I. Introduction
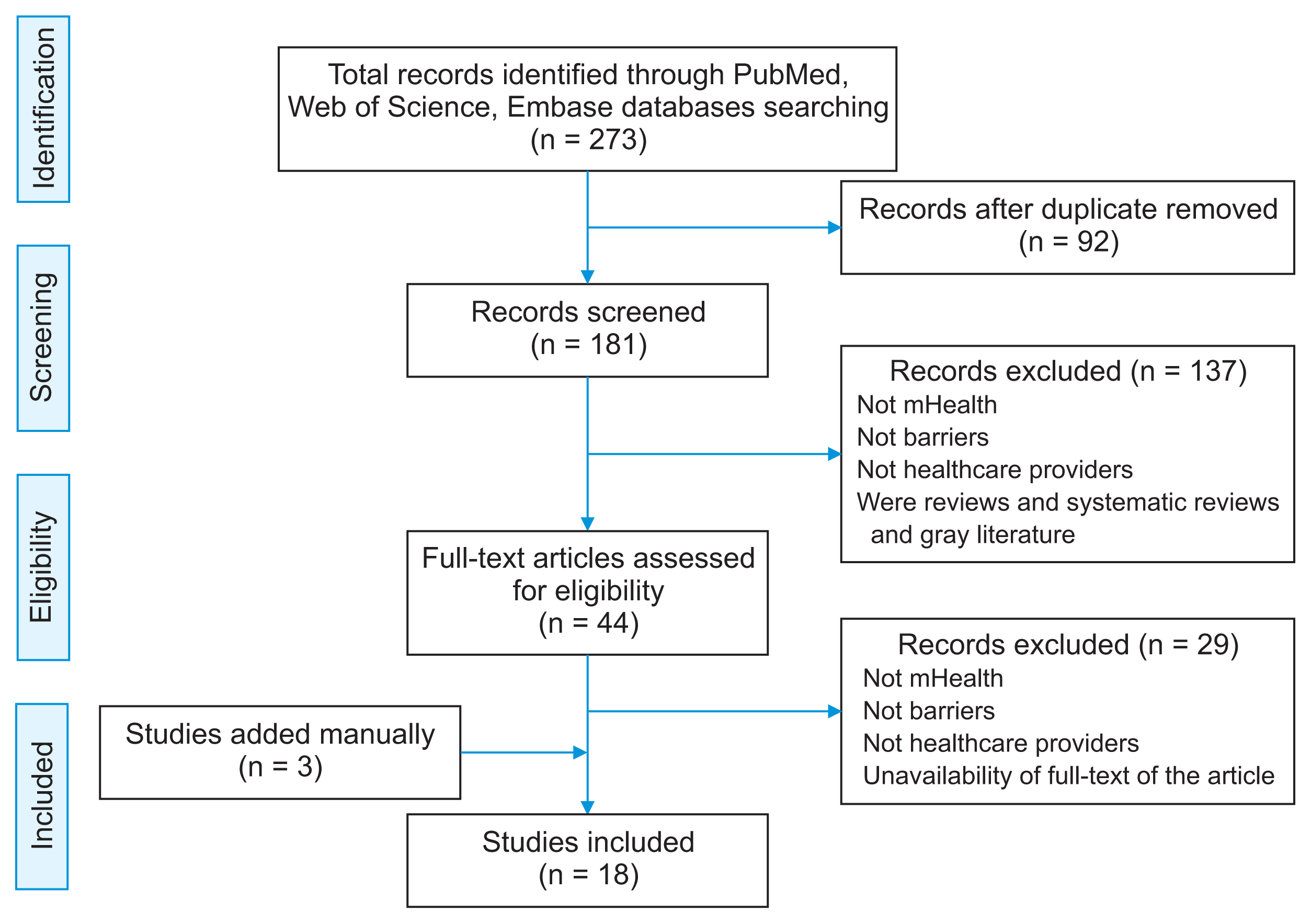
II. Methods
1. Search Strategy
Table 1
2. Study Selection
3. Inclusion Criteria
4. Exclusion Criteria
5. Data Extraction
III. Results
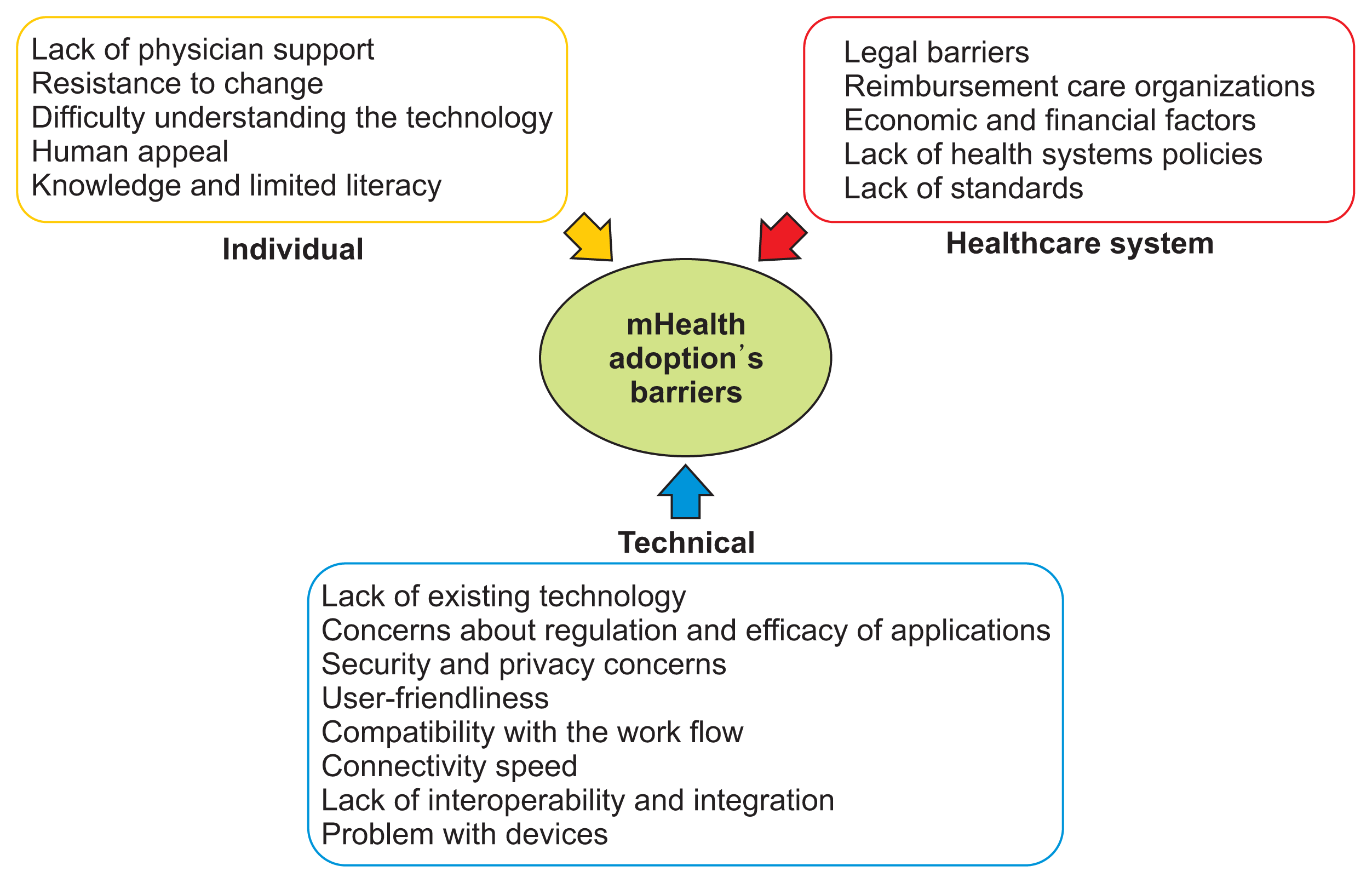
1. Included Studies
Table 2
| Study | Year | Country | Type of study | Barriers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical barriers | Individual barriers | Healthcare system barriers | ||||
| Laxman et al. [17] | 2015 | New Zealand | Qualitative |
Lack of existing technology Regulation and efficacy of application Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed |
Lack of physician support Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors |
| Gleason [18] | 2015 | USA | Qualitative |
Security and privacy concerns Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration |
Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies Lack of standards |
| O’Connor & O’Donoghue [19] | 2015 | United Kingdom | Qualitative |
Lack of existing technology User-friendliness Connectivity speed |
Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies |
| Medhanyie et al. [20] | 2015 | Ethiopia | Quantitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Problem with devices |
Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
- |
| Lavariega et al. [21] | 2016 | Mexico | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Problems with devices |
Lack of physician support Resistance to change Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of standards |
| Nebeker et al. [23] | 2017 | USA | Qualitative or quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns Lack of interoperability and integration |
Lack of physician support Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers |
| Kao & Liebovitz [24] | 2017 | USA | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration |
Knowledge and limited literacy |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies Lack of standards |
| Van Heerden et al. [25] | 2017 | South Africa | Quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and Integration Problems with devices |
Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
- |
| Abelson et al. [26] | 2017 | USA | Qualitative |
Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Problems with devices User-friendliness |
Human appeal Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
- |
| Faber et al. [27] | 2017 | Netherlands | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications Lack of interoperability and integration Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Problems with devices |
