Abstract
Objective
Acute mechanical thrombectomy (AMT) in patients with acute ischemic stroke from large vessel occlusion (LVO) is performed without directly identifying the occluded vessels. In this study, we evaluated whether 1.5 T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with 3D-fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition (FIESTA) could visualize the occluded intracranial middle cerebral artery (MCA) and internal carotid artery (ICA) before AMT.
Methods
This retrospective study included 21 consecutive patients who underwent time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF MRA) and 3D-FIESTA MRI immediately before AMT. The patients also underwent TOF MRA after AMT and achieved TICI 2b or 3 by AMT at our hospital between February 2018 and April 2019. When LVO in the anterior circulation was detected by TOF MRA, 3D-FIESTA MRI was additionally performed. Then, the occluded intracranial MCA and ICA, including their branches, were constructed on the workstation with volume rendering. The obtained images were fused with the TOF MRA images to create combined 3D images.
Results
The length and top-to-bottom distance of the affected M1 segment (calculated by the ipsilateral-to-contralateral ratio) were 1.29 and 1.17, respectively, on 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT and 1.34 and 1.24, respectively, on TOF MRA after AMT. We assessed the number of M2 segments branching from the affected M1/M2 junction and visualized the affected anterior temporal artery. The 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT and TOF MRA after AMT were consistent in all patients, except for two who moved vigorously during imaging.
Recent trials have established the benefits of acute mechanical thrombectomy (AMT) over medical management alone in patients with acute ischemic stroke from large vessel occlusion (LVO) of the anterior circulation [4,6,8,12,20]. However, device-related complications such as intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), vasospasm, arterial dissection, and arterial perforation can occur during AMT (4-31%) [3,4,6,8,12,20]. Identifying the target occluded vessels is important for the safety and efficacy of AMT. However, time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF MRA), computed tomography angiography, and conventional angiography, which are generally performed before AMT, visualize only vessels with blood flow. For this reason, AMT is performed without directly identifying the target occluded vessels.
In a previous study, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with three-dimensional (3D) constructive interference in steady state sequence, which produces images similar to those of MRI with 3D fast imaging employing steadystate acquisition (FIESTA), was used to measure the outer-diameter of the narrowing middle cerebral artery (MCA) and internal carotid artery (ICA) [14]. Thus, we speculated that 3D-FIESTA MRI could visualize the outer-diameters of even such occluded vessels.
In this study, we evaluated whether 1.5 T 3D-FIESTA MRI could be used to evaluate the occluded intracranial MCA and ICA before AMT in patients with LVO.
Of the 52 patients with LVO who underwent AMT at our hospital between February 2018 and April 2019, this study included 21 consecutive patients with occluded intracranial MCA and ICA who underwent TOF MRA and 3D-FIESTA MRI immediately before AMT, additionally underwent TOF MRA after AMT, and achieved thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) score 2b or 3 by AMT (Fig. 1). The exclusion criteria included any type of occlusion except MCA and ICA occlusion, TICI score ≤2a, unavailable pre-and-postoperative MR (Fig. 1).
When LVO of the anterior circulation was detected by TOF MRA, 3D-FIESTA MRI was additionally performed. Then, the occluded intracranial MCA and ICA (including their branches) were constructed with volume rendering on the workstation. The obtained images were fused with TOF MRA to create a 3D image. These processes were performed by a radiologic technologist.
TOF MRA and 3D-FIESTA were acquired using a Signa Excite HDx 1.5T (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). The parameters of the 3D TOF MRA sequence were: repetition time/echo time, 25/6.8 ms; flip angle, 18; thickness, 1.4 mm; matrix, 320×192; field of view, 20×20 cm; area imaged, 80 mm (2 slabs); zero-fill interpolation, 2; acquisition time, 3 min 14s. The parameters of the 3D-FIESTA sequence were: repetition time/echo time, 6.12/3.0 ms; flip angle, 20; thickness, 1.2 mm; matrix, 288×224; field of view, 20×20 cm; zero fill interpolation, 2; area imaged, 150 mm (coronal); acquisition time, 1 min 29 s.
For patients with occlusion of the anterior circulation, a 9 F balloon guiding catheter (9 F Optimo; Tokai Medical Products, Aichi, Japan) was advanced as far distally into the cervical or proximal petrous ICA as possible. The target vessel for thrombectomy was navigated with a microguidewire and a microcatheter. After passage of the thrombus, intraarterial contrast medium was injected to verify that the microcatheter was positioned distally to the thrombus. The stent retriever was deployed by withdrawing the microcatheter. The direct aspiration technique was used with the Penumbra system (Penumbra, Inc., Alameda, CA, USA). A Penumbra aspiration catheter (Penumbra, Inc., Alameda, CA, USA) was advanced just to the proximal level of the thrombus, and aspiration was applied by an aspiration pump.
