Introduction
Material and Methods
Chemical and reagents
Animals and treatments
Measurement of lipid peroxidation
Measurement protein carbonyl in testis and epididymides
Measurement of glutathione
Sperm count and motility assay
Sperm morphology assay
Histopathological assay
Statistical analysis
Results
Effects of zinc and selenium on lipid peroxidation in rat testis
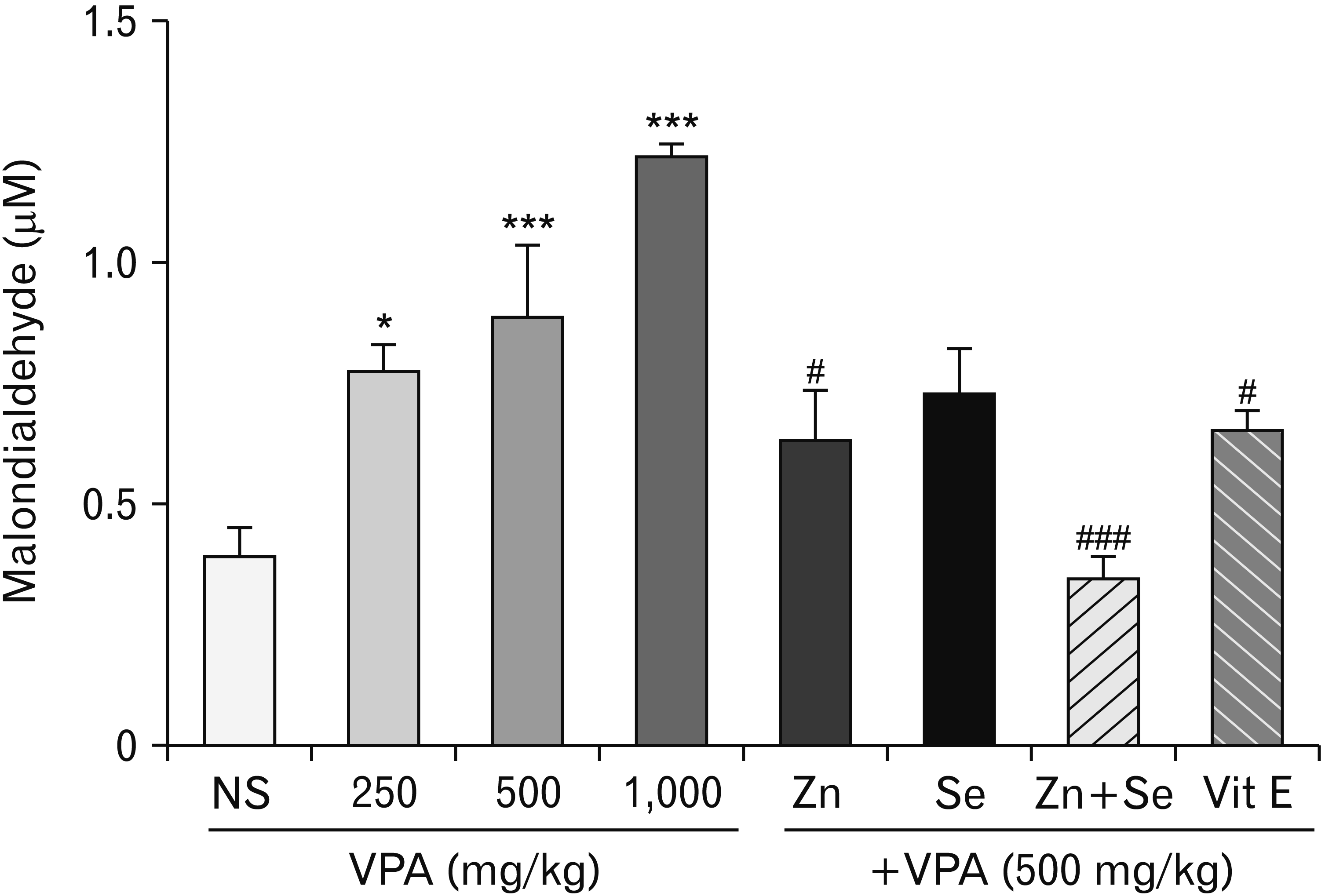 | Fig. 1Effects of Selenium (Se) and Zinc (Zn) on valproic acid (VPA)-induced lipid peroxidation in testis tissue. Data were expressed as mean. NS, normal salin (control group); Vit E, vitamin E. *P<0.05 compared to control. ***P<0.001 compared to control. #P<0.05 compared to VPA (500 mg/kg). ###P<0.001 compared to VPA (500 mg/kg). |
Effects of zinc and selenium on protein carbonyl in rat testis
