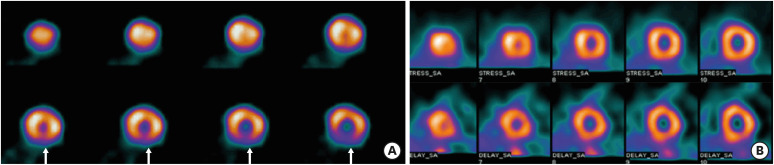
 | Figure 1Dipyridamole stress thallium 201 SPECT at 8 years old showing a reversible perfusion defect (arrows) in the inferior wall of the left ventricle (A), and normal perfusion at 6 months after the PTCRA (B).PTCRA = percutaneous transluminal coronary rotational ablation; SPECT = single-photon emission computed tomography.
|
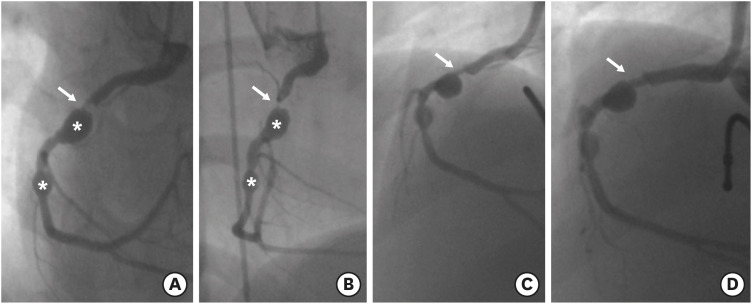 | Figure 2Coronary angiographies of RCA at 8 years of age, showing two coronary aneurysms (asterisks) and severe stenosis (>90% in diameter) at the proximal segment of the RCA (arrows) (A, B), a residual stenosis after coronary balloon angioplasty (C), and an improved coronary stenosis (arrow) after the PTCRA (D).PTCRA = percutaneous transluminal coronary rotational ablation; RCA = right coronary artery.
|
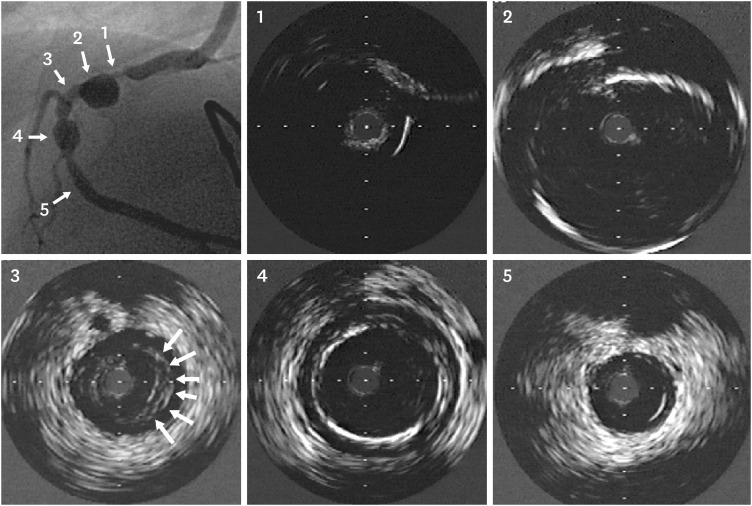 | Figure 3Intravenous ultrasound images before PTCRA at 8 years of age. Each numbered image corresponds to the sites indicated by numbers and arrows in the angiography image (far left and upper image). Severe stenosis and calcification (360°) (1), a huge aneurysm (about 7 mm in diameter), wall thickening, and calcifications (2), an intimal proliferation and thickening (arrows) (3), another aneurysm with calcification (4), and a nearly normal coronary artery (5) are demonstrated, all of which are unique characteristics of coronary artery lesions associated with Kawasaki disease.PTCRA = percutaneous transluminal coronary rotational ablation.
|
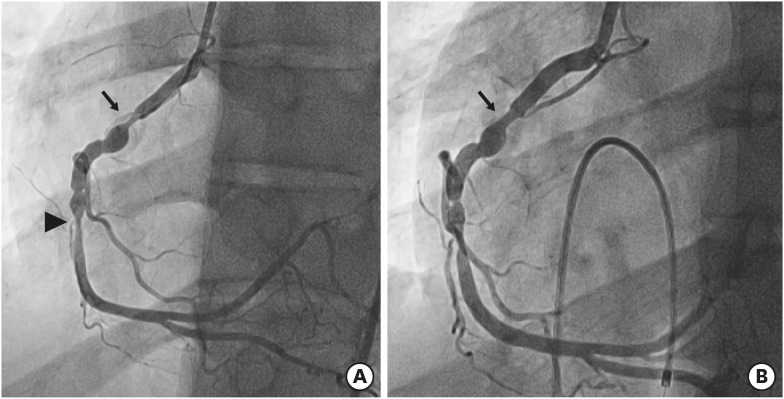 | Figure 4Coronary angiographies at 20 years of age (12 years after the first PTCRA), showing a restenosis of the target lesion (arrow) and another stenosis at the mid RCA (arrowhead) (A), and an improved target lesion stenosis after the second PTCRA (arrow) (B).PTCRA = percutaneous transluminal coronary rotational ablation; RCA = right coronary artery.
|
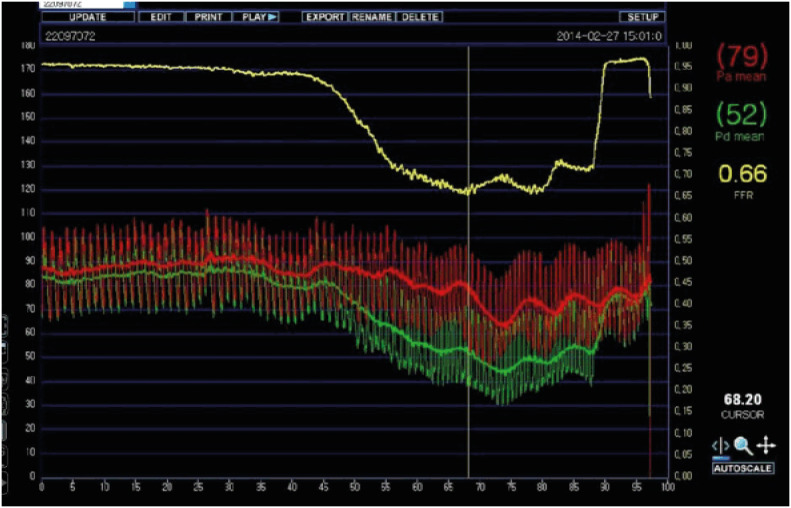 | Figure 5FFR measurement image after intracoronary adenosine administration at 20 years of age (12 years after the first PTCRA). Measured FFR was 0.66 at the time of the lowest FFR (vertical line). The yellow line, red line, and green line indicate FFR, a mean aortic pressure, and a mean coronary artery pressure distal to the target lesion stenosis in the Figure 4A (arrow), respectively.FFR = fractional flow reserve; PTCRA = percutaneous transluminal coronary rotational ablation.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download