Data collection included age, sex, site of target occluded vessel, successful recanalization (defined as TICI score≥2b), and symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage or SAH after AMT. The clinical characteristics of the patients were described using mean and standard deviation or number and percentage. Additionally, the consistency between the images obtained with the present technique before AMT and those obtained with TOF MRA after AMT was retrospectively evaluated with regard to the length of the affected M1 segment (calculated by the ipsilateral-to-contralateral ratio) (Fig. 2). Consistency was also evaluated in terms of the top-to-bottom distance of the affected M1 segment (Fig. 2).23) The latter was calculated by the ipsilateral-to-contralateral ratio, the number of M2 segments branching from the affected M1/M2 junction, and visualization of the affected anterior temporal artery (that is, the first branch to the temporal lobe). These MRI and angiography findings were all estimated by at least two individuals, and the agreement was excellent.
The ethics committee of our hospital approved this study, and the requirement for informed consent was waived (2020005).
The mean age of all 21 patients was 77.6±12.8 years. The number of male patients was 14 (66.7%). Neither symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage nor SAH was observed in any patients. The other demographic data of the 21 patients are shown in Table 1. The TICI scores were 2b and 3 in 3 and 18 patients, respectively (Table 1).
The length and top-to-bottom distance of the affected M1 segment (calculated by the ipsilateral-to-contralateral ratio) were 1.29 and 1.17, respectively, on 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT and 1.34 and 1.24, respectively, on TOF MRA after AMT. We assessed the number of M2 segments branching from the affected M1/M2 junction and visualized the affected anterior temporal artery (the first branch to the temporal lobe). The 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT and TOF MRA after AMT were consistent in all patients, except for two who moved vigorously during imaging. Among the 13 patients whose anterior temporal arteries were detected by angiography performed immediately after AMT, the present technique and TOF MRA performed after AMT failed to visualize the anterior temporal artery in two patients (artery widths: 0.8 and 0.7 mm). However, when doctors retrospectively confirmed the source images used for the FIESTA MRI in these two patients, the anterior temporal artery was detectable in both patients. In this study, the narrowest anterior temporal artery that could be visualized by 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT was 1.2 mm. Thus, if doctors confirm the source images used for FIESTA MRI, they can detect even an anterior temporal artery less than 1 mm in diameter unless the patient’s movement is vigorous.
Production of the fusion 3D images was completed before AMT in all patients. During insertion of the microguidewire and microcatheter, we were able to select the affected M2 segment in all patients. No complications were caused by lesion crossing during this process.
The direct aspiration technique was used with the Penumbra system for right MCA (M1 segment) occlusion [26]. The M2 segment was recanalized, but the anterior temporal artery was not patent. A stent retriever was deployed into the anterior temporal artery, and recanalization was achieved (TICI score 2b) (Fig. 3).
After the first pass of a stent retriever, only one M2 segment of the trifurcation of the MCA (M1 segment) was recanalized. When second pass was attempted afterwards, a lesion crossing was comfortably performed because the present technique had previously revealed the location of the M1/M2 junction and the M2 segment to be a branch of the trifurcation. A TICI score of 3 was achieved (Fig. 4).
The branching patterns of the MCA vary, including single trunk (4-6%), bifurcation (64-66%), trifurcation (26-29%), and quadrifurcation (1-4%) [13,27]. Of these patterns, bifurcation is further divided into equal bifurcation (18%), inferior trunk dominant (32%), and superior trunk dominant (28%) [7]. In this study, 3D-FIESTA MRI before AMT was able to detect these occluded MCAs in all patients except for two who moved vigorously during imaging.
Although the first-pass effect is reportedly important for achieving TICI score 3, the inability to recognize the branching site of the target occluded vessel before the second pass (as seen in cases 1 and 2) may be a cause of reduced of successful recanalization (TICI scores≥2b) on the second pass and subsequent passes [19]. In this study, the proportion of patients with a TICI score of 3 was higher than that of those with a TICI score of 2b. However, as seen in cases 1 and 2, the performance of AMT after confirmation of the branching sites, courses, and number of target occluded vessels may enable us to increase the TICI score to ≥2b even if it is ≤2a after the first pass. Even in cases 1 and 2, successful recanalization might not have been achieved if the present technique had not been performed. Thus, identifying the target occluded vessels before AMT with the present technique appears to be important for improving the efficacy of AMT. However, further studies with additional case accumulation are needed.