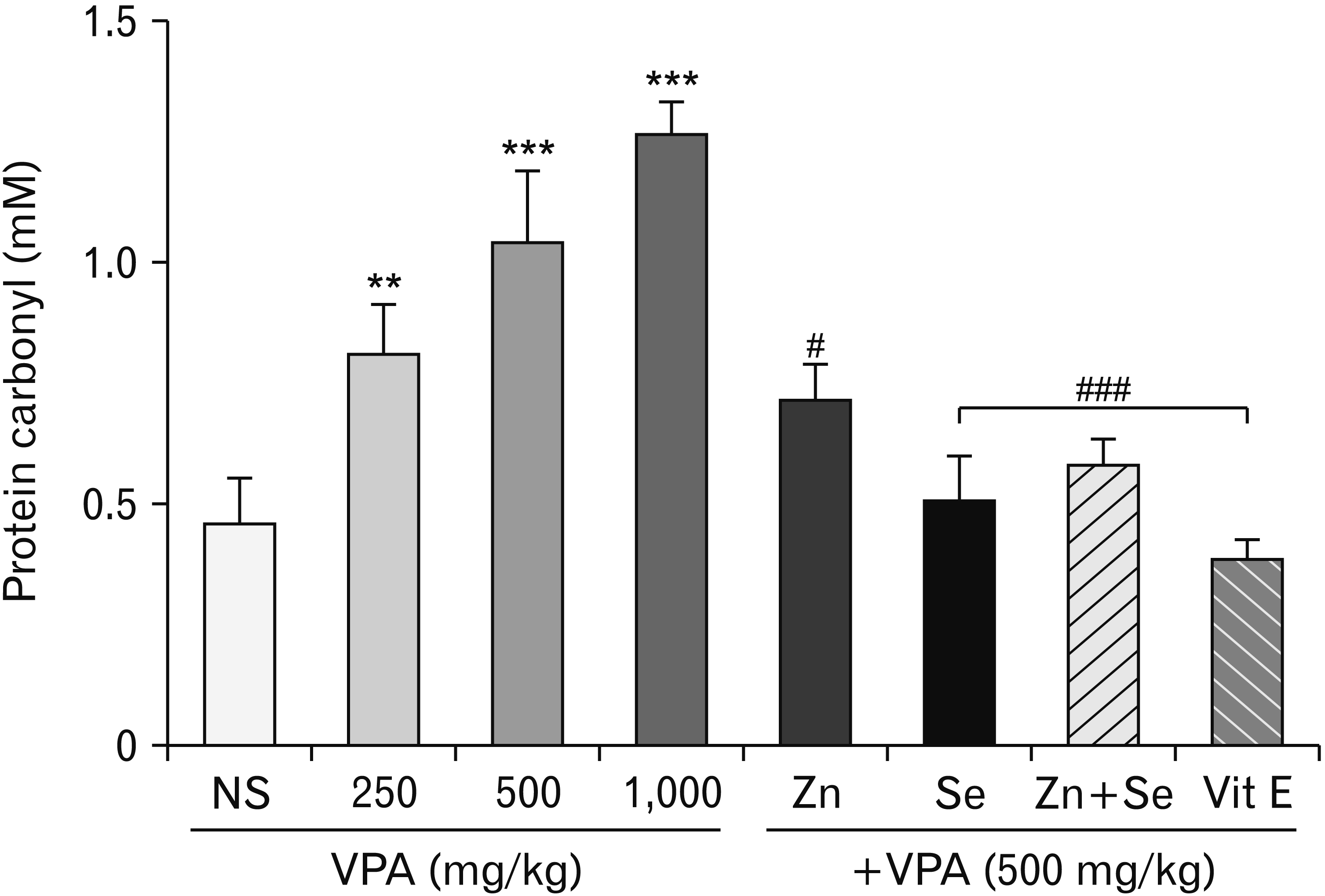 | Fig. 2Effects of Selenium (Se) and Zinc (Zn) on valproic acid (VPA)-induced protein carbonyl in testis tissue. Data were expressed as mean. NS, normal salin (control group); Vit E, vitamin E. **P<0.01 compared to control. ***P<0.001 compared to control. #P<0.05 compared to VPA (500 mg/kg). ###P<0.001 compared to VPA (500 mg/kg). |
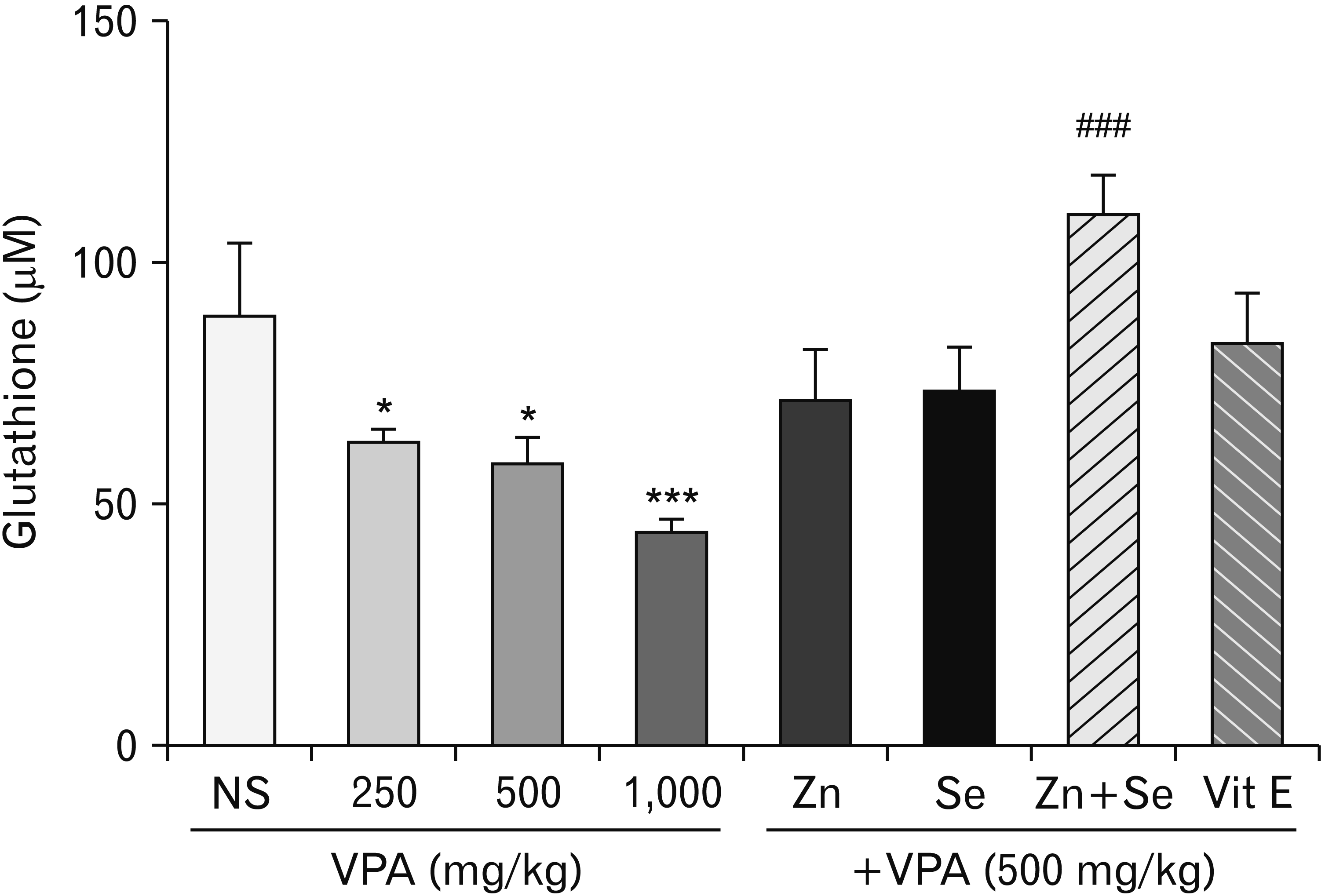
Effects of zinc and selenium on glutathione in rat testis
Effects of zinc and selenium on sperm motility
Table 1
| Group | Sperm abnormality (%) | Sperm motility (%) | Sperm count (×106/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NS | 13.6±3 | 94.1±1 | 39±4 |
| VPA | 47±4a) | 71±1a) | 24.3±2.5a) |
| VPA+Se | 35±3c) | 85.3±1.5d) | 26±3 |
| VPA+Zn | 34.2±3c) | 84±1d) | 26.6 ±4 |
| VPA+(Zn+Se) | 30.8±3d) | 81.1±1d) | 26.6±2.5 |
| VPA+Vit E | 10±3d) | 81.7±0.7d) | 34±2b) |
