INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study population
Clinical evaluation
Biochemical measurements
IR, prediabetes, and T2DM assessment
Radiology examination
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Non-NAFLD (n=2,220) | NAFLD (n=1,790) | NAFLD defined by MRI-PDFF (n=941) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 46.3±15.8 | 45.6±20.6 | 45.8±19.9 | 0.455 |
| Male sex, % | 62.5 | 63.7 | 63.1 | 0.121 |
| Current smoker, % | 9.6 | 9.8 | 9.9 | 0.324 |
| Anthropometric parameters | ||||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 21.9 (19.7–24.4)b | 25.7 (23.7–28.0)a | 26.3 (23.8–28.7)a | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference, cm | 77 (71–85)b | 89 (83–95)a | 89 (83–95)a | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 125 (117–138)b | 130 (120–142)a | 130 (120–141)a | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 81 (74–88)b | 85 (76–93)a | 86 (77–95)a | <0.001 |
| Liver enzyme | ||||
| Alanine aminotransferase, U/L | 25 (17–39)b | 34 (22–55)a | 37 (24–61)a | <0.001 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, U/L | 25 (20–34)b | 28 (22–40)a | 29 (23–40)a | <0.001 |
| γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase, U/L | 23 (16–37)b | 38 (25–62)a | 39 (26–67)a | <0.001 |
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/L | 75 (65–90) | 76 (65–89) | 76 (65–89) | 0.276 |
| Metabolic parameters | ||||
| Uric acid, μmol/L | 339 (279–401)b | 399 (332–458)a | 408 (339–472)a | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol, mmol/L | 4.7 (4.0–5.5)b | 5.0 (4.3–5.7)a | 5.1 (4.4–5.8)a | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 1.0 (0.8–1.5)b | 1.5 (1.1–2.1)a | 1.5 (1.1–2.1)a | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.2 (1.0–1.5)b | 1.1 (1.0–1.3)a | 1.1 (1.0–1.3)a | <0.001 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 2.8 (2.4–3.5)b | 3.2 (2.6–3.7)a | 3.2 (2.7–3.7)a | <0.001 |
| Free fatty acids, μmol/L | 561±234 | 562±218 | 567±206 | 0.405 |
| Fasting plasma glucose, mmol/L | 4.7 (4.3–5.3)b | 5.0 (4.6–5.7)a | 4.9 (4.5–5.4)a | <0.001 |
| Fasting insulin, μU/mL | 5.7 (4.0–8.2)b | 8.9 (6.5–12.5)a | 9.0 (6.5–12.8)a | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.2 (0.8–1.8)b | 2.3 (1.4–4.0)a | 2.3 (1.4–4.1)a | <0.001 |
| Adipo-IR | 22.0 (14.3–34.2)b | 34.8 (21.6–53.1)a | 35.4 (21.9–56.1)a | <0.001 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.9 (5.4–7.2)b | 7.8 (6.2–10.0)a | 7.6 (6.0–9.4)a | <0.001 |
| 2-hr plasma glucose, mmol/L | 10.1 (7.0–13.4) | 9.2 (7.1–14.7) | 9.1 (7.2–14.5) | 0.909 |
| Insulin resistance, % | 10.2b | 40.2a | 40.5a | <0.001 |
| Prediabetes, % | 11.5b | 14.3a | 13.3a | 0.024 |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus, % | 16.6b | 31.1a | 29.9a | <0.001 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation and median (interquartile range). NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; MRI-PDFF, magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; Adipo-IR, adipose tissue insulin resistance; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin.
Associations among FFAs, lipid profiles, and IR
Fig. 1.