During AMT, various device-related complications can occur (4-31% total incidence) [3]. The incidence rates of specific complications have been reported as 1.9-15.8% for intracerebral hemorrhage, 0.6-5.5% for SAH, 3-23% for vasospasm, 0.6-6.7% for arterial dissection, and 0.7-4.9% for arterial perforation [3]. The treatment of curved vessels is associated with increased incidence of hemorrhagic complications and a reduced chance of successful recanalization with a stent retriever [18,22,23,28]. If the target vessels are found to be curved with the use of the present technique before AMT, the direct aspiration technique (instead of a stent retriever) can be selected [26]. Therefore, the present technique may contribute to the safety of AMT. Additionally, migration of a microcatheter and deployment of a stent retriever may be associated with the risk of device-related complications in arteries such as the lenticulostriate artery and the anterior temporal artery, which have narrow diameters. The present technique enables us to distinguish whether the target occluded vessel is a major artery or a small branching vessel. Because the present technique is capable of identifying not only the MCA and ICA but also the posterior communicating artery and the anterior cerebral artery along with their diameters, it may be useful for early detection of migration of the microguidewire and microcatheter to these arteries during AMT. A variation in which the anterior temporal artery branches directly from the ICA instead of from the MCA is referred to as duplicated MCA and is observed at 0.3-4.0% frequency [1,16,25]. A combination of this duplicated MCA and cerebral aneurysm has been reported [15,16]. When LVO is accompanied by an aneurysm, a microguidewire or microcatheter may perforate the aneurysm during AMT and cause a life-threatening hemorrhagic complication [9]. Indeed, in this series, a case of MCA occlusion was accompanied by a contralateral unruptured MCA aneurysm. When an aneurysm is suspected after employing the present technique before AMT, alternative treatments such as switching to the direct aspiration technique can be employed [26]. Further studies are needed to determine whether the present technique reduces the incidence of device-related complications.
Previous reports that have attempted to visualize the target occluded vessels on images before AMT included the use of computed tomography angiography and conebeam computed tomography [2,5,10,11,24]. The visualization ability of these modalities depends on the development of leptomeningeal anastomosis, and thus, these modalities cannot visualize the target occluded vessels themselves. Additionally, Kuribara et al. reported the use of MRI in a small number of patients (five total: one with TICI score 3, two with TICI score 2b, two with TICI score 2a, and one with TICI score 0) [17]. Furthermore, the utility of their study is limited because it used 3T MRI, and its scanning time was 2 minutes 17 seconds longer. Conversely, the scanning time of the present technique is 1 minute 29 seconds. Because the time to recanalization is an important determinant of good outcomes in AMT, further studies are necessary to determine whether the benefits of the present technique outweigh the costs of the additional scanning time [21].
In this study, the present technique could not be performed in patients who had difficulty undergoing MRI because of body motion or other factors.
Although a radiologic technologist created this study’s fusion 3D images, it seems important for the operators themselves to confirm the FIESTA MRI source images if time allows.
The mean age of the patients enrolled in this study was 77.6±12.8 years. Because of the patients’ advanced age, brain atrophy had progressed, which might have facilitated identification of the courses of the vessels in the subarachnoid space by 3D-FIESTA MRI. In patients with tightly packed subarachnoid space, such as young people, it may be difficult to visualize the target occluded vessels using the present technique.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the members of the MRI team. We thank Richard Lipkin, PhD, from Edanz Group (https://en-author-services.edanzgroup.com/) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
REFERENCES
1. Abanou A, Lasjaunias P, Manelfe C, Lopez-lbor L. The accessory middle cerebral artery (MCA). diagnostic and therapeutic consequences. Anat Clin. 1984; 6(4):305–9.
2. Amano T, Sato M, Matsumaru Y, Sakuma H, Yoda S, Hamada Y. Intra-arterial contrasted cone-beam computed tomography assessment of vessels distal from occluded site in acute ischemic stroke with major vessel occlusion. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2017; Jun. 57(6):292–8.