Lack of physician support Knowledge and limited literacy |
Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of standards |
| Graves et al. [28] | 2018 | Canada | Qualitative or quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration Problems with devices |
Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
Lack of standards |
| Rassi et al. [29] | 2018 | United Kingdom | Qualitative or quantitative |
User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Connectivity speed Lack of interoperability and integration Problems with devices |
Lack of physician support Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Knowledge and limited literacy |
Economic and financial factors Lack of standards |
| Spann & Stewart [30] | 2018 | United Kingdom | Qualitative |
Regulation and efficacy of applications User-friendliness Connectivity speed Compatibility with the workflow Security and privacy concerns Problems with devices |
Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy Difficulty understanding the technology |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies |
| Bally & Cesuroglu [31] | 2019 | Netherlands | Qualitative or quantitative |
Lack of existing technology Regulation and efficacy of applications Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness Compatibility with the workflow Lack of interoperability and integration |
Resistance to change Difficulty understanding the technology Human appeal Knowledge and limited literacy |
Legal barriers Reimbursement care organizations Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies Lack of standards |
| Zhou et al. [32] | 2019 | USA | Qualitative or quantitative |
Security and privacy concerns Connectivity speed Regulation and efficacy of applications User-friendliness |
Difficulty understanding the technology |
Economic and financial factors Lack of health systems policies |
| Byambasuren et al. [1] | 2019 | Australia | Qualitative |
Security and privacy concerns Lack of existing technology Lack of interoperability and integration User-friendliness |
Knowledge and limited literacy Difficulty understanding the technology |
- |
| Anastasiadou et al. [33] | 2019 | Spain | Qualitative |
Compatibility with the workflow Lack of interoperability and integration Security and privacy concerns User-friendliness |
Knowledge and limited literacy Lack of physician support Difficulty understanding the technology Resistance to change Human appeal |
Lack of health systems policies Economic and financial factors Lack of standards Reimbursement care organizations |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download