57세 여자가 찢어지는 듯한 흉골 하 및 명치 부위 통증으로 응급실을 방문하였다. 활력징후는 혈압 90/60 mmHg, 맥박 71회/분, 호흡수 16회/분, 체온 36.3℃였다. 통증은 일주일 전부터 시작되었으며 물이나 음식을 먹으면 증상이 악화되어 1-2분간 지속되다 호전되는 양상을 반복하였고, 일주일전 같은 증상으로 응급실에 왔다 호전되어 퇴실하였다. 20년전 타 병원에서 만성 C형간염으로 인터페론을 투여한 후 완치 판정 받은 기왕력이 있으며, 15년 전 간경변증으로 진단받았고, 당시 복수가 있어 이뇨제를 복용하였다. 최근까지 3차례 식도정맥류출혈로 치료한 병력이 있었다. 당뇨병이 있어 투약 중이었고, 음주와 흡연은 하지 않았다. 내원 당시 혈압 저하로 승압제를 투여하였고 2병일째부터 발생한 38℃ 이상의 고열로 ceftriaxone을 투여하였다. 내원 6개월 전 간기능은 total bilirubin 1.48 mg/dL, albumin 3.0 g/dL, PT (INR) 1.23, AST 57 U/L, ALT 23 U/L였으나, 내원 당시 total bi-lirubin 6.27 mg/dL, albumin 2.3 g/dL, AST 128 U/L, ALT 48 U/L, ALP 270 U/L, GGT 180 U/L, PT (INR) 1.71로 악화된 소견을 확인할 수 있었다. 그 외 혈액 검사에서 혈색소 15.1 g/dL, 백혈구 17,880/mm
3 (중성구 14,100/mm
3), 혈소판 42,000/mm
3였고, BUN 49.0 mg/dL, 크레아티닌 0.93 mg/dL, 나트륨 123 mEq/L, 칼륨 4.1 mEq/L, 암모니아 35 μmol/L, CRP 8.05 mg/dL, HbA1c 10.3%, anti-HCV (+), HCV RNA (-), AFP 1.79 ng/mL, PIVKA II 16 mAU/mL로 염증 지표가 높았다. 혈액배양 검사에서 B군 사슬알균(group B
streptococcus,
Streptococcus agalactiae)이 2회 이상 배양되어 의미 있는 병원체로 판단하였고 ceftriaxone에 감수성이 있었다. 통증의 원인을 찾기 위해 시행한 복부 CT에서 문맥기에 주문맥과 양측 문맥에 혈전증이 진행되어 완전히 폐색된 상태였고(
Fig. 1A), 복벽에 뿌옇게 증가된 음영과 복강 내 소량의 복수가 관찰되어 문맥의 완전 폐색에 의한 전신 울혈이 확인되었다. 또한 조영 전 복부 CT에서 새로 진행된 문맥혈전은 고밀도(hyperdense, 58 housefield unit [HU])로 관찰되었다(
Fig. 1B). 한편 일주일 전 실시한 복부 CT에서는 주문맥 및 왼쪽 문맥 가지의 부분 문맥혈전증(
Fig. 1C)이 확인되었고, 이 부분은 조영 전 CT에서 저밀도(low density, 27 HU)로 관찰되었다(
Fig. 1D). 따라서 급격하게 진행된 완전 폐색을 동반한 급성의 광범위한 문맥혈전증에 의한 증상들로 판단하고 enoxaparin을 4주간 투여하였다. Enoxaparin 투여 15일 후 실시한 복부 초음파의 미세혈관 영상(super microvascular imaging; Aplio i800 with a convex broadband probe, Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan)에서는 우측 문맥의 근위부에 흐름신호(flow signal)가 관찰되지 않고 원위부 일부에서 약한 흐름신호만 관찰되었으나(
Fig. 2A), enoxaparin 투여 3주 후 실시한 복부 초음파에서는 문맥의 흐름신호가 근위부까지 복원되었음을 확인할 수 있었다(
Fig. 2B). 치료 1개월 후 실시한 복부 CT (
Fig. 2C)에서 우측 문맥의 혈류가 회복되었음을 확인할 수 있었으나 일부 만성 혈전이 남아있었다. 환자는 증상과 혈액 검사 소견(
Fig. 3)이 호전되어 퇴원하였고, 이후 외래를 통해 증상의 악화 없이 이뇨제를 서서히 감량할 수 있었다. 퇴원 6개월 후 실시한 복부 CT (
Fig. 2D, E)에서 복수의 유의미한 감소와 함께 우측 문맥의 부분 혈전의 일부가 호전되었음과 해면 변형(cavenous transformation) (
Fig. 2E) 및 좌측 문맥의 혈류가 회복되었음을 확인할 수 있었고, 치료 후 1년 이상 증상과 혈액 검사 소견의 악화 없이 외래 추적 검사 중이다.
 | Fig. 1Pre-treatment axial view of abdominal computed tomography (CT) images. (A, B) At admission, the axial portal phase CT image showed an occluded right and main portal vein (arrow of A, right portal vein; arrowhead of A, main portal vein). In addition, the precontrast CT image showed a newly developed hyperdense thrombosis in the right portal vein compared to the main portal vein (arrow of B, 58 HU indicated acute thrombus; arrowhead of B, 27 HU indicated chronic thrombus). (C, D) Seven days before admission, axial portal phase CT image showed partial thrombosis in the right portal vein (arrow of C). This thrombosis showed low density in the precontrast image (arrow of D, 27 HU). HU, housefield unit. 