3. Balami JS, White PM, McMeekin PJ, Ford GA, Buchan AM. Complication of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke: prevention and management. Int J Stroke. 2018; Jun. 13(4):348–61.
4. Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; Jan. 372(1):11–20.
5. Blanc R, Pistocchi S, Babic D, Bartolini B, Obadia M, Alamowitch S, et al. Intravenous flat-detector CT angiography in acute ischemic stroke management. Neuroradiology. 2012; Apr. 54(4):383–91.

6. EXTEND- IA TNK Investigators. Tenecteplase versus alteplase before thrombectomy for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2018; Apr. 378(17):1573–82.
7. Gibo H, Carver CC, Rhoton AL Jr, Lenkey C, Mitchell RJ. Microsurgical anatomy of the middle cerebral artery. J Neurosurg. 1981; Feb. 54(2):151–69.

8. Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; Mar. 372(11):1019–30.
9. Hayashi K, Takahashi N, Furuichi S, Yoshioka T, Shibata S. Two cases of cerebral aneurysm detected after recanalization of the middle cerebral artery. No Shinkei Geka. 1998; Dec. 26(12):1103–7.
10. Hoelter P, Goelitz P, Lang S, Luecking H, Kalmuenzer B, Struffert T, et al. Visualization of large vessel occlusion, clot extent, and collateral supply using volume perfusion flat detector computed tomography in acute stroke patients. Acta Radiol. 2019; Nov. 60(11):1504–11.

11. Iwasaki M, Saito M, Nemoto A, Suzuki T, Hikita C, Fukuta S, et al. Diluted contrast-enhanced cone-beam CT during acutephase recanalization therapy for occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. J Neuroendovascular Therapy. 2019; Feb. 13(2):91–4.

12. Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; Jun. 372(24):2296–306.

13. Kahilogullari G, Ugur HC, Comert A, Tekdemir I, Kanpolat Y. The branching pattern of the middle cerebral artery: is the intermediate trunk real or not? An anatomical study correlating with simple angiography. J Neurosurg. 2012; May. 116(5):1024–34.

14. Kaku Y, Morioka M, Ohmori Y, Kawano T, Kai Y, Fukuoka H, et al. Outer-diameter narrowing of the internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries in moyamoya disease detected on 3D constructive interference in steady-state MR image: is arterial constrictive remodeling a major pathogenesis? Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; Dec. 154(12):2151–7.

15. Kimura T, Morita A. Treatment of unruptured aneurysm of duplication of the middle cerebral artery--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2010; 50(2):124–6.
16. Komiyama M, Nakajima H, Nishikawa M, Yasui T. Middle cerebral artery variations: duplicated and accessory arteries. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; Jan. 19(1):45–9.
17. Kuribara T, Haraguchi K, Ogane K, Matsuura N, Ito T. 3D-FIESTA magnetic resonance angiography fusion imaging of distal segment of occluded middle cerebral artery. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015; 55(10):805–8.

18. Mokin M, Fargen KM, Primiani CT, Ren Z, Dumont TM, Brasiliense LBC, et al. Vessel perforation during stent retriever thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: technical details and clinical outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017; Oct. 9(10):922–8.

19. Nikoubashman O, Dekeyzer S, Riabikin A, Keulers A, Reich A, Mpotsaris A, et al. True first-pass effect. Stroke. 2019; Aug. 50(8):2140–6.

20. Saber H, Narayanan S, Palla M, Saver JL, Nogueira RG, Yoo AJ, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke with occlusion of the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery: a meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018; Jul. 10(7):620–4.

21. Saver JL, Goyal M, van der Lugt A, Menon BK, Majoie CB, Dippel DW, HERMES Collaborators, et al. Time to treatment with endovascular thrombectomy and outcomes from ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016; Sep. 316(12):1279–88.

22. Schwaiger BJ, Gersing AS, Zimmer C, Prothmann S. The Curved MCA: Influence of vessel anatomy on recanalization results of mechanical thrombectomy after acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015; May. 36(5):971–6.

23. Shirakawa M, Yoshimura S, Uchida K, Shindo S, Yamada K, Kuroda J, et al. Relationship between hemorrhagic complications and target vessels in acute thrombectomy. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017; Aug. 26(8):1732–8.

24. Smit EJ, Vonken EJ, van Seeters T, Dankbaar JW, van der Schaaf IC, Kappelle LJ, et al. Timing-invariant imaging of collateral vessels in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2013; Aug. 44(8):2194–9.

