INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials & reagents
Cell culture
Cell proliferation
Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GPDH) activity
mRNA expressions of transcription factors related to adipocyte differentiation
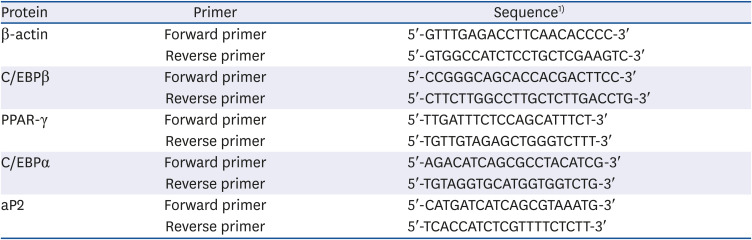
Table 1
Primer sequences of transcription factors related to adipogenesis
Neovascularization factors and MMPs mRNA expression
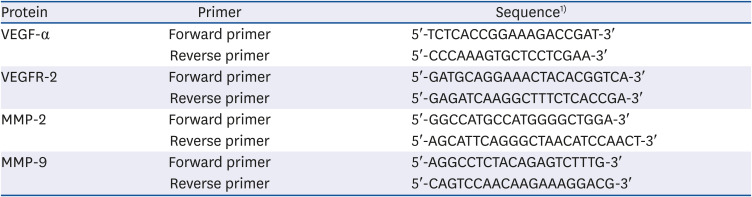
Table 2
Primer sequences for transcription factors related to angiogenesis
Concentration and activity of MMPs
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
MTT assay
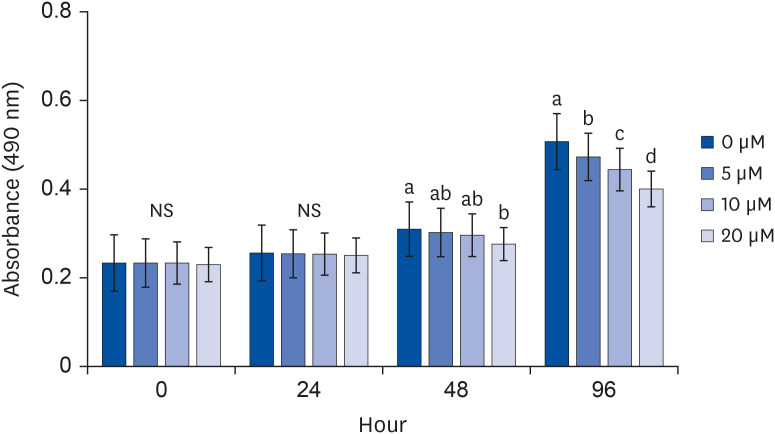 | Fig. 1Effect of quercetin on cell proliferation in 3T3-L1 cells.After differentiation induction, as described in Methods, a cell monolayer was incubated in post-differentiation medium with 0, 5, 10, or 20 μM quercetin. Viable cell numbers were estimated by MTT assay at 0, 24, 48, and 96 h after quercetin treatments. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. Comparisons among different concentrations of quercetin that produced significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above each bar.
MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.
|
GPDH activity assay for fat accumulation
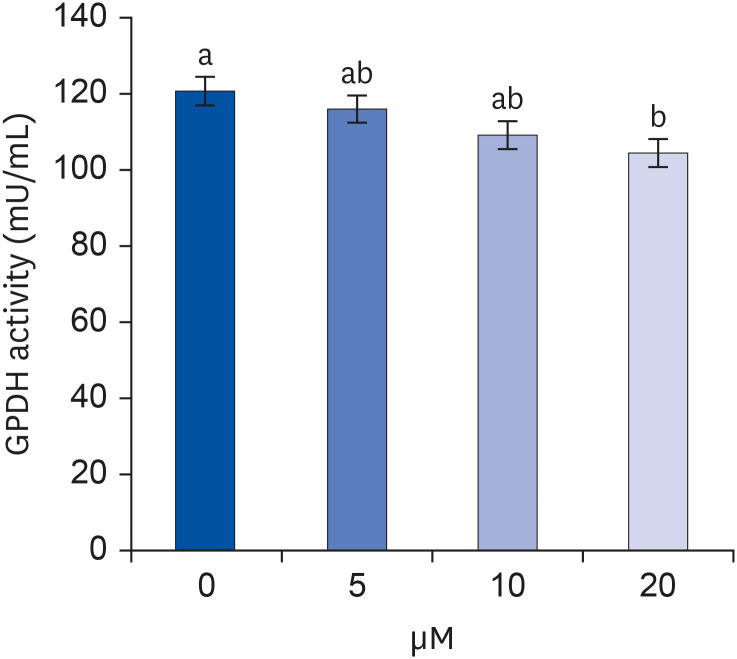 | Fig. 2Effect of quercetin on GPDH activity in 3T3-L1 cells.After differentiation induction, the cell monolayer was incubated in post-differentiation medium with 0, 5, 10, or 20 μM quercetin for 24 h. GPDH activity was estimated by using a commercial GPDH activity assay kit. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. Comparisons among different concentrations of quercetin that produced significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above each bar.