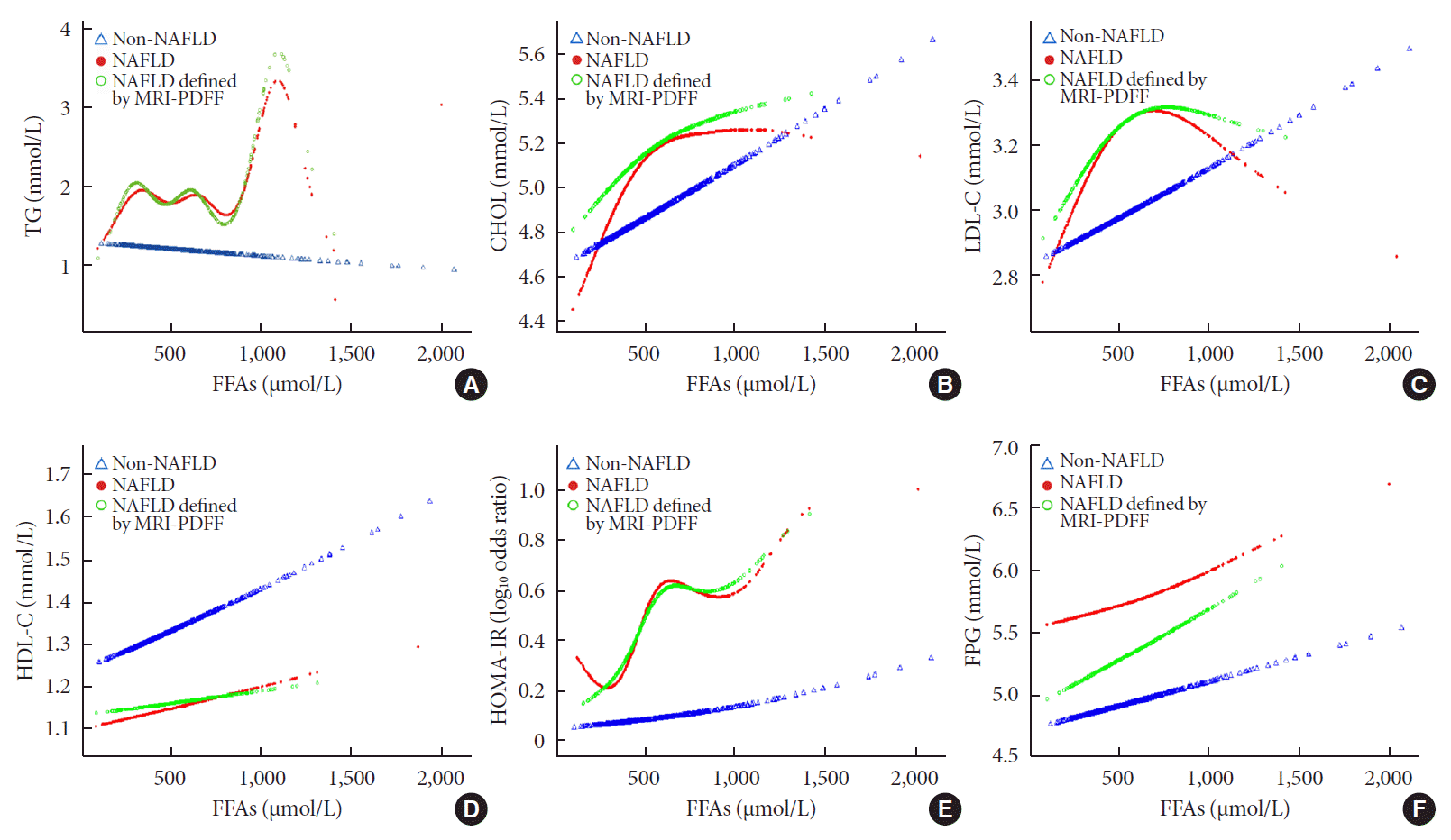
Associations among FFAs, fat distribution and diabetes progression
Fig. 2.