25. Teal JS, Rumbaugh CL, Bergeron RT, Segall HD. Anomalies of the middle cerebral artery: accessory artery, duplication, and early birfurcation. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1973; Jul. 118(3):567–75.
26. Turk AS, Frei D, Fiorella D, Mocco J, Baxter B, Siddiqui A, Spiotta A, et al. ADAPT FAST study: a direct aspiration first pass technique for acute stroke thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014; May. 6(4):260–4.

Fig. 1.
Data collection process for patients who underwent 3D-FIESTA MRI and TOF MRA immediately before acute mechanical thrombectomy (AMT), additionally underwent TOF MRA after AMT, and achieved thrombolysis in cerebral infarction (TICI) grade 2b or 3 by AMT at our hospital between February 2018 and April 2019. We excluded 31 patients for various reasons, and 21 patients were included in this study. 3D-FIESTA, three-dimensional fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; TOF MRA, time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography.
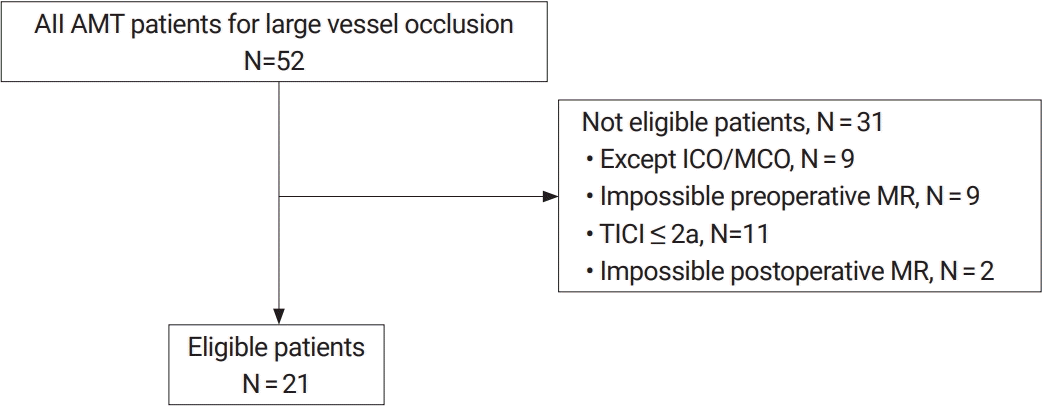
Fig. 2.
Example of a patient with measured top-to-bottom distance (dotted line) and length of the affected M1 segment (solid line) on time-of-flight MR angiography.
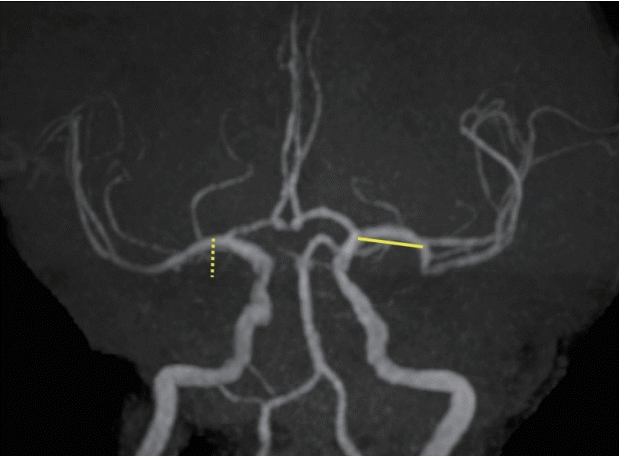
Fig. 3.
Preoperative TOF MRA (A), DWI (B), FLAIR (C), FIESTA MRI (D), fusion (TOF MRA and FIESTA MRI) MR (E), and cerebral angiography (F) in a case in which right MCA (M1 segment) occlusion was observed. Cerebral angiography after the direct aspiration technique using the Penumbra system in the right MCA (M1 segment) showed occlusion