INTRODUCTION
METHODS
NHIS-Health Screening cohort
Study subjects
Clinical variables
Table 1.
| Variable | All (n=268,241) | Missing, % |
Incident T2DM |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n=23,420) | Missing, % | No (n=244,821) | Missing, % | |||
| Age, yr | 51.8±9.1 | 0.00 | 54.6±9.3 | 0.00 | 51.5±9.0 | 0.00 |
| Male sex | 149,723 (55.82) | 0.00 | 14,306 (61.08) | 0.00 | 135,417 (55.31) | 0.00 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.9±2.9 | 0.08 | 25.2±3.1 | 0.08 | 23.8±2.8 | 0.08 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 126.0±17.6 | 0.03 | 132.0±18.4 | 0.02 | 125.4±17.4 | 0.04 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 79.3±11.6 | 0.05 | 82.5±11.9 | 0.03 | 79.0±11.5 | 0.06 |
| FBG, mg/dL | 90.8±12.6 | 0.10 | 97.6±14.0 | 0.10 | 90.2±12.3 | 0.10 |
| TC, mg/dL | 199.6±37.3 | 0.14 | 208.3±39.7 | 0.12 | 198.8±36.9 | 0.14 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.0±1.5 | 0.09 | 14.2±1.5 | 0.09 | 13.9±1.5 | 0.09 |
| AST, IU/L | 26.5±16.4 | 0.08 | 30.4±20.7 | 0.06 | 26.1±15.9 | 0.08 |
| ALT, IU/L | 25.5±20.4 | 0.08 | 32.4±25.2 | 0.07 | 24.8±19.8 | 0.08 |
| GGT, IU/L | 35.5±47.2 | 0.08 | 51.7±69.9 | 0.07 | 34.0±44.1 | 0.08 |
| Proteinuria | 4,048 (1.51) | 0.25 | 594 (2.54) | 0.30 | 3,454 (1.41) | 0.24 |
| Smoking | 85,774 (31.98) | 4.35 | 8,718 (37.22) | 4.51 | 77,056 (31.47) | 4.34 |
| Alcohol | 118,972 (44.35) | 1.82 | 10,886 (46.48) | 1.79 | 108,086 (44.15) | 1.83 |
| Exercise | 113,809 (42.43) | 3.01 | 9,450 (40.35) | 3.18 | 104,359 (42.63) | 2.99 |
| Personal history | ||||||
| Hypertension | 17,365 (6.47) | 0.00 | 2,849 (12.16) | 0.00 | 14,516 (5.93) | 0.00 |
| Heart disease | 2,709 (1.01) | 0.00 | 428 (1.83) | 0.00 | 2,281 (0.93) | 0.00 |
| Stroke | 901 (0.34) | 0.00 | 118 (0.50) | 0.00 | 783 (0.32) | 0.00 |
| Othersa | 27,406 (10.22) | 0.00 | 2,708 (11.56) | 0.00 | 24,698 (10.09) | 0.00 |
| Family history | ||||||
| Hypertension | 22,306 (8.32) | 11.58 | 2,056 (8.78) | 11.99 | 20,250 (8.27) | 11.54 |
| Heart disease | 7,910 (2.95) | 12.07 | 650 (2.78) | 12.40 | 7,260 (2.97) | 12.04 |
| Stroke | 15,259 (5.69) | 11.81 | 1,342 (5.73) | 12.15 | 13,917 (5.68) | 11.78 |
| DM | 14,778 (5.51) | 11.83 | 1,689 (7.21) | 12.00 | 13,089 (5.35) | 11.81 |
| Othersa | 39,946 (14.89) | 11.65 | 3,031 (12.94) | 12.03 | 36,915 (15.08) | 11.61 |
| Follow-up, yr | 10.4±1.7 | 0.00 | 6.7±2.6 | 0.00 | 10.8±1.1 | 0.00 |
| Check-up, n | 2.9±1.0 | 0.00 | 2.8±1.0 | 0.00 | 2.9±1.0 | 0.00 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBG, fasting blood glucose; TC, total cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase.