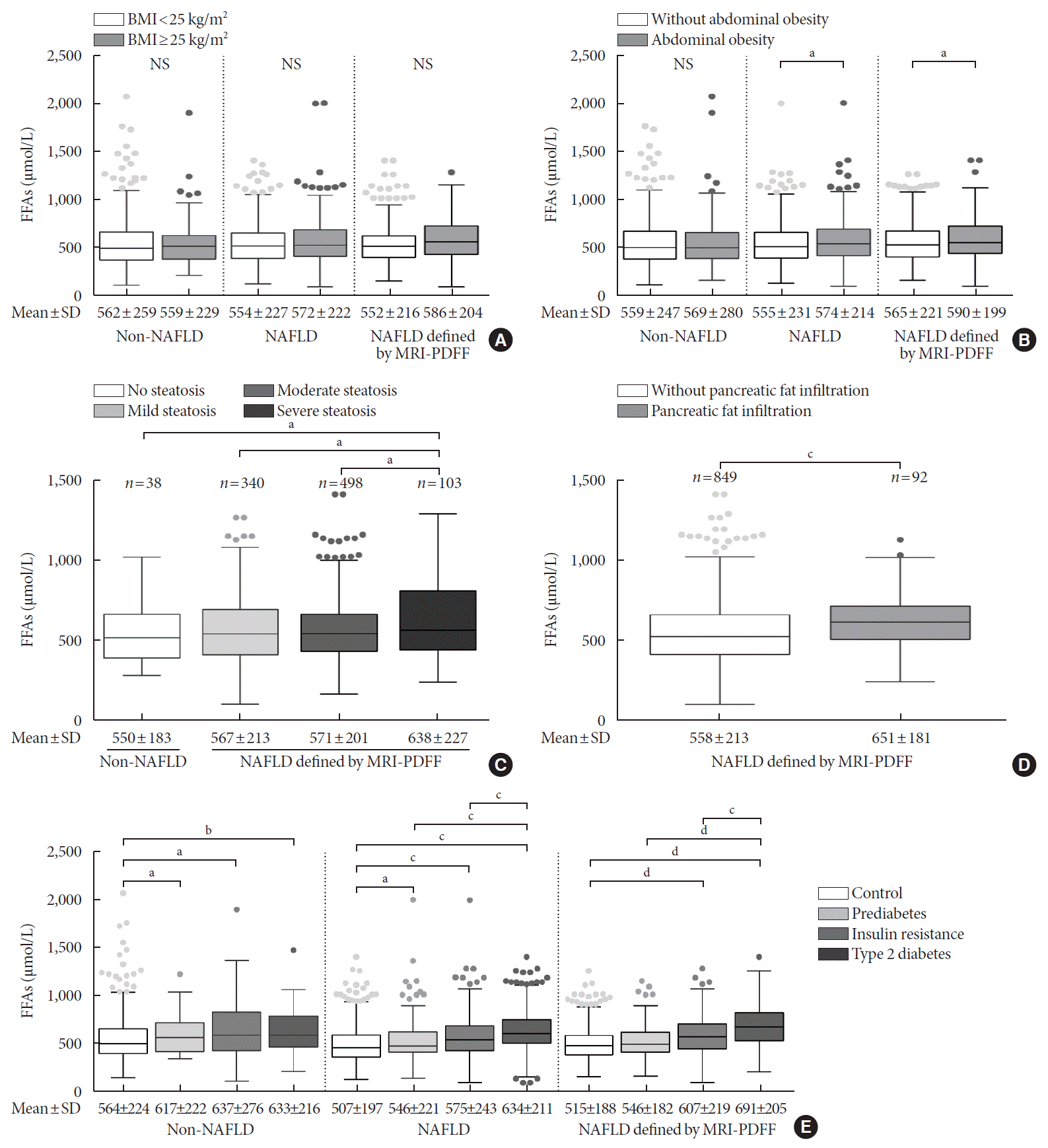
Dose-dependent association of serum FFA levels with IR, prediabetes, and T2DM in NAFLD patients
Table 2.
