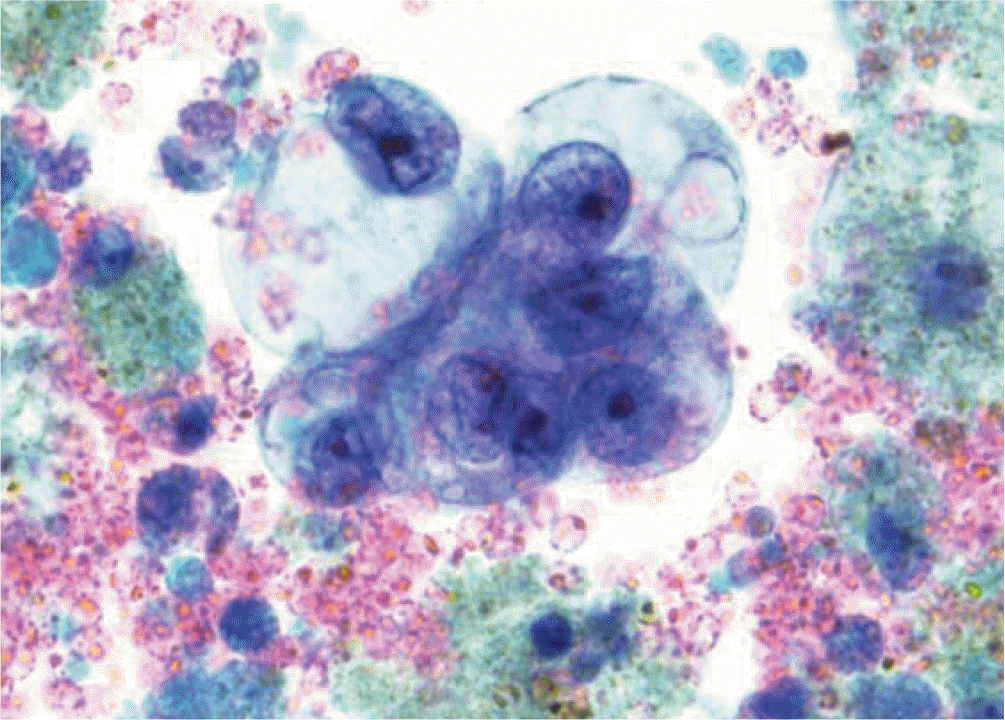
Fig. 5.
Cytology of endometrioid ovarian carcinoma with crowded overlapping clusters containing columnar tumor cells (Diff-Quik, ×400).
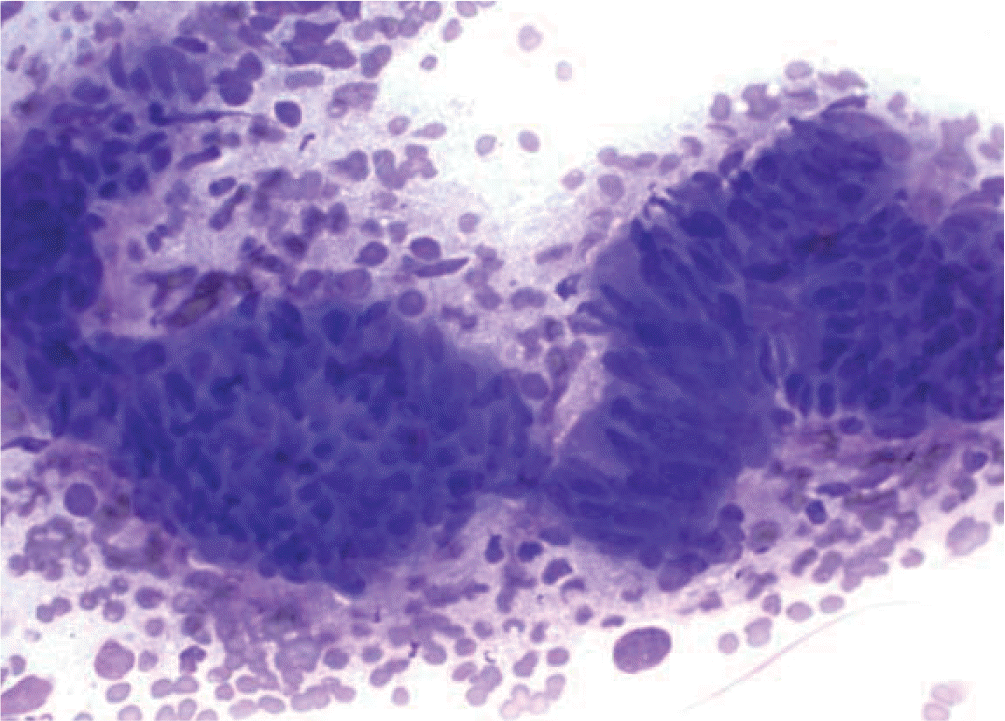
Fig. 6.