Identification of new DM cases
Construction of prediction models
Converting the output variables for longitudinal study
Solution to the problem of understanding classification decisions
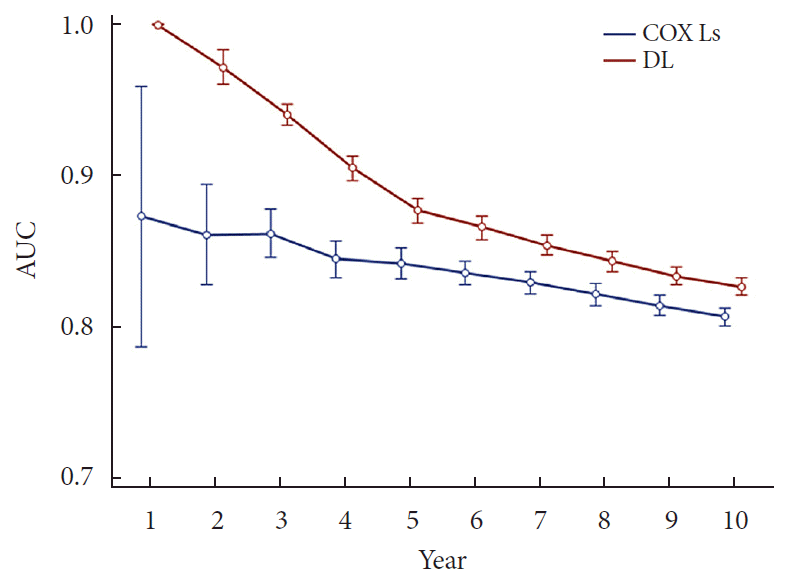
Evaluation of prediction performance
Statistical tools
RESULTS
Characteristics of the subjects
Hazard ratio for new onset T2DM in the Cox model
Table 2.
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, /10 yr | 1.369 | 1.348–1.391 | <0.0001 | |
| Male sex | 0.809 | 0.773–0.846 | <0.0001 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | Mean | 1.105 | 1.100–1.110 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 0.986 | 0.973–0.999 | 0.041 | |
| SBP, mm Hg | Mean | 1.007 | 1.006–1.009 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 1.002 | 1.000–1.004 | 0.0342 | |
| DBP, mm Hg | Mean | 1.001 | 0.999–1.004 | 0.3908 |
| SD | 1.001 | 0.999–1.004 | 0.3334 | |
| FBG, mg/dL | Mean | 1.059 | 1.058–1.060 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 0.970 | 0.969–0.970 | <0.0001 | |
| TC, mg/dL | Mean | 1.003 | 1.003–1.003 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 1.003 | 1.002–1.004 | <0.0001 | |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | Mean | 1.082 | 1.066–1.098 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 1.102 | 1.075–1.131 | <0.0001 | |
| AST, IU/L | Mean | 0.991 | 0.989–0.993 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 1.006 | 1.004–1.008 | <0.0001 | |
| ALT, IU/L | Mean | 1.019 | 1.018–1.020 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 0.989 | 0.987–0.990 | <0.0001 | |
| GGT, IU/L | Mean | 1.002 | 1.002–1.002 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 1.000 | 1.000–1.000 | 0.9787 | |
| Proteinuria | Yesa | 1.217 | 1.090–1.359 | 0.0005 |
| SD | 1.230 | 1.071–1.413 | 0.0035 | |
| Smoking | Yesa | 1.355 | 1.308–1.405 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 0.938 | 0.885–0.994 | 0.0306 | |
| Alcohol | Yesa | 0.844 | 0.816–0.873 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 1.180 | 1.118–1.244 | <0.0001 | |
| Exercise | Yesa | 0.876 | 0.852–0.901 | <0.0001 |
| SD | 1.069 | 1.022–1.118 | 0.004 | |
| Personal history | Hypertension | 1.192 | 1.152–1.233 | <0.0001 |
| Heart disease | 1.343 | 1.254–1.439 | <0.0001 | |
| Stroke | 1.156 | 1.027–1.302 | 0.0162 | |
| Othersb | 1.106 | 1.072–1.141 | <0.0001 | |
| Family history | Hypertension | 0.937 | 0.903–0.973 | 0.0007 |
| Heart disease | 0.876 | 0.822–0.933 | <0.0001 | |
| Stroke | 0.954 | 0.912–0.997 | 0.0382 | |
| DM | 1.523 | 1.462–1.586 | <0.0001 | |
| Othersb | 0.937 | 0.907–0.967 | <0.0001 |
T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index; SD, standard deviation; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FBG, fasting blood glucose; TC, total cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase.
Clinical variables frequently observed in DL-based models
Table 3.
| Rank | Sum of ranksa | Feature name | Mean of valuesb | Feature name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 225139 | FBG | 0.540717434 | FBG |
| 2 | 390825 | Age | 0.225780582 | Age |
| 3 | 415586 | Sexc | 0.198429918 | ALT |
| 4 | 452213 | ALT | 0.183752354 | BMI |
| 5 | 474756 | BMI | 0.155880525 | GGT |
| 6 | 506423 | GGT | 0.131993265 | SBP |
| 7 | 528990 | SBP | 0.11983712 | TC |
| 8 | 590453 | TC | 0.099701395 | Sex |
| 9 | 686835 | AST | 0.080821141 | Alcohol |
| 10 | 696361 | Alcoholc | 0.068915813 | Exercise |
FBG, fasting blood glucose; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BMI, body mass index; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; SBP, systolic blood pressure; TC, total cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.
a Ranking each sample by absolute value of layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP), then ascending order by summing the ranks by variables in all samples,




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download