|
 | Fig. 2Post-treatment ultrasonography (US) and axial view of abdominal computed tomography (CT) images. (A) After 2 weeks of anticoagulant therapy, the US image showed no flow signal at the right proximal portal vein using super microvascular imaging (SMI) (arrow). (B) After 3 weeks of anticoagulant therapy, the US image showed a restored portal vein flow signal on SMI (arrow). (C) After 1 month of anticoagulant therapy, the axial portal phase CT image showed recanalization of the right portal vein (arrow), but remaining preexisting chronic thrombus. (D) At 6 months after the end of anticoagulant therapy, the axial portal phase CT image showed improvements of partial thrombosis (arrow), recanalized left portal vein (dotted arrow), and decreased ascites. (E) At 6 months after the end of anticoagulation therapy, axial portal phase CT image showed cavernous transformation (arrow). 
|
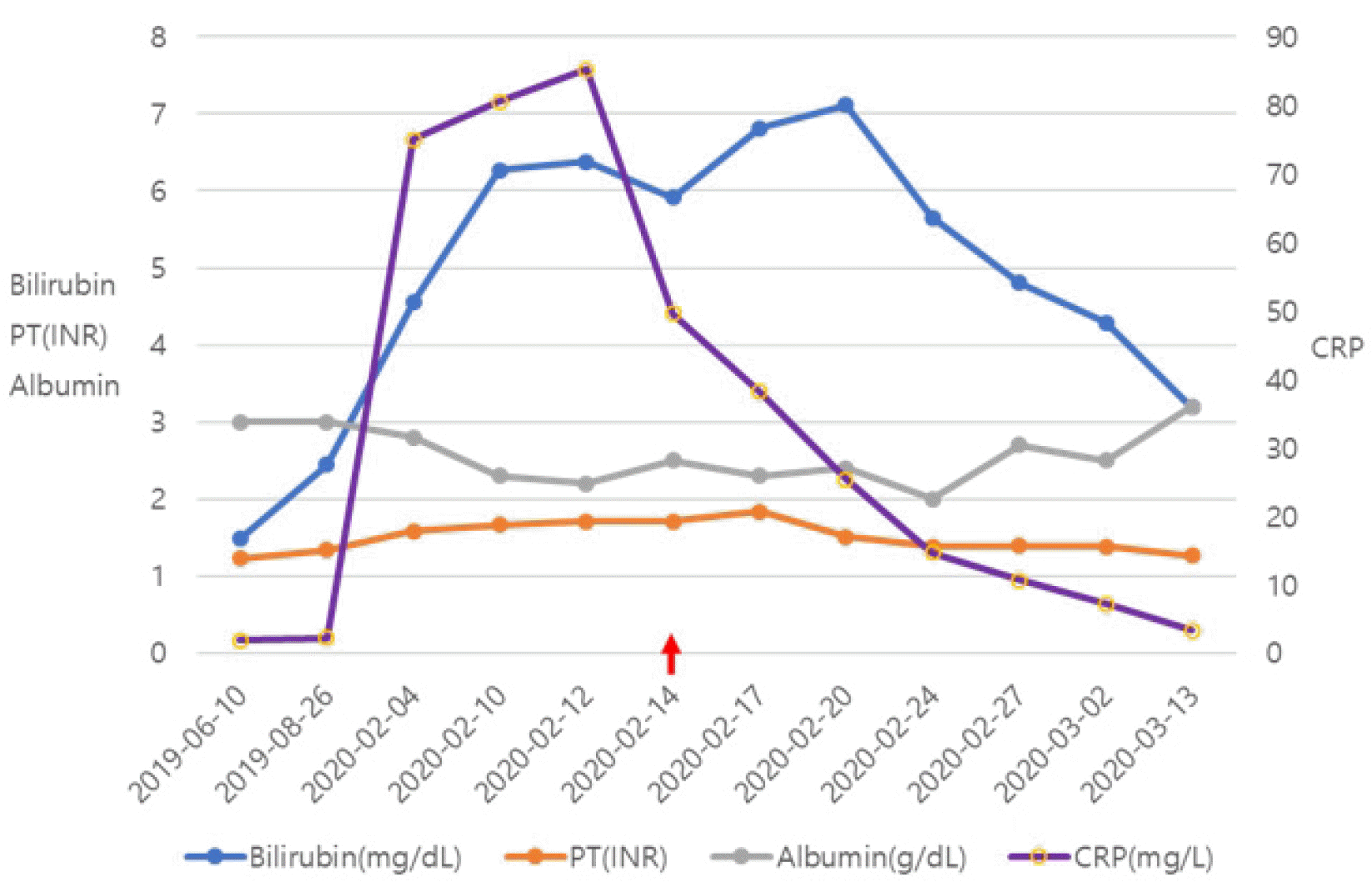 | Fig. 3Changes in the laboratory findings during anticoagulant therapy. LMWH (enoxaparin) was administered for 1 month, starting with HD 4 (2020-02-14) (red arrow). LMWH, low molecular weight heparin; PT, prothrombin time; INR, international normalized ratio; HD, hospital day; CRP, C-reactive protein. 
|







 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download