Cytology of granulosa cell tumor with Call-Exner bodies and intranuclear grooves (Diff-Quik, ×600).
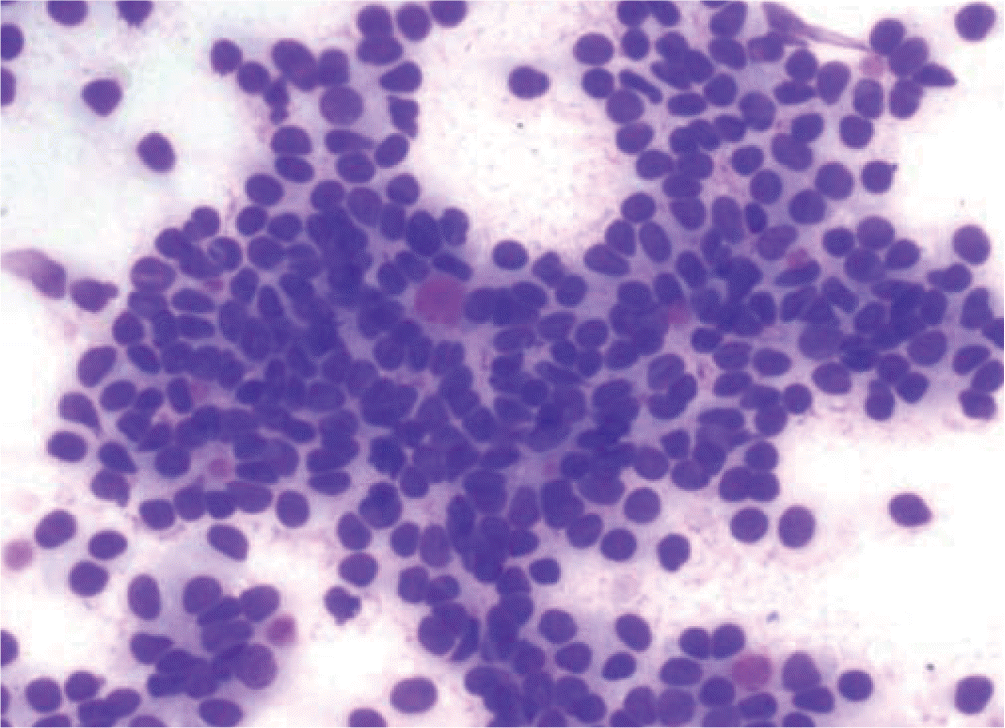
Fig. 7.
Metastatic pulmonary adenocarcinoma showing pseudopapillary cluster with nuclear enlargement and cellular crowding (Diff-Quik, ×400).
Table 1.
Ovarian needle aspiration/biopsy diagnosis and patient age (144 cases)
| Cytologic diagnosis | No. (%) of cases | Mean age (range) |
|---|---|---|
| Benign | 135 (94) | 41 (13–83) |
| Cyst | 134 (93) | 41 (13–83) |
| Infection | 1 (1) | 43 (43) |
| Malignant | 9 (6) | 54 (23–74) |
| Total | 144 (100) | 42 (13–83) |
Table 2.
Ovarian cytologic diagnosis by biopsy operator/clinician (144 cases)
| Operator | Total (%) | Benign | Malignant neoplasms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyst | Infection | |||
| Gynecologist/surgeon | 126 (88) | 124 | 1 | 1 |
| Radiologist | 9 (6) | 1 | – | 8 |
| Other | 9 (6) | 9 | – | – |
| Total | 144 (100) | 134 | 1 | 9 |
Table 3.
Cytologic-histologic correlation of ovarian lesions (92 cases with corresponding histology)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download