서론
수근 불안정
Table 1.
Reproduced from Larsen et al. [4].
1. 해리성 불안정
3. 복합성 불안정
4. 적응성 불안정
중수근 불안정
1. 중수근 관절의 인대
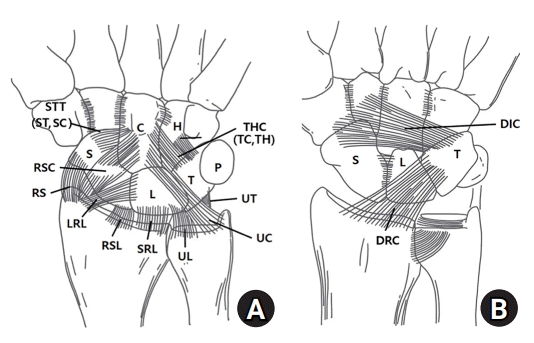 | Fig. 1.Palmar extrinsic ligaments and dorsal extrinsic ligament. THC, triquetral-hamate-capitate ligament (triquetrocapitate [TC]+triquetrohamate [TH]); STT, scapho-trapeizum-trapezoid ligament (scaphocapitate [SC]+scaphotraphezium [ST]); RSC, radioscaphocapitate ligament; LRL, long radio-lunate ligament; SRL, short radio-lunate ligament; UL, ulnolunate ligament; UC, ulnocapitate ligament; DIC, dorsal intercarpal ligaments; DRC, dorsal radiocarpal ligament. |
주상–대능형-소능형 인대
삼각-유구-유두 인대
요-월상 인대
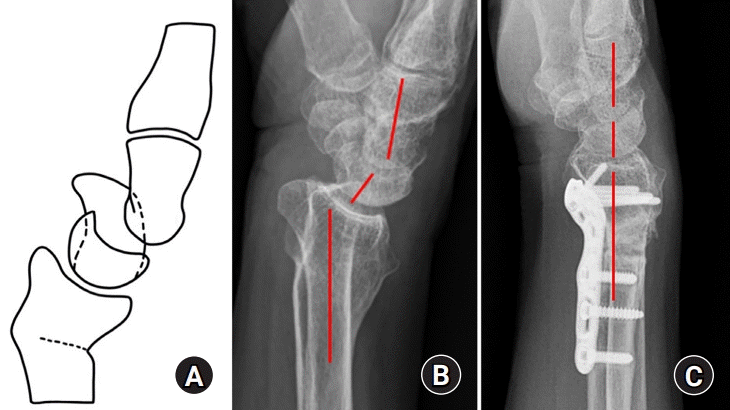
2. 전방 중수근 불안정
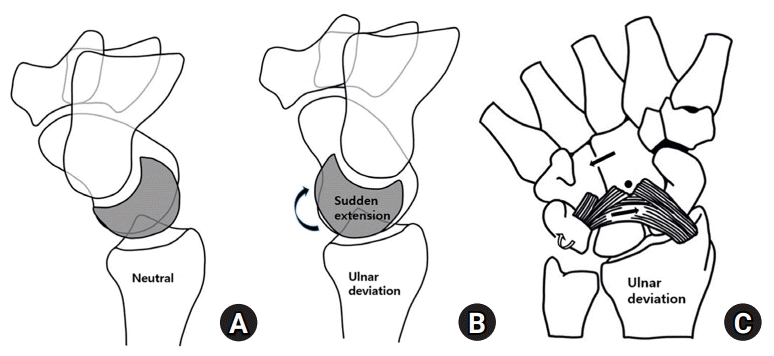 | Fig. 2.Palmar midcarpal instability. (A) The proximal row is abnormally flexed (volar intercalated segmental instability pattern) with palmar translation of the distal row in the neutral position of the wrist. (B) The proximal row is suddenly extended with clunk during ulnar deviation, suddenly extended (rotated arrow). (C) The hyperlaxity of the ulnar arm of the arcuate ligament (triquetral-hamate-capitate ligament) and dorsal radiotriquetral ligament induced palmar midcarpal instability, ulnar deviation (left side arrow) and arcuate ligament direction (right side arrow). |
전방 중수근 불안정의 발생 기전