in the recanalized right M2 segment, except for the right anterior temporal artery (G). Cerebral angiography after stent retriever deployment in the right anterior temporal artery (H). Postoperative TOF MRA (I). TOF MRA, time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography; DWI, diffusion weighted image; FLAIR, fluid attenuated inversion recovery; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MCA, middle cerebral artery.
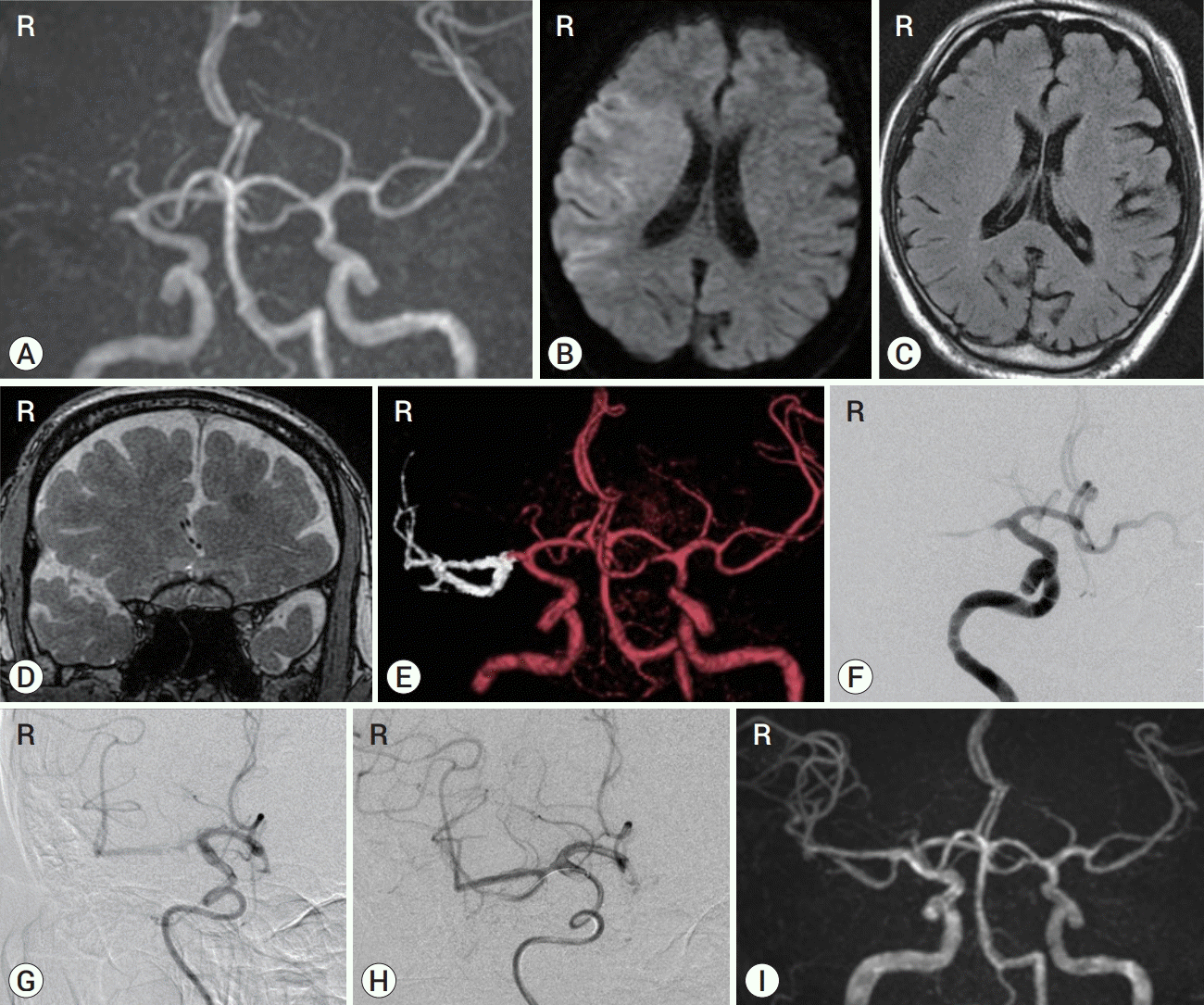
Fig. 4.
Preoperative TOF MRA (A), fusion (TOF MRA and FIESTA MRI) MR (B), and cerebral angiography (C) in a case in which left MCA (M1 segment) occlusion was observed. Cerebral angiography after the first pass of stent retriever deployment in the left MCA (D). Cerebral angiography after the second pass of stent retriever deployment in the left residual occluded M2 segment of the trifurcation of the MCA (E). Postoperative TOF MRA (F). TOF MRA, time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography; FIESTA, fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MCA, middle cerebral artery.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics and MRI findings of patients
MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; TICI, thrombolysis in cerebral infarction; AMT, acute mechanical thrombectomy; TOF MRA, time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography; FIESTA, fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition; ATA, anterior temporal artery; ICA, internal carotid artery; MCA, middle cerebral artery




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download