INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study population
Echocardiographic study
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Baseline clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic characteristics
Table 1.
| Variable |
Baseline study |
Follow-up study after 3 years |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n=191) | Men (n=94) | Women (n=97) | P valuea | Total (n=191) | Men (n=94) | Women (n=97) | P valuea | |
| Age, yr | 56.2±4.4 | 56.2±4.7 | 56.2±4.1 | 0.993 | 58.7±4.5 | 58.7±4.6 | 58.8±4.3 | 0.861 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.7±3.0 | 26.0±2.9 | 25.4±3.0 | 0.186 | 25.8±3.1 | 26.0±3.0 | 25.6±3.1 | 0.390 |
| WC, cm | 87.5±8.2 | 91.2±6.8 | 84.0±8.0 | <0.001 | 88.9±8.4 | 91.2±7.6 | 86.7±8.5 | <0.001 |
| WHR | 0.87±0.05 | 0.90±0.04 | 0.85±0.05 | <0.001 | 0.92±0.06 | 0.94±0.05 | 0.90±0.06 | <0.001 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 124.3±15.0 | 126.3±14.1 | 122.3±15.7 | 0.066 | 129.8±13.7 | 130.7±13.6 | 128.9±13.8 | 0.372 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 76.0±9.8 | 77.8±10.0 | 74.4±9.4 | 0.015 | 81.8±8.5 | 83.4±8.4 | 80.3±8.5 | 0.010 |
| PP, mm Hg | 48.2±9.7 | 48.5±8.7 | 47.9±10.7 | 0.684 | 48.0±9.9 | 47.3±9.5 | 48.7±10.4 | 0.341 |
| Underlying diseases | ||||||||
| HTN | 12 (6.3) | 4 (4.3) | 8 (8.8) | 0.367 | 30 (15.7) | 13 (13.4) | 17 (18.1) | 0.245 |
| DM | 3 (1.5) | 1 (1.1) | 2 (2.2) | 0.598 | 16 (8.4) | 6 (6.2) | 10 (10.6) | 0.198 |
| Dyslipidemia | 19 (9.9) | 13 (14.0) | 6 (6.7) | 0.105 | 48 (25.1) | 32 (33.0) | 16 (17.0) | 0.008 |
| Lifestyle | ||||||||
| Current smoker | 24 (12.7) | 24 (25.8) | 0 (0.0) | < 0.001 | 22 (11.5) | 22 (23.4) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol intake | 117 (61.9) | 75 (80.6) | 42 (43.8) | < 0.001 | 103 (53.9) | 75 (79.8) | 28 (28.9) | <0.001 |
| Regular exercise | 128 (67.4) | 68 (73.1) | 60 (61.9) | 0.067 | 104 (54.5) | 55 (58.5) | 49 (50.5) | 0.168 |
| Laboratory parameters | ||||||||
| FBG, mg/dL | 99.5±14.2 | 103.4±15.4 | 95.7±11.8 | <0.001 | 107.4±18.7 | 111.7±20.0 | 102.1±19.4 | 0.001 |
| TC, mg/dL | 198.3±31.2 | 190.7±27.9 | 205.7±32.6 | 0.001 | 190.9±36.8 | 183.6±32.8 | 198.1±39.3 | 0.007 |
| TG, mg/dL | 155.9±94.2 | 184.4±116.3 | 128.2±53.6 | <0.001 | 164.1±85.1 | 178.5±100.2 | 148.4±66.0 | 0.015 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 51.5±14.1 | 48.1±14.5 | 54.7±13.0 | 0.001 | 52.6±13.1 | 49.1±12.3 | 55.4±14.1 | 0.001 |
| TG/HDL ratio | 3.50±3.52 | 4.47±4.60 | 2.56±1.52 | <0.001 | 3.5±2.8 | 4.09±3.44 | 2.94±1.76 | 0.004 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; WHR, waist hip ratio; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; PP, pulse pressure; HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; FBG, fasting blood glucose; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; HDL, high-density lipoprotein.
Table 2.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation.