Values are presented as mean±SD. VPA, valproic acid; Se, selenium; Zn, zinc; Vit E, vitamin E. Sperm morphology, motility and count were evaluated in control (normal saline), VPA, VPA+Se, VPA+Zn, VPA+Zn+Se and VPA+Vit E groups. a)Significantly different from control group (P<0.001). b)Significantly different from VPA-treated group (P<0.05). c)Significantly different from VPA-treated group (P<0.01). d)Significantly different from VPA-treated group (P<0.001).
Effects of zinc and selenium on sperm morphology
Effects of zinc and selenium on sperm count
Histopathological examination
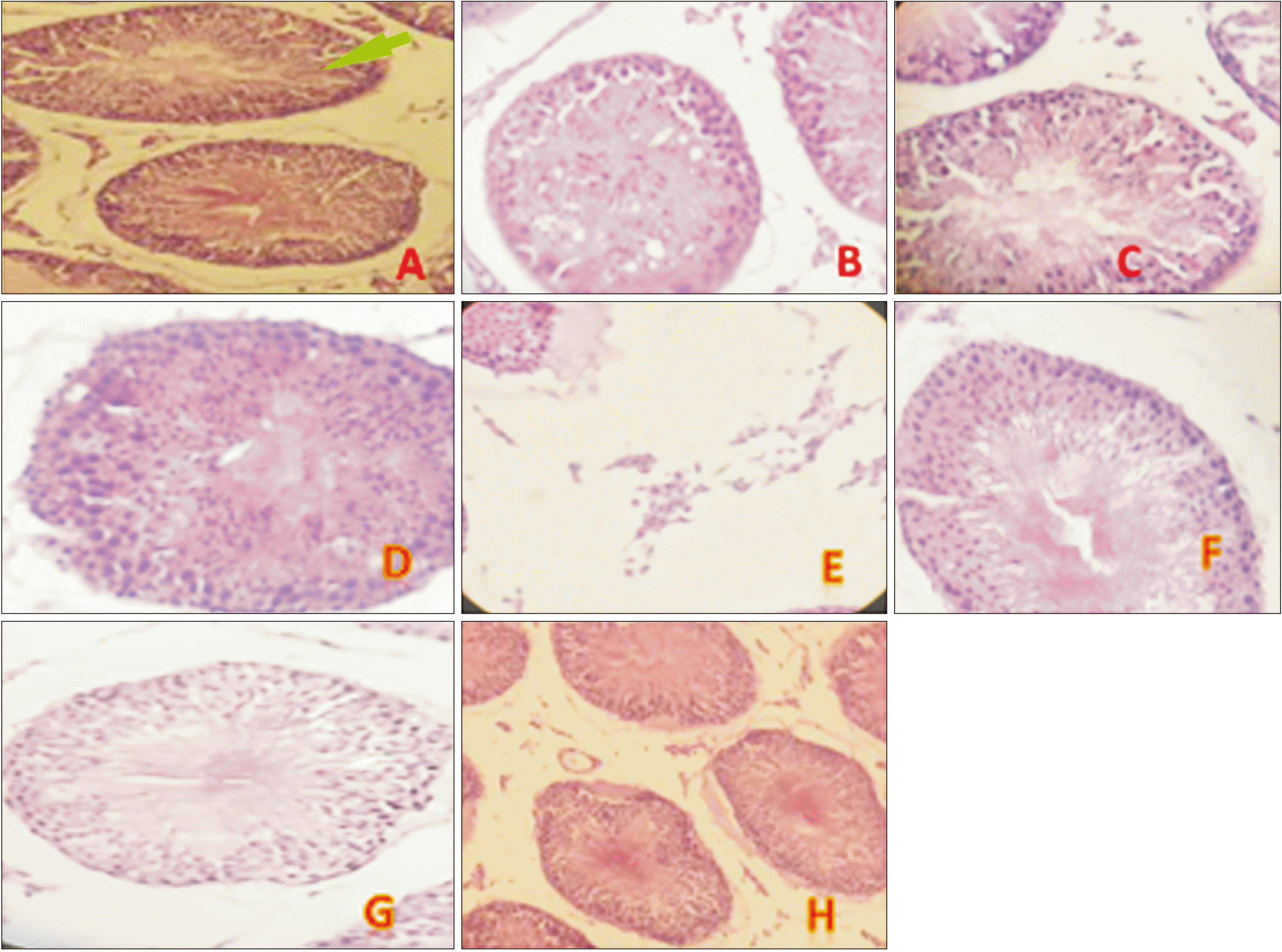 | Fig. 4H&E-stained testis histology pictures (with ×40 objective lens) showing normal testis. Morphology (control) (A), VPA-treated groups showed a decrease in germinal cell layer thickness (B), degenerative. changes and vacuolization in germinal cells (C), impaired spermatogenesis, stop maturation in some parts (D), increase in leydig cells (E). VPA+Zn-treated group (F), and VPA+Se-treated group (G) showed a normal germinal cell layer thickness and improve maturation. (H) VPA+Zn+Se-treated groups (combination therapy) showed better effect than Zn and Se alone. VPA, valproic acid; Zn, zinc; Se, selenium. |
Table 2
| Parameter | NS | VPA | VPA+Se | VPA+Zn | VPA+Sn+Zn | VPA+Vit E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testicular weight (g) | 1.65±0.09 | 1.36±0.11a) | 1.56±0.06c) | 1.59±0.08d) | 1.63±0.05e) | 1.54±0.07b) |
| Johnson score | 9.3±0.74 | 4±0.57a) | 5.8±0.68c) | 7±0.81e) | 8.3±0.74e) | 6.3±0.74d) |
Values are presented as mean±SD. NS, normal salin (control group); PA, valproic acid; Se, selenium; Zn, zinc; Sn, selenium; Vit E, vitamin E. Johnsen score - scale of 10 to 1: 10, normal spermatogenesis with open lumen; 9, many spermatozoa with obliteration of lumen; 8, only a few sprmtozoa; 7, no spermatozoa but many spermatids present; 6, no spermatozoa and only a few spermatids; 5, no sperms/spermatids but several sprmatocytes; 4, only a few spermatocytes present; 3, spermatogonia only germ cells present; 2, no germ cells but sertoli cells only present; 1, no cells in tubular section. a)Significantly different from control group (P<0.0001). b)Significantly different from VPA-treated group (P<0.05). c)Significantly different from VPA-treated group (P<0.01). d)Significantly different from VPA-treated group (P<0.001). e)Significantly different from VPA-treated group (P<0.0001).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download