| Variable |
OR (95% CI) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Non-NAFLD |
NAFLD |
NAFLD defined by MRI-PDFF |
||||||||
| Crude | Model 1a | Model 2b | Crude | Model 1a | Model 2b | Crude | Model 1a | Model 2b | ||
| Insulin resistance | ||||||||||
| FFA quartile 1 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | |
| FFA quartile 2 | 1.18 (0.70–1.92) | 1.19 (0.70–1.97) | 0.77 (0.42–1.37) | 1.41 (1.08–1.80) | 1.41 (1.11–1.83) | 1.24 (0.82–1.82) | 1.71 (1.23–2.35) | 1.66 (1.19–2.28) | 1.24 (0.85–1.85) | |
| FFA quartile 3 | 1.05 (0.60–1.75) | 1.08 (0.61–1.81) | 0.74 (0.38–1.35) | 2.86 (2.27–3.61) | 2.88 (2.27–3.63) | 1.95 (1.34–2.82) | 2.84 (2.10–3.81) | 2.75 (2.03–3.69) | 1.95 (1.34–2.83) | |
| FFA quartile 4 | 1.73 (1.10–2.71) | 1.62 (1.01–2.56) | 2.29 (1.35–3.85) | 9.77 (7.83–12.22) | 9.66 (7.75–12.11) | 9.24 (6.43–13.36) | 12.52 (9.32–16.81) | 12.13 (9.03–16.28) | 9.24 (6.44–13.32) | |
| P for trend | 0.179 | 0.267 | 0.335 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Prediabetes | ||||||||||
| FFA quartile 1 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | |
| FFA quartile 2 | 0.39 (0.25–0.60) | 0.34 (0.20–0.53) | 0.23 (0.08–0.56) | 1.08 (0.77–1.51) | 1.11 (0.78–1.55) | 2.03 (1.06–3.69) | 1.82 (1.18–2.81) | 1.82 (1.18–2.82) | 3 (1.75–5.16) | |
| FFA quartile 3 | 0.51 (0.33–0.77) | 0.4 (0.25–0.63) | 1.65 (0.79–3.36) | 2.08 (1.51–2.83) | 2.14 (1.55–2.91) | 2.81 (1.48–5.15) | 2.35 (1.56–3.53) | 2.39 (1.58–3.58) | 3.93 (3.07–4.43) | |
| FFA quartile 4 | 0.79 (0.54–1.15) | 0.7 (0.46–1.05) | 1.16 (0.59–2.24) | 2.87 (2.09–3.90) | 2.88 (2.11–3.95) | 10.48 (5.66–19.39) | 2.81 (2.19–3.70) | 2.77 (2.18–3.67) | 4.93 (3.70–6.05) | |
| P for trend | 0.817 | 0.59 | 0.255 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.014 | |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | ||||||||||
| FFA quartile 1 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference | |
| FFA quartile 2 | 1 (0.7–1.38) | 1.06 (0.73–1.52) | 0.81 (0.38–1.58) | 1.1 (0.84–1.42) | 1.19 (0.91–1.55) | 3.68 (2.25–5.93) | 2.23 (1.85–4.15) | 2.08 (1.77–4.00) | 3.47 (2.12–5.65) | |
| FFA quartile 3 | 0.87 (0.61–1.23) | 0.83 (0.56–1.22) | 1.08 (0.52–2.11) | 1.7 (1.34–2.16) | 1.89 (1.46–2.40) | 6.5 (4.06–10.18) | 3.23 (2.46–5.85) | 3.23 (2.38–6.85) | 6.06 (3.82–9.53) | |
| FFA quartile 4 | 1.45 (1.06–1.97) | 1.4 (1.01–1.96) | 2.23 (1.25–3.98) | 6.02 (4.86–7.44) | 6.4 (5.12–8.02) | 19.43 (12.75–29.81) | 10.15 (8.23–14.31) | 10.31 (8.62–15.85) | 18.29 (11.94–27.94) | |
| P for trend | 0.153 | 0.258 | 0.071 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
Test for trend based on variable containing median value for each quartile. FFAs were categorized by 397, 510, and 647 mmol/L for the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles, represented by FFA quartile 1, quartile 2, quartile 3, and quartile 4.
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; MRI-PDFF, magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction; FFA, free fatty acid.
b Adjusted for age, sex, smoking status, body mass index, waist circumference, triglycerides, cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, uric acid and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index (except for insulin resistance analysis) in both groups. Liver fat content and pancreatic fat content were additionally adjusted in subgroup NAFLD defined by MRI-PDFF.
Predictive value of serum FFA levels for IR, prediabetes, and T2DM
Fig. 3.