전방 중수근 불안정의 원인
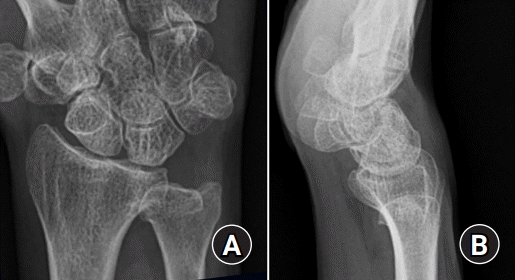
3. 후방 중수근 불안정
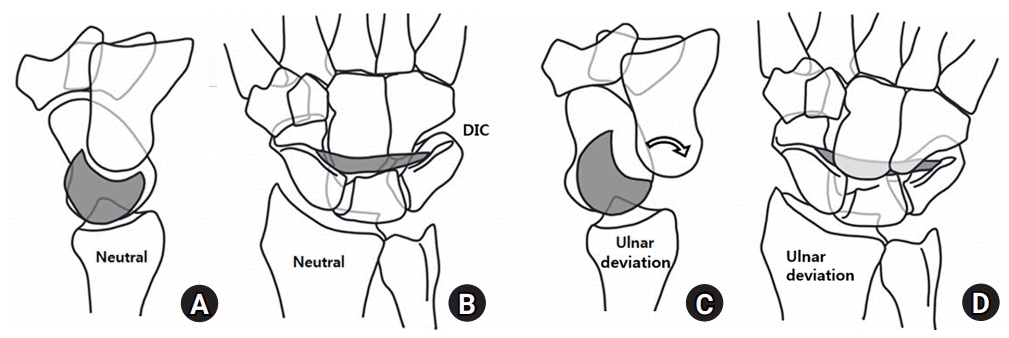 | Fig. 3.Dorsal midcarpal instability. (A, B) The proximal row is slightly extended in the neutral position of the wrist (dorsal intercalated segmental instability pattern). (C, D) The capitate and the distal row is suddenly subluxated posteriorly with clunk during ulnar deviation. (rotated arrow). Hyperlaxity of the scaphotriquetral ligament (a part of dorsal intercarpal ligament) in the posterior, and that of the radioscaphocapitate ligament and long radiolunate ligament in the anterior induced dorsal midcarpal instability. |
후방 중수근 불안정의 원인
4. 복합성 중수근 불안정
5. 외재성 중수근 불안정
중수근 불안정성의 중중도 분류(GRADING SYSTEM)
Table 3.
진단
1. 임상 증상과 이학적 검사
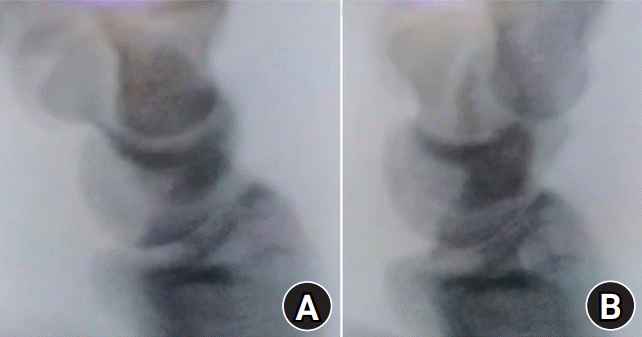
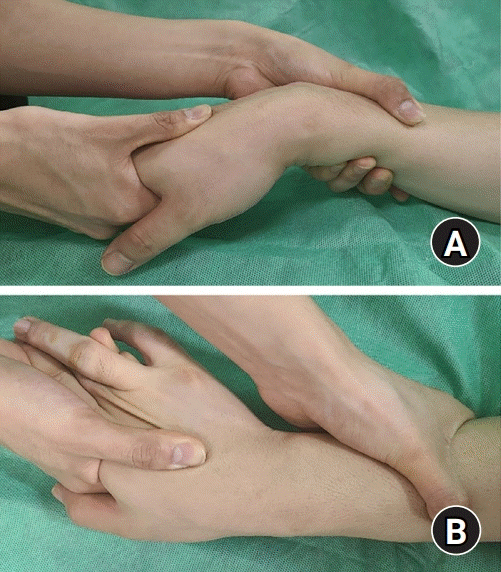 | Fig. 7.The midcarpal shift test can be diagnostic for palmar midcarpal instability. This maneuver accentuates the existing palmar subluxation of the distal row and disengages the normal intercarpal contact points. (A) The examiner then moves the wrist into ulnar deviation. (B) As the wrist reaches near the complete ulnar deviation, a strong clunk is felt, and often can be heard, as the distal row snaps back to its physiologic position. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download