GPDH, glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
mRNA expressions of transcription factors related to adipocyte differentiation
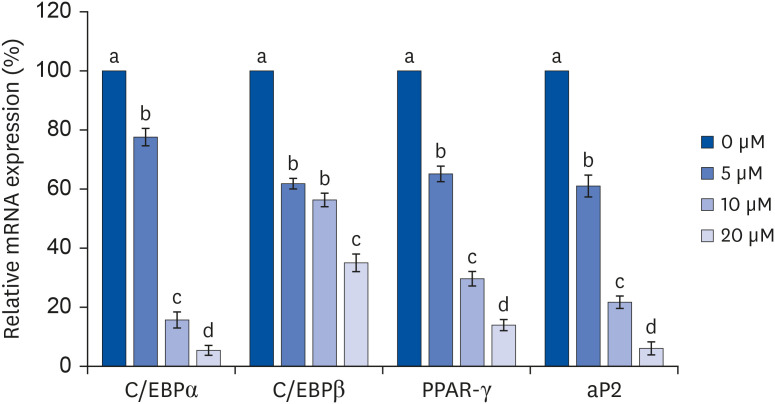 | Fig. 3Effect of quercetin on C/EBPα, C/EBPβ, PPAR-γ, and aP2 mRNA expressions in 3T3-L1 cells.After differentiation induction, the cell monolayer was incubated in post-differentiation medium with 0, 5, 10, or 20 μM quercetin for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated, and real-time PCR was performed. β-actin levels were compared, acting as the equal loading control. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. Comparisons among different concentrations of quercetin that generated significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above each bar.
C/EBP, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein; PPAR, peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptors; aP2, adipocyte protein 2; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
|
mRNA expressions of vascular remodeling factors related to adipogenesis
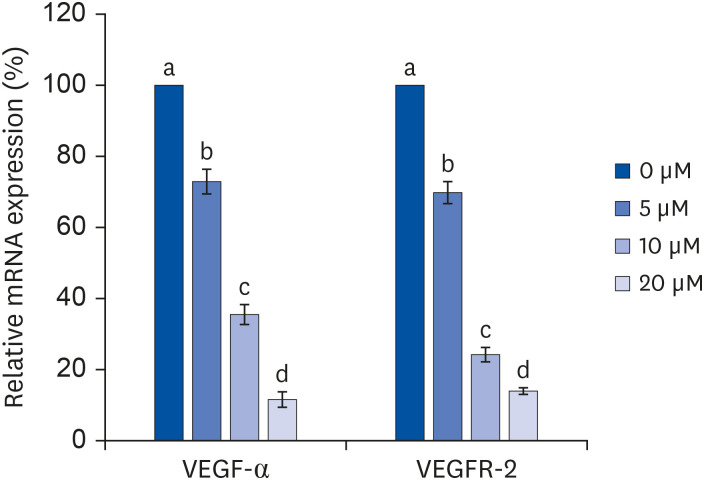 | Fig. 4Effect of quercetin on VEGF-α and VEGFR-2 mRNA expressions in 3T3-L1 cells.After differentiation induction, the cell monolayer was incubated in post-differentiation medium with 0, 5, 10, or 20 μM quercetin for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated, and real-time PCR was performed. β-actin levels were compared, acting as the equal loading control. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. Comparisons among different concentrations of quercetin that produced significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above each bar.
VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
|
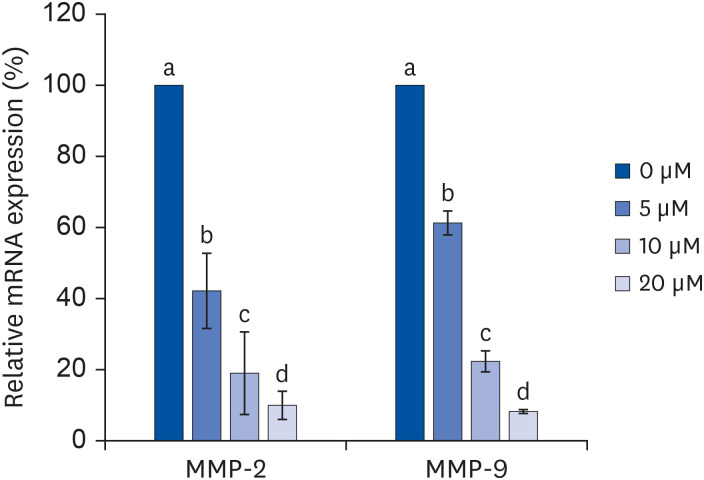 | Fig. 5Effect of quercetin on MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA expressions in 3T3-L1 cells.After differentiation induction, the cell monolayer was incubated in post-differentiation medium with 0, 5, 10, or 20 μM quercetin for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated, and real-time PCR was performed. β-actin levels were compared, acting as the equal loading control. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. Comparisons among different concentrations of quercetin that resulted in significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above each bar.
MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
|
Enzyme activity and concentrations of MMP-2 and MMP-9
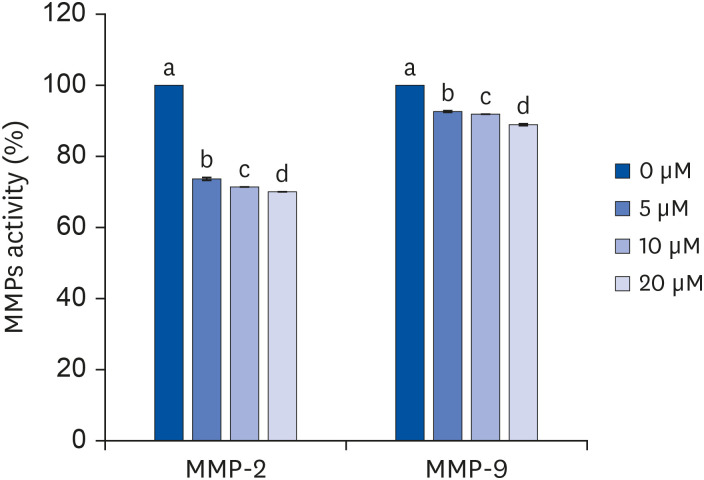 | Fig. 6Effect of quercetin on activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in 3T3-L1 cells.After differentiation induction, the cell monolayer was incubated in post-differentiation medium with 0, 5, 10, or 20 μM quercetin for 24 h. The MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity levels were estimated by colorimetric assay. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. Comparisons among different concentrations of quercetin that produced significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above each bar.
MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
|
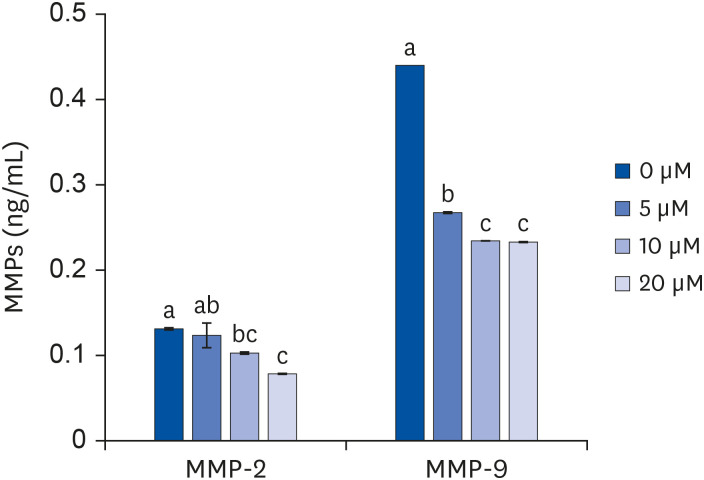 | Fig. 7Effect of quercetin on concentrations of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in 3T3-L1 cells.After differentiation induction, as described in Methods, the cell monolayer was incubated in post-differentiation medium with 0, 5, 10, or 20 μM quercetin for 24 h. The MMP-2 and MMP-9 concentrations were estimated by using ELISA kits. Each bar represents the mean ± SE. Comparisons among different concentrations of quercetin that resulted in significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated by different letters above each bar.
MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download