LVEDD, left ventricular end diastolic dimension; LVESD, left ventricular end systolic dimension; RWT, relative wall thickness; LVMI, left ventricular mass index; LAVI, left atrial volume index; LVEDVI, left ventricular end diastolic volume index; LVESVI, left ventricular end systolic volume index; LV, left ventricular; EF, ejection fraction; E, early diastolic mitral inflow velocity; DT, deceleration time; e´, early mitral tissue velocity; s´, systolic mitral tissue velocity; GLS, global longitudinal strain.
Longitudinal changes in clinical and laboratory parameters
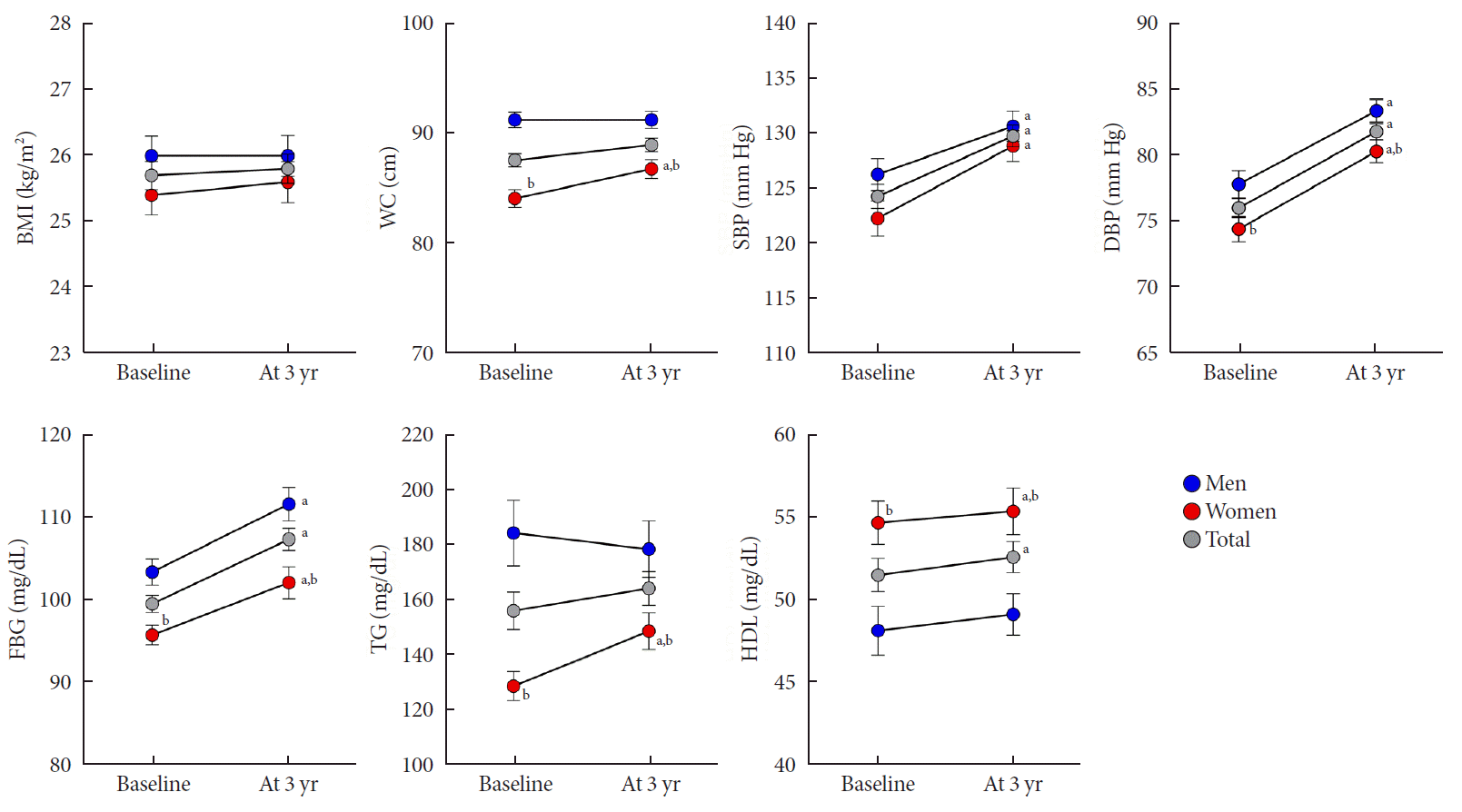 | Fig. 1.Changes in clinical and laboratory parameters in men and women. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBG, fasting blood glucose; TG, triglyceride; HDL, high-density lipoprotein. aP<0.05 vs. baseline, bP<0.05 vs. men. |
Longitudinal changes in cardiac geometry and functional parameters
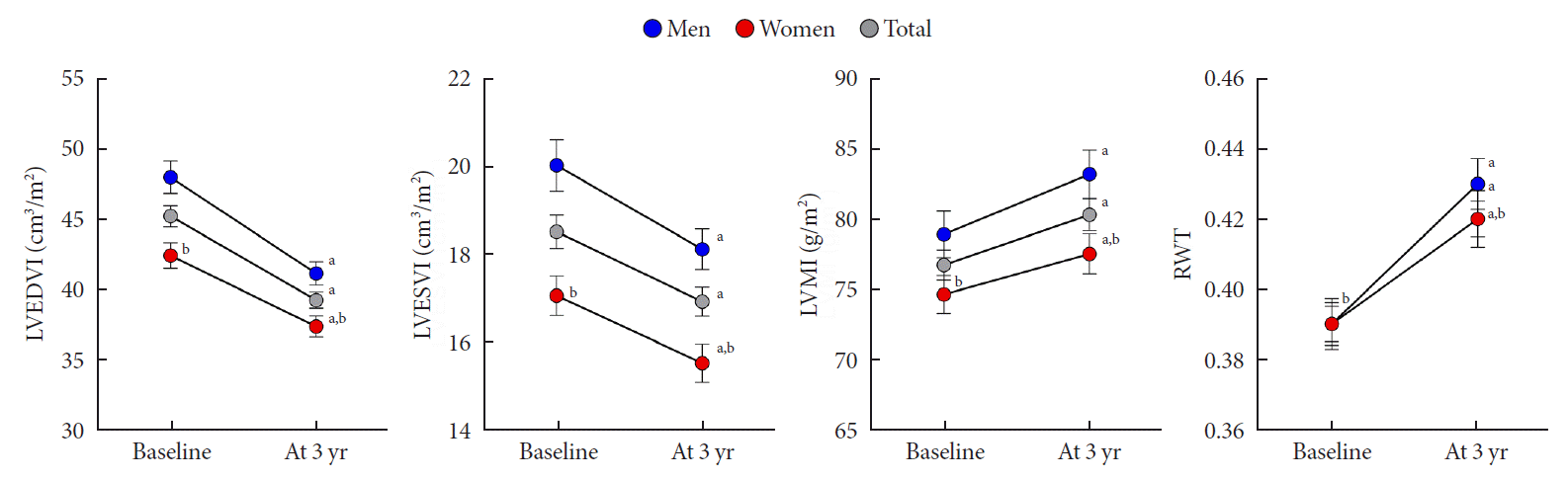 | Fig. 2.Changes in cardiac geometry in men and women. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. LVEDVI, left ventricular end diastolic volume index; LVESVI, left ventricular end systolic volume index; LVMI, left ventricular mass index; RWT, regional wall thickness. aP<0.05 vs. baseline, bP<0.05 vs. men. |
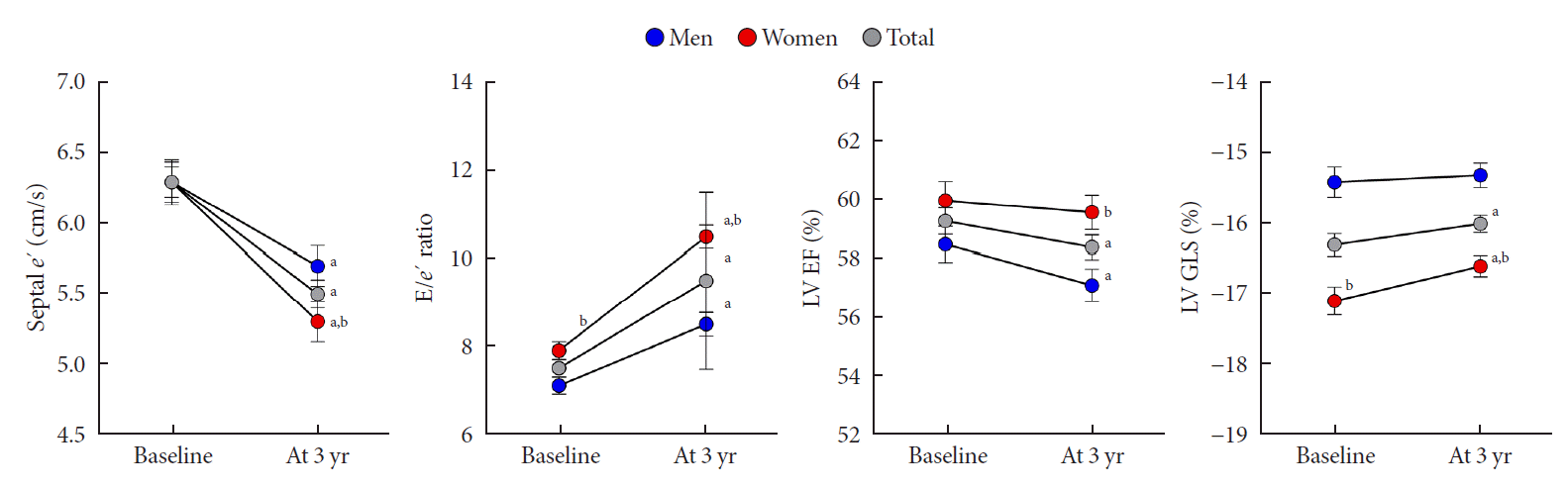 | Fig. 3.Changes in cardiac function in men and women. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. e’, early diastolic velocity of mitral annulus; E, mitral peak velocity of early filling; LV, left ventricular; EF, ejection fraction; GLS, global longitudinal strain. aP<0.05 vs. baseline, bP<0.05 vs. men. |
The association between changes in metabolic profile and cardiac function
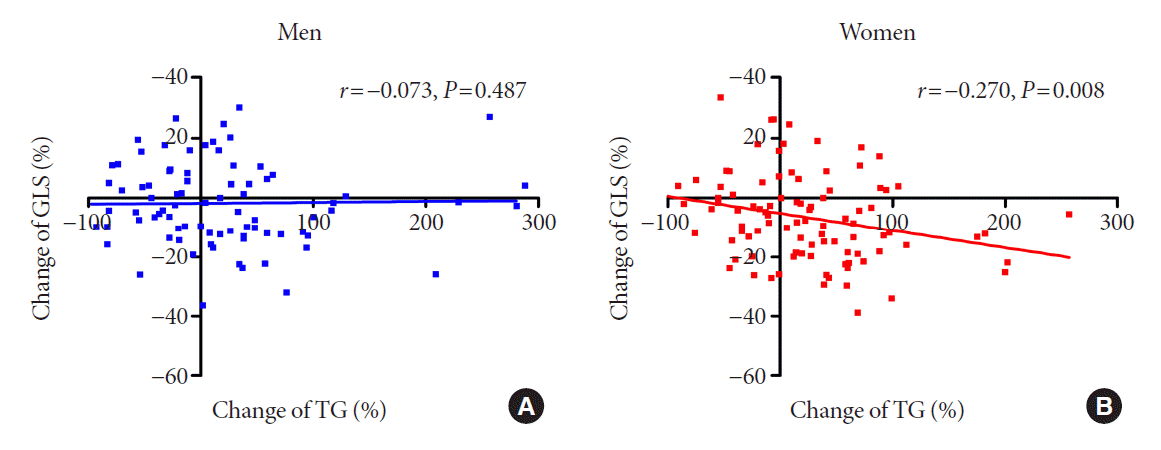 | Fig. 4.The association between changes in triglyceride (TG) and global longitudinal strain (GLS) during the 3-year period. (A) Men and (B) women. |
Table 3.
LV, left ventricular; GLS, global longitudinal strain; β, regression coefficient; CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; HDL, high-density lipoprotein.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download