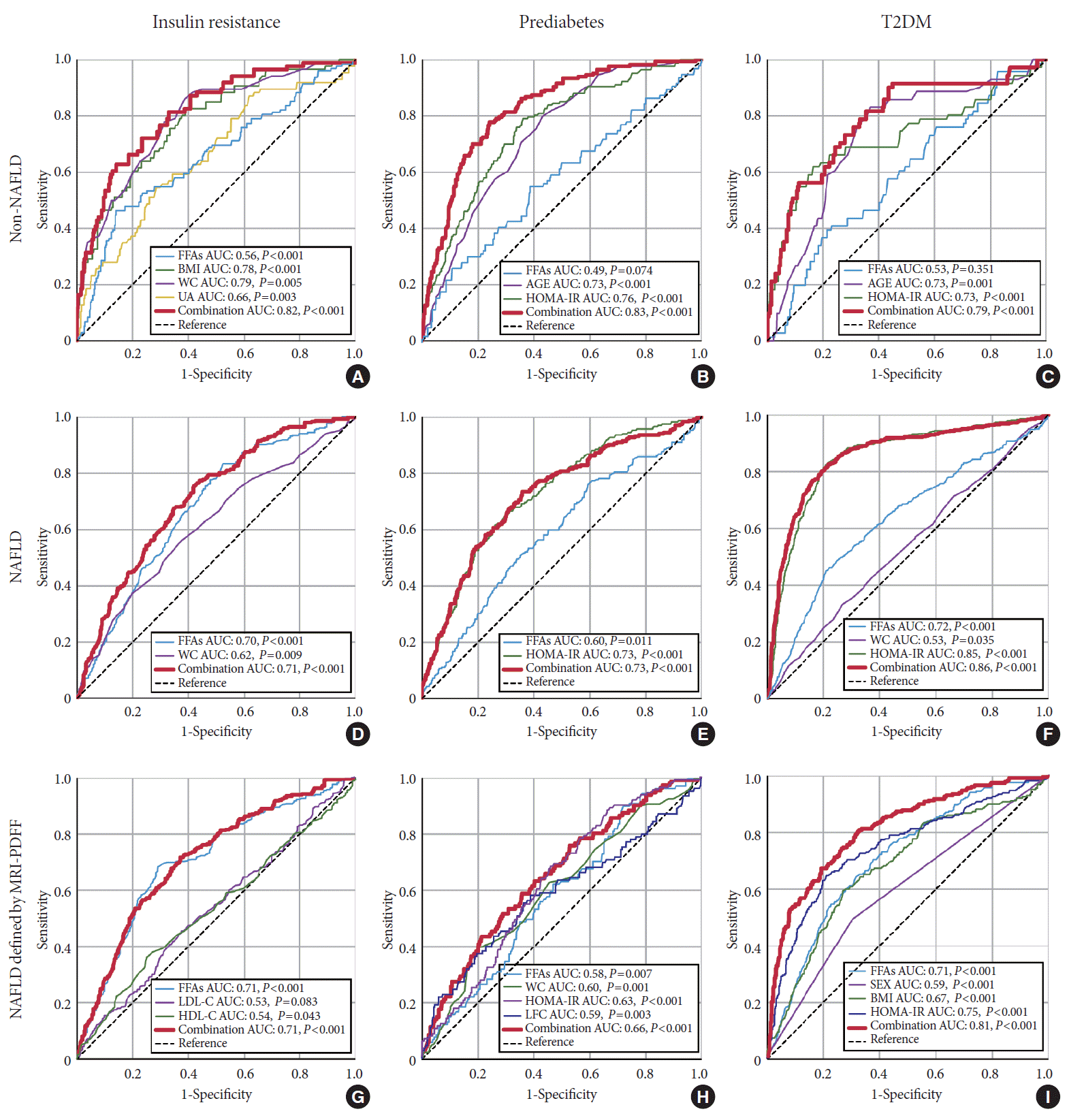




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 represented as the mean value of liver fat contents in each FFA quantantile. NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. aP<0.05.
represented as the mean value of liver fat contents in each FFA quantantile. NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. aP<0.05. XML Download
XML Download